Volkswagen
Buses, Coaches, Trucks and Vans
VW Argentina, VW Australia, VW Brazil, VW Mexico.
| Volkswagen Type 2 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Volkswagen |
| Also called | Volkswagen Bus Volkswagen Camper Volkswagen Delivery Van Volkswagen Kombi Volkswagen Microbus Volkswagen Pick-up Volkswagen Transporter |
| Production | Nov 1949–Dec 2013 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Van (Minibus) |
| Body style | 4-door panel van 4-door minibus 2-door pickup (regular cab) 3-door pickup (crew cab) |
| Layout | Longitudinal rear engine, rear-wheel drive |
| Platform | Volkswagen Group T platform |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Volkswagen Type 2 (T3) |
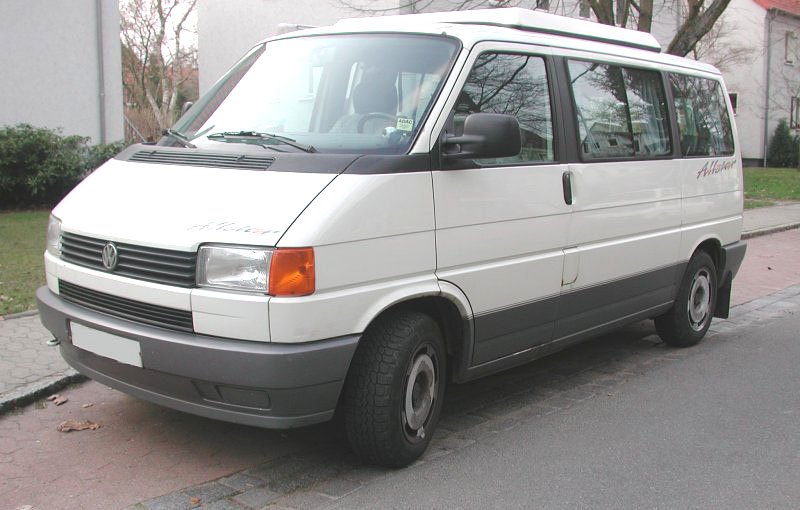
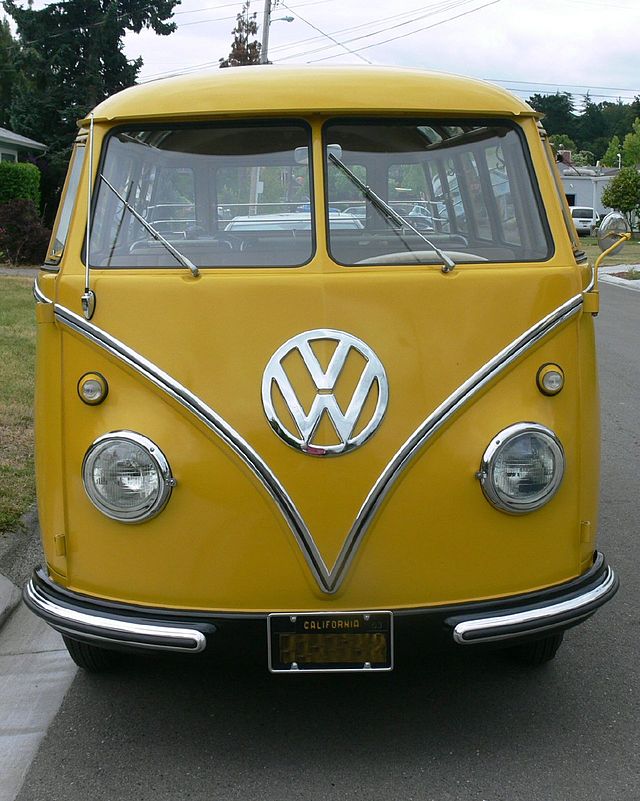
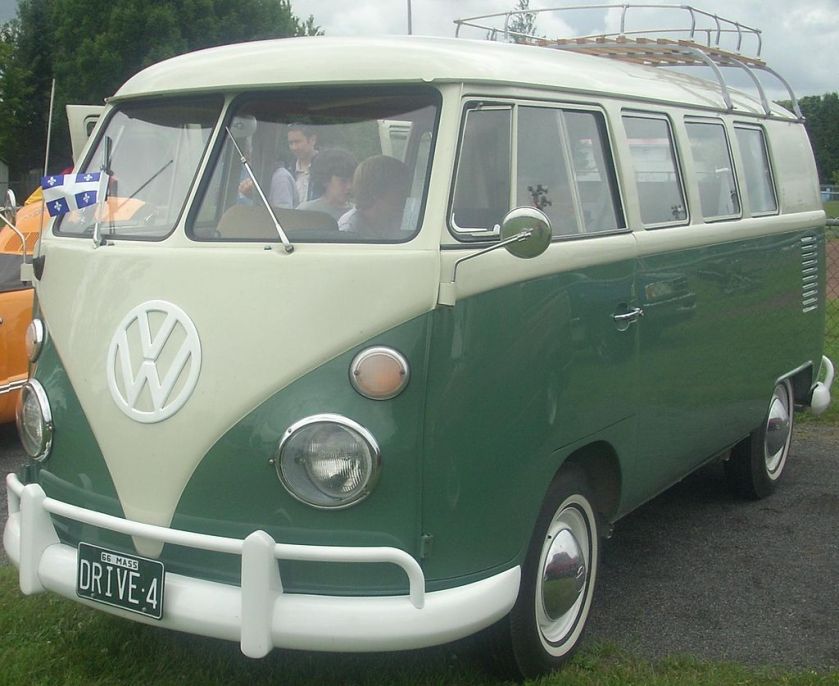
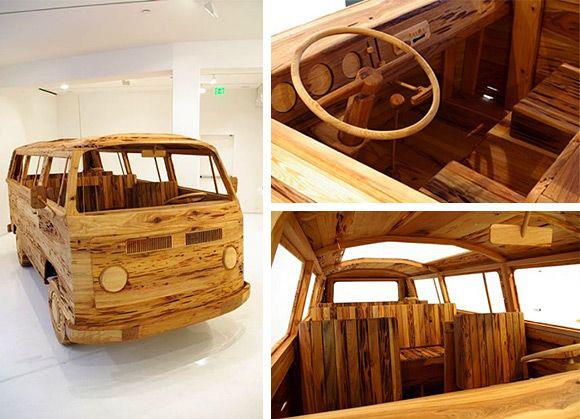
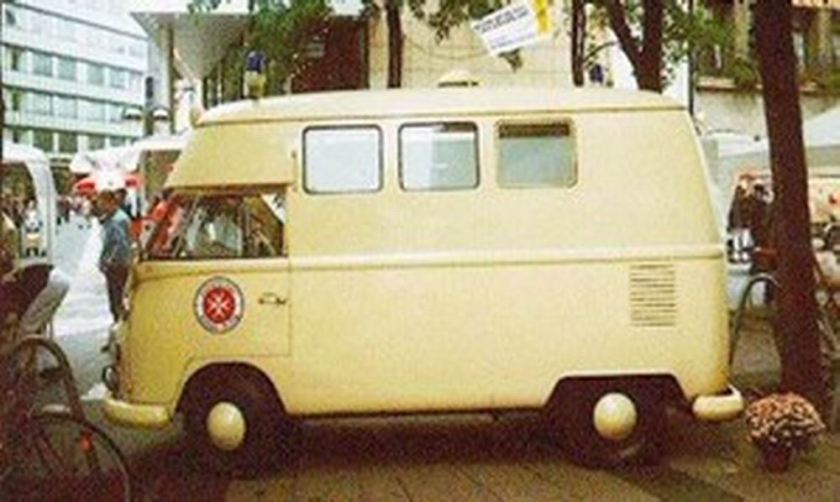
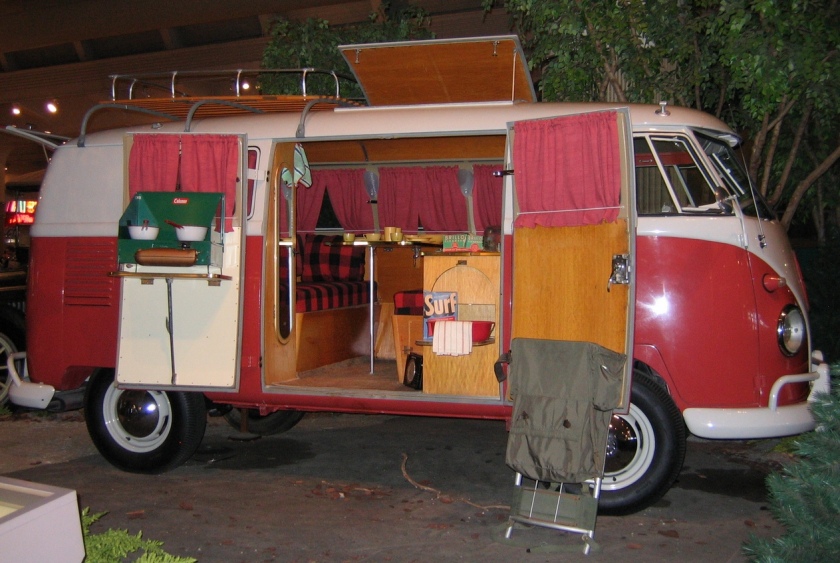
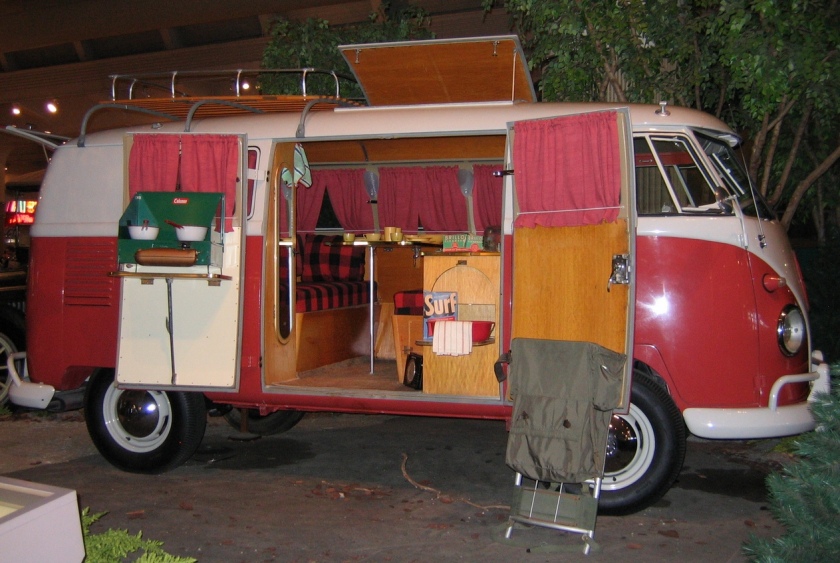 A “Camper” at The Henry Ford
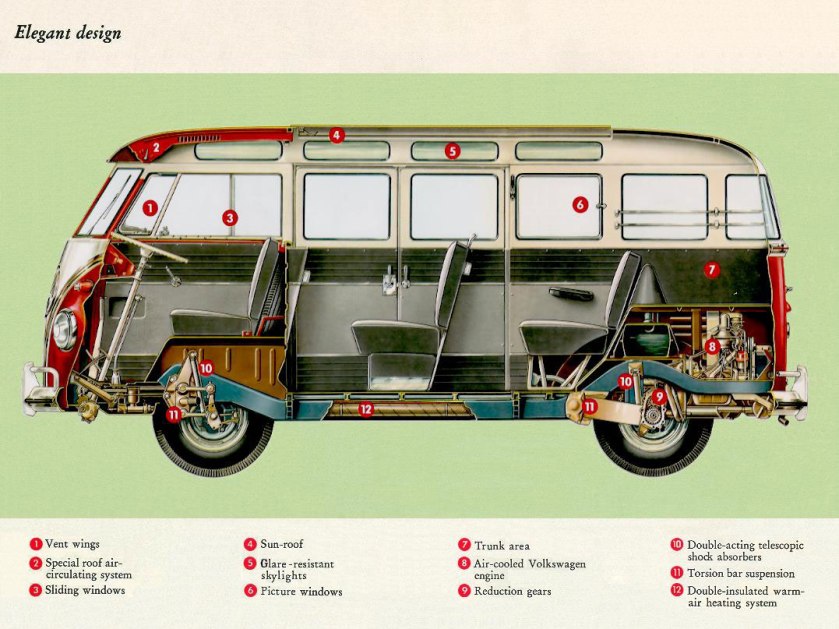
A “Camper” at The Henry FordThe Volkswagen Type 2, known officially (depending on body type) as the Transporter, Kombi or Microbus, or, informally, as the Bus (US) or Camper (UK), is a panel van introduced in 1950 by the German automaker Volkswagen as its second car model. Following – and initially deriving from Volkswagen’s first model, the Type 1 (Beetle) – it was given the factory designation Type 2.
As one of the forerunners of the modern cargo and passenger vans, the Type 2 gave rise to forward control competitors in the United States in the 1960s, including the Ford Econoline, the Dodge A100, and the Chevrolet Corvair 95 Corvan, the latter adopting the Type 2’s rear-engine configuration. European competition included the 1960s FF layout Renault Estafette and the FR layout Ford Transit.
Like the Beetle, the van has received numerous nicknames worldwide, including the “microbus”, “minibus”, and, because of its popularity during the counterculture movement of the 1960s, “Hippie van”.
Brazil contained the last factory in the world that produced the T2. Production in Brazil ceased on December 31, 2013, due to the introduction of more stringent safety regulations in the country. This marks the end of an era with the rear-engine Volkswagens manufactured (after the 2002 termination of its T3 successor in South Africa), which first originated in 1935 with their Type 1 prototypes.
History
The concept for the Type 2 is credited to Dutch Volkswagen importer Ben Pon. (It has similarities in concept to the 1920s Rumpler Tropfenwagen and 1930s Dymaxion car by Buckminster Fuller, neither of which reached production.) Pon visited Wolfsburg in 1946, intending to purchase Type 1s for import to the Netherlands, where he saw an improvised parts-mover and realized something better was possible using the stock Type 1 pan. He first sketched the van in a doodle dated April 23, 1947, proposing a payload of 690 kg (1,520 lb) and placing the driver at the very front. Production would have to wait, however, as the factory was at capacity producing the Type 1.
When capacity freed up, a prototype known internally as the Type 29 was produced in a short three months. The stock Type 1 pan proved to be too weak so the prototype used a ladder chassis with unit body construction. Coincidentally the wheelbase was the same as the Type 1’s. Engineers reused the reduction gear from the Type 81, enabling the 1.5 ton van to use a 25 hp (19 kW) flat four engine.
Although the aerodynamics of the first prototypes were poor (with an initial drag coefficient of Cd=0.75), engineers used the wind tunnel at the Technical University of Braunschweig to optimize the design. Simple changes such as splitting the windshield and roofline into a “vee” helped the production Type 2 achieve Cd=0.44, exceeding the Type 1’s Cd=0.48. Volkswagen’s new chief executive officer Heinz Nordhoff (appointed 1 January 1948) approved the van for production on 19 May 1949 and the first production model, now designated Type 2, rolled off the assembly line to debut 12 November. Only two models were offered: the Kombi (with two side windows and middle and rear seats that were easily removable by one person), and the Commercial. The Microbus was added in May 1950, joined by the Deluxe Microbus in June 1951. In all 9,541 Type 2s were produced in their first year of production.
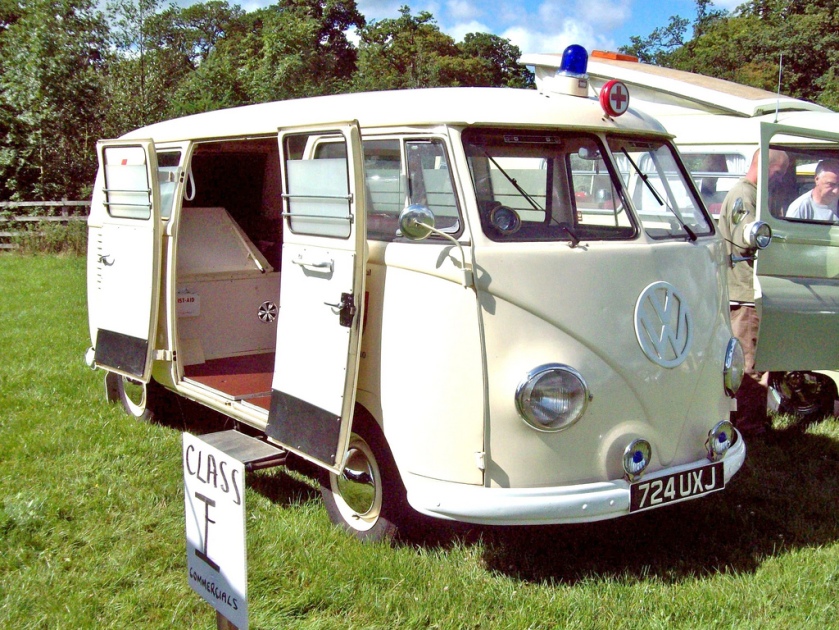
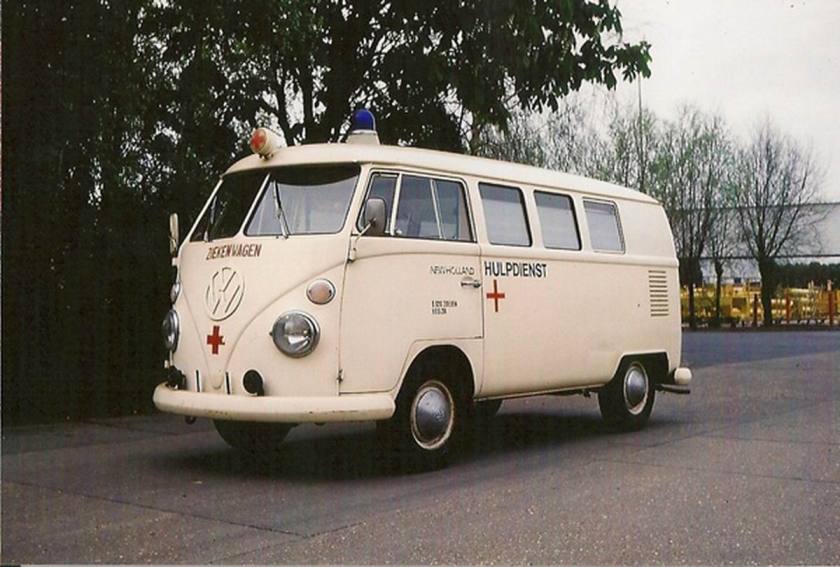
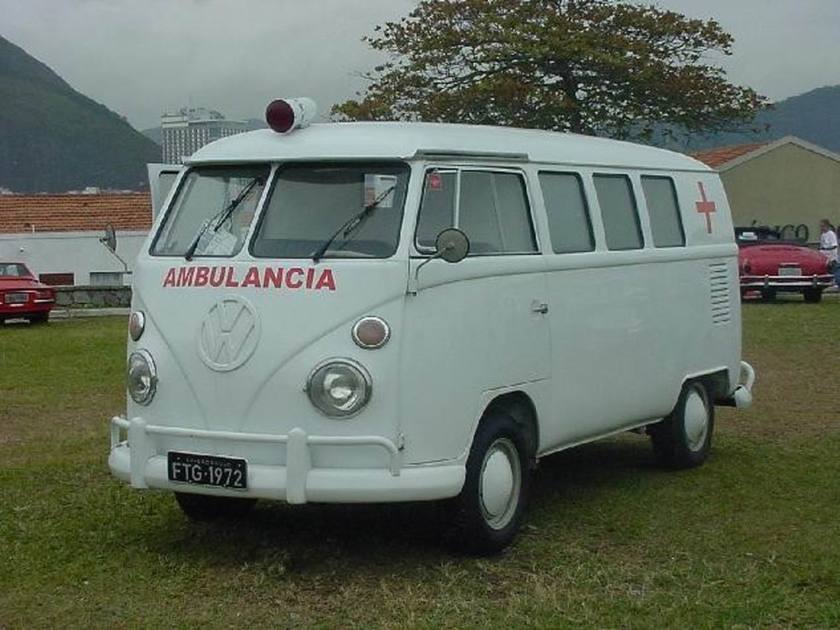
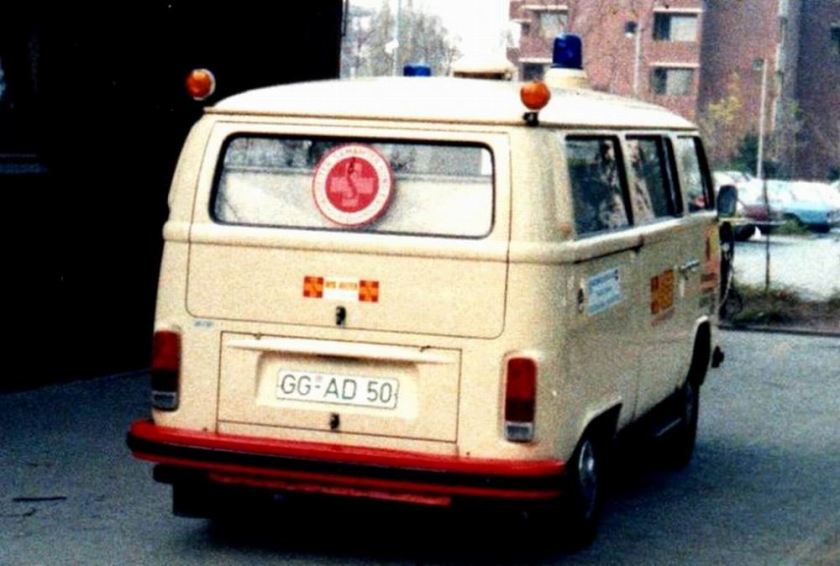
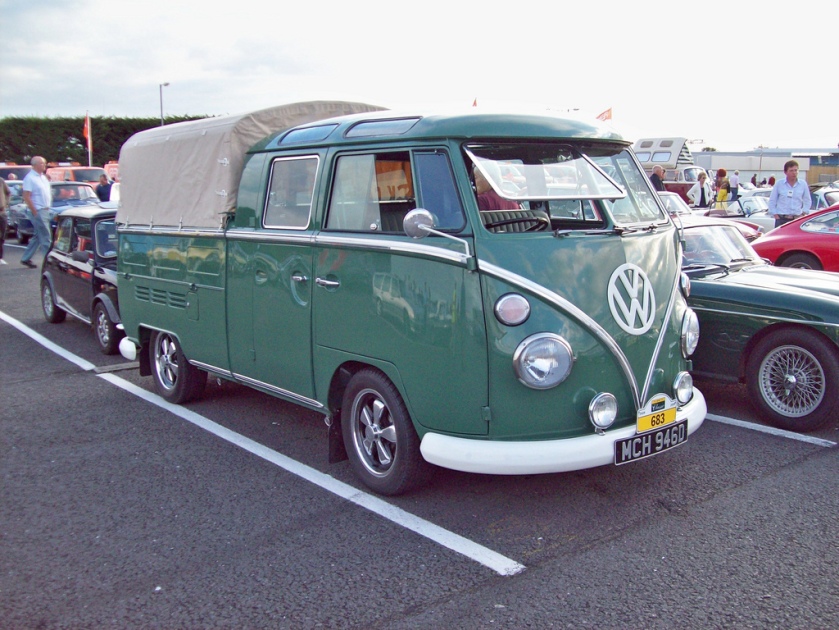
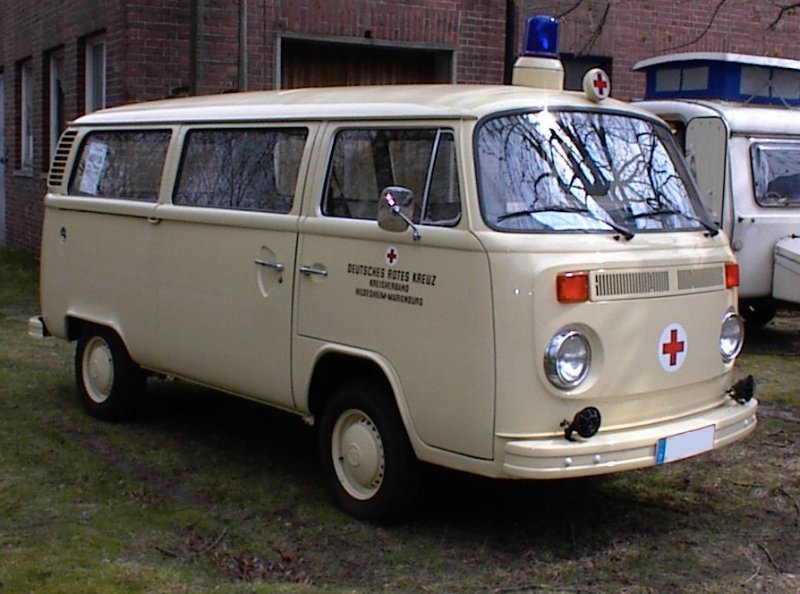
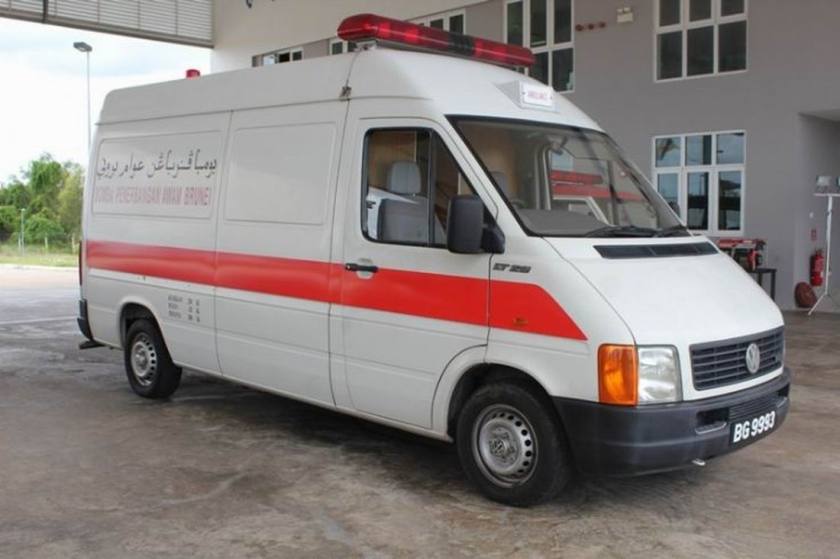
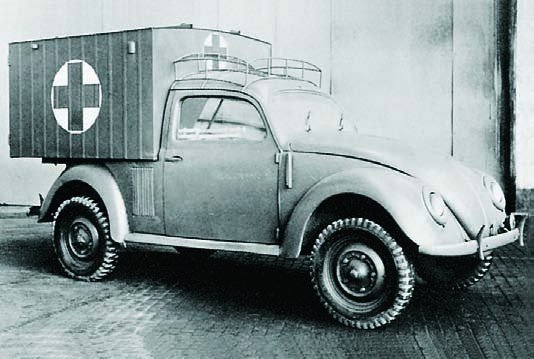
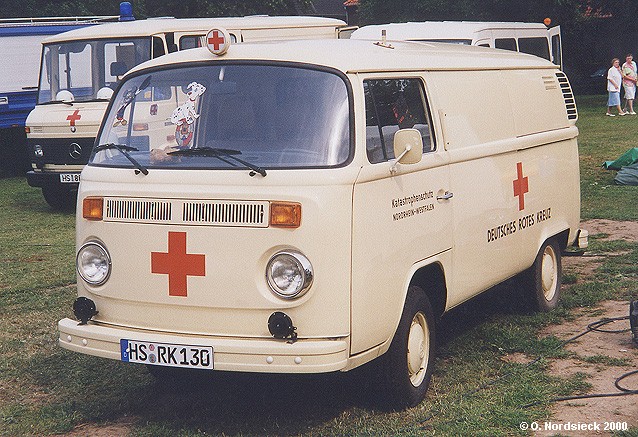
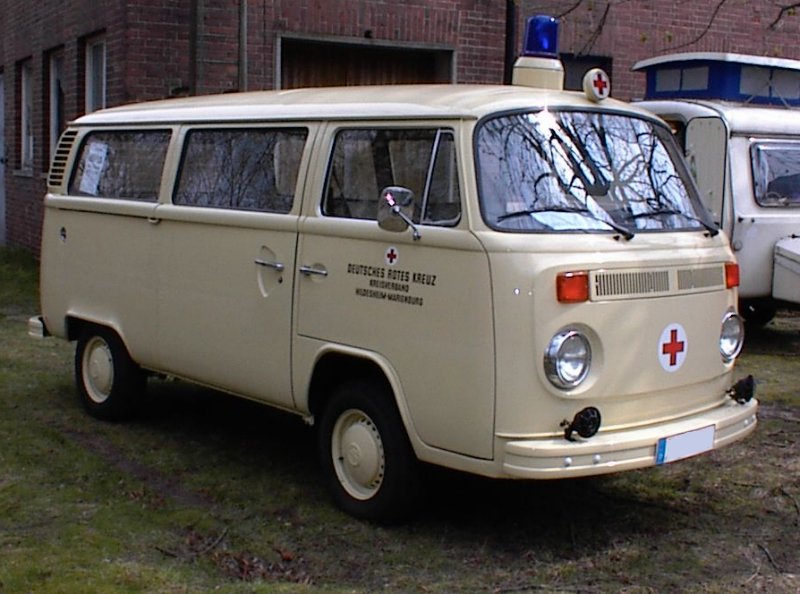
An ambulance model was added in December 1951 which repositioned the fuel tank in front of the transaxle, put the spare tire behind the front seat, and added a “tailgate“-style rear door. These features became standard on the Type 2 from 1955 to 1967. 11,805 Type 2s were built in the 1951 model year. These were joined by a single-cab pickup in August 1952, and it changed the least of the Type 2s until all were heavily modified in 1968.
Unlike other rear engine Volkswagens, which evolved constantly over time but never saw the introduction of all-new models, the Transporter not only evolved, but was completely revised periodically with variations retrospectively referred to as versions “T1” to “T5” (a nomenclature only invented after the introduction of the front-drive T4 which replaced the T25). However only generations T1 to T3 (or T25 as it is still called in Ireland and Great Britain) can be seen as directly related to the Beetle (see below for details).
The Type 2, along with the 1947 Citroën H Van, are among the first ‘forward control’ vans in which the driver was placed above the front roadwheels. They started a trend in Europe, where the 1952 GM Bedford CA, 1958 RAF-977, 1959 Renault Estafette, 1960 BMC Morris J4, and 1960 Commer FC also used the concept. In the United States, the Corvair-based Chevrolet Corvan cargo van and Greenbrier passenger van went so far as to copy the Type 2’s rear-engine layout, using the Corvair’s horizontally opposed, air-cooled engine for power. Except for the Greenbrier and various 1950s–70s Fiat minivans, the Type 2 remained unique in being rear-engined. This was a disadvantage for the early “barndoor” Panel Vans, which could not easily be loaded from the rear because the engine cover intruded on interior space, but generally advantageous in traction and interior noise.
Variants
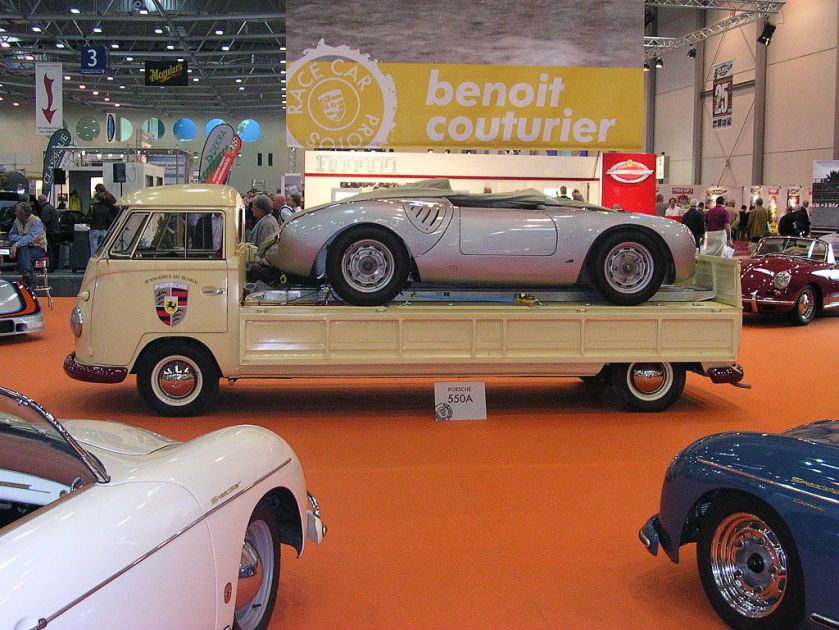
 Example of a 1961 Volkswagen Type II flatbed pickup truck.
Example of a 1961 Volkswagen Type II flatbed pickup truck.
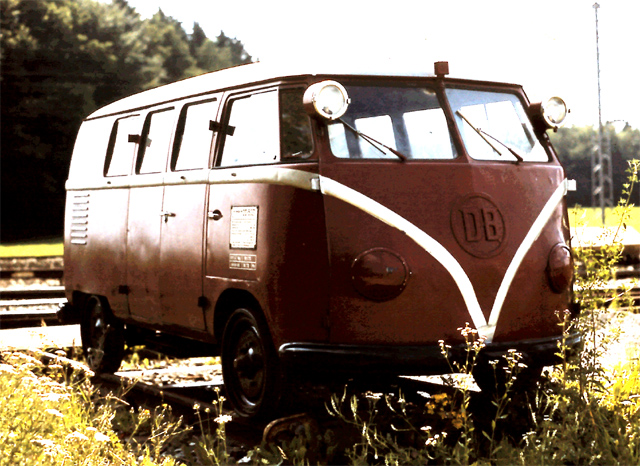
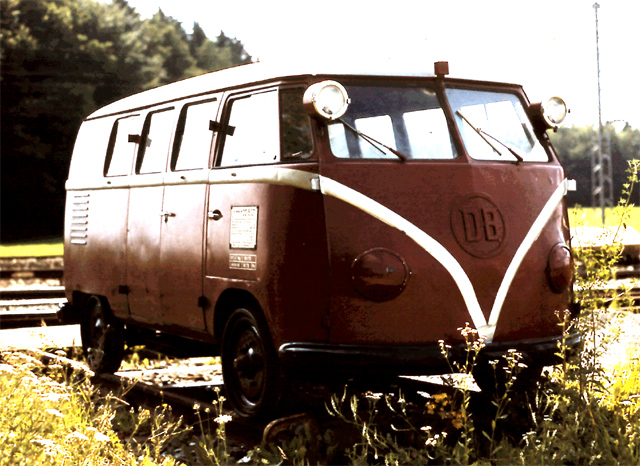 Rail-going draisine
Rail-going draisine
The Type 2 was available as a:
- Panel van, a delivery van without side windows or rear seats.
- Double-door Panel Van, a delivery van without side windows or rear seats and cargo doors on both sides.
- High Roof Panel Van (German: Hochdach), a delivery van with raised roof.
- Kombi, from German: Kombinationskraftwagen (combination motor vehicle), with side windows and removable rear seats, both a passenger and a cargo vehicle combined.
- Bus, also called a Volkswagen Caravelle, a van with more comfortable interior reminiscent of passenger cars since the third generation.
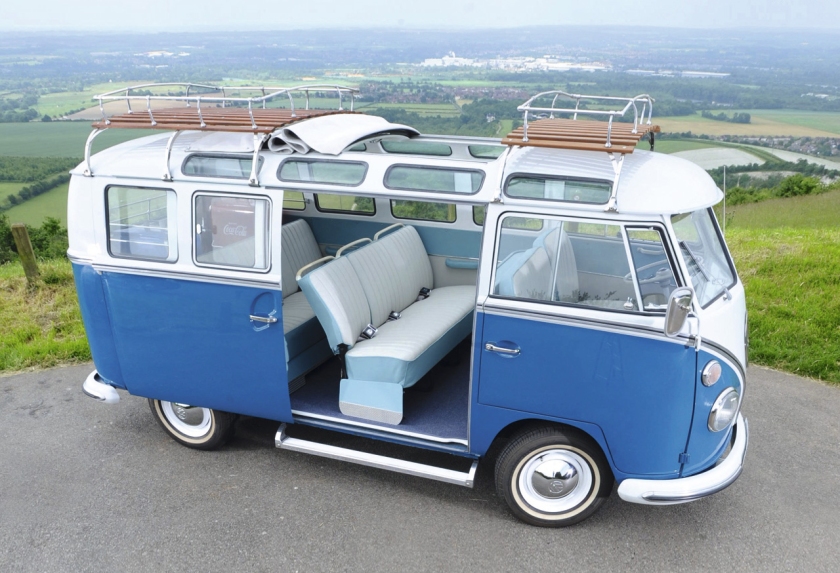
- Samba-Bus, a van with skylight windows and cloth sunroof, first generation only, also known as a Deluxe Microbus. They were marketed for touring theAlps.
- Flatbed pickup truck, or Single Cab, also available with wider load bed.
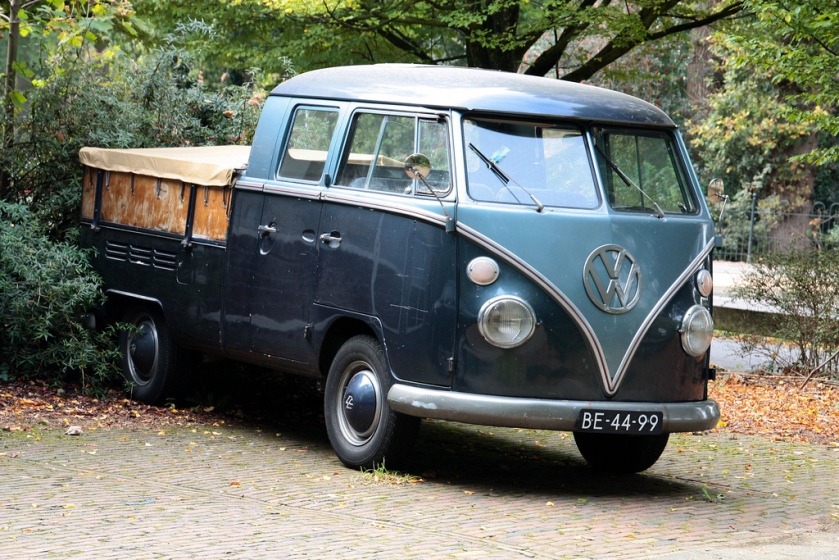
- Crew cab pick-up, a flatbed truck with extended cab and two rows of seats, also called a Doka, from German: Doppelkabine.
- Westfalia camping van, “Westy”, with Westfalia roof and interior. Included optional “pop up” top.
- Adventurewagen camping van, with high roof and camping units from Adventurewagen.
- Semi-camping van that can also still be used as a passenger car and transporter, sacrificing some camping comforts. “Multivan” or “Weekender”, available from the third generation on.
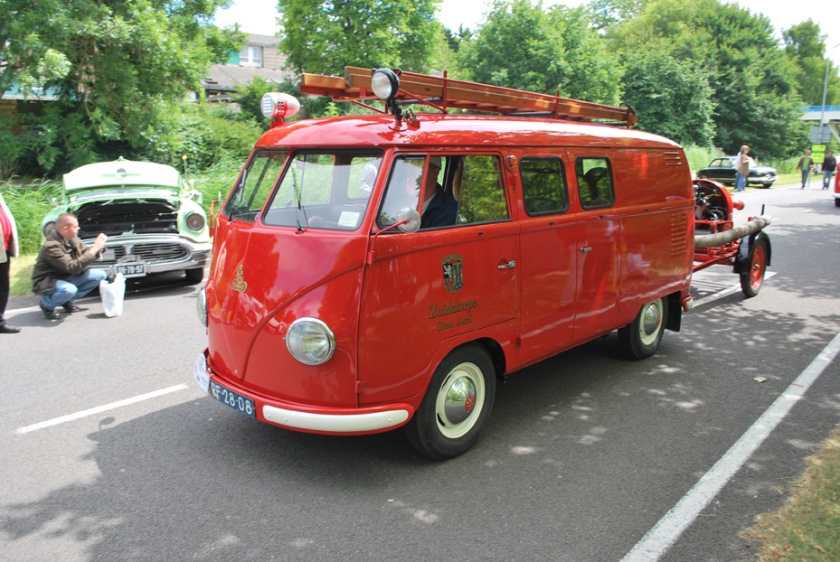
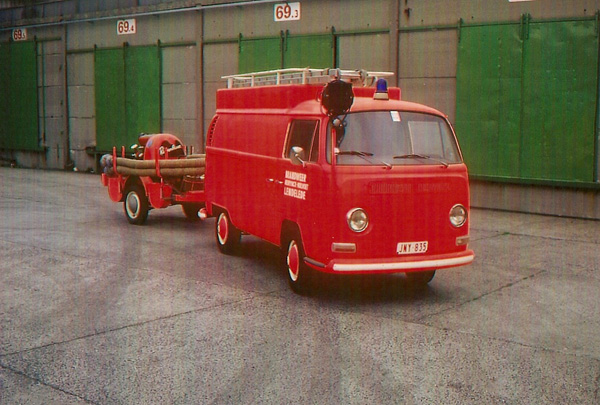
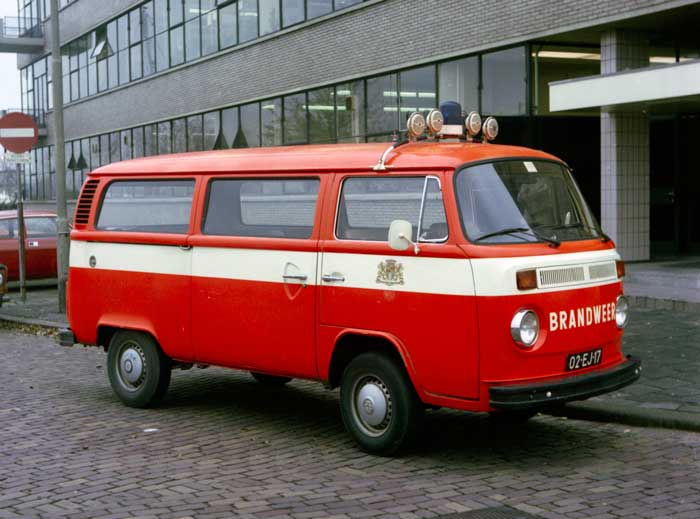
Apart from these factory variants, there were a multitude of third-party conversions available, some of which were offered through Volkswagen dealers. They included, but were not limited to, refrigerated vans, hearses, ambulances, police vans, fire engines and ladder trucks, and camping van conversions by companies other than Westfalia. There were even 30 Klv 20 rail-going draisines built for Deutsche Bundesbahn in 1955.
In South Africa, it is known as a well-loved variation of the ice cream van (first, second and third generations). The mere sight of one (in South Africa) sparks the familiar rhyme: I scream, We scream, We all scream for Ice-Cream!
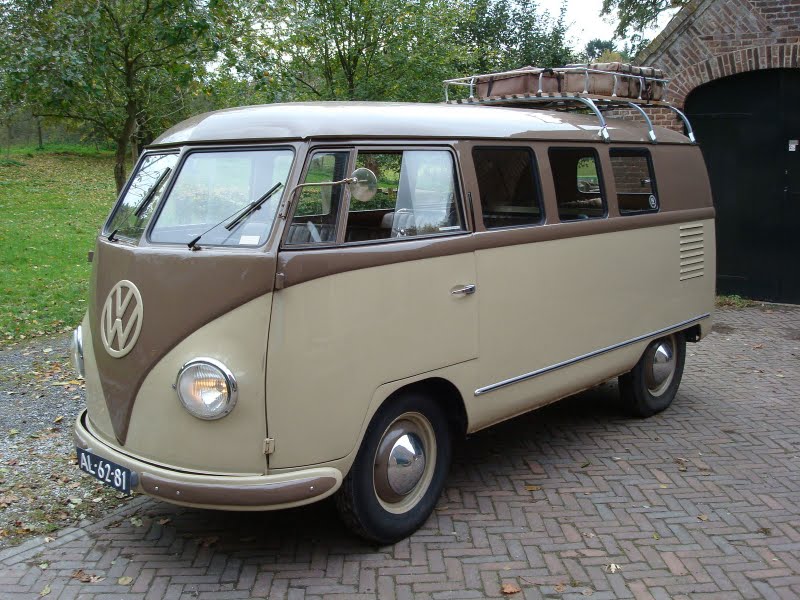
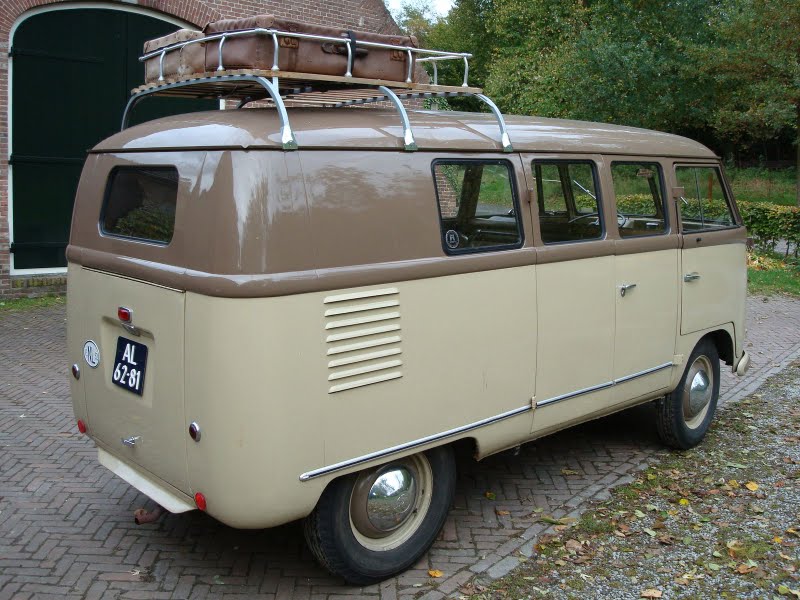
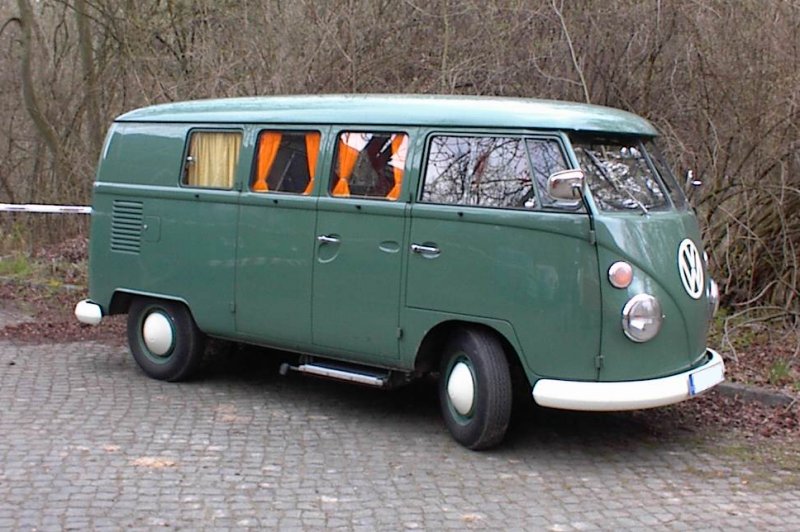
First generation (T1; 1950–1967)
| Volkswagen Type 2 (T1) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1950–1967 (Europe and US) 1950–1975 (Brazil) |
| Assembly | Wolfsburg, Germany Hanover, Germany São Bernardo do Campo, Brazil Melbourne, Australia |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | Volkswagen Group T1 platform |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.1 L B4 (petrol) 1.2 L B4 (petrol) 1.5 L B4 (petrol) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) |
| Length | 4,280 mm (168.5 in) |
| Width | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
| Height | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
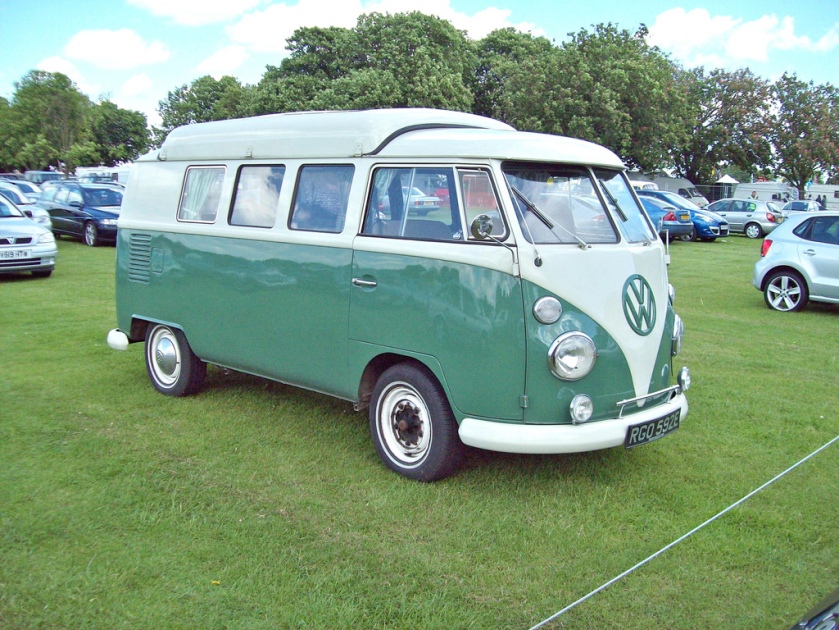
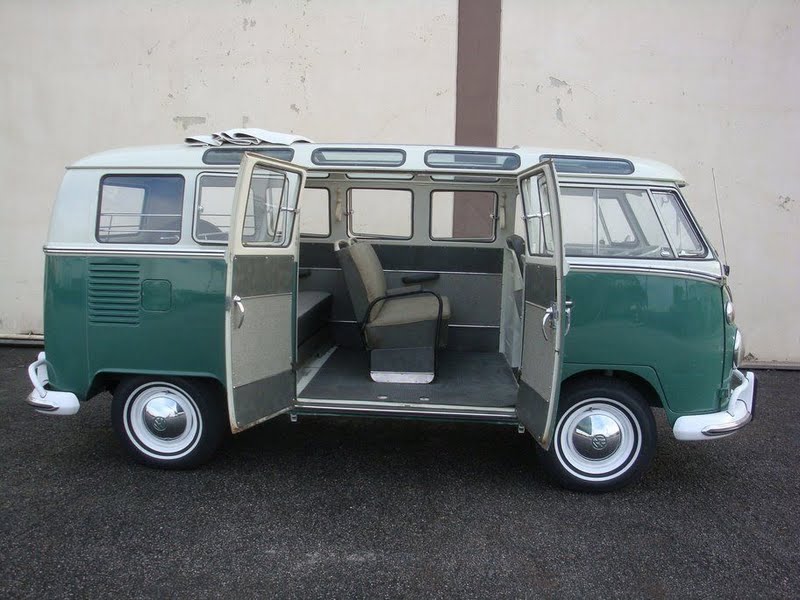
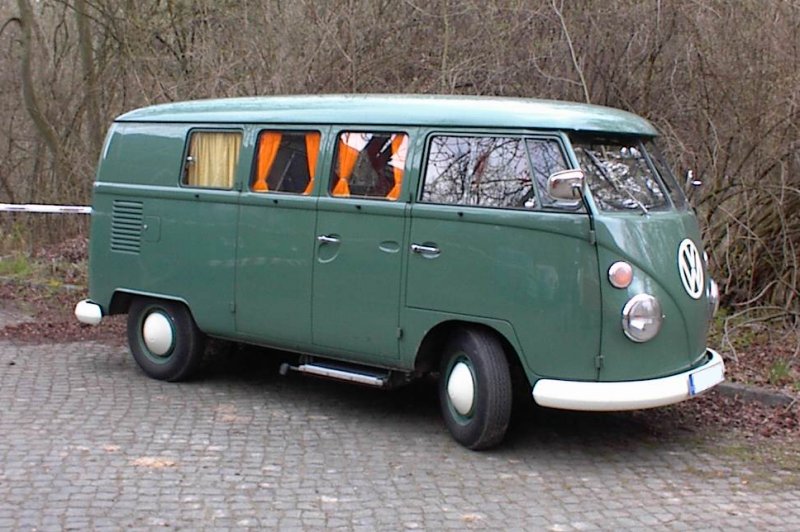
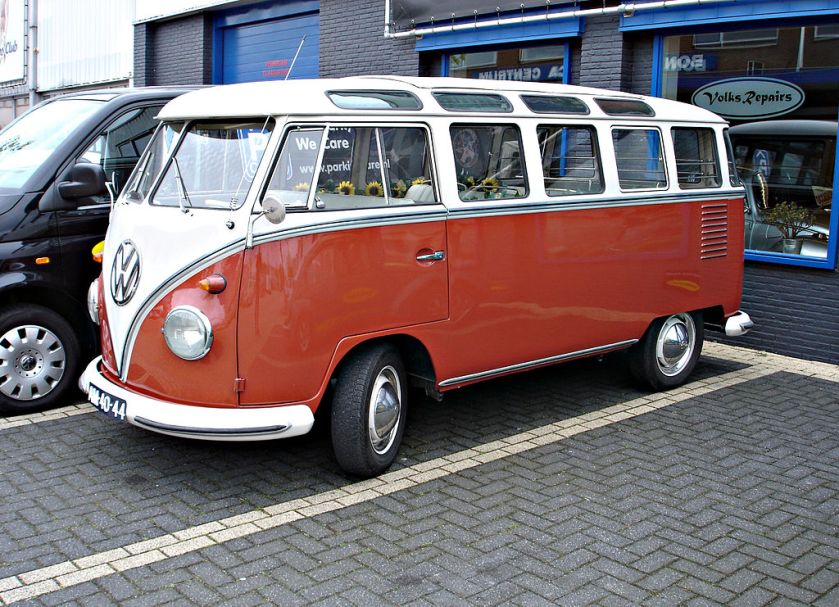
The first generation of the Volkswagen Type 2 with the split windshield, informally called the Microbus, Splitscreen, or Splittie among modern fans, was produced from 8 March 1950 through the end of the 1967 model year. From 1950 to 1956, the T1 (not called that at the time) was built in Wolfsburg; from 1956, it was built at the completely new Transporter factory in Hanover. Like the Beetle, the first Transporters used the 1100 Volkswagen air-cooled engine, an 1,131 cc (69.0 cu in),DIN-rated 18 kW (24 PS; 24 bhp), air-cooled flat-four-cylinder ‘boxer’ engine mounted in the rear. This was upgraded to the 1200 – an 1,192 cc (72.7 cu in) 22 kW (30 PS; 30 bhp) in 1953. A higher compression ratio became standard in 1955; while an unusual early version of the 30 kW (41 PS; 40 bhp) engine debuted exclusively on the Type 2 in 1959. This engine proved to be so uncharacteristically troublesome that Volkswagen recalled all 1959 Transporters and replaced the engines with an updated version of the 30 kW engine. Any 1959 models that retain that early engine today are true survivors. Since the engine was totally discontinued at the outset, no parts were ever made available.
The early versions of the T1 until 1955 were often called the “Barndoor” (retrospectively called T1a since the 1990s), owing to the enormous rear engine cover, while the later versions with a slightly modified body (the roofline above the windshield is extended), smaller engine bay, and 15″ roadwheels instead of the original 16″ ones are nowadays called the T1b (again, only called this since the 1990s, based on VW’s restrospective T1,2,3,4 etc. naming system.). From the 1963 model year, when the rear door was made wider (same as on the bay-window or T2), the vehicle could be referred to as the T1c. 1964 also saw the introduction of an optional sliding door for the passenger/cargo area instead of the outwardly hinged doors typical of cargo vans.
In 1962, a heavy-duty Transporter was introduced as a factory option. It featured a cargo capacity of 1,000 kg (2,205 lb) instead of the previous 750 kg (1,653 lb), smaller but wider 14″ roadwheels, and a 1.5 Le, 31 kW (42 PS; 42 bhp) DIN engine. This was so successful that only a year later, the 750 kg, 1.2 L Transporter was discontinued. The 1963 model year introduced the 1500 engine – 1,493 cc (91.1 cu in) as standard equipment to the US market at 38 kW (52 PS; 51 bhp) DIN with an 83 mm (3.27 in) bore, 69 mm (2.72 in) stroke, and 7.8:1 compression ratio. When the Beetle received the 1.5 L engine for the 1967 model year, its power was increased to 40 kW (54 PS; 54 bhp) DIN.
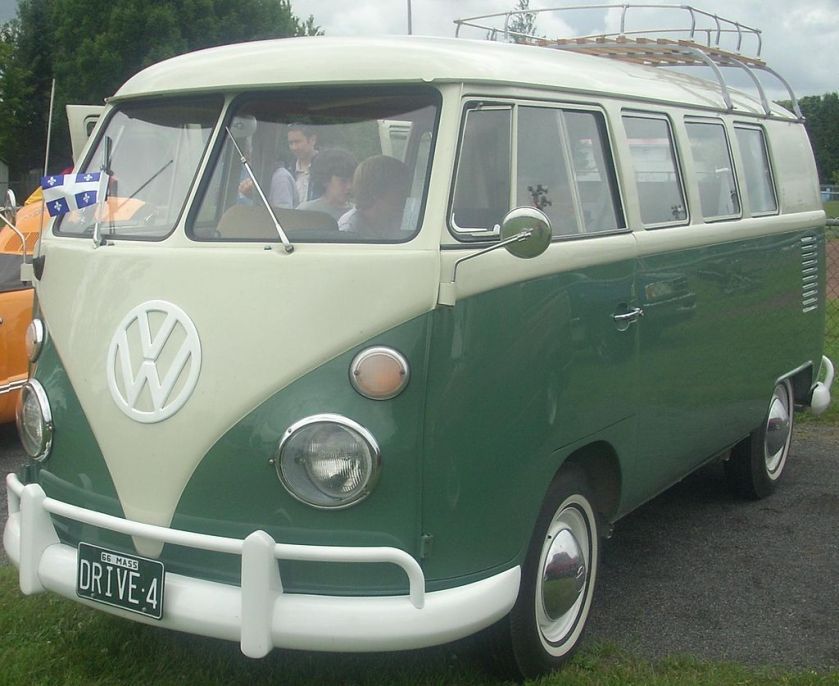 1966 Volkswagen Kombi (North America)
1966 Volkswagen Kombi (North America)
German production stopped after the 1967 model year; however, the T1 still was made in Brazil until 1975, when it was modified with a 1968–79 T2-style front end, and big 1972-vintage taillights into the so-called “T1.5” and produced until 1996. The Brazilian T1s were not identical to the last German models (the T1.5 was locally produced in Brazil using the 1950s and 1960s-era stamping dies to cut down on retooling, alongside the Beetle/Fusca, where the pre-1965 body style was retained), though they sported some characteristic features of the T1a, such as the cargo doors and five-stud 205 mm (8.1 in) PCD rims. Wheel tracks varied between German and Brazilian production and with 14″,15″ and 16″ wheel variants but commonly front track varied from 1290mm to 1310mm and rear track from 1370mm to 1390mm.
 VW Bus Type 2 (T1),hippie colors
VW Bus Type 2 (T1),hippie colors
Among American enthusiasts, it is common to refer to the different models by the number of their windows. The basic Kombi or Bus is the 11-window(a.k.a. three-window bus because of three side windows) with a split windshield, two front cabin door windows, six rear side windows, and one rear window. The DeLuxe model featured eight rear side windows and two rear corner windows, making it the 15-window (not available in Europe). Meanwhile, the sunroof DeLuxe with its additional eight small skylight windows is, accordingly, the 23-window. From the 1964 model year, with its wider rear door, the rear corner windows were discontinued, making the latter two the 13-window and 21-window respectively. The 23- and later 21-window variants each carry the nickname ‘Samba’, or in Australia, officially ‘Alpine’.
US Chicken Tax
Certain models of the Volkswagen Type 2 played a role in a historic episode during the early 1960s, known as theChicken War. France and West Germany had placed tariffs on imports of U.S. chicken. Diplomacy failed, and in January 1964, two months after taking office, President Johnson imposed a 25% tax (almost ten times the average U.S. tariff) on potato starch, dextrin, brandy, and light trucks. Officially, the tax targeted items imported from Europe as approximating the value of lost American chicken sales to Europe.
In retrospect, audio tapes from the Johnson White House, revealed a quid pro quo unrelated to chicken. In January 1964, President Johnson attempted to convince United Auto Workers‘ president Walter Reuther not to initiate a strike just before the 1964 election, and to support the president’s civil rights platform. Reuther, in turn, wanted Johnson to respond to Volkswagen‘s increased shipments to the United States.
The Chicken Tax directly curtailed importation of German-built Type 2s in configurations that qualified them as light trucks – that is, commercial vans (panel vans) and pickups. In 1964, U.S. imports of automobile trucks from West Germany declined to a value of $5.7 million – about one-third the value imported in the previous year. After 1971, Volkswagen cargo vans and pickup trucks, the intended targets, “practically disappeared from the U.S. market”. While post-1971 Type 2 commercial vans and single-cab and double-cab pickups can be found in the United States today, they are exceedingly rare. Any post-1971 specimen found ostensibly has had its import tariff paid. As of 2013, the “chicken tax” remains in effect.
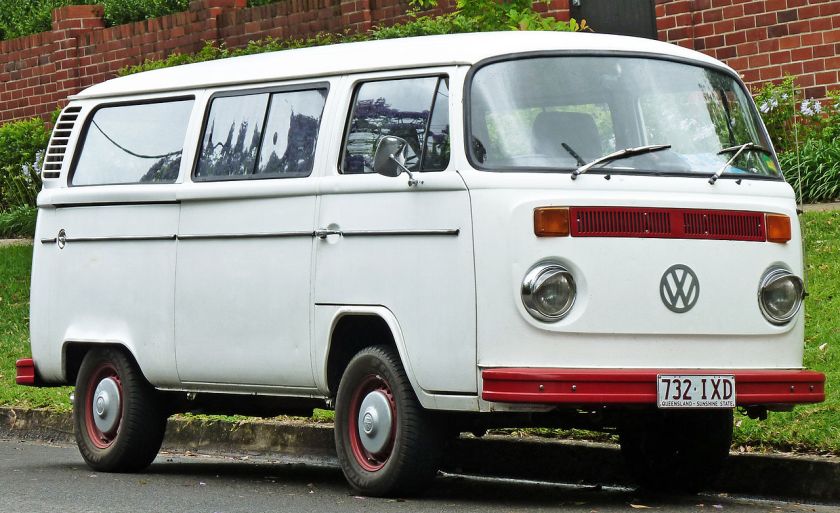
Second generation (T2; 1967–1979)
| Volkswagen Type 2 (T2) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | Aug 1967–Jul 1979 (Europe and US) 1971–1996 (Mexico) 1976–Dec 2013 (Brazil) 1981–1986 (Argentina) |
| Assembly | Hanover, Germany Emden, Germany General Pacheco, Argentina São Bernardo do Campo, Brazil Puebla, Puebla, Mexico Melbourne, Australia |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | Volkswagen Group T2 platform |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L B4 (petrol) 1.7 L B4 (petrol) 1.8 L B4 (petrol) 1.8 L I4 (petrol) 2.0 L B4 (petrol) |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,400 mm (94.5 in) |
| Length | 4,505 mm (177.4 in) |
| Width | 1,720 mm (67.7 in) |
| Height | 1,940 mm (76.4 in) |
In late 1967, the second generation of the Volkswagen Type 2 (T2) was introduced. It was built in Germany until 1979. In Mexico, the Volkswagen Kombi and Panel were produced from 1970 to 1994. Models before 1971 are often called the T2a (or “Early Bay”), while models after 1972 are called the T2b (or “Late Bay”).
 1978 Volkswagen Transporter Pickup (The Netherlands)
1978 Volkswagen Transporter Pickup (The Netherlands)
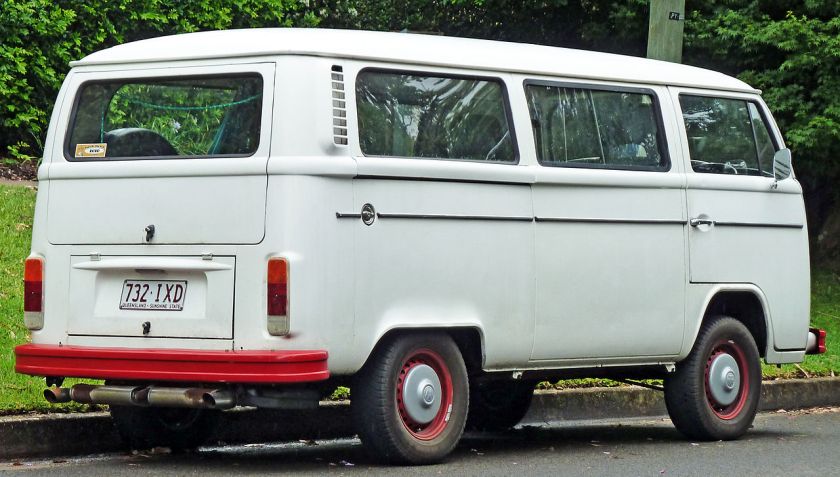 1973–1980 Volkswagen Kombi (T2) van (Australia)
1973–1980 Volkswagen Kombi (T2) van (Australia)
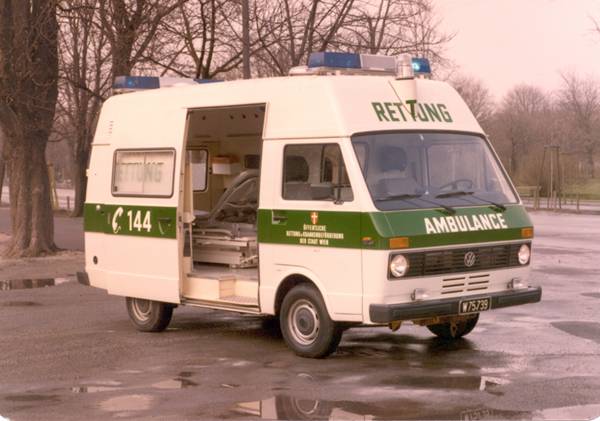
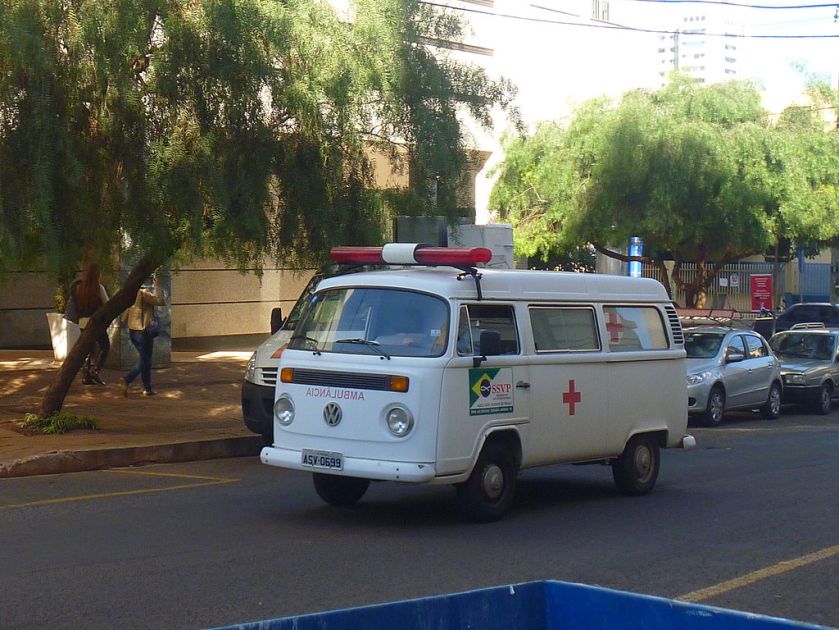
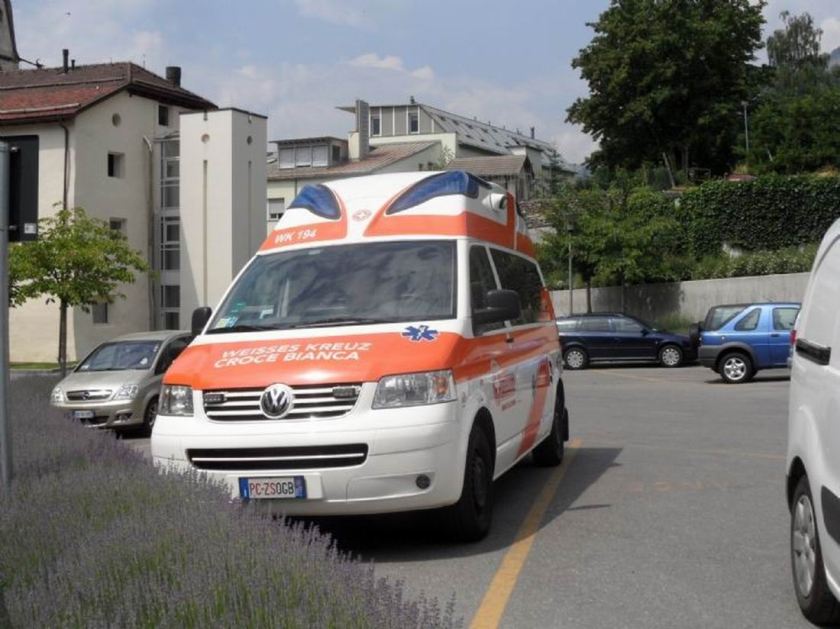
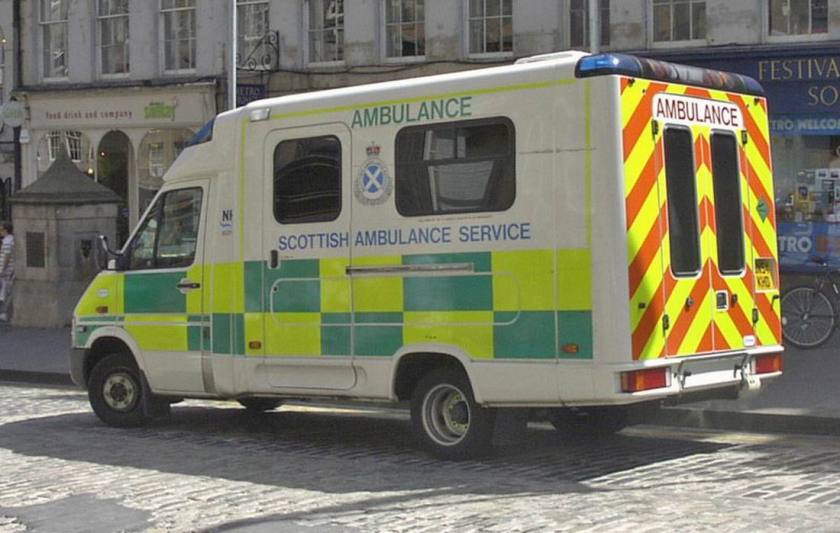
 T2 used as an ambulance in Brazil
T2 used as an ambulance in Brazil
This second-generation Type 2 lost its distinctive split front windshield, and was slightly larger and considerably heavier than its predecessor. Its common nicknames are Breadloaf and Bay-window, orLoaf and Bay for short. At 1.6 L and 35 kW (48 PS; 47 bhp) DIN, the engine was also slightly larger. The new model also did away with the swing axle rear suspension and transfer boxes previously used to raise ride height. Instead, half-shaft axles fitted with constant velocity joints raised ride height without the wild changes in camber of the Beetle-based swing axle suspension. The updated Bus transaxle is usually sought after by off-road racers using air-cooled Volkswagen components.
The T2b was introduced by way of gradual change over three years. The first models featured rounded bumpers incorporating a step for use when the door was open (replaced by indented bumpers without steps on later models), front doors that opened to 90° from the body, no lip on the front guards, unique engine hatches, and crescent air intakes in the D-pillars (later models after the Type 4 engine option was offered, have squared off intakes). The 1971 Type 2 featured a new, 1.6 L engine with dual intake ports on each cylinder head and was DIN-rated at 37 kW (50 PS; 50 bhp). An important change came with the introduction of front disc brakes and new roadwheels with brake ventilation holes and flatter hubcaps. Up until 1972, front indicators are set low on the nose rather than high on either side of the fresh air grille – giving rise to their being nicknamed “Low Lights”. 1972’s most prominent change was a bigger engine compartment to fit the larger 1.7- to 2.0-litre engines from the Volkswagen Type 4, and a redesigned rear end which eliminated the removable rear apron and introduced the larger late tail lights. The air inlets were also enlarged to accommodate the increased cooling air needs of the larger engines.
In 1971 the 1600cc Type 1 engine as used in the Beetle, was supplemented with the 1700cc Type 4 engine – as it was originally designed for the Type 4 (411 and 412) models. European vans kept the option of upright fan Type 1 1600 engine but the 1700 Type 4 became standard for US spec models.
 Pre-facelift (left) and facelifted (right)Volkswagen Kombi (T2) vans (Australia)
Pre-facelift (left) and facelifted (right)Volkswagen Kombi (T2) vans (Australia)
In the Type 2, the Type 4 engine was an option for the 1972 model year onward. This engine was standard in models destined for the US and Canada. Only with the Type 4 engine did an automatic transmission become available for the first time in the 1973 model year. Both engines displaced 1.7 L, DIN-rated at 49 kW (67 PS; 66 bhp) with the manual transmission and 46 kW (63 PS; 62 bhp) with the automatic. The Type 4 engine was enlarged to 1.8 L and 50 kW (68 PS; 67 bhp) DIN for the 1974 model year and again to 2.0 L and 52 kW (71 PS; 70 bhp) DIN for the 1976 model year. The 1978 2.0 L now featured hydraulic valve lifters, eliminating the need to periodically adjust the valve clearances as on earlier models. The 1975 and later U.S. model years received Bosch L-Jetronic electronic fuel injection as standard equipment; 1978 was the first year for electronic ignition, utilizing a hall effect sensor and digital controller, eliminating maintenance-requiring contact-breaker points. As with all Transporter engines, the focus in development was not on power, but on low-end torque. The Type 4 engines were considerably more robust and durable than the Type 1 engines, particularly in Transporter service.
In 1972, for the 1973 model year, exterior revisions included relocated front turn indicators, squared off and set higher in the valance, above the headlights. Also, square-profiled bumpers, which became standard until the end of the T2 in 1979, were introduced in 1973. Crash safety improved with this change because of a compressible structure behind the front bumper. This meant that the T2b was capable of meeting US safety standards for passenger cars of the time, though not required of vans. The “VW” emblem on the front valance became slightly smaller.
Later model changes were primarily mechanical. By 1974, the T2 had gained its final shape. Very late in the T2’s design life, during the late 1970s, the first prototypes of Type 2 vans with four-wheel drive (4WD) were built and tested.
1979 Volkswagen Type 2 (T2) “Silverfish” last-edition bus. These were a limited edition model to mark the final production of T2 models in Europe
 1968 Volkswagen Type 2 (T2) Hard-Top Westfalia “Cream” bus
1968 Volkswagen Type 2 (T2) Hard-Top Westfalia “Cream” bus
Brazilian Volkswagen Type 2 (T2) – 2005 Limited Edition
Brazilian water-cooled Volkswagen Type 2 (T2)
-
VW Kombi, turned into a party bar in Thailand
T2c
The T2c, which has a slightly raised roof – by about 10 cm (3.9 in) – in the early 1990s, is built for the South American and Central American markets. It can be imported into other countries, such as the United Kingdom.
Since 1991, the T2c has been built in México with the water-cooled 1.8 L inline four-cylinder 53 kW (72 PS; 71 bhp) carbureted engine, easily identified by their large, black-coloured, front-mounted radiators, and since 1995 with the 1.6 L air-cooled engines for the Brazilian market.
Since production of the original Beetle was halted in late 2003 as a 2004 model, the T2 remained the only Volkswagen model with the traditional air-cooled, rear-mounted boxer engine until the Brazilian model shifted to a water-cooled engine on 23 December 2005. There was a 1.6 L 50 hp (37 kW; 51 PS) water-cooled diesel engined version of the T2, which was manufactured from 1981 to 1985 in Brazil. This version was very economical – values from 15 km/l to 18 km/l are reported – but it suffered from low performance and an insufficiently capable cooling system, which led to short engine life.
The end of the Volkswagen air-cooled engine on a worldwide basis was marked by a Special Edition Kombi. An exclusive Silver paint job, and limited edition emblems were applied to only 200 units in late 2005, and were sold as 2006 models.
More onerous emissions laws introduced by the Brazilian government for 2006 forced a shift to water-cooled engines. The new “Flex Fuel” water-cooled engine will run on petrol as well as alcohol. Borrowed from the Volkswagen Fox, the engine is a rear-mounted EA-111 1.4 L 8v Total Flex1,390 cc (84.8 cu in), 58 kW (79 PS; 78 bhp) on petrol, and 60 kW (82 PS; 80 bhp) when run on ethanol, and 124 N·m (91 lbf·ft) torque. This version has been very successful, despite the minor changes made to the overall T2-bodied vehicle. It still includes the four-speed transmission, but with a new final drive ratio it can cruise at 120 km/h (75 mph) at 4,100 rpm. Top speed is 130 km/h (81 mph). 0 to 100 km/h (0 to 62 mph) is achieved in 22.7 seconds (vs. 29.5 seconds for the last air-cooled version). Improvements were made with 6.6% better fuel economy, and nearly 2 decibel (dB) less noise (again vs. the air-cooled version).
The Volkswagen Type T2 is by far the longest model run in Brazil, having been introduced in September 1950 as the Volkswagen “Kombi”, a name it has kept throughout production. The fierce competition from European front-wheel drive newer generation vans still cannot match the Kombi’s unparalleled cost-benefit equation. Only produced in two versions, bus (nine-seater or 12-seater – a fourth row is added for metro transportation or school bus market) or panel van, it offers only one factory option: the rear window defog. As of June 2009, the T2 is built at the Volkswagen Group’s São Bernardo do Campo plant at a rate of 97 per day.
The production of the Brazilian Volkswagen Kombi ended in 2013 with a production run of 600 Last Edition vehicles. The phaseout of the T2c marks the end of an era which lasted since 1945 (when started the second generation of Volkswagen Type-1 – it will be the final production of metal-made bumper cars after 68 years. A short movie called “Kombi’s last wishes” was made by VW Brazil.
Post-Type 2 generations
Third generation (T3; 1979–1992)
The Volkswagen Type 2 (T3) also known as the T25, (or Vanagon in the United States), the T3 platform was introduced in 1980, and was one of the last new Volkswagen platforms to use an air-cooled engine. The Volkswagen air-cooled engine was phased out for a water-cooled boxer engine (still rear-mounted) in 1984. Compared to its predecessor the T2, the T3 was larger and heavier, with square corners replacing the rounded edges of the older models. The T3 is sometimes called “the wedge” by enthusiasts to differentiate it from earlier Kombis.
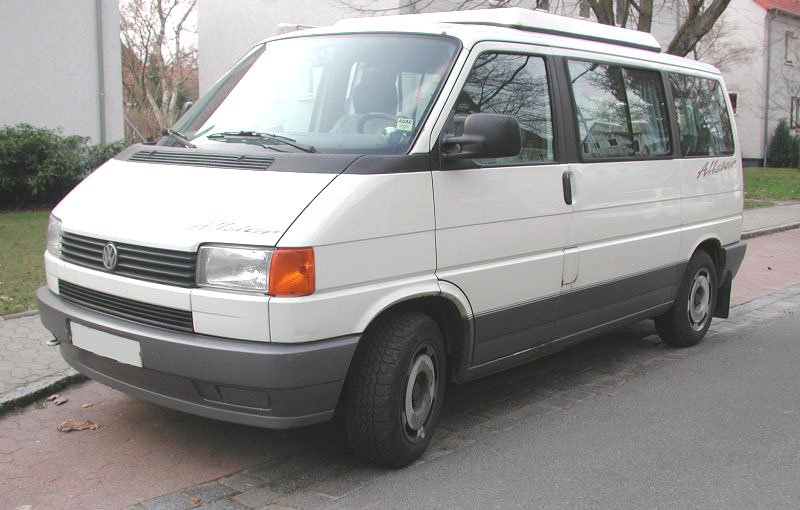
Fourth generation (T4; 1990–2003)
Since 1990, the Transporter in most world markets has been front-engined and water-cooled, similar to other contemporary Volkswagens, almost two decades later than it did for the passenger cars. T4s are marketed as Transporter in Europe. In the United States, Volkswagen Eurovan is the brand name.
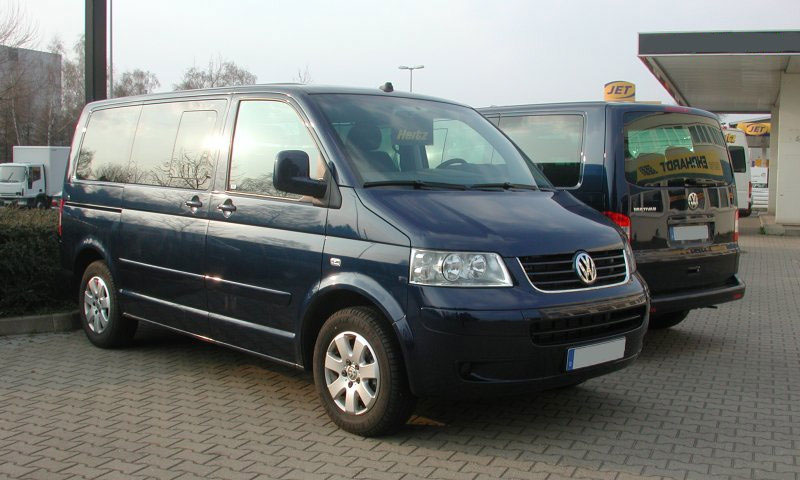
Fifth generation (T5; 2003–present)
The Volkswagen Transporter T5 range is the fifth generation of Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles medium-sized light commercial vehicle and people movers. Launched 6 January 2003, the T5 went into full production in April 2003, replacing the fourth generation range.
Key markets for the T5 are Germany, the United Kingdom, Russia, France and Turkey. It is not sold in the US market because it is classed as a light truck, accruing the 25% chicken tax on importation. The T5 has a more aerodynamic design. The angle of the windshield and A-pillar is less; this makes for a large dashboard and small bonnet.
In June 2009, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles announced the one-millionth T5 rolled off the production line in Hanover.
Additional developments
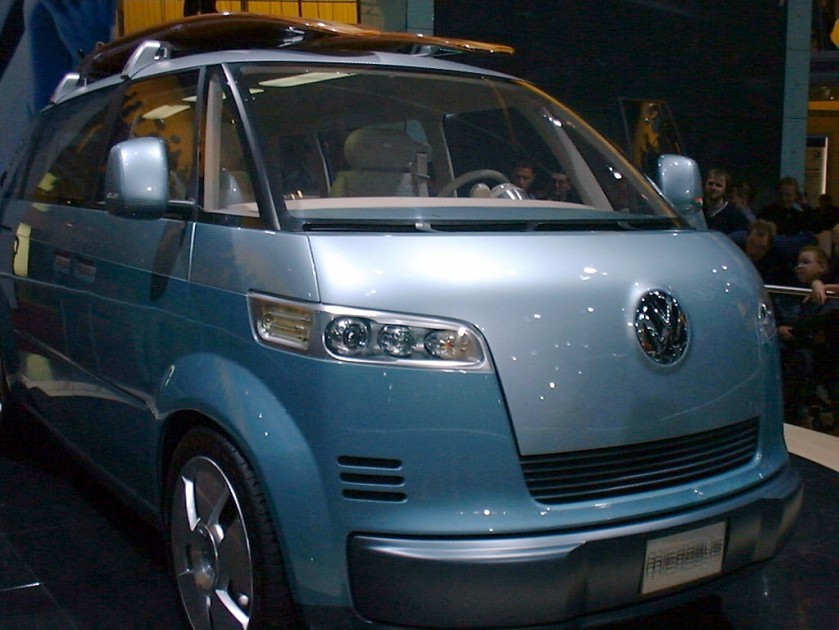
In 2001, a Volkswagen Microbus Concept was created, with design cues from the T1 generation in a spirit similar to the New Beetle nostalgia movement. Volkswagen planned to start selling it in the United States market in 2007, but it was scrapped in May 2004 and replaced with a more cost-effective design to be sold worldwide.
Names and nicknames
Like the Beetle, from the beginning, the Type 2 earned many nicknames from its fans. Among the most popular, at least in Germany, are VW-Bus and Bulli (or Bully) or Hippie-van or the bus. The Type 2 was meant to be officially named the Bully, but Heinrich Lanz, producer of the Lanz Bulldog farm tractor, intervened. The model was then presented as the Volkswagen Transporter and Volkswagen Kleinbus, but the Bully nickname still caught on.
The official German-language model names Transporter and Kombi (Kombinationskraftwagen, combined-use vehicle) have also caught on as nicknames. Kombi is not only the name of the passenger variant, but is also the Australasian and Brazilian term for the whole Type 2 family; in much the same way that they are all called VW-Bus in Germany, even the pickup truck variations. In Mexico, the German Kombi was translated as Combi, and became a household word thanks to the vehicle’s popularity in Mexico City‘s public transportation system. In Peru, where the term Combi was similarly adopted, the term Combi Asesina (Murdering Combi) is often used for buses of similar size, because of the notorious recklessness and competition of bus drivers in Lima to get passengers. In Portugal it is known as Pão-de-Forma (Breadloaf) because its design resembles a bread baked in a mold. Similarly, in Denmark, the Type 2 is referred to as Rugbrød (Rye bread). Finns dubbed it Kleinbus (mini-bus), as many taxicab companies adopted it for group transportation; the name Kleinbus has become an appellative for all passenger vans. The vehicle is also known as Kleinbus in Chile.
In the US, however, it is a VW bus, a “vee-dub”, a minibus, a hippie-mobile, hippie bus, or hippie van, “combie”, Microbus or a Transporter to aficionados. The early versions produced before 1967 used a split front windshield (giving rise to the nickname “Splitty”), and their comparative rarity has led to their becoming sought after by collectors and enthusiasts. The next version, sold in the US market from 1968 to 1979, is characterised by a large, curved windshield and is commonly called a “bay-window”. It was replaced by the Vanagon, of which only the Westfalia camper version has a common nickname, “Westy”.
It was called Volksie Bus in South Africa, notable in a series of that country’s TV commercials. Kombi is also a generic nickname for vans and minibuses in South Africa and Swaziland, often used as a means of public transportation. In Nigeria it was called Danfo.
In the UK, it is known as a “Campervan”. In France, it was called a “camping-car” (usually hyphenated) though this has been expanded to include other, often more specialized vehicles in more recent times.
Mexican production
T2 production began in 1970 at the Puebla assembly factory.
Offered initially only as a nine-passenger version called the Volkswagen Kombi, and from 1973 also its cargo van version called the Volkswagen Panel, both variants were fitted with the 1.5 L air-cooled boxer engine and four-speed manual gearbox. In 1974, the 1.6 L 44 bhp (33 kW; 45 PS) boxer engine replaced the 1.5 previous one, and production continued this way up to 1987. In 1987, the water-cooled 1.8 L 85 bhp (63 kW; 86 PS) inline four-cylinder engine replaced the air-cooled 1.6 L. This new model is recognisable by its black grille (for its engine coolant radiator), bumpers and moldings.
In 1975, Volkswagen de Mexico ordered two specially-made pickups from Germany, one single cab and one double cab, for the Puebla plant. These were evaluated for the possibility of building pickups in Mexico, and were outfitted with every option except the Arctic package, including front and rear fog lights, intermittent wipers, trip odometer, clock, bumper rubber, PVC tilt, and dual doors on the single cab storage compartment. VW de Mexico was interested in having the lights, wiring, brake systems and other parts manufactured in Mexico. Ultimately, VW de Mexico declined to produce pickups, and the pickups were sold to an Autohaus, a Volkswagen dealer in San Antonio, Texas, since they could not be sold in Mexico. By law, no German-made Volkswagens were to be sold in Mexico. These are probably the only pickups that were produced in Germany for Mexican import, and have the “ME” export code on the M-code plate. The green double cab was sold to a new owner in New York, and has been lost track of. The light gray (L345, licht grau) single cab still exists. Pickups were not manufactured in Mexico, nor were they imported into Mexico from Germany, save for these two examples.
In 1988, a luxury variant – the Volkswagen Caravelle – made its debut in the Mexican market to compete with the Nissan Ichi Van, which was available in cargo, passenger and luxury versions.
The main differences between the two are that the Caravelle was sold as an eight-passenger version, while the Combi was available as a nine-passenger version, the Caravelle was only painted in metallic colors, while the Combi was only available in non-metallic colors, and the Caravelle was fitted with an AM/FM stereo cassette sound system, tinted windows, velour upholstery, reading lights, mid and rear headrests, and wheel covers from the European T25 model.
In 1991, the 10 cm (3.9 in) higher roof made its debut in all variants, and the Combi began to be offered in eight- or nine-passenger variants. In 1991, since Mexican anti-pollution regulations required a three-way catalytic converter, a Digifant fuel injection system replaced the previous carburetor. The three variants continued without change until 1994.
In 1994, production ended in Mexico, with models being imported from Brazil. The Caravelle was discontinued, and both the Combi and the Panel were only offered in white color and finally in 2002, replaced by the T4 EuroVan Pasajeros and EuroVan Carga, passenger and cargo van in long wheelbase version, inline five-cylinder 2.5 L 115 bhp and five-speed manual gearbox imported from Germany.