History FIAT
part VI 1990-1999
1990-1999
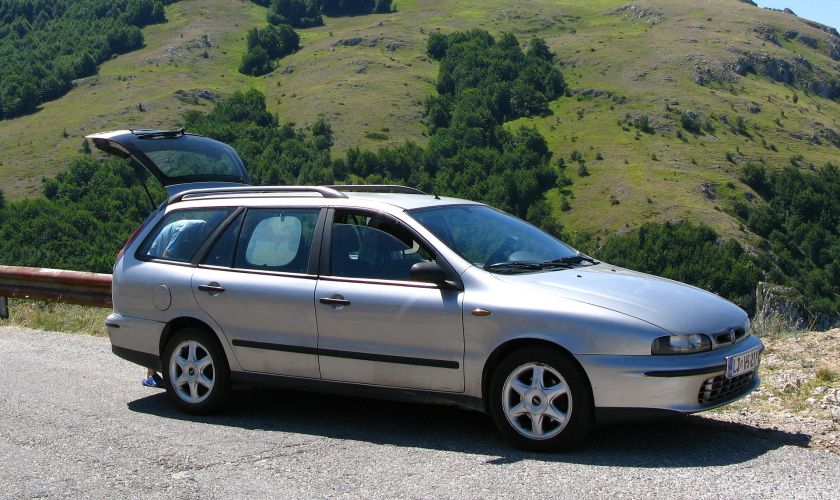
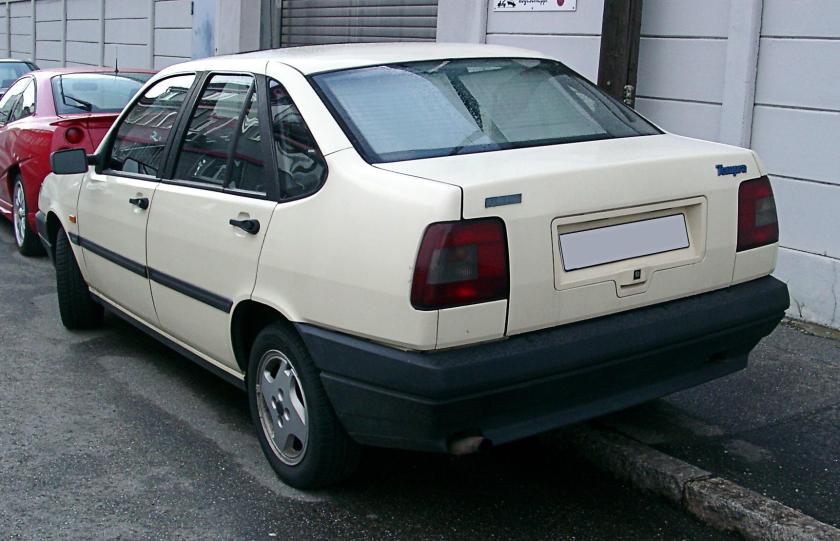
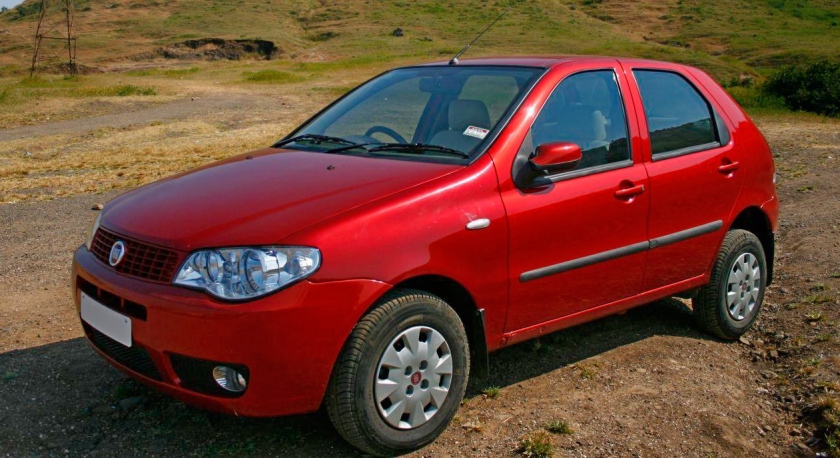
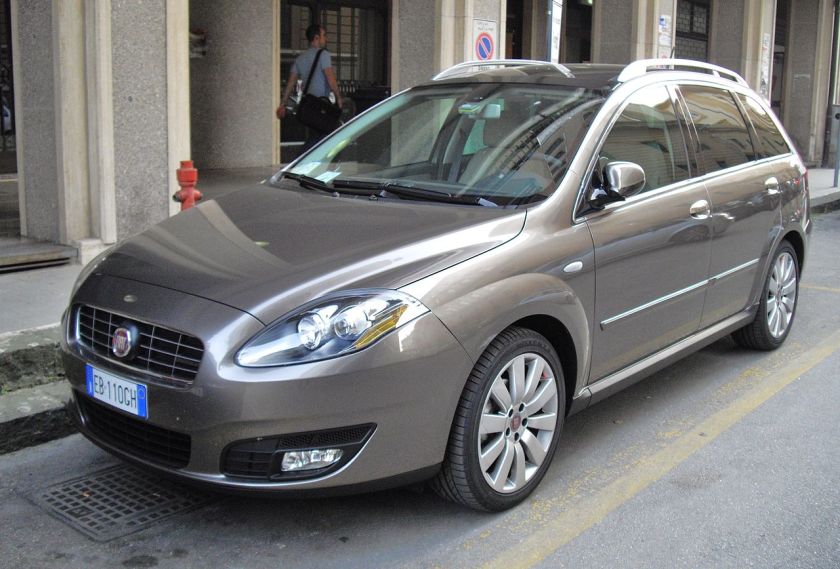
- 1990 Fiat Tempra
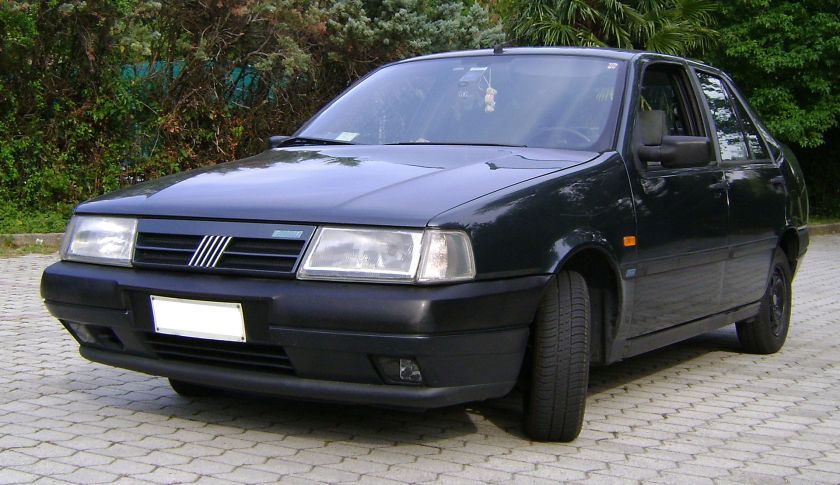
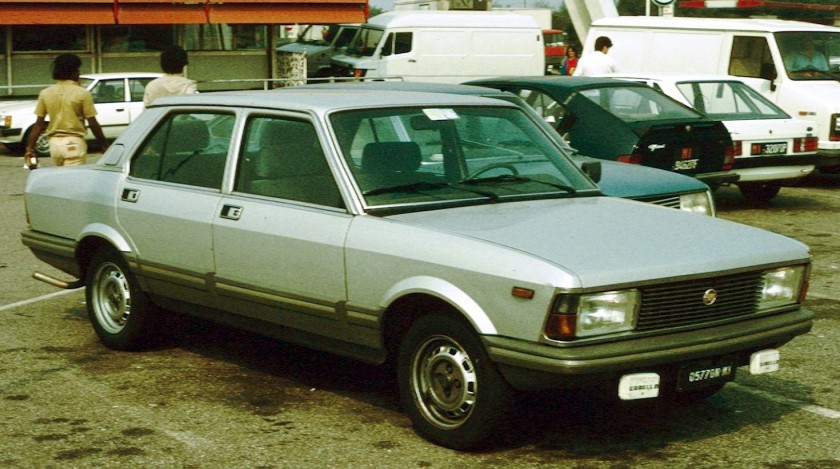
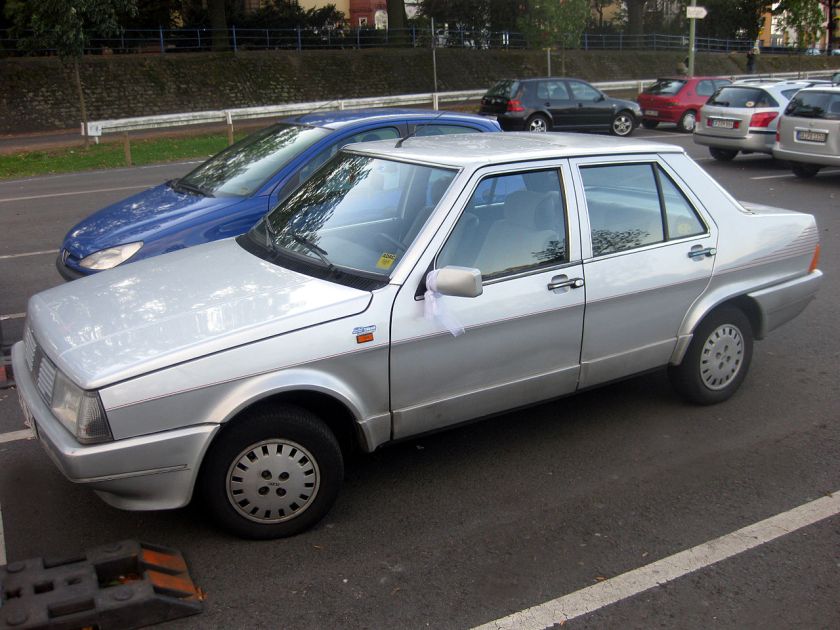
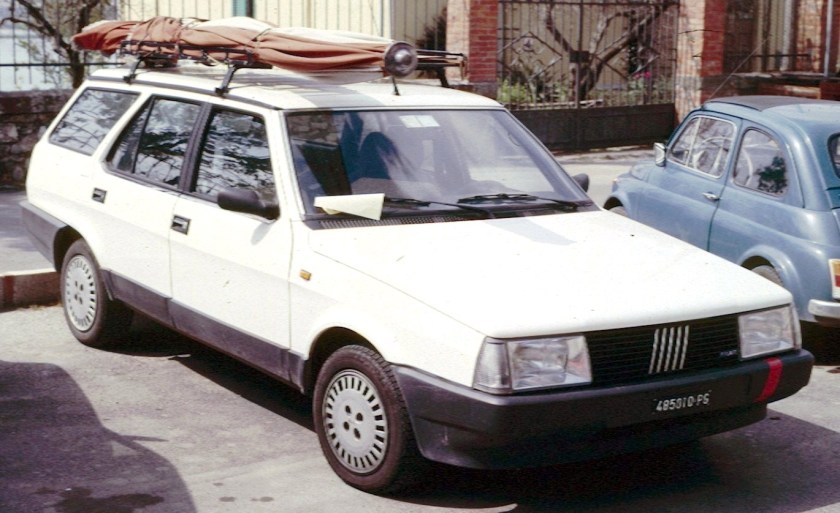
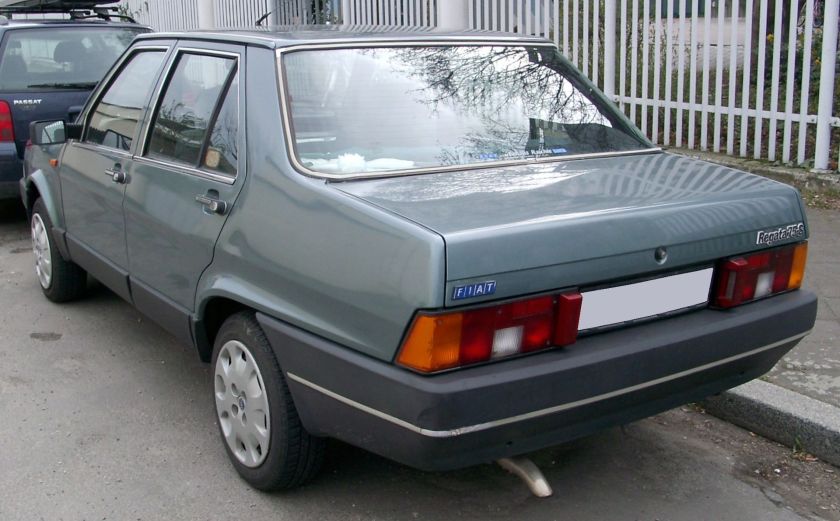
1990 Fiat Tempra
| Fiat Tempra | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat Tofaş Mekong Auto |
| Also called | Fiat Marengo (panel van) |
| Production | 1990—1998 |
| Assembly | Cassino, Italy (1990—1996) Bursa, Turkey (1990—1999) Betim, Brazil (1991—1998) Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam (1996-?) |
| Designer | Ercole Spada at I.DE.A Institute |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Family car |
| Body style | 2-door saloon (Brazil) 4-door saloon 5-door station wagon 5-door panel van |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel drive /four-wheel drive (estate) |
| Platform | Type Three platform (Tipo Tre) |
| Related | Alfa Romeo 145/146 Alfa Romeo 155 Fiat Tipo Fiat Coupé Lancia Delta Lancia Dedra |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.4 L I4 1.6 L I4 1.8 L I4 2.0 L I4 2.0 L turbo I4 1.9 L diesel I4 1.9 L turbodiesel I4 |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 4-speed automatic “Selecta” CVT |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,540 mm (100 in) |
| Length | Saloon: 4,355 mm (171.5 in) Station Wagon: 4,472 mm (176.1 in) |
| Width | 1,695 mm (66.7 in) |
| Height | 1,445 mm (56.9 in) |
| Curb weight | 1,030 kg (2,271 lb)-1,220 kg (2,690 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat Regata |
| Successor | Fiat Marea |
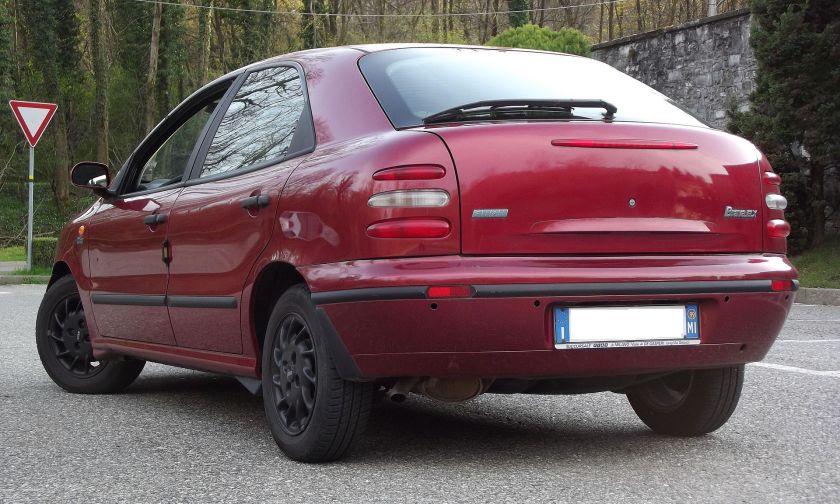
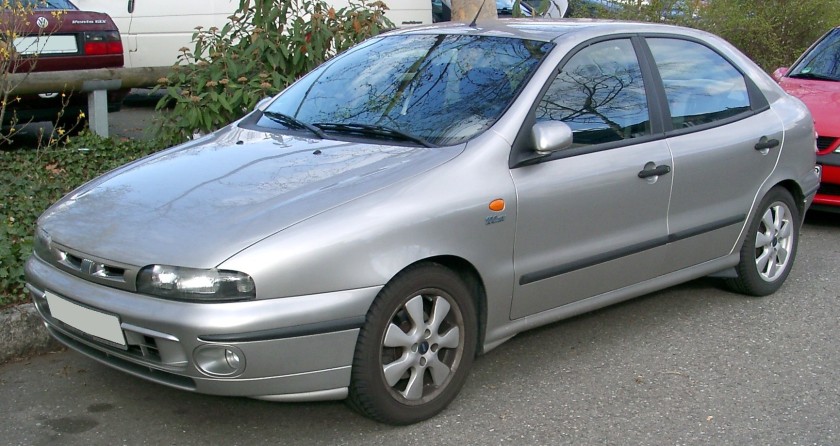
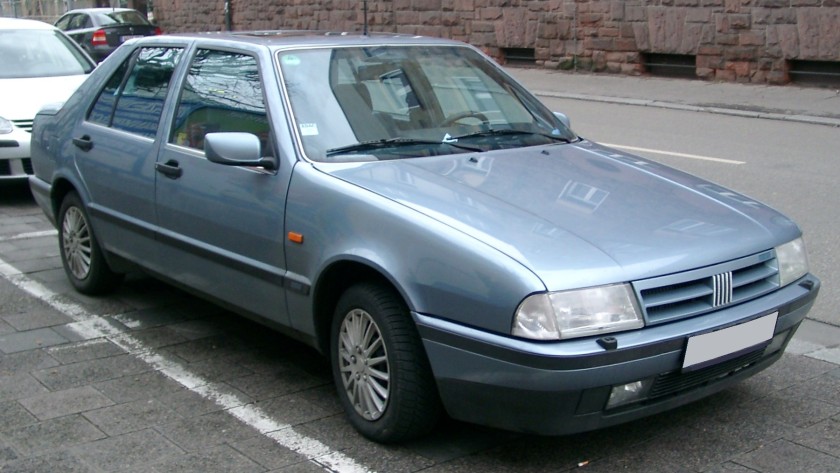
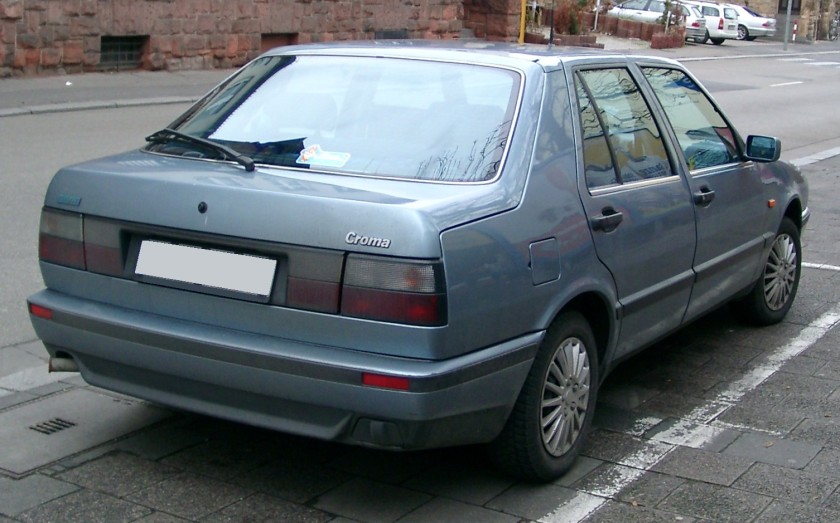
The Fiat Tempra (Type 159) is a small family car produced by the Italian automaker Fiat from 1990 to 1998. The Tempra was intended as a replacement for the Fiat Regata. The original project was called Tipo 3, being a mid-size car between the Fiat Tipo (project Tipo 2) and the bigger Fiat Croma (project Tipo 4). The Tempra shares its Type Three platform with the Lancia Dedra and Alfa Romeo 155.
The Tempra was named the 1991 Semperit Irish Car of the Year in Ireland.
Overview
The Tempra saloon was introduced in February 1990 at the Geneva Salon, with the station wagon (marketed as the “Tempra SW”) arriving two months later in Turin. The initial engine range comprised 1.4, 1.6 and 1.8 petrol units and normally aspirated and turbocharged 1.9-litre diesel units. The car began to be produced in Brazil for Latin American markets after being introduced in Aruba, September 1991. First seen in September 1992, a two-door coupé version of it was produced exclusively for the Brazilian market. It was built until 1995 and a turbocharged petrol version was also available there.
Mechanics
The Tempra’s engine range was similar to that of the Tipo. Initially 1.4- and 1.6-litre models had carburettor engines. Both of these models were discontinued in 1992 due to the new European emission standards and thus all models from 1992 on had catalytic converters and electronic injection. Transmission was a standard five speed manual, but for the first time a midsize sedan was offered as with a continuously variable transmission which was previously available on the Fiat Uno, Panda, Ritmo and Tipo. This, called the “Selecta”, was available only with the 1.6 litre engine with either bodystyle. As of July 1991, the 2.0-litre SX model became available with an optional four-speed automatic transmission. Presented in Geneva 1992 (March), there was a version of the station wagon which offered the 2-litre engine combined with permanent four-wheel drive. The four-wheel drive version had a slight front bias (56/44%).
During its 6 year production run, few changes were made apart from a minor facelift in April 1993 which resulted in a new front grille and other minor styling changes, as well as new equipment levels.
Chassis and main parts (most notably, the doors) were shared with the Fiat Tipo. Other vehicles, derived from the same project were Lancia Dedra (Tempra’s most similar cousin, sharing all mechanical components),Lancia Delta second generation, Alfa Romeo 155, Alfa 145 and Alfa 146.
Equipment and trim levels
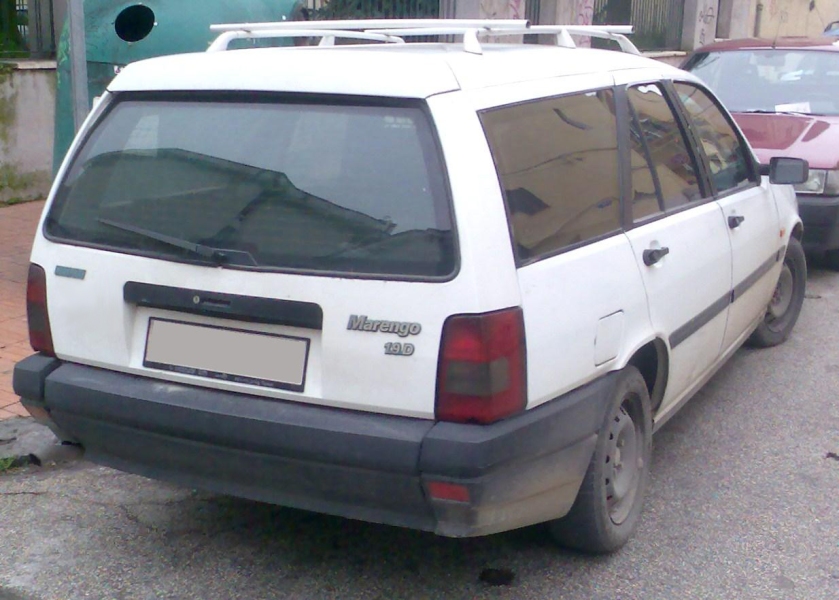 Fiat Marengo (Tempra commercial) |
Only two trim levels were available in its early years: standard (S) and SX, both reasonably equipped considering the Tempra’s low price.
SX models for example, featured power windows, power locks, adjustable belts and steering wheel, front fog lights, body coloured bumpers, velvet upholstery, a futuristic digital dashboard and many other standard extras. They were also available with optional extras like anti-lock brakes, alloy wheels, sunroof, electronic climate control, etc.
A facelift in April 1993 featured more trim levels, now ranging from the standard models (“L” in the UK, where it was only available with 1.4 engine) via the S and SX to the top SLX, which was only available with 1.8- and 2.0-litre engines in the UK. An optional driver’s airbag was another innovation that year. The four-wheel drive Station Wagons continued to be available in some markets such as Switzerland. In Turkey, where Tofaş built the car, there were also “SX A” (automatic transmission) and “SX AK” (climate control added) versions available. The 1,000,000th Tofaş built was a Tempra 2.0 i.e. 16V. The Turkish 16 valve Tempra was not sold in the rest of Europe; it was also available with station wagon bodywork and has a 148 PS (109 kW) engine.
There was also the domestic market Marengo, a name also used before with the Regata Weekend and later again with the Marea Wagon. This is a commercial version of the Tempra which was based on the Station Wagon version, but with basic equipment, heavily tinted rear windows, and no rear seats. The engines were most commonly the naturally aspirated diesels.
Reports
Quattroruote, a popular Italian motoring magazine, reported some failures and defects with the Tempra. The first issue to be reported was some water ingress through thewindscreen seals, an issue that previously plagued some other Fiat vehicles, especially Alfa 33, which in rainy conditions would carry a significant quantity of water on board. This problem was reported from 1990–92 and was resolved with using a higher quantity of sealant when fitting the glass.
Another reported problem was a high oil consumption, especially the 1,581 cc engine, which was a common defect with Tipo (with the same engine) and Panda (1000 FIRE engine). The same was reported for other Fiat’s vehicles, but disappeared with the new 1.6 L 66 kW engine.
On the same model, from 1994, the car started to show some electronic malfunctions, with items such as the electronic control unit, code key and electric system. A design flaw of the Tempra was that its rear window was too small and inclined and the tail too tall, so that rear visibility was poor. This issue was common with the 155 and Dedra, and was one of the reason the estate had more success than the saloon, especially in the UK.
Qualities
Since the beginning, the Tempra was presented as a cheap and reliable car. 1.4 and 1.6 engines were able to run long distances with good fuel economy, also aided by a high capacity tanks of 65 litres (17 US gal; 14 imp gal) for the sedan and 70 L (18 US gal; 15 imp gal) for the Station Wagon. Average range for a 55 kW 1.6 litre sedan was around 920 km (572 mi) (14 km/L or 7.1 l/100 km or 39.5 mpg-imp), and consumption at constant speed was of 16.5 km/L (6.1 l/100 km; 46.6 mpg-imp) at 90 km/h (56 mph) and 11.6 km/L (8.6 l/100 km; 32.8 mpg-imp) at 130 km/h (81 mph). All these were aided by a favorable aerodynamic (Cx 0.297) and only 17.2 PS subtracted at 100 km/h (62 mph), which was the best result among all the rivals.
Another advantage was the galvanized structure, which allowed the model to be resistant against rust over the time, also showing a good response to weather and bad climate conditions after many years. Other qualities were the strength and reliability of the mechanics, thanks to the engine that could be used in urban drive, extra-urban and highways. For its luggage capacity, especially the Marengo version, was also one of the favourites among companies with the 1929 diesel engine, and the interior space was comfortable for 5 persons during long travels.
Another
End of production
The Tempra was discontinued in Europe in 1996, and in Brazil in 1998. It was replaced by the Fiat Marea, which is based on the Fiat Bravo and Fiat Brava platform, the replacements for the Tempra’s sister car the Fiat Tipo.
In Brazil 204,795 Tempras were produced in eight years, and in Turkey, where the car was manufactured by Tofaş from November 1990 until 1999, 129,590 were made.
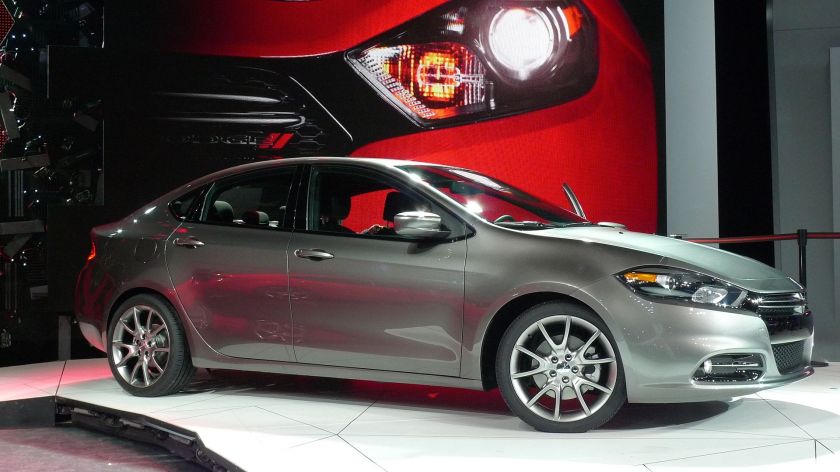
Return in 2014
Dodge Dart will be the future Fiat Tempra in Brazil
According to news recently published, Fiat has the intention of launching its Italian version of Dodge Dart, known as Fiat Viaggio in Europe and Asia, as Fiat Tempra in Brazil. The sedan’s debut might happen between the end of 2013 and the beginning of 2014.
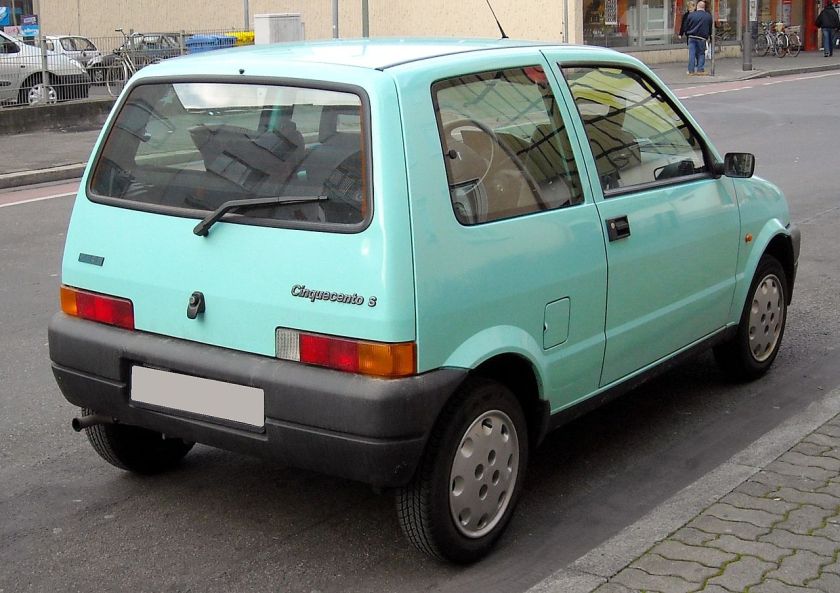
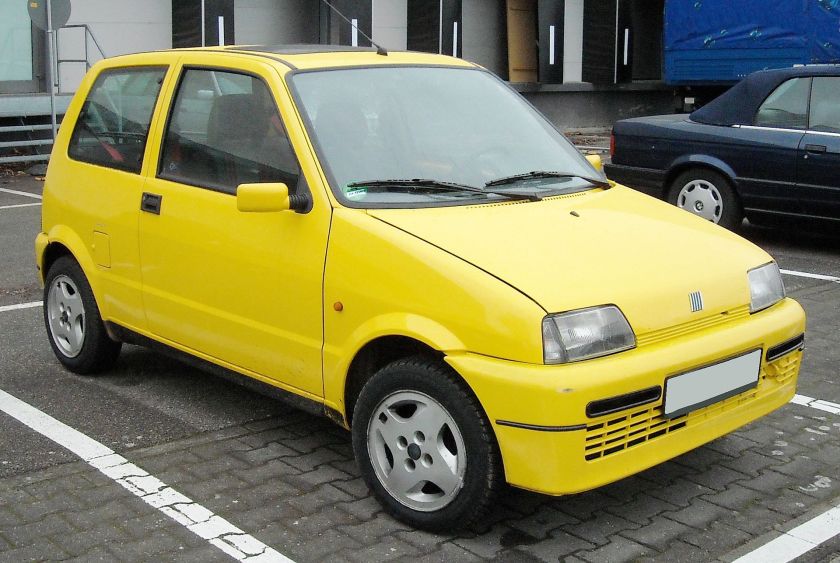
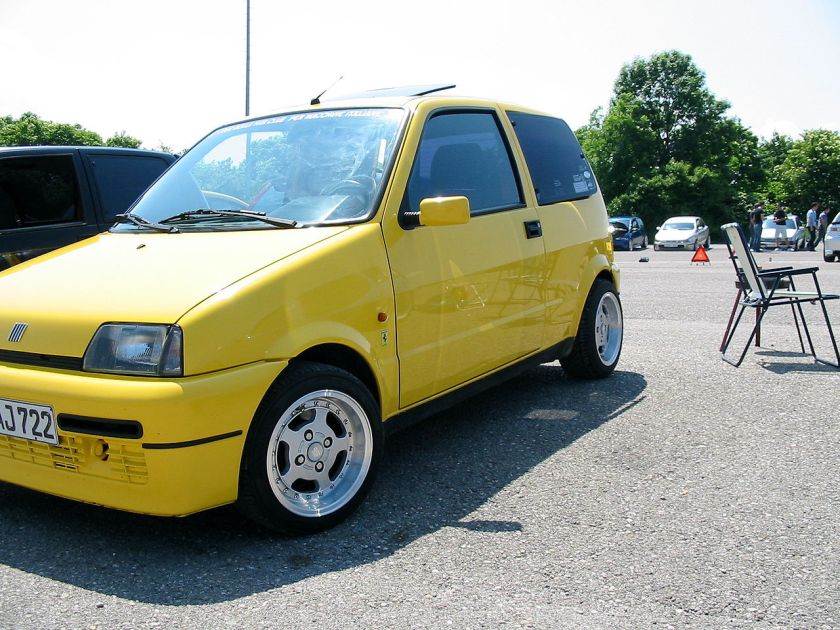
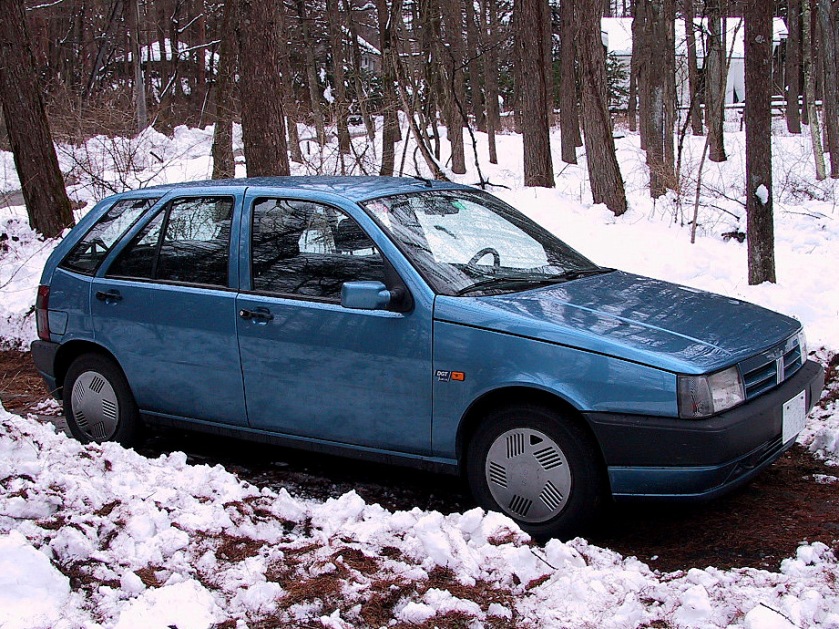
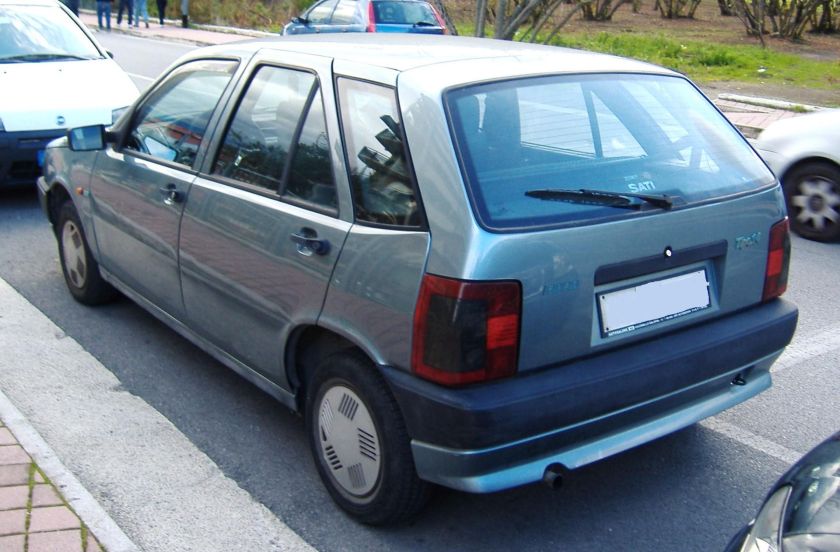
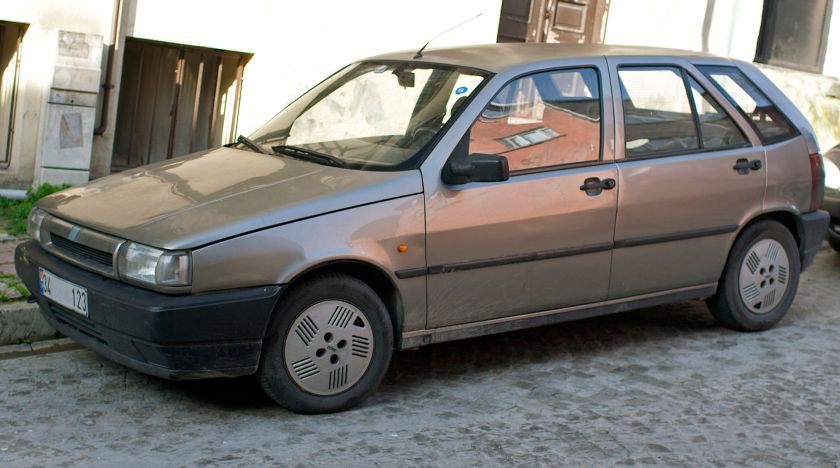
- 1992 Fiat Cinquecento
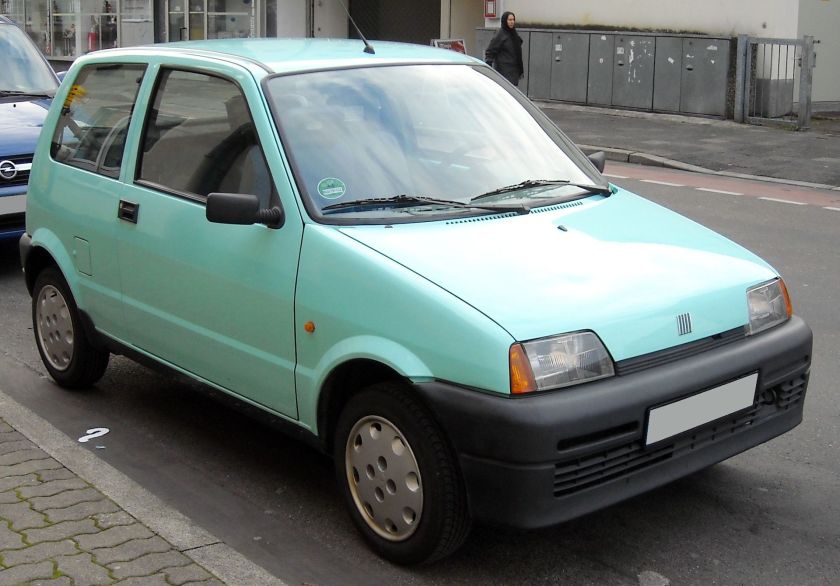
1992 Fiat Cinquecento
| Fiat Cinquecento | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Production | 1991–1998 |
| Assembly | Tychy, Poland |
| Designer | Giorgetto Giugiaro |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | City car |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 704 cc I2 (petrol) 903 cc I4 (petrol) 899 cc I4 (petrol) 1108 cc I4 (petrol) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200 mm (86.6 in) |
| Length | 3,230 mm (127.2 in) 3,226 mm (127.0 in) (Sporting) |
| Width | 1,490 mm (58.7 in) 1,486 mm (58.5 in) (Sporting) |
| Height | 1,435 mm (56.5 in) |
| Curb weight | 675–727 kg (1,488–1,603 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat 126 |
| Successor | Fiat Seicento |
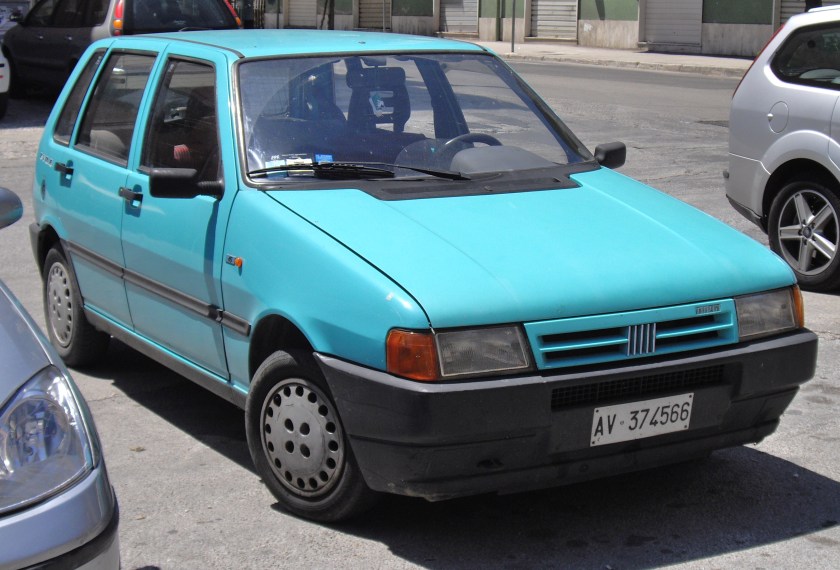
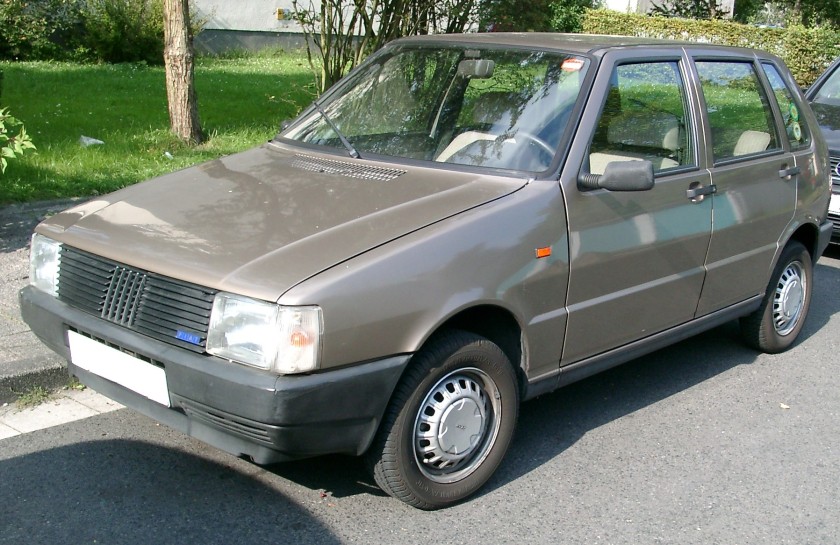
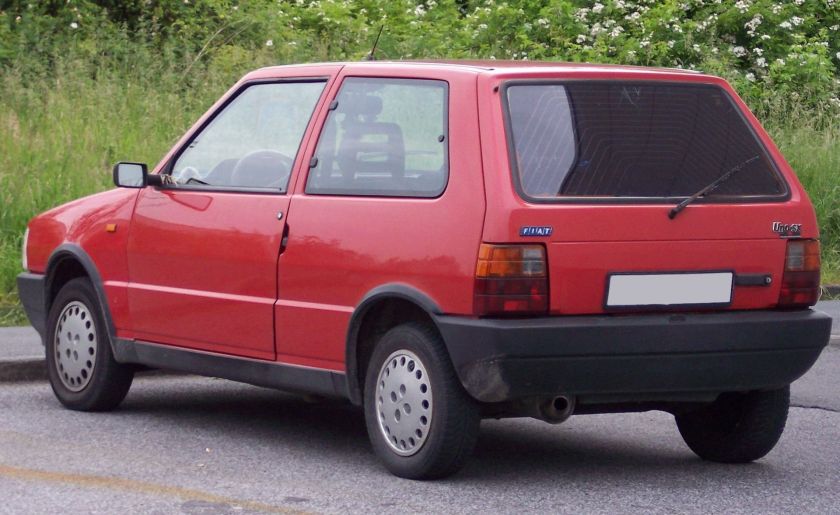
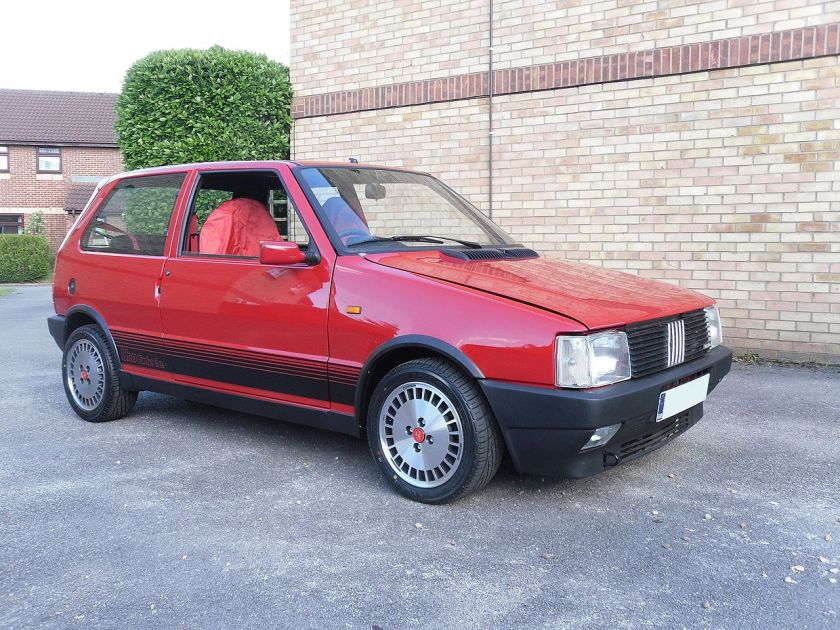
The Fiat Cinquecento (Type 170) (/ˌtʃɪŋkwəˈtʃɛntoʊ/; Italian pronunciation: [tʃiŋkweˈtʃɛnto]) was a city car designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro launched by Fiat in late 1991 to replace the Fiat 126. It was the first Fiat model to be solely manufactured in the FSM plant in Tychy, Poland, which had been sold to Fiat by the Polish state, and where production of the Polish variant of the Fiat 126, the Polski Fiat 126p, was still running. Production of the Cinquecento ended in 1998, when it was replaced by the Seicento. Despite its name, its lowest displacement was 704 cc.
The Cinquecento was available in one body style only, a small, angular 3-door hatchback, with a favorable drag coefficient of only 0.33 that bore similarities to the Lancia Y10. It featured several advances compared to older Fiat city cars, including independent suspension both in the front and in the rear similar to the Fiat Tipo, front disc brakes, side impact bars along with crumple zones incorporated in the design and galvanized body panels to fend off corrosion. Steering was by rack and pinion, and although power steering was never offered, the car could be ordered with a number of extras, including central locking, power windows, sunroof(or full-length retractable canvas roof in the Soleil version) and even air conditioning.
Engines
Unlike the rear-wheel drive 126, the Cinquecento was a front-wheel drive car. Whereas the 126 had a rear mounted engine, the Cinquecento now featured a front mounted engine.
It was initially available with two engine choices, with the 1.1 L FIRE or “sporting” joining the lineup later. Interestingly, while the 704 cc engine was mounted longitudinally, the bigger units were fitted transversely, making the little Fiat one of the few cars in the world available with both configurations at the same time.
704 cc
The smallest engine, intended for sale in Poland only, was a 704 cc ohv two-cylinder unit, delivering 31 metric horsepower (23 kW) or 30 metric horsepower (22 kW) with catalyst. Cinquecento inherited this unit from the 126p BIS, an evolution of the 126p which was cancelled when the Cinquecento production started. In order to be fitted in the front-wheel drive Cinquecento, it underwent a major refurbishment (although the engine still employed a carburettor), which resulted, among other changes, in the crankshaft revolving in the opposite direction than in the 126p BIS!
903/899 cc
The bigger engine was the 903 cc 40 PS (29 kW; 39 hp) version of the veteran ohv four-cylinder engine, which saw service in many small Fiat models, starting with Fiat 850. (This engine dates back to the initial 633 cc unit as introduced in the 1955 FIAT 600.) It was fitted with single point fuel injection and was the base engine in most markets. Due to fiscal limitations, the displacement of this unit was limited to 899 cc in 1993, with a slight reduction of output, now producing 39 PS (29 kW; 38 hp). This engine is derived from that used in the Fiat 127. While it still retains OHV chain drive pushrod layout it now has hydraulic tappets. Also now uses twin coil distributorless ignition.
1.1 FIRE (Sporting)
In 1994, Fiat introduced the Cinquecento Sporting, featuring the 1108 cc SOHC FIRE 54 PS (40 kW; 53 hp) engine from the entry-level Punto of the same era, mated to a close-ratio gearbox. Other additions were a drop in standard ride height, front anti-roll bar, 13″ alloy wheels, plus colour-coded bumpers and mirrors. The interior saw a tachometer added, along with sports seats, red seatbelts and a leather steering wheel and gear knob.
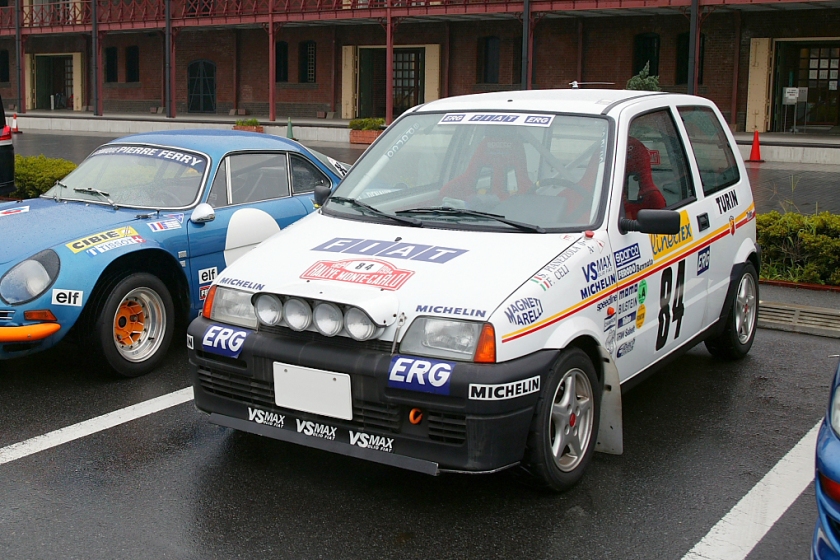
It is the Sporting model which gave birth to a rallying trophy and a Group A Kit-Car version.
Elettra
From 1992-1996 Fiat also produced and sold an electric variant of the Cinquecento called the Elettra. The car was offered with either a Lead-acid or NiCd batterypack, providing a ranges of 62 mi (100 km) and 93 mi (150 km) respectively. Unlike purpose built electric cars, the Cinquecento Elettra used two battery packs, one in the engine bay and one under the rear seats, replacing the fuel tank. Although selling for 140,000 francs (~US$159,000), the Cinquecento Elettra enjoyed relative popularity in Italy, France and Switzerland.
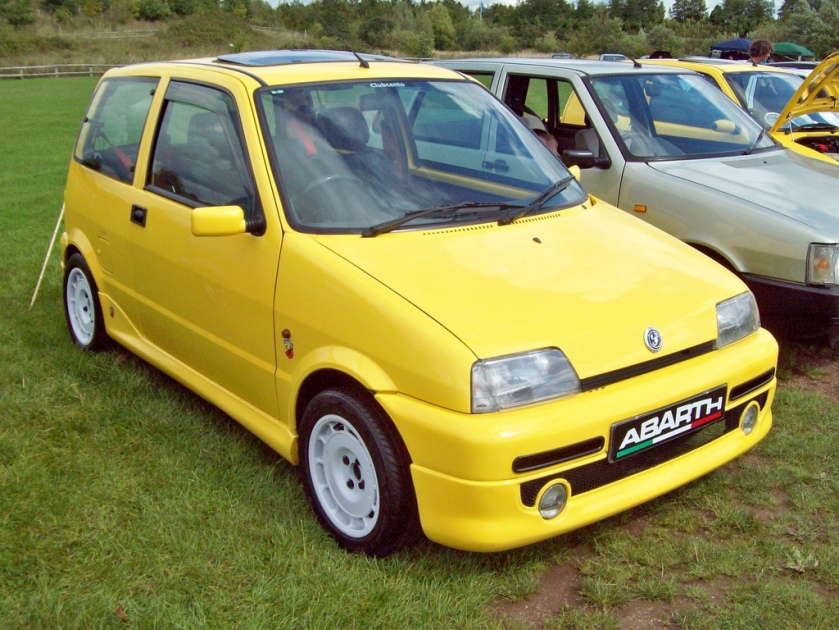
Abarth
Fiat offered optional extras from the factory labelled with the Abarth name. The Abarth extras for the Cinquecento consisted of cosmetic changes only. A front apron with fitted fog lights, a rear apron, side skirts and a rear spoiler with a fitted 3rd brake light. There were also a set of 13″ Speedline 5-spoke alloys wheels available instead of the standard Sporting alloys.
Unlike true Abarth models, there were no engine upgrades available from the factory and the car could not be purchased as a whole separate model. The Abarth parts were to be added by the purchaser at the time of ordering, hence why it is common to see cars with only some of the Abarth extras.
Concepts
In the mid-1990s, a number of concept cars based on the Fiat Cinquecento were developed by a number of design houses including one that featured half of the car’s interior and a running board to place a bike. Another of these designs was the Lucciola, a proposal for a new Cinquecento by Giorgetto Giugiaro. However instead of the car becoming the next small Fiat city car, a version of the design ended up being put into production by the South Korean Daewoo Motor as their Matiz.
In popular culture
A Fiat Cinquecento appears in several episodes of the British sitcom The Inbetweeners in which main character Simon Cooper owns a yellow, fictional model known as a Fiat Cinquecento ‘Hawaii’ (the model used in filming appears to be a Sporting edition). Its appearance and features (including a tape deck and a replacement red side door) are frequently ridiculed by the characters. Over the course of the series, the car ends up with the following misfortunes:
- Simon driving the car into the middle of a funeral procession (Thorpe Park)
- Main character Jay Cartwright tearing off the passenger door when Simon is trying to park it at Thorpe Park (Thorpe Park)
- The Happy Foundation charity trashing the car after main character Will McKenzie insults them on Nemesis Inferno (Thorpe Park)
- Main character Neil Sutherland having sex with a goth girl, causing the seats to go damp (Caravan Club)
- The car getting clamped after Simon parks in front of a no ‘parking’ sign (A Night Out in London)
- An angry Chinese man rocking the car after he missed all his work placements, because of Simon’s car blocking his van (A Night Out in London)
- The car drifting into a lake after the handbrake fails (The Camping Trip)
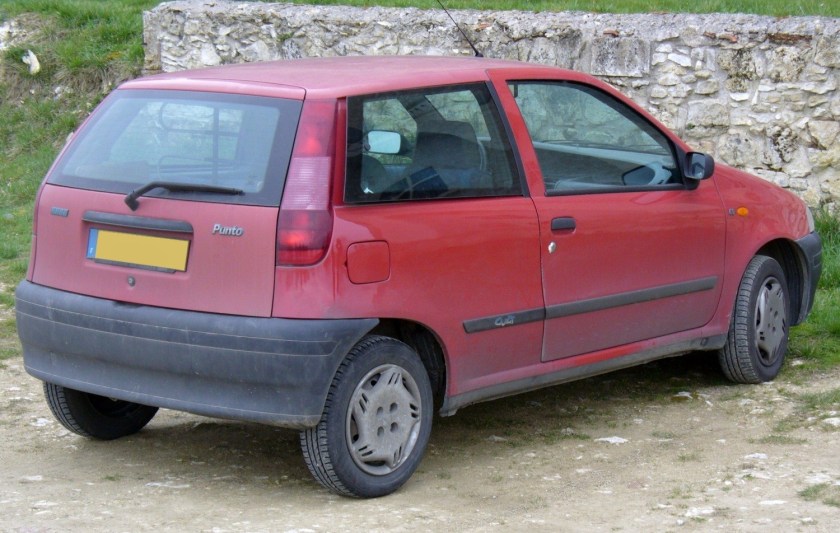
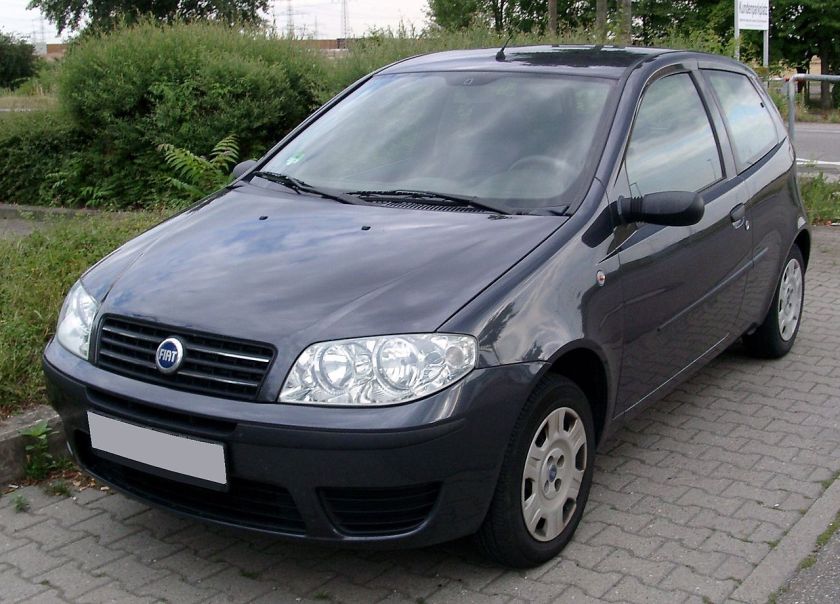
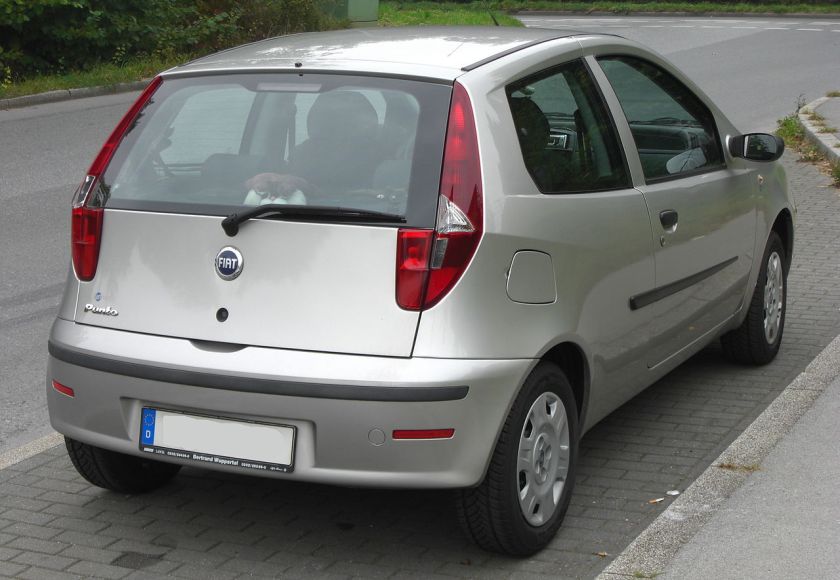
- 1994 Fiat Punto
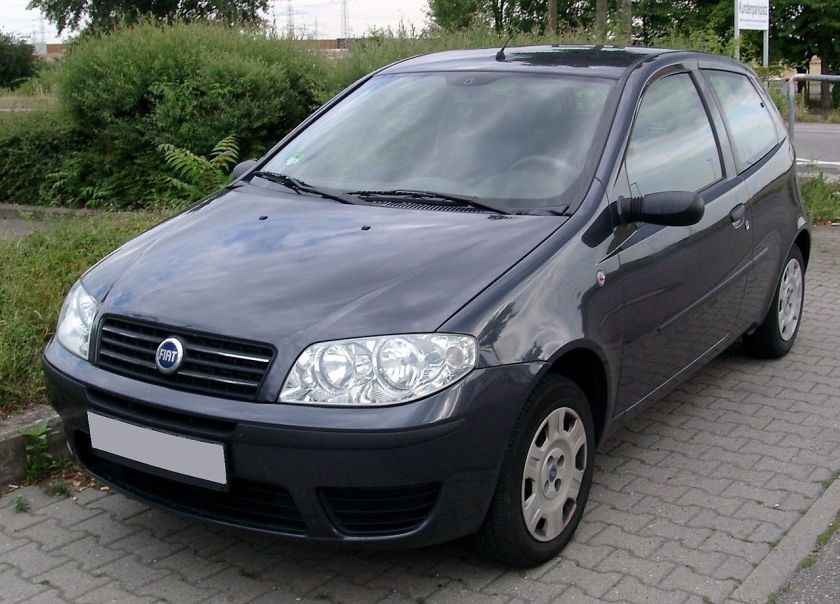
1994 Fiat Punto
| Fiat Punto | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Also called | Fiat Grande Punto Fiat Punto Evo |
| Production | 1993–present |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Supermini |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback 5-door hatchback 2-door convertible 3-door van |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat Uno |
The Fiat Punto is a supermini car produced by the Italian manufacturer Fiat since 1993, spanning over three generations. The third generation of the car was marketed as the Grande Punto, between 2005 and 2009, and the Punto Evo, between 2009 and 2012, when the bare Punto name was re-introduced. As of February 2012, nearly 8.5 million units had been produced.
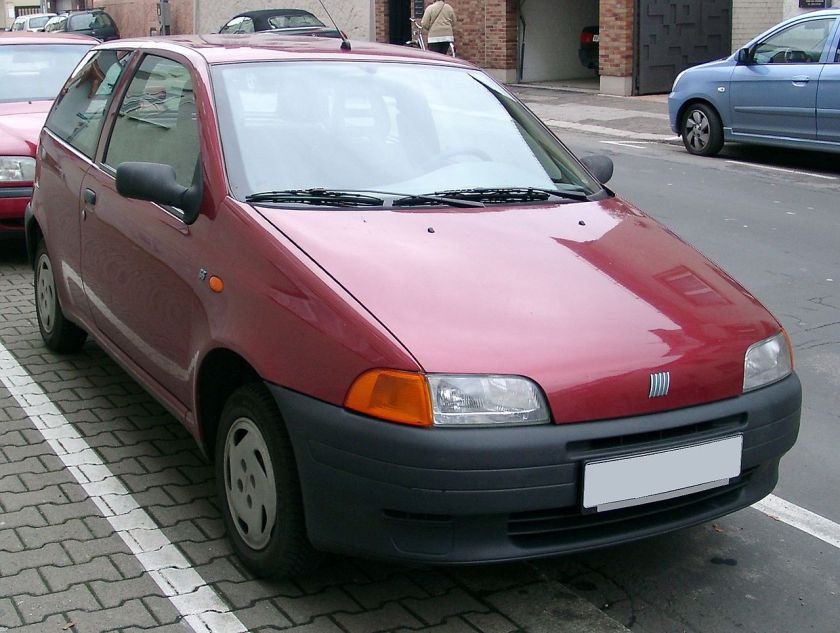
First generation (1993–1999)
| First generation (176) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1993–1999 |
| Assembly | Melfi, Potenza, Italy Mirafiori, Torino, Italy Termini Imerese, Palermo, Italy |
| Designer | Giorgetto Giugiaro (hatchback) Bertone (convertible) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback 5-door hatchback 2-door convertible 3-door van |
| Related | Fiat Barchetta Fiat Albea Fiat Doblò Fiat Palio Fiat Siena Fiat Strada Lancia Y |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.1 L I4 (petrol) 1.2 L I4 (petrol) 1.2 L I4 16-valve (petrol) 1.4 L I4 turbo (petrol) 1.6 L I4 (petrol) 1.7 L I4 (diesel) 1.7 L I4 (turbo-diesel) |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 6-speed manual CVT automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,450 mm (96.5 in) |
| Length | 3,760 mm (148.0 in) |
| Width | 1,625 mm (64.0 in) |
| Height | 1,450 mm (57.1 in) |
| Curb weight | 830–1,040 kg (1,830–2,290 lb) 1,070 kg (2,360 lb) (cabrio) |
Internally codenamed Project 176, the Punto was announced in September 1993 as a replacement for the ageing Fiat Uno and launched in late 1993/early 1994 depending on the market. The Fiat Punto was voted European Car of the Year for 1995, defeating rival Volkswagen Polo by only 78 points.
The Punto was designed by Giorgetto Giugiaro and was available as a three-door or five-door hatchback, and a two-door cabriolet.
Entry level
Entry-level in the Punto range were the 1.1 and 1.2 L petrol engines and the 1.7 diesel engine. The 1.2 engine’s actual capacity is 1242 cc, available in three versions. The first, was fitted in the Punto ELX 75 and produced 75 hp (56 kW) at 6000 rpm while the second, fitted to Punto ELX 85 produced 86 hp (64 kW) at 6000 rpm. The third was a 60 hp (45 kW) engine which eventually replaced the 1.1 54 hp (40 kW) engine.
Sporting versions
A Sporting model was also available with an 1.6 8v updated 128 SOHC engine, producing 88 hp (66 kW), later replaced in 1997 by the 1.2 16v FIRE engine used in the 85 ELX, and a power drop to 86 hp (64 kW).
GT versions
The top of the range model was the 136 PS (100 kW; 134 hp) 1.4 GT, using an evolution of the turbocharged 128 SOHC engine originally found in the Fiat Uno Turbo Mk II – capable of running over 200 km/h (120 mph) and reaching 100 km/h (62 mph) in just 7.9 seconds and came fitted with a five-speed manual gearbox. During the years the GT was made in three different “series” with power 136 PS (100 kW; 134 hp) (1993–1995),133 PS (98 kW; 131 hp) (1995–1997) and 130 PS (96 kW; 130 hp) (1997–1999).
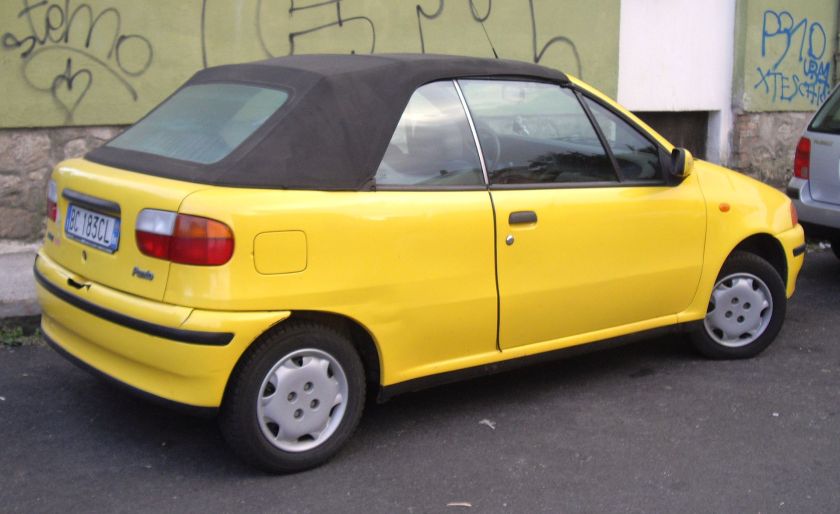
Convertible
A cabriolet (convertible) version was also available; built by Bertone (rather than at the main Fiat factory), it featured an electric powered fully retracting roof and was one of the cheapest open-top cars in the world at the time. In Europe, it was also made with a manual roof. Available in both ELX and SX trim, initially powered by the 90 hp (67 kW) 1.6 Mpi unit (replaced in 1995 by the 86 hp (64 kW) 1.2-L 16v FIRE unit). Approximately 55,000 cars were built between 1994 and 1999, although the last cars were registered in 2000.
Other versions
Particular versions of the first generation Punto were the Punto 6Speed, a 1.1 FIRE Punto 55 with a six-speed gearbox, the Punto Selecta with a CVT-type automatic gearbox, and the Punto ED (Economical Drive), a 1.1 Punto whose five-speed gearbox was designed for high fuel efficiency.
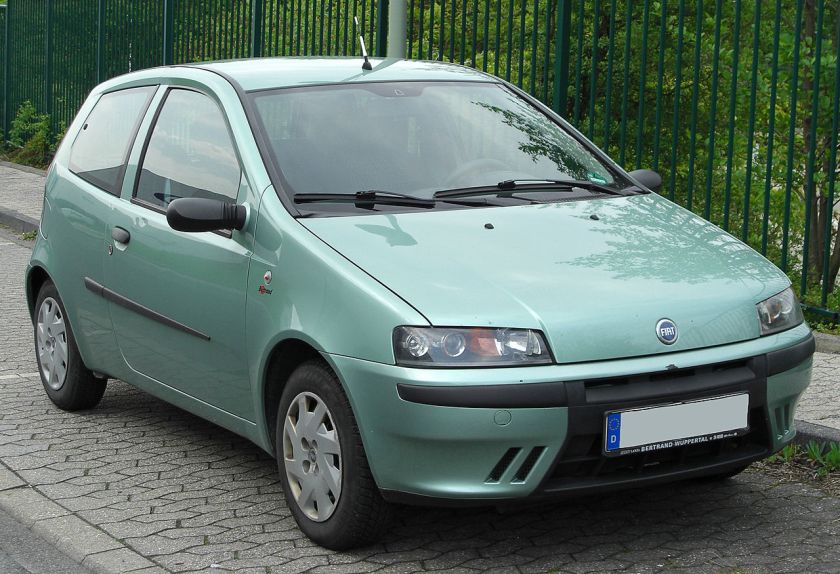
Second generation (1999–2010)
| Second generation (188) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Fiat Punto Classic Zastava 10 |
| Production | 1999–2010 (Italy) 2005–2011 (Serbia) |
| Assembly | Melfi, Potenza, Italy Mirafiori, Torino, Italy Termini Imerese, Palermo, Italy Kragujevac, Serbia (Zastava) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback 5-door hatchback 3-door van |
| Related | Fiat Barchetta Fiat Idea Lancia Ypsilon Lancia Musa |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.2 L I4 (petrol) 1.2 L I4 16-valve (petrol) 1.4 L I4 16-valve (petrol) 1.8 L I4 16-valve (petrol) 1.3 L I4 MultiJet (diesel) 1.9 L I4 DS (diesel) 1.9 L I4 JTD (diesel) |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 6-speed manual (Sporting) 5-speed semi-automatic (Dualogic) 6-speed semi-automatic(Speedgear) 7-speed semi-automatic(Speedgear) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,460 mm (96.9 in) |
| Length | 3,800 mm (149.6 in) (3-door, 1999–03) 3,835 mm (151.0 in) (5-door, 1999–03) 3,840 mm (151.2 in) (3-door, 2003–10) 3,865 mm (152.2 in) (5-door, 2003–10) |
| Width | 1,660 mm (65.4 in) |
| Height | 1,480 mm (58.3 in) |
| Curb weight | 860–1,050 kg (1,900–2,310 lb) |
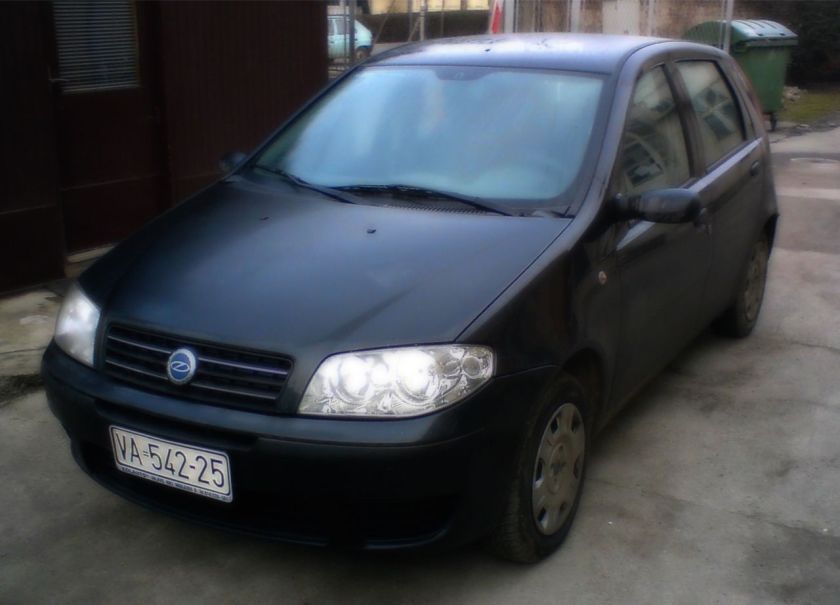
The second generation Punto, codenamed Project 188, was launched in September 1999 at the Frankfurt Motor Show. The styling was all-new while retaining the original Punto’s distinctive shape and design, while the chassis and interior were completely overhauled. The new Punto also became the first Fiat in decades to carry the original round Fiat badge, to celebrate Fiat’s centenary.
At the launch event of the hatchback, the Fiat Wish concept car was also presented, which was hardtop convertible version of the Fiat Punto, very similar in styling with the Peugeot 206 CC. The model was conceived by Pininfarina to celebrate the centenary of Fiat.
Entry level
The 1.1 and 1.4-L turbo engines were discontinued due to emissions issues and the entry-level models had only a 1.2-L petrol unit, with either 8 or 16 valves, giving 60 hp (45 kW) and 80 hp (60 kW) respectively, or a 1.9-L diesel, with or without common rail injection.
Sporting versions
Two sporty versions were offered. The 1.2-L 16 valve Sporting model with a six-speed manual, and the 1.8-L HGT which could reach almost 130 mph (210 km/h). The 1.2-L 16V model also has a Speedgear CVT-equipped variant (with a sequential manual shift mode consisting of six gears, seven for the Sporting model). The 1.8-L HGT accelerates from 0-60 in 8.0 seconds. It was considered a big improvement in handling over the Punto GT. The HGT was also available (in limited numbers) as an “HGT Abarth” which added deeper bumpers, rear spoiler, side skirts, new alloy wheels and interior trim. The HGT Abarth had no technical improvements over the regular HGT.
Power steering
The second generation Punto has also adopted the Dualdrive electric power steering and came with two operation modes, using an electric motor, rather than a hydraulic pump driven by the engine. This resulted in reduced fuel consumption and less environmental impact. It has a fuel economy of 5.6 l/100 km (50 mpg-imp; 42 mpg-US) – urban and 3.9 l/100 km (72 mpg-imp; 60 mpg-US) – extra urban for the 1.9-L diesel. The 1.8-L petrol does 8.8 l/100 km (32 mpg-imp; 27 mpg-US) – urban and 5.3 l/100 km (53 mpg-imp; 44 mpg-US) – extra urban.
Facelift
In early 2003, Fiat celebrated the rollout of the 5,000,000th production Punto. In the same year, the second-generation facelift brought further revisions to the platform, including extensive changes to the exterior styling and engines, partly due to changes in pedestrian safety regulations.
The round Fiat badge, found only on the bonnet of second-generation models, was introduced on the tailgate of the second generation facelift. On 1 June 2005, Fiat produced the 6,000,000th Punto at the Melfi plant.
Engine changes included a new 1.4 L 16v engine, alongside the staple 1.2 and 1.2 L 16v variants, and the introduction of two HGT versions, the 1.9 L MultiJet diesel engine and the 1.8 L 16v petrol engine, which could reach almost 130 mph (210 km/h) continued over from the pre-facelift version. There was an introduction also of the 1.3 L common rail diesel MultiJet engine.
Punto Classic
Despite the launch of the slightly larger Grande Punto at the end of 2005, the second-generation Punto remained in production, marketed as the Punto Classic, and has been sold in many emerging markets in addition to the newer versions. It was launched for the first time in Chile in 2007. It ended production in Italy in November 2010.
Zastava 10
In October 2005, Serbian manufacturer Zastava reached an agreement with Fiat to assemble this version under licence in Kragujevac, Serbia, with the model name Zastava 10. After acquiring a majority stake in Zastava in the autumn of 2008, Fiat continued production of this vehicle under the Fiat Punto Classic name from March 2009. Production was stopped in mid 2011, and it never got restarted despite some rumors. It has been available with the 1.2-litre petrol engine and later, also with the 1.3-litre diesel engine.
Trim levels
The Punto was initially released in four different trim leveles: S, SX, ELX and HLX, that were later renamed to Actual, Active, Dynamic and Emotion. Three special versions of the three-door hatchback were also available: Sporting, HGT and Abarth. The top level included such features as ABS, front and side airbags, window bags, remote locking, front power windows, electrical power steering, air conditioning, trip computer with four functions, CD player, CD changer, alloy rims and fog lamps. Options such as navigation and burglar alarm were also offered. After the facelift, it also received EBD, ESP with ASR and hill holder, climate control with double zone heating, MP3 player and subwoofer (HGT only), rear parking sensors and cruise control as an option. A revised instrument panel with a larger display could now show the instant consumption too.
Engines
Four petrol engines with single-point injection system were available, as well as one indirect injection diesel and three common rail turbocharged diesel engines with intercooler (JTD and MultiJet). The 1.8-L 16v and the 1.9-L MultiJet engines were available only with the three-door version in the HGT trim level.
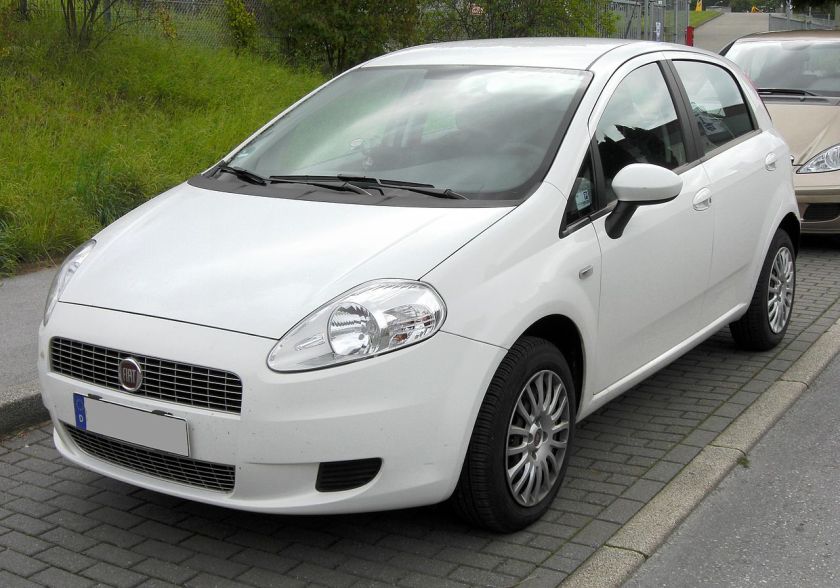
Third generation (2005–present)
The Grande Punto, codenamed Project 199, was unveiled at the 2005 Frankfurt Motor Show and went on sale later on that year. Again styled by Giugiaro, the car is using the Fiat SCCS platform, a variation of the General Motors Gamma Platform.
Punto Evo
In 2009, the Grande Punto was facelifted, with the replacement known as the Punto Evo. It received a new front end in addition to revised rear lights and a new interior.
Punto
In 2012, the Punto name was bought back when the Punto Evo was facelifted and given a similar front end to the 2005 Grande Punto. The new Punto kept the revised rear lights and interior of the 2009 Punto Evo, but not on the base ‘Pop’ trim level which reverted to the older Grande Punto interior.
In October 2014, Top Gear magazine placed the Punto Pop 1.2-L 8v 69 on its list of “The worst cars you can buy right now”, describing the car as “An outclassed elderly supermini that kicks out 126 g/km yet takes 14.4 secs to wheeze to 62 mph, and it costs more than £10k.”
The Grande Punto in India went through a facelift changing the front face and a revised rear and giving it a more aggressive look and was named Punto Evo. This car also sports an SUV-like ground clearance of 185mm for diesel and 195mm for petrol to suit Indian roads.
In October 2014, Fiat India released the Avventura, which was a crossover variant of the Punto Evo.
Punto Van
The Punto Van is a compact van designed for the commercial market. It features a petrol 1.2-L 8v engine, a petrol/CNG 1.2-L 8v engine and a diesel 1.3-L MultiJet 16v engine.
Motorsport
The Punto has always been popular with amateur racing drivers due to its low cost and the wide availability of spare parts. Several competition and homologated versions of the Punto have been produced, such as the Punto Rally, the S1600 and the Punto Abarth. A new rally car based on the third generation Punto, the Super 2000 Punto Abarth, was unveiled in 2005. It is four-wheel drive and powered by a 2.0 L 16 valve engine capable of producing 280 hp (210 kW). Also, a turbodiesel front-wheel-drive rally car has been produced, the Fiat Grande Punto R3D.
The Punto was the first diesel car to compete in the Targa Tasmania.
The Punto has won several rally championships, specifically:
- Italian Rally Championship (2003 and 2006)
- European Rally Championship (2006)
- 2006 International Rally Challenge season
A motorsport version of the car can be found in several liveries in the video games Colin McRae Rally 04, Colin McRae: DiRT, Sega Rally Revo and Gran Turismo 6.
- 1994 Fiat Fiorino (third generation)
- 1995 Fiat Barchetta
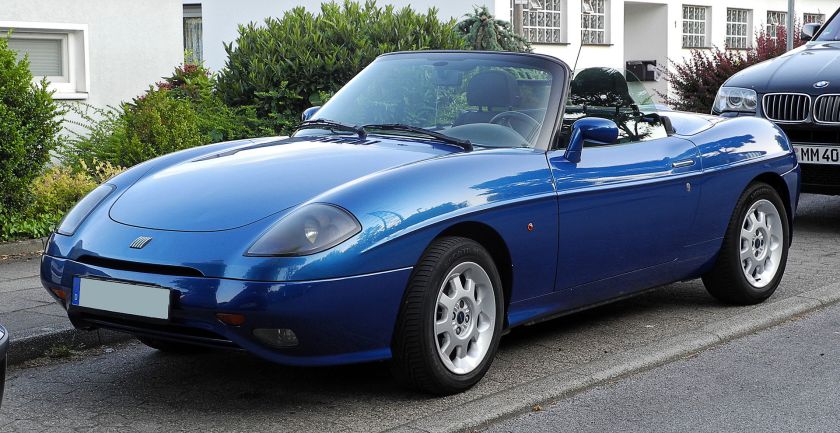
1995 Fiat Barchetta
| Fiat Barchetta | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Production | 1995–2002 2004–2005 |
| Assembly | Chivasso, Italy (Maggiora) Mirafiori plant, Turin, Italy |
| Designer | Andreas Zapatinas and Alessandro Cavazza 1992 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Sport compact |
| Body style | Roadster |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Related | Fiat Punto I |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.8L l4 16V |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,443 mm (96.2 in) |
| Length | 3,916 mm (154.2 in) |
| Width | 1,640 mm (65 in) |
| Height | 1,265 mm (49.8 in) |
| Curb weight | 1,056 kg (2,328 lb) |
The Fiat Barchetta (Italian pronunciation: [ˈfiat barˈketta]) (Type 183) is a roadster produced by the Italian manufacturer Fiat from 1995 to 2005 (though production was paused between May 2002 and 2004). “Barchetta” in Italian means ‘little boat‘.
History
The Barchetta was developed between 1990 and 1994 under the project name Tipo B Spider 176. It was designed by Andreas Zapatinas and Alessandro Cavazza under the supervision of Peter Barrett Davis and other car designers at the Fiat Centro Stile, and prototyping was carried out by Stola.
Production began in February 1995 and lasted until June 2005, with a brief pause due to the bankruptcy of coachbuilder Maggiora. The Barchetta was based on the chassis of the Mark 1 Fiat Punto. The Barchetta has 1,747 cc DOHC petrol engine fitted with variable camshaft timing, used for the first time in a Fiat production car, after being patented in 1970. The engine has 132 PS (97 kW; 130 hp) and 164 N·m (121 lb·ft) of torque. The Barchetta weighs 1056 kg (2328 lb) without air conditioning and can accelerate to 100 km/h (62 mph) in 8.9 seconds and has a top speed of 200 km/h (124 mph). It came in various trim levels which offered different features, for example, diamond cross stitch – patterned red leather instead of the standard black leather or fabric seats, alloy wheels instead of steel wheels, or fog-lights as an option. Arguably one of the biggest external cosmetic changes was made by the addition of the third brake light, first introduced by Fiat on the Lido and Riviera in 2000, and on sub models thereafter.
The Barchetta was revised in 2003 for its relaunch the following year, with some alterations inside and out. The most notable changes were the revised front spoiler and rear bumper. Production of the car eventually stopped in June 2005.
Production
Car bodies were welded at ILCAS in Sparone Canavese, and final assembly was done in Chivasso by the coachbuilder Maggiora.
After Maggiora’s bankruptcy in 2002, Fiat relocated production of the Barchetta to its Mirafiori plant and resumed production two years later. Around 57,700 cars were built up to 2005.
Production of the Barchetta was limited to LHD cars only, even though the car was marketed and sold in two RHD markets, the United Kingdom and Japan.
Bertone concept car
The Italian styling house of Bertone created a one-off roadster show car for Fiat called the Barchetta in 2007.
This picture was taken at the Bertone facility near Turin, Italy.
Notable examples
Perhaps the most well known ‘review’ of a Barchetta was one which featured in a Top Gear special which aired in December 2010. In the episode, the three presenters (Jeremy Clarkson, Richard Hammond and James May) attempted to follow the path of the Three Wise Men to Bethlehem. Hammond drove the Fiat Barchetta (specifically a Riviera Special Edition featuring a black paint job and red quilted leather), compared to Clarkson’s Mazda MX-5 and May’s BMW Z3. At the end of the episode, the Barchetta was declared the most desirable and reliable of the three cars.
- 1995 Fiat Brava
- 1995 Fiat Bravo
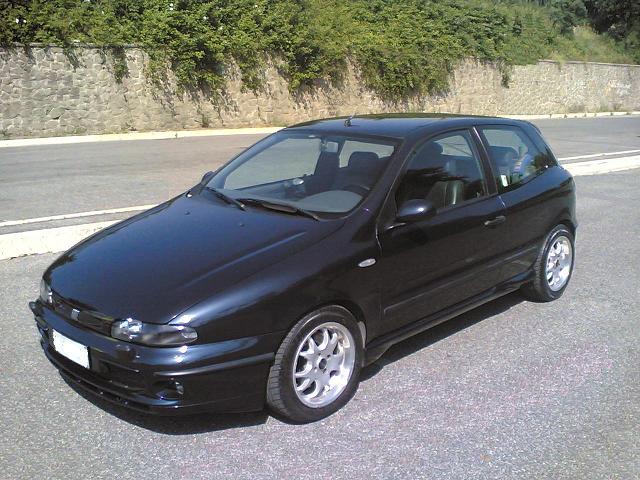
1995 Fiat Bravo/Brava
| Fiat Bravo Fiat Brava |
|
|---|---|

Fiat Bravo
|
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Fiat Bravissimo (Japan) |
| Production | 1995–2001 |
| Assembly | Cassino, Piedimonte San Germano, Italy Bursa, Turkey (Brava only) |
| Designer | Centro Stile Fiat 1992 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Small family car |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback (Bravo) 5-door hatchback (Brava) |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Platform | Type Two platform (Tipo Due) |
| Related | Fiat Marea Fiat Multipla |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,540 mm (100.0 in) |
| Length | 4,020 mm (158.3 in) (Bravo) 4,190 mm (165.0 in) (Brava) |
| Width | 1,750 mm (68.9 in) |
| Height | 1,420 mm (55.9 in) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat Tipo |
| Successor | Fiat Stilo |
The Fiat Bravo and Fiat Brava (Type 182) are small family cars produced by the Italian automaker Fiat from 1995 to 2001. They were effectively two versions of the same car, the Bravo a three-door hatchback and the Brava a five-door hatchback.
The Bravo name was revived in 2007 with the all-new Fiat Bravo, a replacement of the Stilo. The new version is available only with five doors. The name Brava was also used in the United States in the 1980s on the earlier Fiat 131.
History
The Bravo and the Brava were replacements for Fiat’s successful but ageing Tipo model. The two cars were very different in styling detail and driving experience, the Bravo chassis being tuned for more precise handling whilst the Brava was tuned for better comfort. Even the interior trim and many of the body colours were unique to either one version or the other. The cars came with all new engines, the base model using a 1.4 L 12-valve engine producing 80 PS (59 kW). Three other petrol engines were available: the 103 PS (76 kW) 1.6 L 16-valve; the 113 PS (83 kW) 1.8 L 16-valve engine and the top of the range 2.0 L 20-valve R5 unit used in the HGT model, which produced 147 PS (108 kW) and which could take the car to a maximum speed of 213 km/h (132 mph), later in 1999 the 155 HGT model replaced the older model, power rising to 155 PS (114 kW). Two turbodiesel engines were also available: both were 1.9 L four cylinder units, one producing 75 PS (55 kW) and the other making 100 PS (74 kW). The Bravo/Brava was voted European Car of the Year on its launch.
fiat-brava
In 1996, the Bravo/Brava chassis spawned saloon and estate versions, badged Fiat Marea, a car which was aimed at Ford Mondeo and Opel/Vauxhall Vectra buyers, which won praise for its large boot. Another car based on the Bravo/Brava underpinnings was launched in 1998: the curious-looking Fiat Multipla, a six-seater compact MPV.
The Bravo/Brava received a mild makeover in 1999, but there were few real changes except the replacement of the 1.4 L 12-valve engine with a 1.2 L 16-valve engine from the smaller Fiat Punto and a restyling of the dashboard. The 1.9 turbodiesel was also phased out in favour of 1.9 JTD diesel units (now with and 105 PS or 77 kW), to give even better economy and refinement.
HGT Abarth
In late 1999 Fiat introduced the Abarth accessories for the Bravo, available were more aggressive wheels and bodykit, performance was the same as the 1.8 HGT model. Was produced since 2000 until 2002.
The Bravo/Brava was discontinued in late 2001, and replaced by the all-new Fiat Stilo.
- 1995 Fiat Cinquecento Sporting
- 1995 Fiat Coupé 16v Turbo
- 1995 Fiat Coupé 1.8 16v
1995 Fiat Coupé
| Fiat Coupé | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Production | 1993–2000 |
| Assembly | Turin, Italy (Pininfarina) |
| Designer | Chris Bangle at Centro Stile Fiat 1991 Pininfarina (Interiors) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Sports car |
| Body style | 2-door coupé |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Platform | Fiat Tipo 2 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.8 l4 16V 2.0 l4 16V 2.0 l5 20V 2.0 l4 16V Turbo 2.0 l5 20V Turbo |
| Transmission | 5 and 6-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,540 mm (100.0 in) |
| Length | 4,250 mm (167.3 in) |
| Width | 1,768 mm (69.6 in) |
| Height | 1,340 mm (52.8 in) |
| Curb weight | 1,250–1,320 kg (2,760–2,910 lb) |
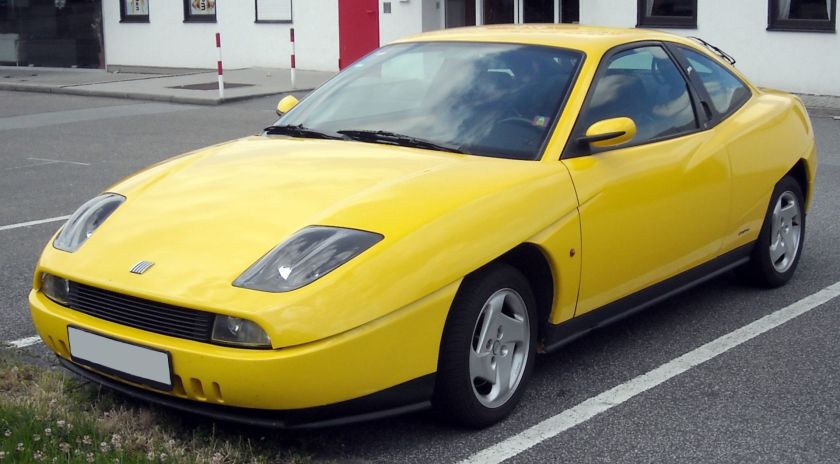
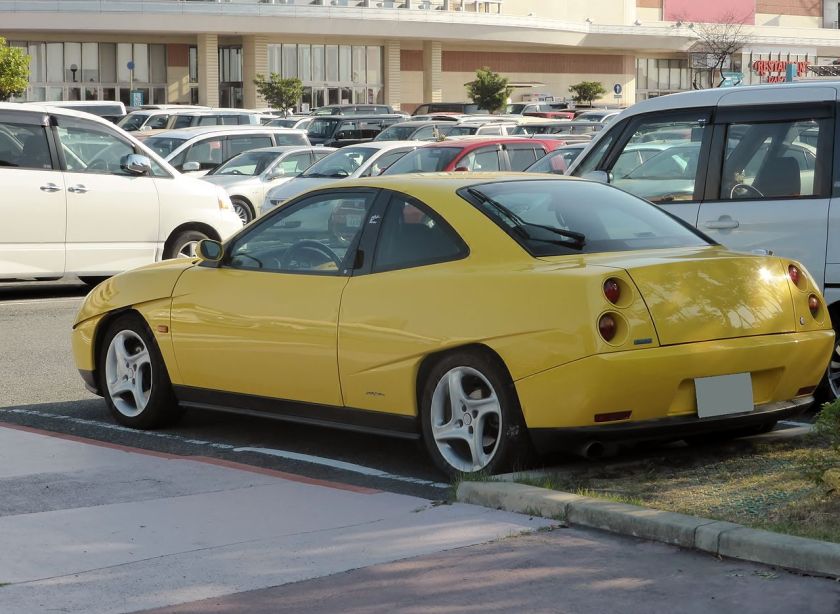
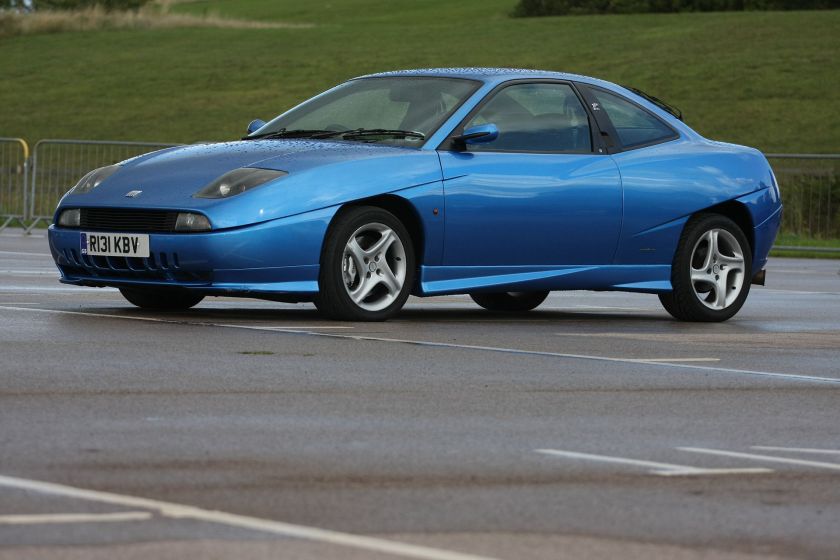
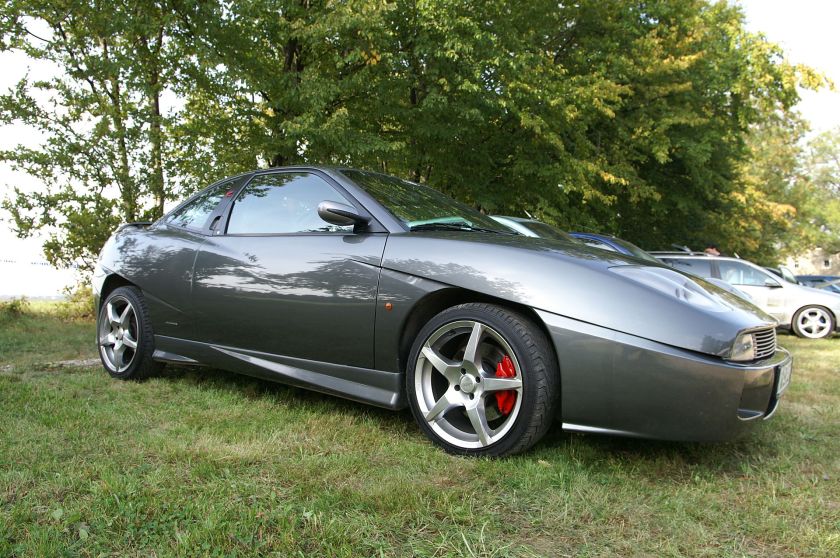
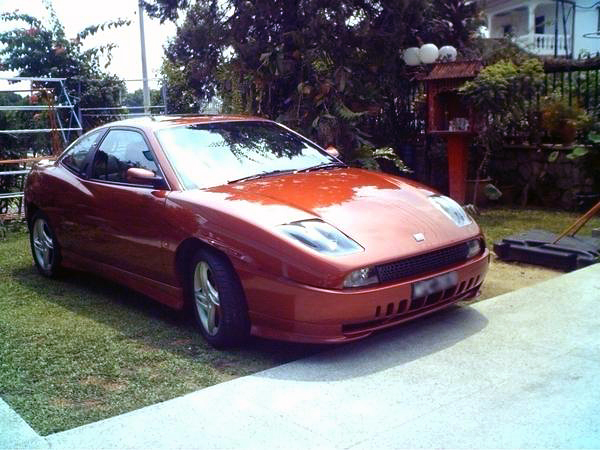
The Fiat Coupé (type 175, officially titled the Coupé Fiat) was a coupé produced by the Italian manufacturer Fiat between 1993 and 2000. The car was introduced at Brussels Motor Show in 1993.
It is most remembered for its distinctive, angular design, with unique scalloped side panels. The body was designed by Chris Bangle from Centro Stile Fiat, while the interior was designed by Pininfarina. The exterior design would foreshadow much of late 1990s and early 2000s car design, acting as a precedent to both Bangle’s somewhat notorious work at BMW, as well as futuristic angular designs by other marques, such as Ford and Renault.
History
The Fiat Coupe made media headlines in auto magazines during 1992 after several spy shots were taken revealing the car on test. On its launch in 1993, the Coupé was available with a four cylinder, 2.0 L 16V engine, in both turbo (190 PS) and normally aspirated (139 PS) versions. Both engines were later versions of Fiat’s twin-cam design and inherited from the Lancia Delta Integrale, winner of the World Rally Championship a record six times. 1996 brought in a 1.8 L 16V engine (not available in the UK, 131 PS), along with a 2.0-litre 5-cylinder 20V (147 PS), and a 5-cylinder 2.0-litre 20V turbo (220 PS).
The turbocharged 16 and 20 valve versions were equipped with a very efficient Viscodrive limited-slip differential to counter the understeer that plagues most powerful front wheel drive cars. Additionally, the coupe featured independent suspension all round: at the front MacPherson struts and lower wishbones anchored to an auxiliary crossbeam, offset coil springs and anti-roll bar; at the rear, trailing arms mounted on an auxiliary subframe, coil springs and an anti-roll bar.
| Year | Units made |
|---|---|
| 1993 | 119 |
| 1994 | 17,619 |
| 1995 | 13,732 |
| 1996 | 11,273 |
| 1997 | 12,288 |
| 1998 | 9,042 |
| 1999 | 6,332 |
| 2000 | 2,357 |
| Total | 72,762 |
1998 saw the release of the Limited Edition which featured red Brembo brake calipers at the front and standard red calipers at the back, a body kit, push-button start, six-speed gearbox, strut brace to make the chassis more rigid and Recaro seats with red leather inserts which offered better support than the standard 20VT seats. The LE was produced in Black (flat), Red (flat), Vinci Grey (metallic), Crono Grey (flat) and Steel Grey (metallic). The bodywork of the LE also benefited from titanium coloured insert around the light bezels and the wing mirrors. Each Limited Edition (‘LE’) Coupé was manufactured with a badge located by the rear-view mirror which contained that car’s unique number (it is rumored that Michael Schumacher was the original owner of LE No. 0001, however when the question was raised to him personally he confirmed he had owned one, but a red one, while LE No. 0001 is a Crono Grey one). Originally a spokesman from Fiat stated only approximately 300 Limited Editions would be built. The final amount was much higher, with numbers as high as 1400 touted by some. This angered many of the owners of the original 300 cars and almost certainly impacted residual values. The original number however was quoted by a Fiat UK spokesman, so probably that number only applied to the UK market. The numbered plaque on every Coupe features enough space for 4 numbers.
In 1998 the 2.0-litre 5-cylinder 20V got a Variable Inlet System which brought the power to 154 PS (113 kW). The 2.0-litre 5-cylinder 20V Turbo received a 6-speed gearbox and a large, satin gloss push starter button. In addition, the sills of the Turbo version were colour matched with the body paintwork. Fiat also released the 2.0 L 5 cylinder Turbo ‘Plus’. This model came with an option kit that made it virtually identical to the LE, except for minor interior design changes and without the unique identification badge of the LE.
In 2000 Fiat released another special version of the Fiat Coupé. Featuring the 1.8-litre engine, it was only available throughout mainland Europe and marketed as an elegant and affordable edition. Fiat also made changes throughout the rest of the range: new seats, side skirts and wheels for the 2.0-litre 20V model, ‘Plus’ edition wheels on turbo models and Fiat manufactured seats on the ‘Plus’ that were virtually identical to the original Plus Recaro seats with the addition of extra airbags. The 2.0-litre 20V Turbo model is capable of accelerating from 0–100 km/h (0 to 62 mph) in 6.5 seconds, with a top speed of 240 km/h (149 mph) or 250 km/h (155 mph) with later 6-speed gearbox. When production finally stopped in September 2000, a total number of 72,762 units had been produced.
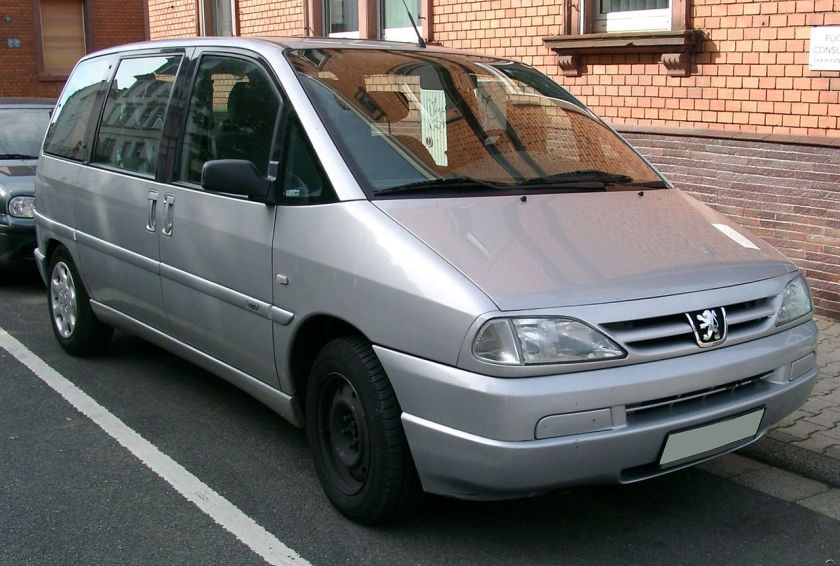
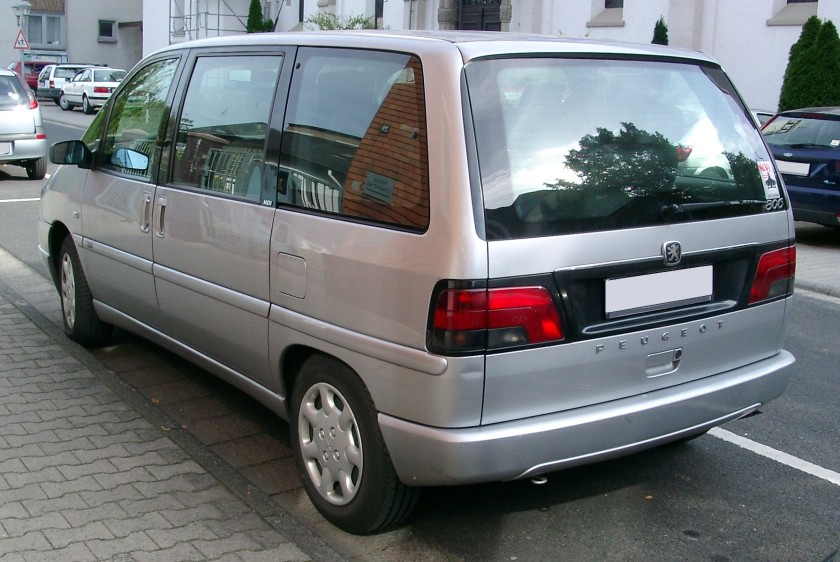
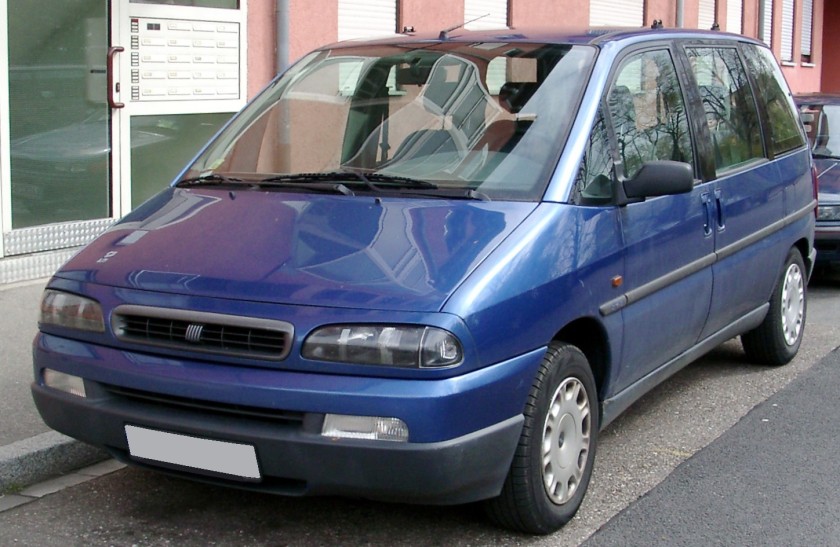
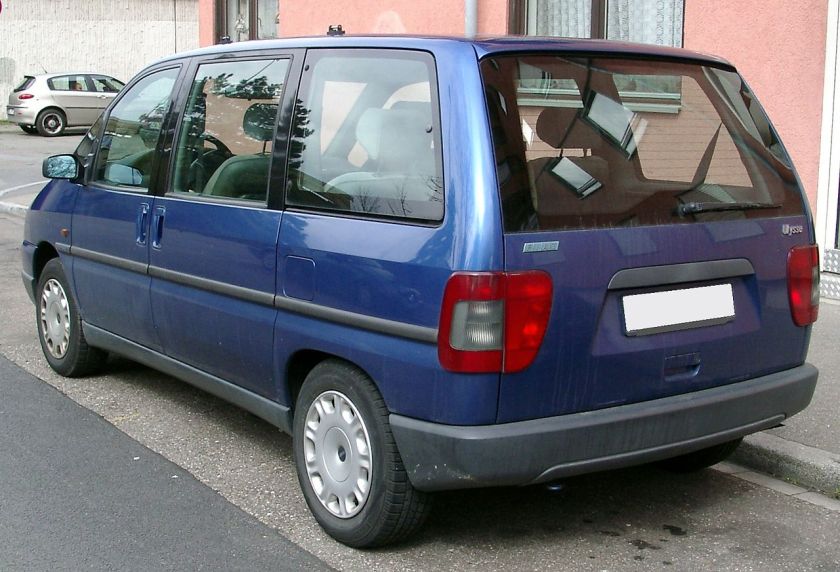
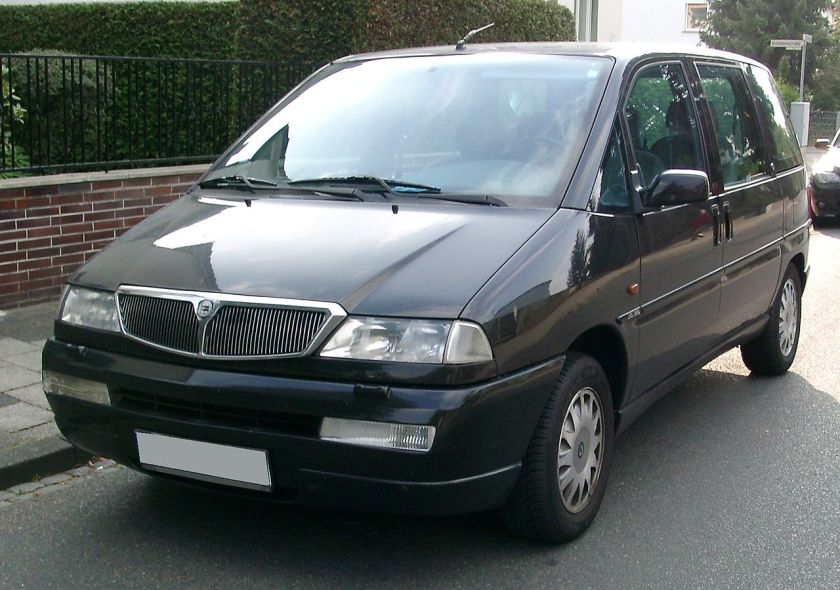
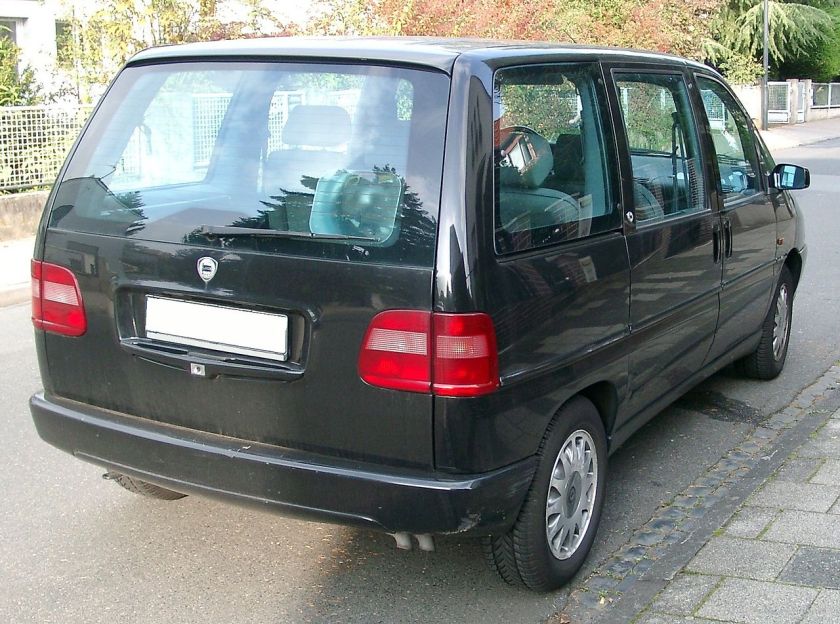
- 1995 Fiat Ulysse
1995 Fiat Ulysse and other Eurovans
| Eurovans | |
|---|---|
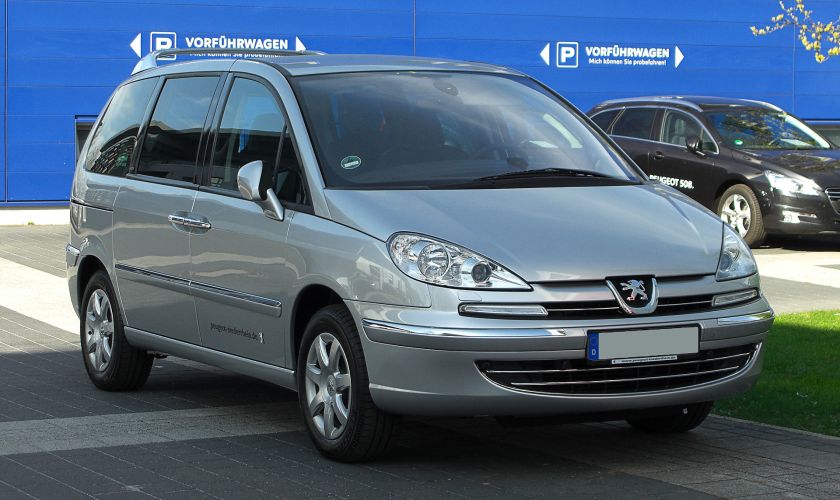

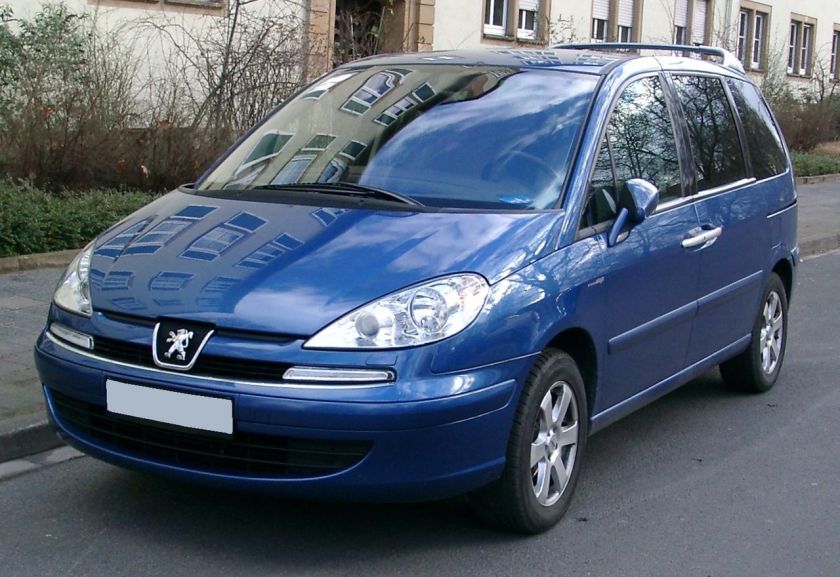
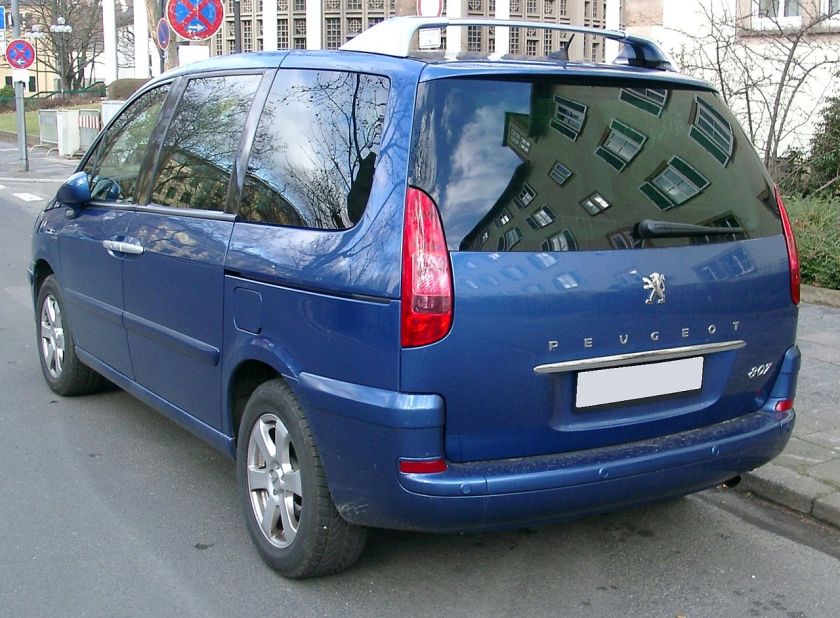
Peugeot 807 (facelift), one of the four Eurovan versions
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Sevel Nord |
| Production | March 1994–June 2014 |
| Assembly | Lieu-Saint-Amand, France (Sevel) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Large MPV |
| Body style | 5-door MPV |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Related | Sevel Nord vans |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Fiat Freemont Lancia Voyager |
The Eurovans are a family of large MPVs from the Citroën, Peugeot, Fiat and Lancia marques, produced at the jointly-owned Sevel Nord factory in France. It was launched in March 1994, and production ceased in November 2010 for the Fiat and Lancia models, and in June 2014 for the Citroën and Peugeot siblings.
The Eurovans differ little technically and visually, being a prime example of badge engineering. They share mechanicals and body structure with the Sevel Nord light commercial vans, the Citroën Jumpy (Dispatch),Fiat Scudo and Peugeot Expert.
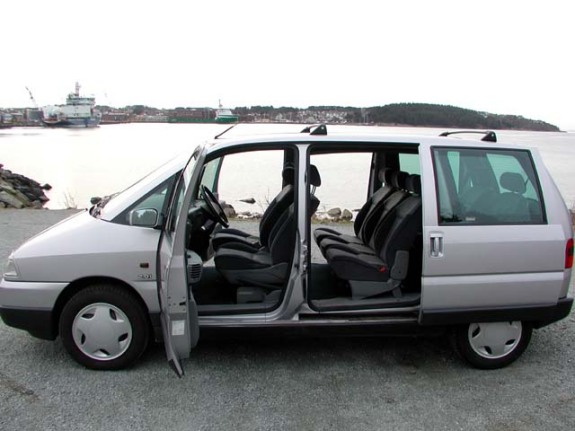
First generation (1994–2002)
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Citroën Evasion (Synergie) Fiat Ulysse Lancia Zeta Peugeot 806 |
| Production | March 1994–February 2002 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | Sevel Nord vans |
The first generation Eurovans were introduced in 1994. They are smaller than American vans, like the Chrysler Voyager, which is also available in Europe. In contrast to the Toyota Previa and like American minivans they had sliding rear side doors, a trait they share with their commercial siblings. In spite of the fact that the Voyager also came in the “Grand” versions with elongated body and wheelbase (and the Espace followed suit in 1997), the Eurovans only came in one size.
The Eurovans were almost identical, the differences consisting in different grilles, lower tailgates/taillights, wheel covers/alloy wheels and exterior and interior badging, as well as different trim levels. In October 1998, the Eurovans were mildly facelifted.
Inside, the gear lever was mounted on the dashboard rather than on the floor, and the handbrake is on the door side of the driver’s seat, which allowed for the removal of middle console and opened up a passage between the front seats. The seating configurations included two fixed seats in front and three individual removable seats in the middle row, along with optional two individual removable seats or a three-seater bench in the third row.
Engines
The first-generation Eurovans utilized PSA’s XU/XUD engines, regardless of brand. They were later replaced by the PSA EW/DW engine. All were mated to 5-speed manual transmissions, apart from the 2.0 16v EW petroleum engine, which had an option of a 4-speed automatic.
Model differences
Citroën Evasion
The Evasion was badged Synergie in the RHD markets of both the United Kingdom and Ireland. However, the car maintained the Evasion name in New Zealand. In 1998, the Citroën Evasion got a slight facelift including a larger logo and a restyling of the front grille and rear bumper. The Citroen brand was sold in Mexico with a headquarters in Detroit.
Peugeot 806
The 806 was named according to Peugeot‘s “x0x” system, where the first digit indicates model series (vehicle size/class) and the last indicates the generation, with a central zero. The largest Peugeot series then available was the executive saloon 605, so Peugeot chose 8, potentially leaving room for an in between model. The Eurovans were launched when Peugeot was replacing the “x05” with “x06” models, so it was appropriately labeled “806”.
Fiat Ulysse
The Fiat was named after Ulysses, the Roman name for Odysseus, the hero of Homer‘s Odyssey. This could have been problematic as Honda used the Odyssey name for their minivan, but the Honda Odyssey was only sold in Europe in its first generation and then named Honda Shuttle. The Ulysse range received a facelift in 1999.
Lancia Zeta
Following the traditional naming theme, Lancia named its variant with the previously unused Greek letter Zeta. With its big chrome grille, the Lancia served as the “premium” Eurovan, not available with base engines and exceptionally well equipped, with prices up to 20% higher than corresponding versions of other Eurovans.
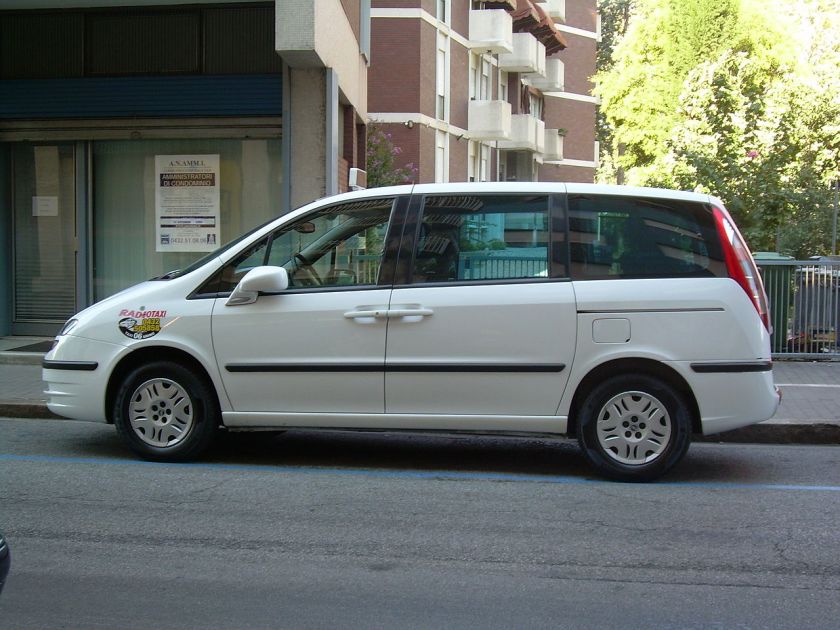
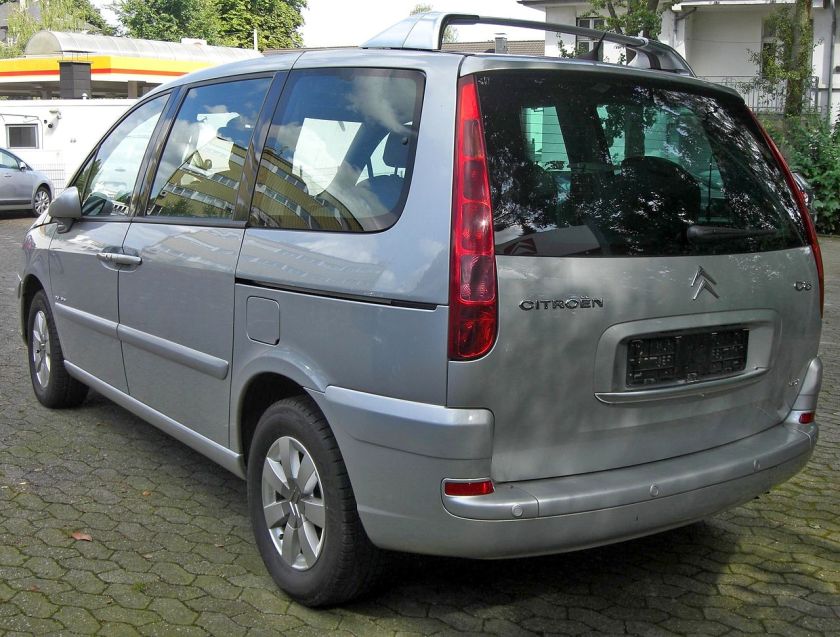
Second generation (2002–2014)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | February 2002–June 2014 (Citroën and Peugeot) February 2002-November 2010 (Fiat and Lancia) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | Sevel Nord vans |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,823 mm (111.1 in) |
| Length | 4,727 mm (186.1 in) (Peugeot 807) |
| Width | 1,854 mm (73.0 in) (Peugeot 807) |
| Height | 1,752 mm (69.0 in) (Peugeot 807) |
In 2002 the second generation of the Eurovans was launched. The 807 itself was launched in June, followed by the C8 in July. The floorpan, wheelbase, and postponement were not transformed, but all exterior dimensions-including front and rear tracks- were increased. The increase in length of almost 30 cm greatly enhanced interior volume. The new Eurovans were afforded a much more bubbly, contemporary look, along with a modern-looking dashboard with centrally mounted gauges.
The differences between the various versions were more marked, surrounding full front fascias and rear sections (including head- and tail-lights), as well as different interior colour themes. The middle and third row seats now had fore/aft sliders to increase flexibility and also adjustable backs. As with the first generation, a three-seater bench seat was available in the third row, slotting into the standard third row seat runners, with back-lowering and tilt forward arrangements to increase boot space.
The Citroën C8 and Peugeot 807 also got a light facelift in 2008.
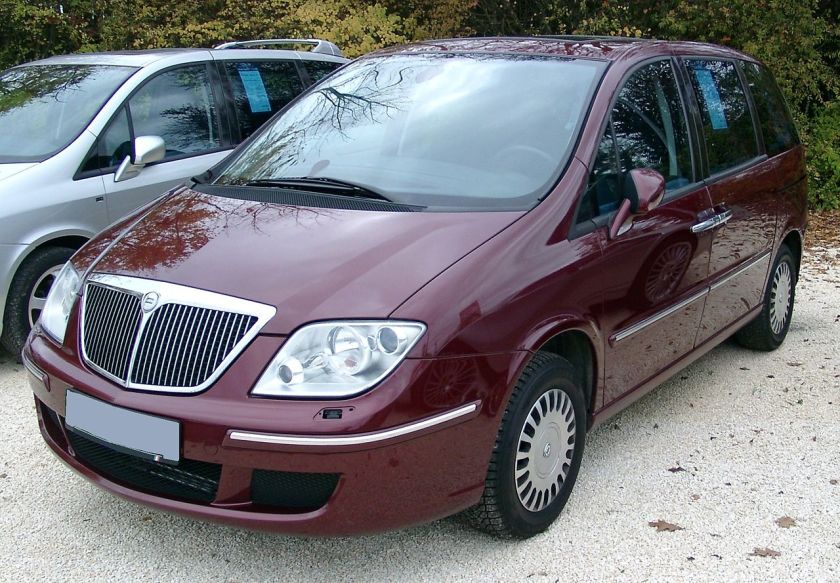
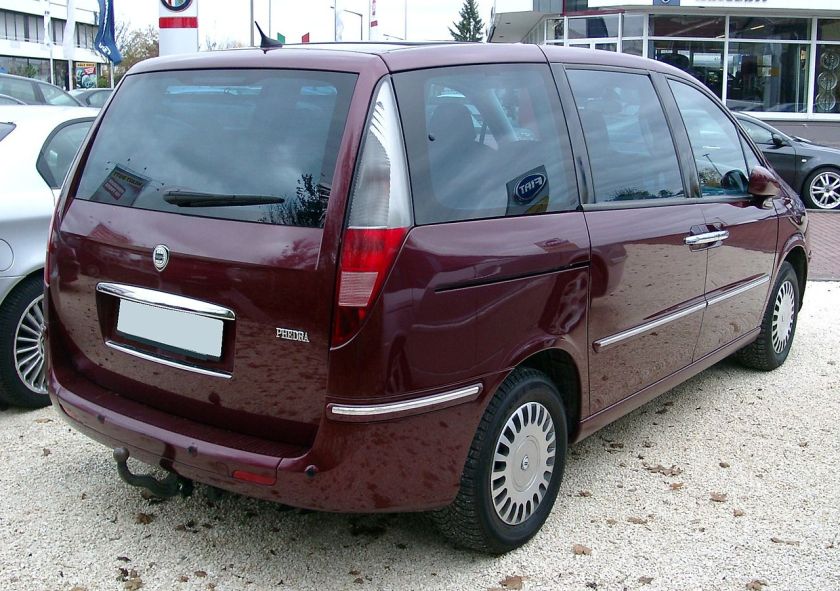
The Fiat and the Lancia were slightly wider than PSA vans, and the Phedra is also longer than other Eurovans.
To highlight the launch of the V6 engine, Peugeot presented a design study called Peugeot 807 Grand Tourisme at the 2003 Geneva Motor Show. Despite the fancier 4-passenger interior and some mechanical and visual tuning, the car was essentially a top-of-the-line 807 in a purple colour.
Engines
The engine range comprised again of different versions of the PSA EW/DW engine, paired with either 5-speed manual or 4-speed automatic transmissions. (A six-speed manual option was added in the UK in late 2004). Additionally, top-of-the-line versions came with the PSA ES V6.
Model differences
Citroën C8
Citroën chose to put the minivan in line with its new naming theme, where models were called Cx (x being a number roughly corresponding to the relative size of a given model), hence the Citroën C8.
Peugeot 807
The 807 replaced the 806.
Fiat Ulysse
Fiat retained the Ulysse name for its second generation. The direct successor is the Fiat Freemont.
Lancia Phedra
As the new Lancias didn’t use Greek letters in the 2000s (until the Lancia Delta was reintroduced in 2008), the new minivan was called Lancia Phedra, in honor of the Greek mythological figure Phaedra. The successor is the Lancia Voyager.
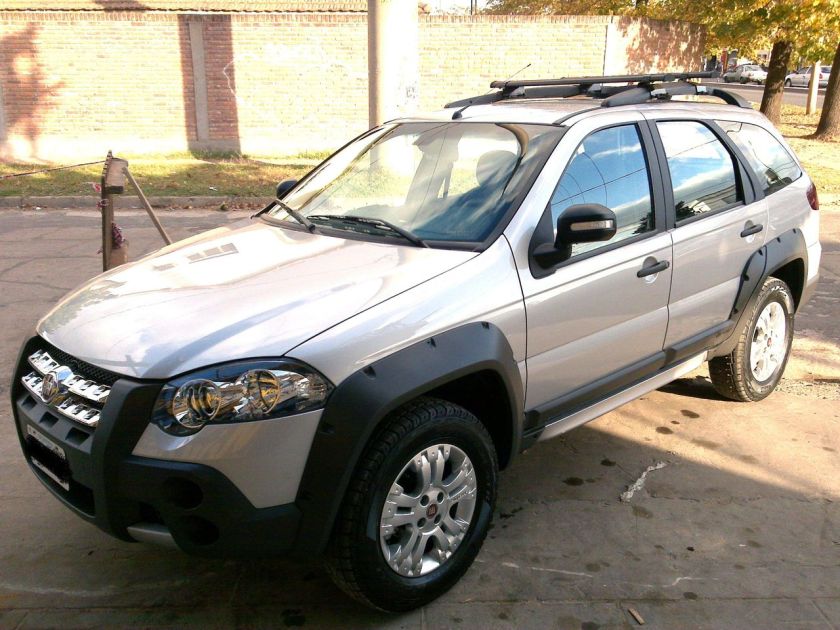
- 1996 Fiat Palio
1996 Fiat Palio
| Fiat Palio | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Production | 1996–present |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Supermini |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat Uno |
The Fiat Palio is a supermini car produced by the Italian manufacturer Fiat since 1996. It is a world car, developed by Fiat Automóveis and aimed at developing countries. It has been produced in various countries worldwide, and its platform was also used in the Siena sedan, the Palio Weekend station wagon, the Palio Adventure crossover and the Strada light pick-up truck.
Origins of the Palio badge
The Palio badge originated on the Mark II Fiat 127, of 1977, where it was a trim designation rather than an actual model. The 127 Palio featured alloy wheels, a more luxurious interior, and a metallic paint finish as found on the 127 Sport. The Palio designation was also used on other Fiat models throughout the 1980s and 1990s in various markets.
First generation (1996–2011)
| First generation (178) | |
|---|---|
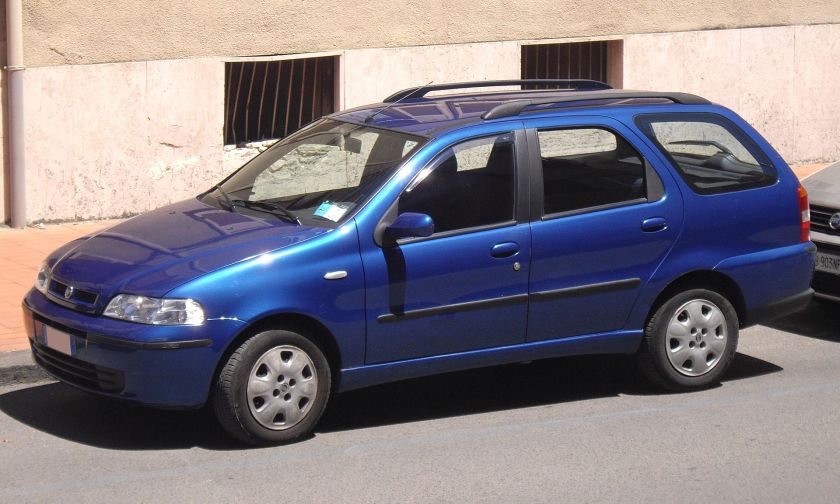

1998 Fiat Palio 1.2-L 75 Weekend
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1996–2011 |
| Assembly | Betim, Brazil (Fiat Brazil) Ferreyra, Argentina (Fiat Argentina) Bursa, Turkey (Tofaş) Bielsko-Biała & Tychy, Poland Nanjing, China (Nanjing Fiat) Pune, India (Fiat India) Casablanca, Morocco (Somaca) Rosslyn, South Africa (Nissan) La Victoria, Aragua, Venezuela Naberezhnye Chelny, Russia(ZMA) |
| Designer | I.DE.A Institute (1996) Giorgetto Giugiaro (2001, 2004) Centre Stile Fiat Brazil (2007) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | Three-door hatchback Five-door hatchback Five-door station wagon |
| Related | Fiat Siena Fiat Strada Fiat Albea Fiat Perla |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.0-L Fire I-4 (gasoline) 1.0-L Fiasa I-4 (gasoline) 1.1-L Fire I-4 (gasoline) 1.2-L Fire I-4 (gasoline) 1.3-L Fiasa I-4 (gasoline) 1.4-L Sevel I-4 (gasoline) 1.4- L Fire I-4 (gasoline) 1.5-L Fiasa I-4 (gasoline) 1.6-L Fiasa I-4 (gasoline) 1.6-L Sporting I-4 (gasoline) 1.6-L E.torQ I-4 (gasoline) 1.8-L X18XE I-4 (gasoline) 1.3-L Multijet I-4 (diesel) 1.7-L Turbo Diesel I-4 1.9 L I-4 (diesel) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,360 mm (92.9 in) (1996–01) 2,420 mm (95.3 in) (Weekend) 2,360 mm (92.9 in) (2001–04) 2,423 mm (95.4 in) (Weekend) 2,370 mm (93.3 in) (2004–07) 2,440 mm (96.1 in) (Weekend) 2,373 mm (93.4 in) (2007–11) 2,437 mm (95.9 in) (Weekend) |
| Length | 3,735 mm (147.0 in) (1996–01) 4,130 mm (162.6 in) (Weekend) 3,740 mm (147.2 in) (2001–04) 4,120 mm (162.2 in) (Weekend) 3,830 mm (150.8 in) (2004–07) 4,210 mm (165.7 in) (Weekend) 3,847 mm (151.5 in) (2007–11) 4,237 mm (166.8 in) (Weekend) |
| Width | 1,614 mm (63.5 in) (1996–01) 1,626 mm (64.0 in) (Weekend) 1,614 mm (63.5 in) (2001–04) 1,627 mm (64.1 in) (Weekend) 1,630 mm (64.2 in) (2004–07) 1,630 mm (64.2 in) (Weekend) 1,640 mm (64.6 in) (2007–11) 1,639 mm (64.5 in) (Weekend) |
| Height | 1,445 mm (56.9 in) (1996–01) 1,510 mm (59.4 in) (Weekend) 1,445 mm (56.9 in) (2001–04) 1,480 mm (58.3 in) (Weekend) 1,430 mm (56.3 in) (2004–07) 1,520 mm (59.8 in) (Weekend) 1,435 mm (56.5 in) (2007–11) 1,515 mm (59.6 in) (Weekend) |
1996–2000
Launched in 1996 in Brazil, as part of Fiat’s “Project 178”, the Palio was Fiat’s first attempt to build a world car, the same basic design being produced in numerous nations around the globe. Four principal models were produced: hatchback, sedan, pickup, and station wagon, with different versions being built for different markets. The powerplants, both diesel and petrol, also varied from region to region depending on local production capability, legislation, and market requirements.
The basic chassis was a development of the Fiat Punto (176), but little remained unchanged. The entire structure was significantly stronger to be suitable on the rougher roads found in some of the markets for which it was intended, as was the suspension. The body was a completely new design by the I.DE.A Institute of Turin, which also designed the new interior.
Production began in 1996 in Brazil and was followed later that year by a plant in Argentina. In 1997, production started in Venezuela, Poland for the European market, and Marocco (at the Somaca plant[1]) whilst Turkey started building the same car in 1998. In India, assembly was at Pune in the new Fiat-Tata Motors factory and in South Africa by Nissan together the pickup version called Fiat Strada. Production in India and South Africa began in 1999, in Egypt in 2001, and in China in 2002. The Palio Weekend station wagon was launched in 1996 in Brazil and later in Europe. The station wagon is the version most commonly sold in Europe.
2001–2003
In 2001, the model had its first facelift. The new design was made by the Italian automobile designer Giorgetto Giugiaro. This facelift included new front and rear fasciae and a brand new interior. Also, new engines came for the Palio: the Fire 16-valve 1.0-L and 1.2-L and the Sporting, a 1.6-L 16-valve engine with 120 hp made in Turkey. The 2001 Palio was the first Fiat to be made in China, by Nanjing Automobile. In some markets, this generation included a Speedgear semiautomatic option. The Palio 2001 facelift is the ultimate version sold in Italy. In 2001, Fiat introduced for the South American market the crossover version, called Palio Adventure and based on the Palio Weekend. In Europe, the Palio Weekend was succeeded in 2003 by the Fiat Idea MPV.
Nanjing Fiat Palio
In November 2001, the Chinese Fiat Palio debuted, with either the 60 PS (44 kW) 1.2-L or the 85 PS (63 kW) 1.5-L. The Siena sedan was added in November 2002, followed by the Palio Weekend in June 2003. The Siena and Palio Weekend were not available with the smaller engine.
Safety rating
A Fiat Albea, the sedan version of the Palio, was tested in Russia according to the Euro NCAP latest standard (offset frontal crash at 64 km/h). The Albea scored 8,5 points in the frontal test, equivalent to three stars. The tested vehicle was equipped with standard driver airbag and regular seatbelts.
The Fiat Perla, the Chinese version of the Albea, was tested in China by China-NCAP in three different tests: 100% front crash test with a wall (similar to the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration test), a 40% offset test (similar to Euro NCAP), and a side crash test. The Perla scored 8.06 points in the 100% frontal crash test, equivalent to three stars; 12.02 pts in the 40% offset crash test, equivalent to four stars, and 10,96 pts in the side crash test, equivalent to three stars; with an average result of 31 points and three stars. The tested vehicle was equipped with standard driver and passenger airbags and regular seatbelts.
2004–2006
The third revision was released in 2004, designed again by Giorgetto Giugiaro. It is basically a facelift from the previous models. The 2004 Palio was the first Brazilian model in the B-segment available with four airbags (two front airbags and two side airbags), parking assistance, and light and rain sensor. In Europe, the new model featured a redesigned front fascia and interior with rear fascia similar to Palio 2001 version. It has also a sport version called the Palio 1.8R’ which has a new version of the General Motors 1.8-L X18XE Powertrain engine rated at 115 hp (ethanol) and 112 hp (gasoline), lowered suspension, new 14-inch alloy wheels, new seats, and other sporting features. The third generation of the Palio had huge sales numbers, even getting higher sales in some months than the VW Gol, the Brazilian best-selling car for over 24 years. It is currently sold as the Palio Fire Economy as a cheaper alternative to its posterior facelift, with alterations derived from the Uno Mille Fire Economy model. The top model is still Weekend Adventure version; it is equipped with a 1.8-L Powertrain Flex fuel engine with 112hp (petrol/gasoline) and 114 hp (ethanol) at 5500 rpm, all-terrain Pirelli Citynet tires, and a higher/reinforced suspension kit but still with 4×2 drive.
Fiat India is manufacturing the 2004 Palio, with 2001-version interiors, at the Ranjangaon plant along with the Grande Punto and Linea. After entering into a partnership with Tata Motors, the Palio has been relaunched as the Palio Stile, with the 1.1-L Fire, 1.6-L Torque, and 1.3-L Multijet engines. Sales have been low at hardly 200 units per month.
2007–2011
The last Palio facelift was launched in 2007, in Natal, Brazil. The design of the body was inspired by the new version of the Grande Punto, which was launched in Brazil in the first quarter of 2008.
This fourth facelift included new front, rear, and side designs, but it kept the original chassis from the 1996 model, being marketed as the New Palio. It also has a minor change in the instrument panel with differences between the two variants sold.
The trims for this new Palio are ELX with the 1.0- or the 1.4-L Fire engines, both flex (ethanol and petrol) and the “sporty” version 1.8R with the current revision of the 1.8-L 8-valve engine from GM, also flexible. The new Torque engines wwere added to the Palio after the launch of the Grande Punto. The Palio Adventure introduced the new limited slip differential and new suspension for off road with front-wheel drive.
Second generation (2011–present)
| Second generation (326) | |
|---|---|
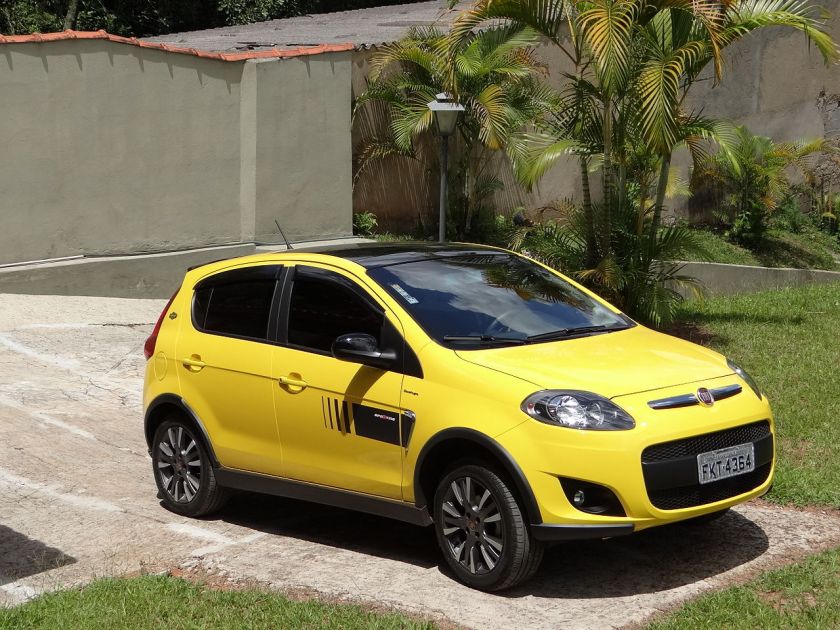

Fiat Palio Sporting 1.6-L 16-V E.torQ engine with Dualogic transmission, second generation (326) – Brazil
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 2011–present |
| Assembly | Betim, Brazil (Fiat Brazil) Ferreyra, Argentina (Fiat Argentina) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | Five-door hatchback |
| Platform | Fiat Economy |
| Related | Fiat “Novo” Uno Fiat Grand Siena |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.0-L Fire I-4 1.4-L Fire I-4 1.6-L E.torQ I-4 |
| Transmission | Five-speed manual Five-speed semiautomatic(Dualogic) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,420 mm (95.3 in) |
| Length | 3,875 mm (152.6 in) |
| Width | 1,670 mm (65.7 in) |
| Height | 1,504 mm (59.2 in) (Attractive) 1,513 mm (59.6 in) (Essence) 1,508 mm (59.4 in) (Sporting) |
An all-new generation of Palio was revealed in October 2011, at the annual Fiat dealers’ meeting in Mykonos, Greece. The official launch, however, took place on 4 November 2011, in Brazil. It is the first total remodeling since launch in 1996. The project, code named 326, was anticipated by the success of the new Fiat Uno in Brazil. One of the new versions will be the Sporting, a trim level known for the sporty versions of the Siena, Uno, Idea, Bravo, and Strada.
Electric versions
Fiat is joining utility companies Cemig and Itaipu to develop new electric vehicles for Brazil, with an initial batch of Fiat Palio cars scheduled to start testing later 2007.
Motorsport
Several competition and homologated versions of the Palio have been produced, such as the A6 class rally car, multiple Brazilian and South American champion of the A6 class with Brazilian Luis Tedesco as driver, and the Turkish Fiat Rally Team-created Palio Super 1600 Abarth rally car, with a 215-hp 1.6-L 16-valve engine and a six-speed sequential transmission. Turkey also boasts an N2 Palio.
Safety
The Fiat Palio has been rated as highly unsafe by Latin NCAP, scoring only one star for adult occupants and two stars for children. Its air bag-equipped version scored three stars, although it is a vast minority in the sales mix. This will change with the Brazilian law requiring dual front airbags from 2014 on. Unfortunately, this is the safety standard of low-cost Brazilian cars.
- 1996 Fiat Coupé 2.0 20v
- 1996 Fiat Marea 1.4 12v
- 1998 Fiat Marea 155 20v
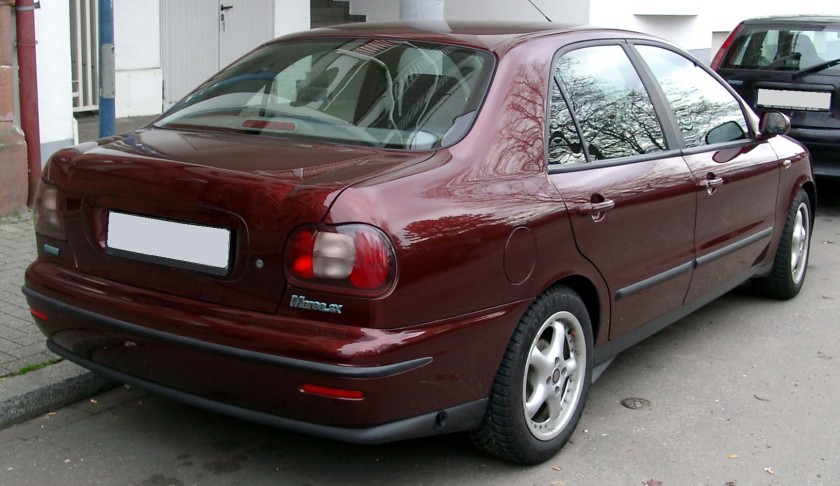
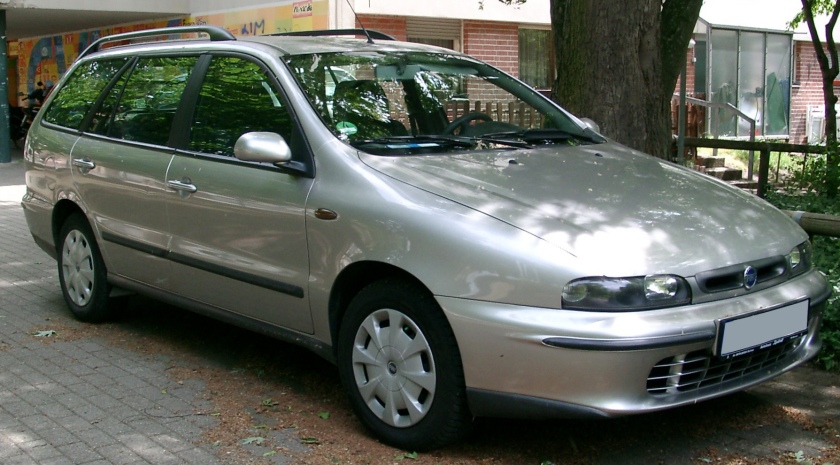
1996 + 1998 Fiat Marea
| Fiat Marea | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Also called | Fiat Marengo (panel van) |
| Production | 1996–2002 (Italy) 1998–2007 (Brazil) |
| Assembly | Mirafiori, Turin, Italy Cassino, Piedimonte San Germano, Italy Betim, Minas Gerais, Brazil Bursa, Turkey (Tofaş) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Small family car |
| Body style | 4-door saloon 5-door estate |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Platform | Type Three platform (Tipo Tre) |
| Related | Fiat Bravo/Brava Fiat Multipla |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.2 L I4 (gasoline) 1.4 L I4 (gasoline) 1.6 L I4 (gasoline) 1.8 L I4 (gasoline) 2.0 L I5 (gasoline) 2.4 L I5 (gasoline) 2.0 L I5 (t/c gasoline) 1.9 L I4 (turbodiesel) 2.4 L I5 (turbodiesel) 1.6 L I4 (BiPower) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,540 mm (100.0 in) |
| Length | 4,391 mm (172.9 in) (saloon) 4,490 mm (176.8 in) (estate) |
| Width | 1,740 mm (68.5 in) |
| Height | 1,420 mm (55.9 in) (saloon) 1,535 mm (60.4 in) (estate) |
| Curb weight | 1,085–1,385 kg (2,392–3,053 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat Tempra |
| Successor | Fiat Linea |
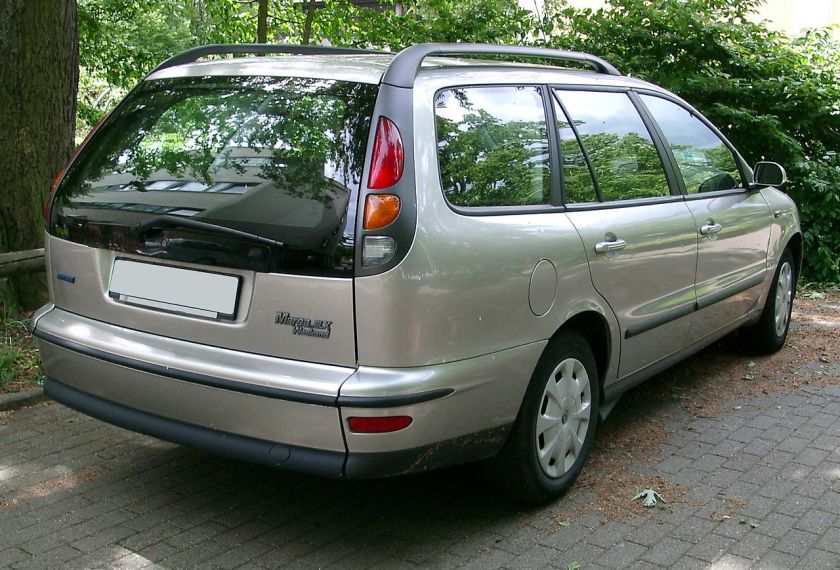
The Fiat Marea (Type 185) is a small family car available as a saloon and an estate, produced by the Italian automaker Fiat. Launched in 1996, the Marea models were essentially different body styles of Fiat’shatchback offerings, the Bravo and Brava. The Marea replaced the earlier Tipo-based Fiat Tempra. While the Fiat Stilo Multiwagon is the successor of the Marea Weekend estate, the Fiat Linea replaced the saloon version in 2007.
Production and markets
The Marea was originally manufactured in Fiat’s Cassino and Mirafiori plants in Italy. Later the Marea also superseded the Tempra in Brazilian (Betim) and Turkish (in Bursa, with Tofaş) plants, which make vehicles mostly for local and other developing markets.
In Europe, production and sales of the Marea ceased in 2002, a year after the Bravo and Brava were replaced with the Fiat Stilo. The Marea Weekend was replaced by the Stilo Multiwagon, while the saloon was dropped altogether due to relatively low popularity of compact saloon cars in Europe. Nevertheless, the Marea (in both body styles) was still manufactured in Turkey and Brazil for local (and other Latin American) markets. The Brazilian version was facelifted in 2001, when it gained a redesigned rear end with taillights taken from the Lancia Lybra. For 2006, the Marea was mildly revised again, gaining a new rear end, and a new grille, similar in style to other current Fiat models.
In mid-2007, Brazilian production of the Marea and Marea Weekend ceased. Their successor, the Fiat Linea, is produced from mid-2008 on, only in saloon body style.
Engines
The Marea petrol and JTD engines 1.6 L, 1.8 L and 2.0 L petrol and 1.9 L were sourced from the Brava and Bravo, and a 2.0 20v turbo option from the Fiat Coupé was also available. For a short time there was also a 2.4 turbodiesel available, dropped in 2001, which has become sought after. A BiPower 1.6 L dual fuel engine was later added to the range. It can run on either petrol or compressed natural gas.
- 1.6 L straight-4 1,581 cc 103 PS (76 kW; 102 hp)
- 1.6 L straight-4 1,581 cc 99 PS (73 kW; 98 hp)
- 1.8 L straight-4 1,747 cc 114 PS (84 kW; 112 hp)
- 2.0 L straight-5 1,998 cc 155 PS (114 kW; 153 hp)
- 2.0 L straight-5 turbo 1,998 cc 182 PS (134 kW; 180 hp)
- 1.9 turbodiesel straight-4 75 PS (55 kW; 74 hp)
- 1.9 turbodiesel straight-4 100 PS (74 kW; 99 hp)
- 1.9 common-rail (JTD) turbodiesel straight-4 105 PS (77 kW; 104 hp)
- 1.9 common-rail (JTD) turbodiesel straight-4 110 PS (81 kW; 108 hp)
- 2.4 turbodiesel 2,387 cc straight-5 126 PS (93 kW; 124 hp)
- 2.4 common-rail (JTD) turbodiesel 2,387 cc straight-5 132 PS (97 kW; 130 hp)
Brazil
The Marea was introduced in 1998 onto the Brazilian market with only one engine: the 2.0 20v. Due to Brazilian production taxes the 2.0 20v engine had its electronic fuel injection remapped to limit the engine power to 128 bhp (95 kW) in the Marea SX and ELX models of 1999. The engine retained its full power (142 bhp) on the more expensive Marea HLX model. Simply exchanging the SX or ELX fuel injection chip with the HLX chip would bring back the original engine power. Fiat initially claimed it to be untrue explaining that other modifications had been made in the SX/ELX models for cost-savings, but this was revealed to be false.
In 2000, the 2.0 20v engine was replaced with the 2.4 20v (160 bhp) engine in the HLX model, and the SX model started using the 1.8 16v engine (130 bhp), while the ELX injection was mapped as it had originally been for the HLX to give the 2.0 20v engine the original engine power (141 bhp).
Later the 2.0 20v engine was dropped and the 1.6 16v (105 bhp) engine was introduced; this engine was the only one produced for model year 2007, when the Marea production has been discontinued. All engines for the Fiat Marea in Brazil were petrol-based, with no diesel variants. This is due to federal legislation prohibiting diesel-powered passenger vehicles, effective since 1976.
There is also the 2.0 20V Turbo (Garrett TB28/10) with 182 bhp, sold from 1999 to 2006.
- 1998 Fiat Marea Weekend 155 20v
- 1998 Fiat Multipla
1998 Fiat Multipla
| Fiat Multipla | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Production | 1998–2010 |
| Assembly | Mirafiori plant, Turin, Italy Arese plant, Milan, Italy (CNGversion) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact MPV |
| Body style | 5-door MPV |
| Platform | Fiat Type Two (Tipo Due) platform |
| Related | Fiat Bravo/Brava Fiat Marea Zotye Mutipla (2nd generation) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L 16V petrol I4 1.6 L 16V LPG/petrol I4 1.6 L 16V CNG I4 1.6 L 16V CNG/petrol I4 1.9 L JTD diesel I4 1.9 L Multijet diesel I4 |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,666 mm (105.0 in) |
| Length | Pre-facelift: 3,994 mm (157.2 in) Post-facelift: 4,080 mm (161 in) |
| Width | 1,871 mm (73.7 in) |
| Height | 1,670 mm (66 in) |
| Curb weight | 1300-1490 kg (2866-3285 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat 600 Multipla |
| Successor | Fiat 500L Living |
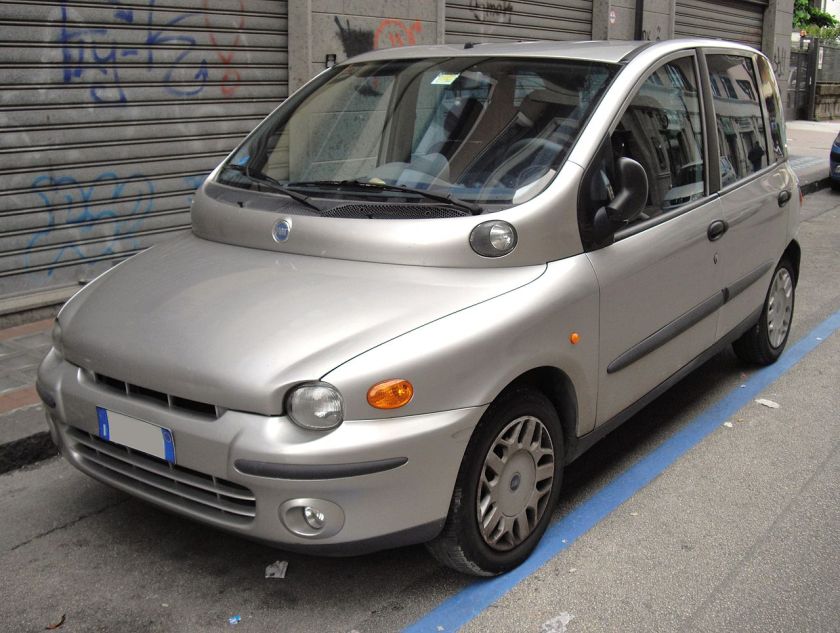
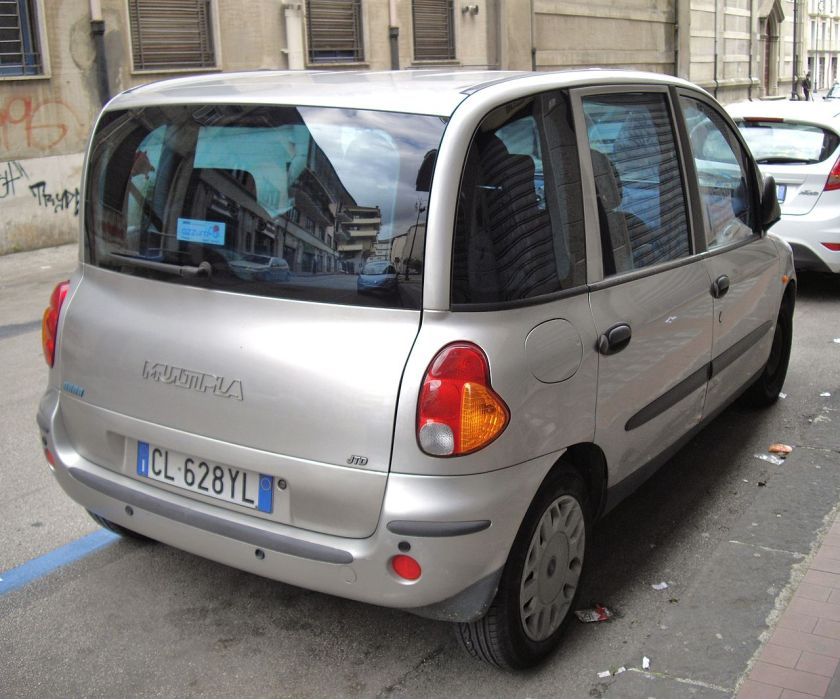
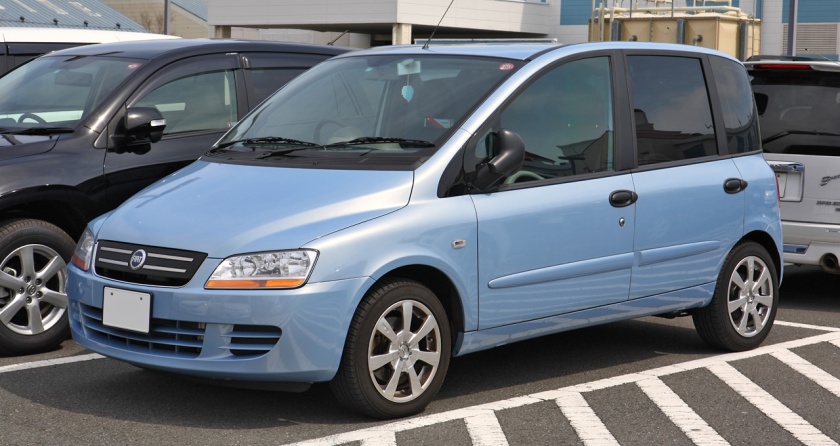
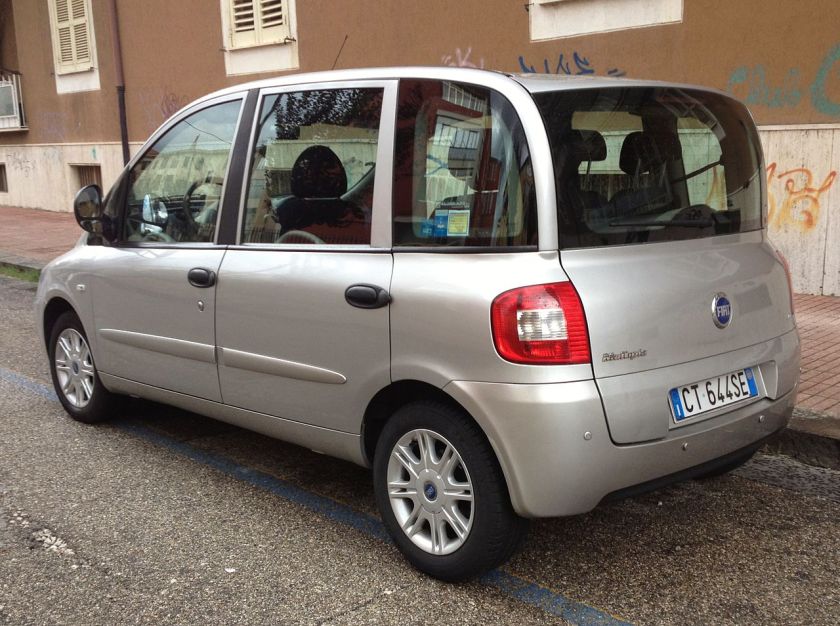
The Fiat Multipla (Type 186) is a family car produced by Italian automaker Fiat from 1998 to 2010. Based on the Brava, the Multipla was shorter and wider than its rivals. It had two rows of three seats, while all its competitors had two seats in the front (the Honda FR-V, which has the same layout, was released in 2004). The Multipla was even shorter than the three-door Fiat Bravo upon which it was based, despite offering substantially more space and seating.
In common with a number of other modern Fiats, the Multipla reused the name of an earlier vehicle, in this case the “Multipla” variant of the Fiat 600 produced during the 1950s and 1960s.
Design
The exterior and interior design of the Multipla was displayed at the Museum of Modern Art (MOMA) in New York during its “Different Roads – Automobiles for the Next Century” exhibition in 1999.
It won the Top Gear Car of the Year (1999) and was voted Top Gear Magazine‘s Family Car of the Year for four years in a row (2001–2004).
Multipla sales began in Italy late in 1998 but most other markets had to wait a year before receiving imports. The Multipla sold well with Italian buyers, but sales elsewhere were less successful. Also when Simon Cowell went on Top Gear he was shown a picture of the car and said it had a disease.
In 2004 the Multipla underwent a major facelift to shed its original styling for a more restrained look, with the intention of attracting more buyers. It did arrive to critical acclaim.
UK trim levels
- Multipla SX – basic model available with petrol or diesel engines.
- Multipla ELX – added Air Conditioning, Twin Electric Sunroofs, alloy wheels and electric rear windows, as well as special wipe-clean, brightly coloured seats.
These trim levels were later replaced with Dynamic, Dynamic Family and Eleganza when the Multipla received its facelift at the end of 2004.
Inner room and flexibility
The new generation Multipla was praised by journalists at its launch for its flexibility. The Multipla’s three-abreast seating configuration allows for adjustment of the front seats and the removal and relocation of the rear seats into many formats. It also affords a big 430 litres (15 cu ft) of luggage space which can increase to 1,900 litres (67 cu ft) of flat floor load space with the rear three seats removed from the vehicle.
Chinese version
Zotye Auto had assembled Multipla 2 from KD kits from late 2008 to 2010 in its Changshan factory, and marketed it in China as Mutiplan. In October 2010, Zotye started to build a version of Multipla 2 employing more locally made parts in order to reduce costs; the new version is called “Langyue” in China.
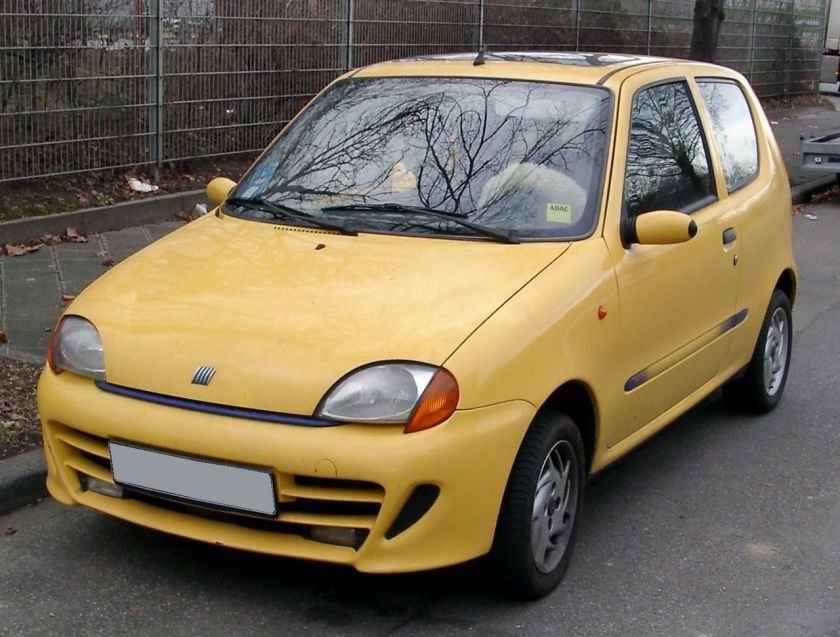
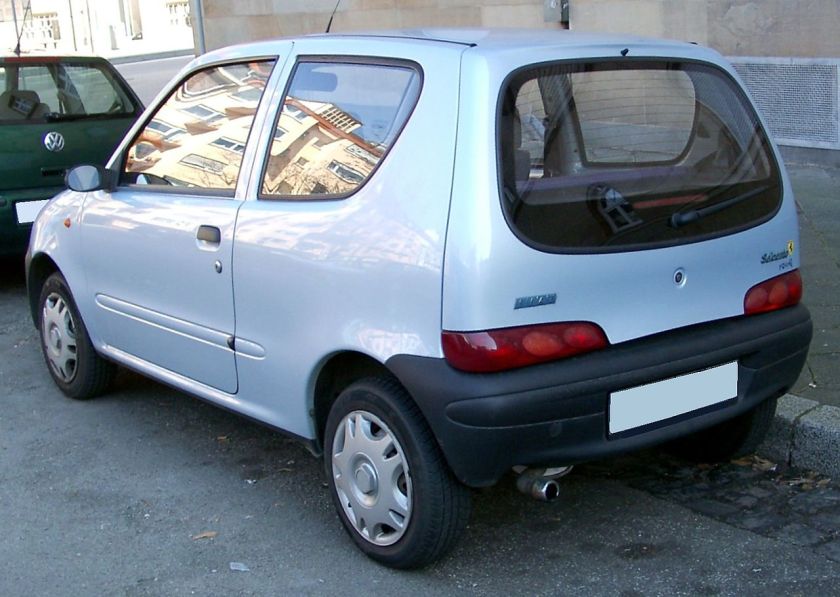
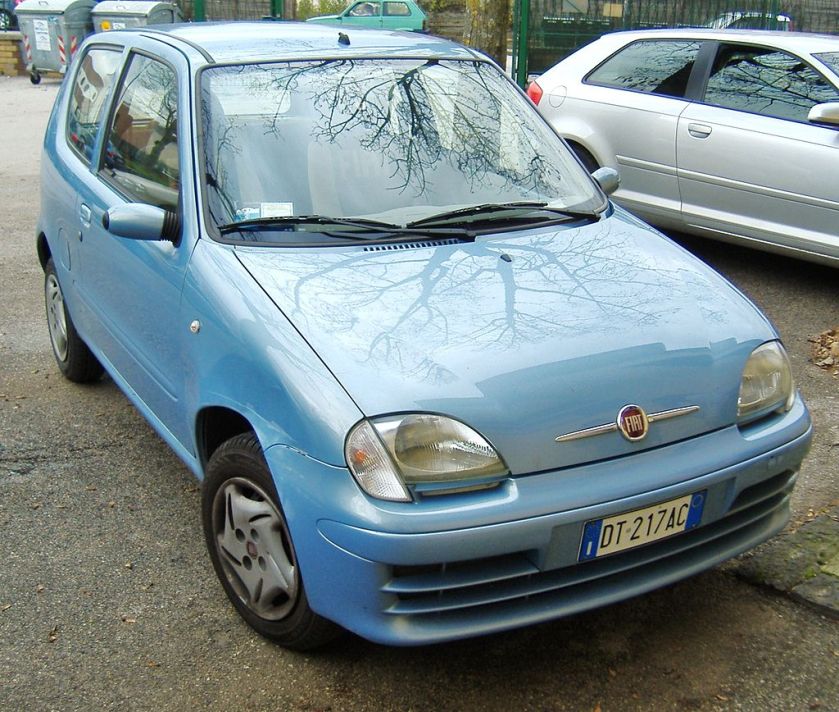
- 1998 Fiat Seicento
1998 Fiat Seicento
| Fiat Seicento | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Fiat |
| Also called | Fiat 600 |
| Production | 1998–2010 (1,328,839 units) |
| Assembly | Tychy, Poland |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | City car |
| Layout | Front-engine, front-wheel-drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 900cc I4 (petrol) 1.1 L I4 (petrol) 30 kW/40 hp (electric) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,200 mm (86.6 in) |
| Length | 3,337 mm (131.4 in) |
| Width | 1,508 mm (59.4 in) |
| Height | 1,420 mm (55.9 in) |
| Curb weight | 730–750 kg (1,610–1,650 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Fiat Cinquecento |
| Successor | Fiat Nuova 500 Fiat Nuova Panda |
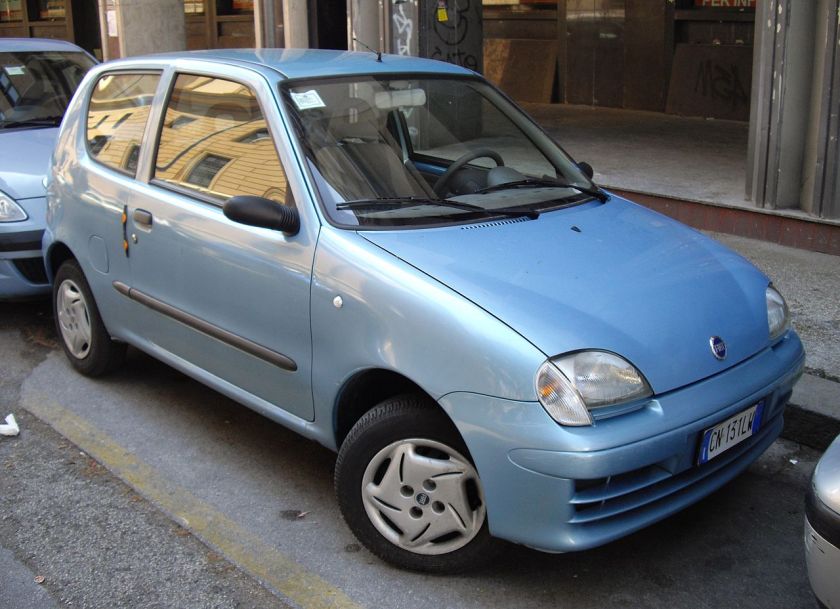
The Fiat Seicento (Type 187) was a city car produced by the Italian company Fiat, introduced in late 1997 as a replacement for the Fiat Cinquecento. It was based on the first generation Fiat Punto. The Seicento did not differ much from its predecessor, retaining the same engines, chassis and general dimensions, although it did gain a minor 9 cm in length (total length of 3.34 m). The design was similar too, in which the Seicento kept the same 3-door hatchback body, instead of the 5-door mini MPV look seen on many Korean and Japanese city cars, such as the Daewoo Matiz and Suzuki Wagon R. Like its predecessors, the Cinquecento and Polski Fiat 126, the Seicento was built in Fiat’s factory in Tychy, Poland. From 1998 to April 2004, 1.1 million examples of the Seicento had been produced.
The Seicento name comes from the Italian word for 600, the Seicento is the spiritual successor to the Fiat 600. The car was rebadged as 600 to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the original model.
EuroNCAP performance
In EuroNCAP crash tests, the Fiat Seicento was only awarded a 1.5 star rating, and fractionally beat the worst contenders in the history of EuroNCAP, namely the Rover 100 and the original Chrysler Voyager MPV. This is not so surprising, as the car has an extremely short front-end and keeps many components from its predecessor, originally conceived in 1991.
In comparison, another small car, the Smart Fortwo (which has a shorter front end), earned three stars in the crash test. These cars started production in 1998 and are not designed for 1997 started EuroNCAP tests.
Versions
Trims/Equipment
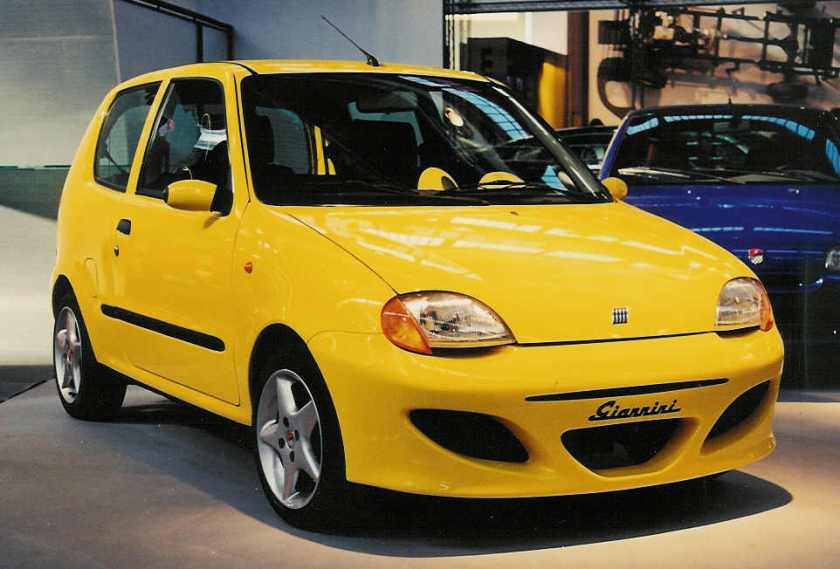
At launch, the Seicento was available with three trim levels; a basic ‘S’ with black bumpers and spartan equipment and initially the 899 cc engine; an ‘SX’ model, a slight upgrade over the ‘S’ with colour-coded bumpers, electric windows, central locking and a sunroof – which was also available as a ‘Citymatic’ with a clutchless manual gearchange – and a ‘Sporting’ with the larger FIRE 1,108 cc engine, 20 mm (0.8 in) lower suspension and anti-roll bars added. Cosmetically, this version gained 13″ alloy wheels, sports seats. An Abarth styling kit was also available with a body kit with optional Abarth 14″ wheels a close-ratio gearbox, sill kick plates, embroidered headrests, leather gear stick and steering wheel, blue highlighted trim in the bumpers, side skirts and a spoiler also available. Both the sporting and the Abarths were available with ABS, air-conditioning and Power steering but due to cost not very many owners took up the options.
In 1999, the FIRE engine was used in the special ‘Suite’ version, which came with air-conditioning. A special edition ‘Soleil’ model was available in some markets, which was based on the ‘SX’ model but came with a full-length electrically-folding fabric roof.
After the 2001 update, all cars were given clear indicator lenses, with the Sporting model getting a restyled bodykit. Cars built from this period also come with Power steering as standard. A ‘Michael Schumacher‘ edition of the Sporting, with ABS and the Abarth styling kit, was also launched at this time to celebrate the Ferrari driver’s Formula One success, This model was almost identical to the Abarth kit with the exception of chrome gear stick surrounds and Michael’s signature on the boot lid and side skirt. A limited edition plate and number was also on the passenger door.
In 2004, the model was withdrawn from the United Kingdom market, and production of RHD models ceased, following the arrival of the new and more practical Panda. The LHD model was facelifted, gaining a new design for the wheel rims and the introduction of the new Fiat logo to the rear.
Fiat 600
In 2005 the name Seicento was replaced by 600 (in occasion of the 50 anniversary of the first edition, in 1955) together with some changes in the front and in versions dotations: now the name Fiat is written on the seats. The new versions now are named “Class” and “50 anniversary”, thus reminding the strict relationship between this model and the previous one.
Engines
The Seicento is available with two engines: the old 899 cc OHV (29 kW / 40 hp) engine used in early base S and SX models (which was removed from West European markets due to emissions regulations), and the 1108 cc FIRE (40 kW / 54 hp and used in the Sporting version since launch), was fitted universally with multi-point fuel injection from 2001, replacing the old pushrod units. There was also a version with an electric engine (30 kW / 41 hp).
Elettra
Until 2005 Fiat also produced a battery-electric version of the Seicento called the Seicento Elettra. Originally produced in serial quantities in Italy from 1996 to 1998, production moved to Poland for the remaining years where it was built on order. The Seicento Elettra featured a 30 kW three-phase asynchronous electric motor powered by 18 12V lead-acid batteries in the engine bay and beneath the rear seats. The Seicento Elettra’s top speed was 100 km/h (62 mph) and its range was 90 kilometres (56 mi).
Tuning
Giannini Seicento
German tuner Novitec created a special edition of the Fiat Seicento, adding a turbocharger and six-speed gearbox to the little car. The German tuner is able to extract 101 hp (74 kW) from the 1,108 cc FIRE engine. Other tuners include the venerable Giannini company, who produced an aggressive bodykit and also considered installing a 1.6 litre engine.
Future replacement
The car ceased production in 2010. Although no direct replacement has been announced, much of the market territory it once occupied had already been filled by the new Fiat Panda (2003) and the 500 (2007), as well as the Fiat Palio budget model.
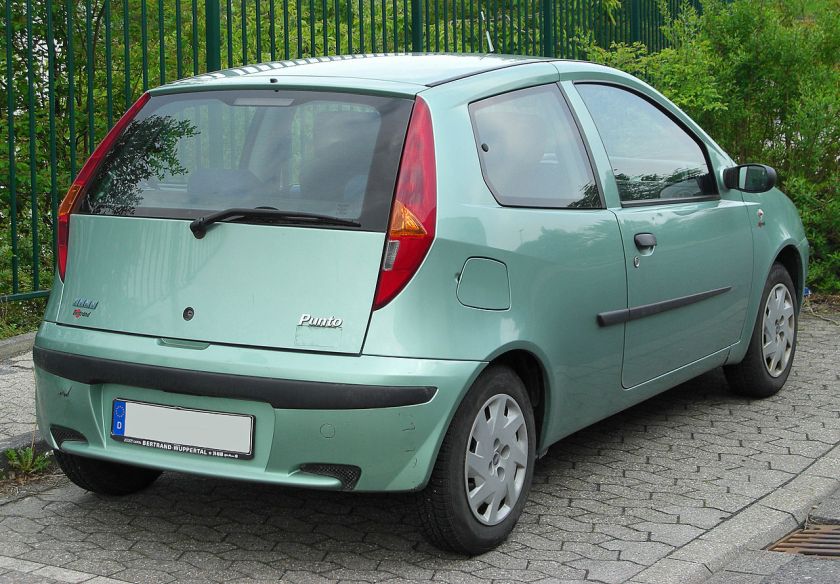
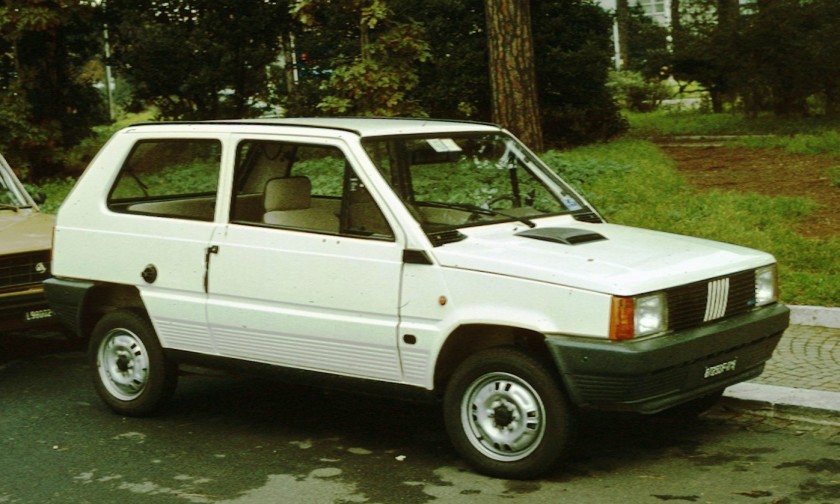
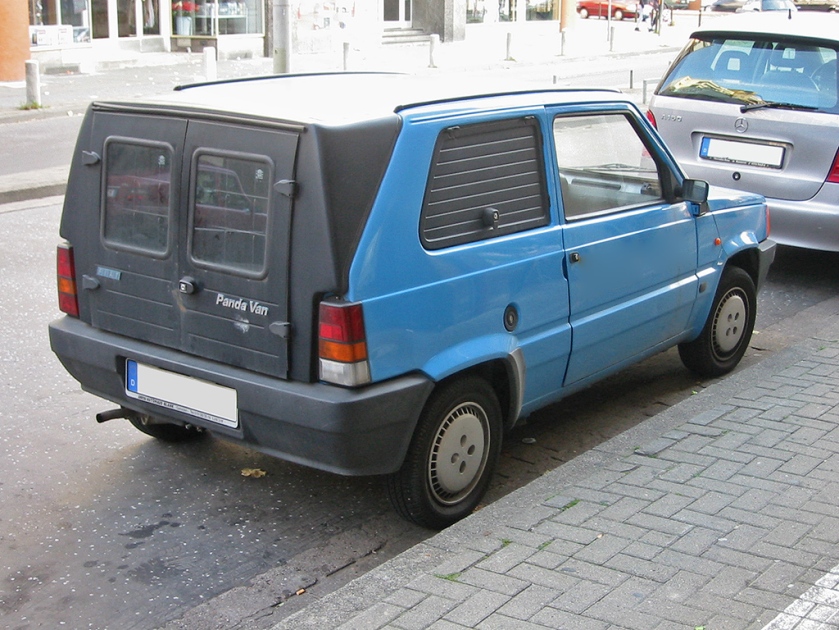
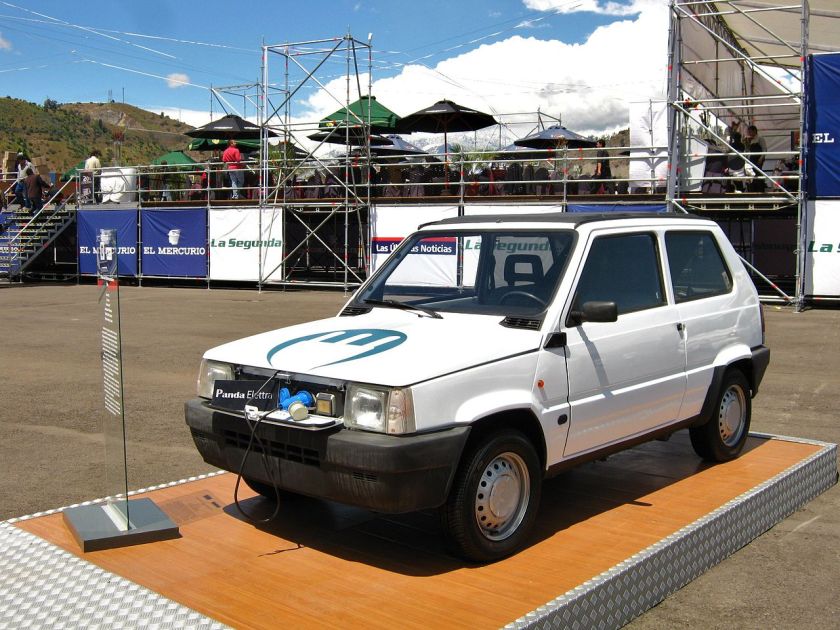
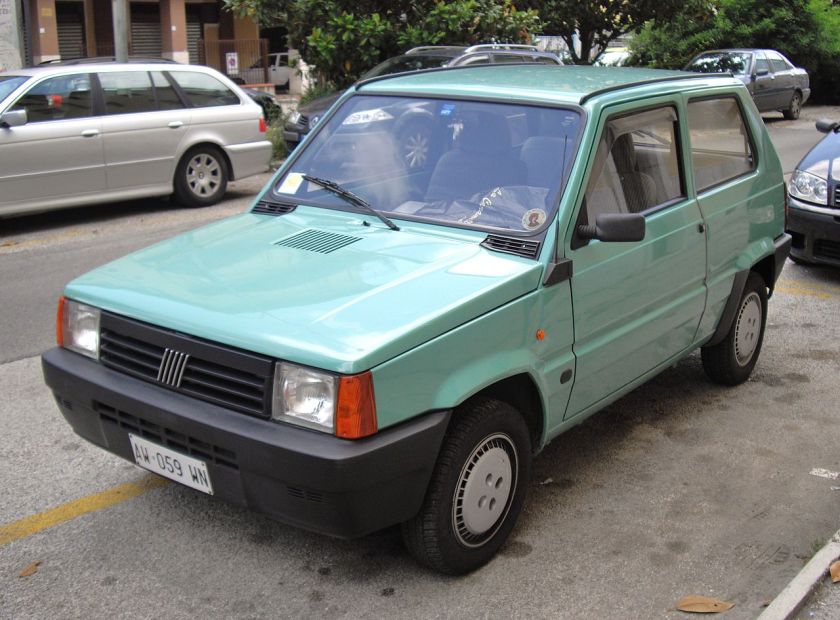
- 1999 Fiat Punto (second generation)






















































































































































































































![1966 Ônibus+antigo.finalizado[1]](https://myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/1966-c3b4nibusantigo-finalizado1.jpg?w=840)