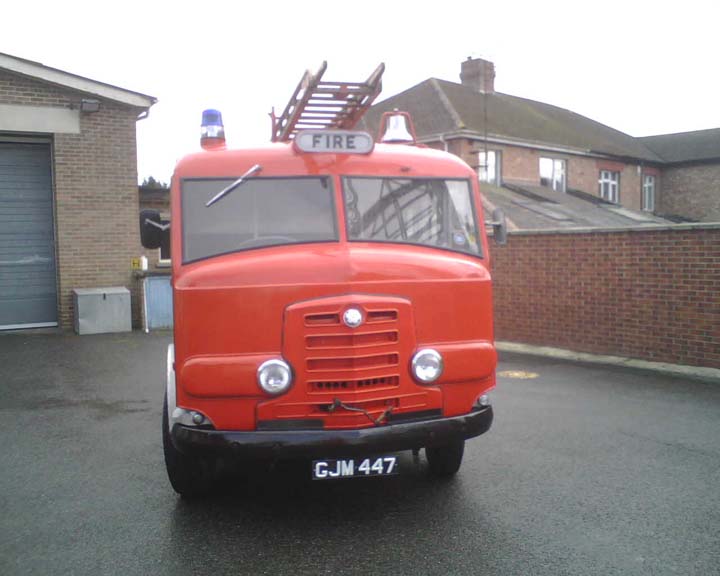
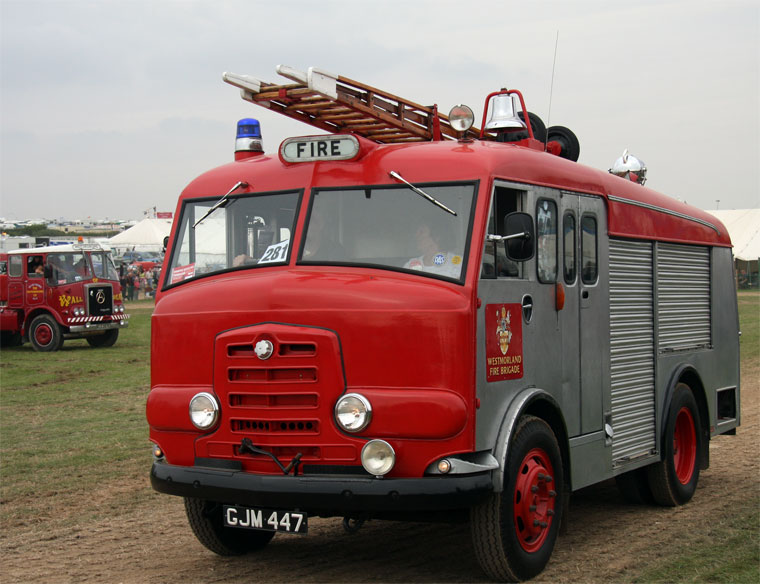
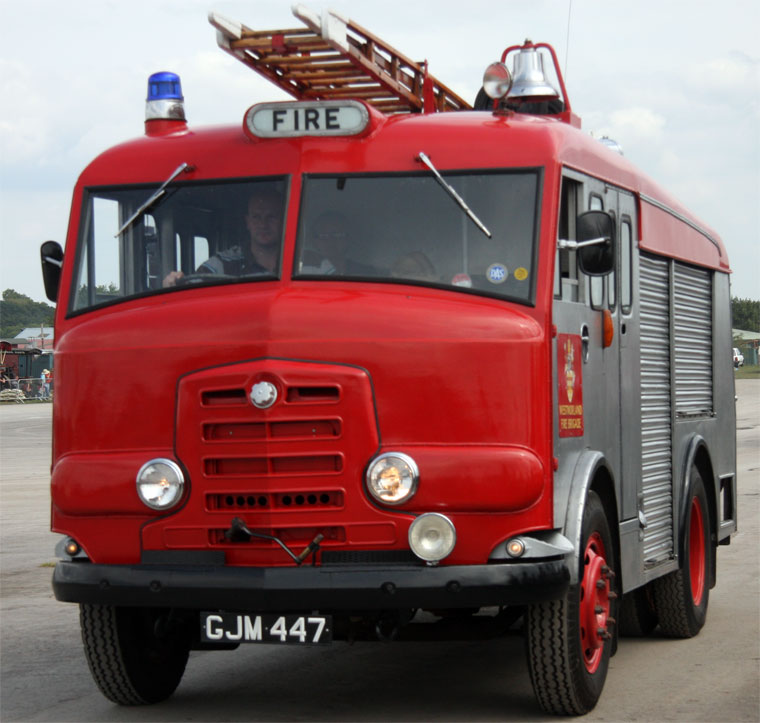
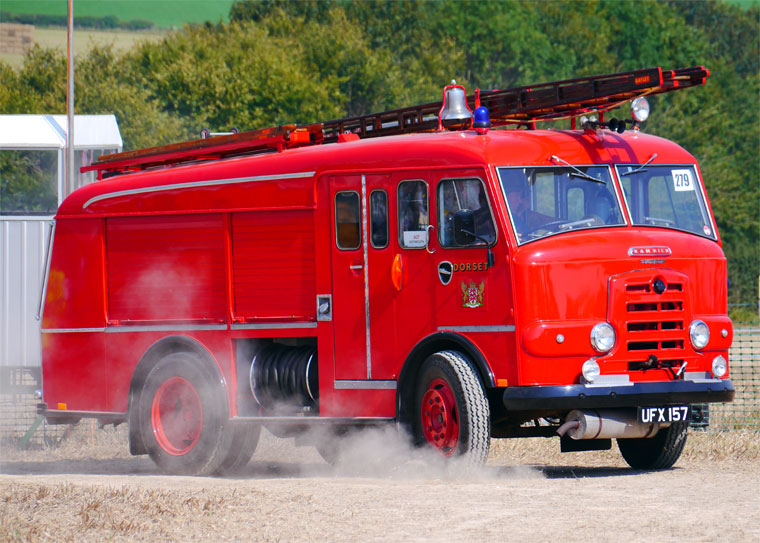
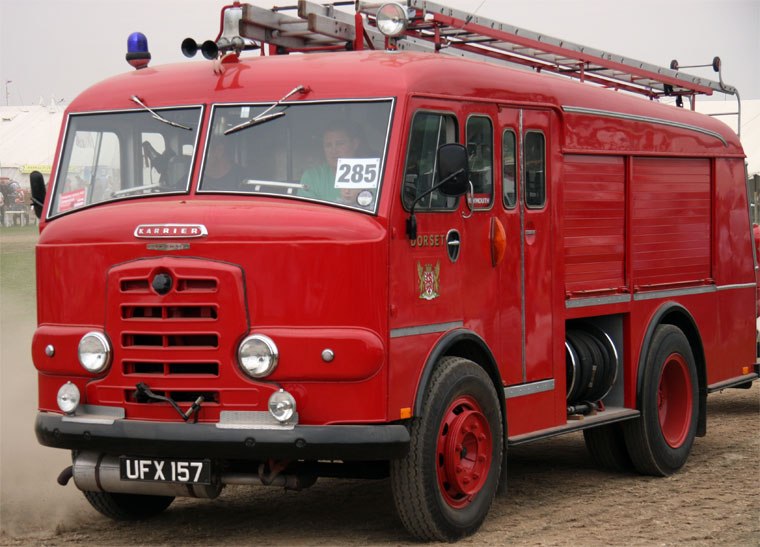
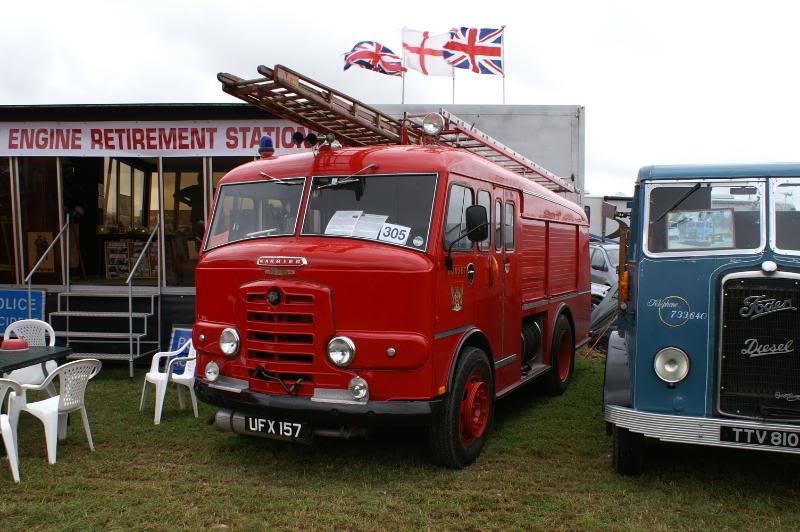
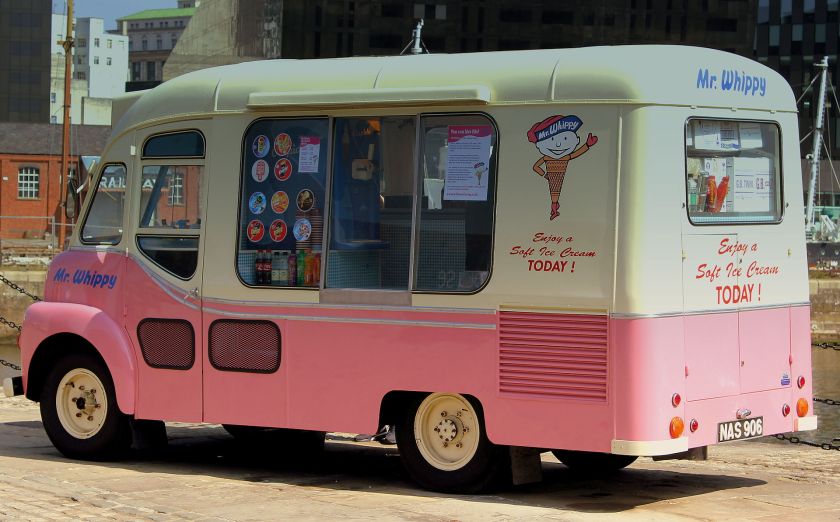
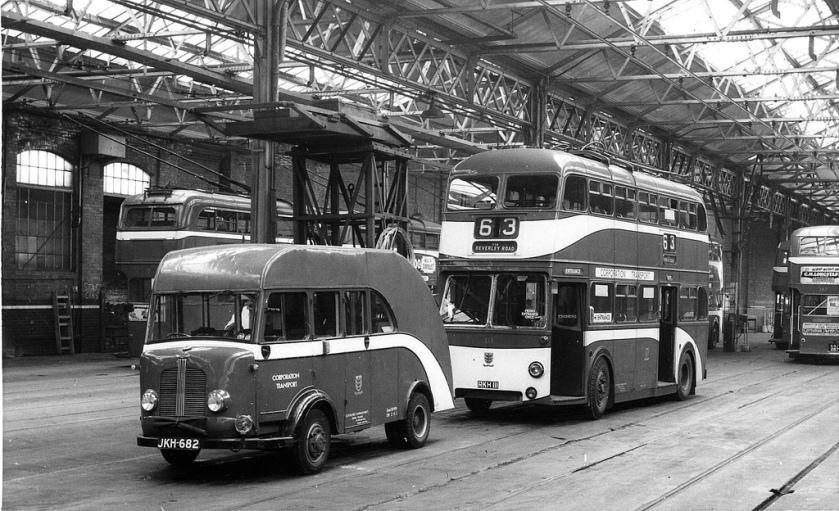
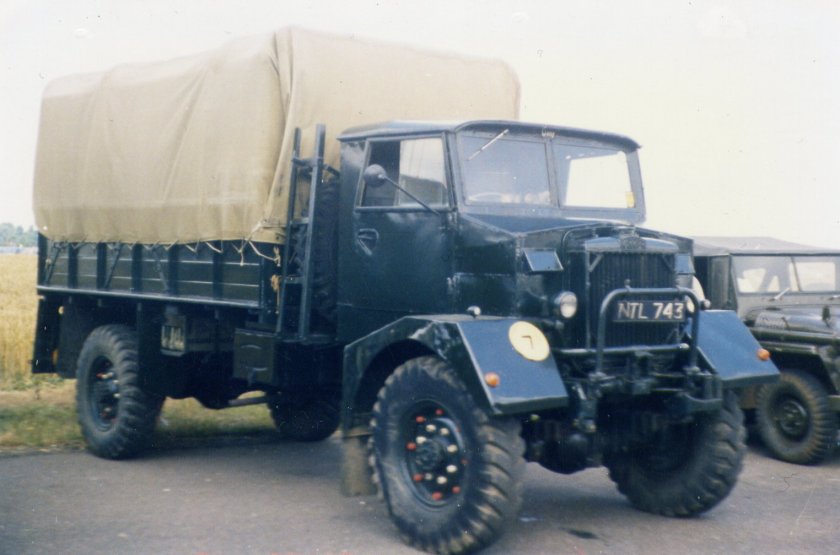
Karrier Motors
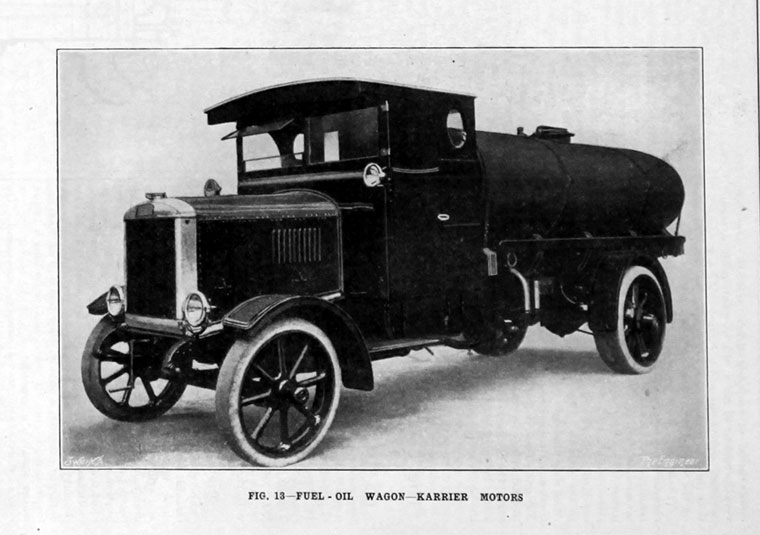
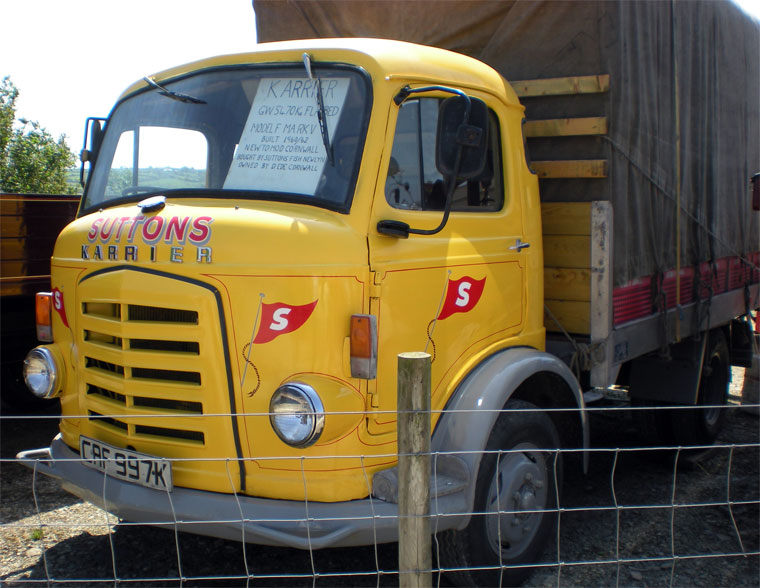
Karrier is a marque of car and commercial vehicle, the origins of which can be traced back to Clayton and Company, a 1904 company founded by Herbert and Reginald Clayton from Huddersfield, West Yorkshire,UK. In 1908, they started making Karrier cars and in 1920 changed the company name to Karrier Motors Ltd. It also produced buses and in latter years, especially during the Second World War, trolleybuses, notably the Karrier ‘W’ model.
Colt, Cob and Bantam
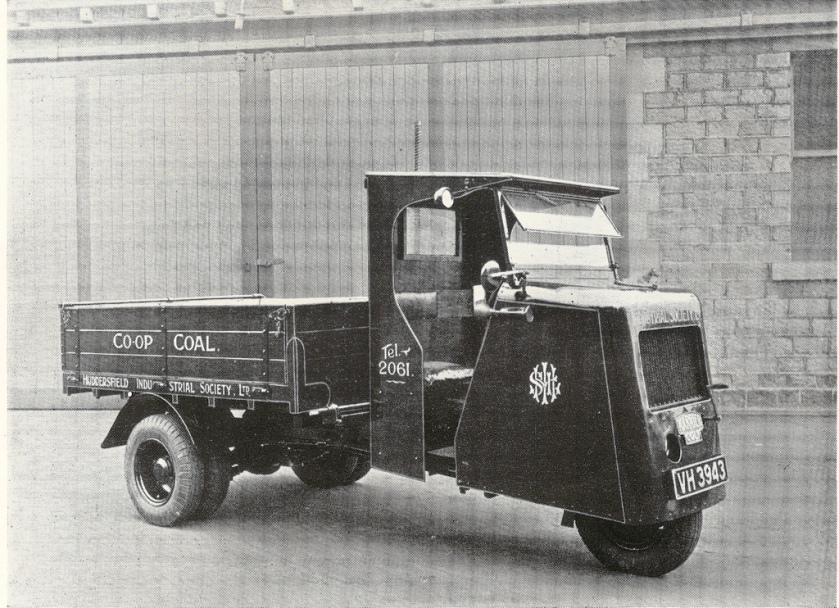
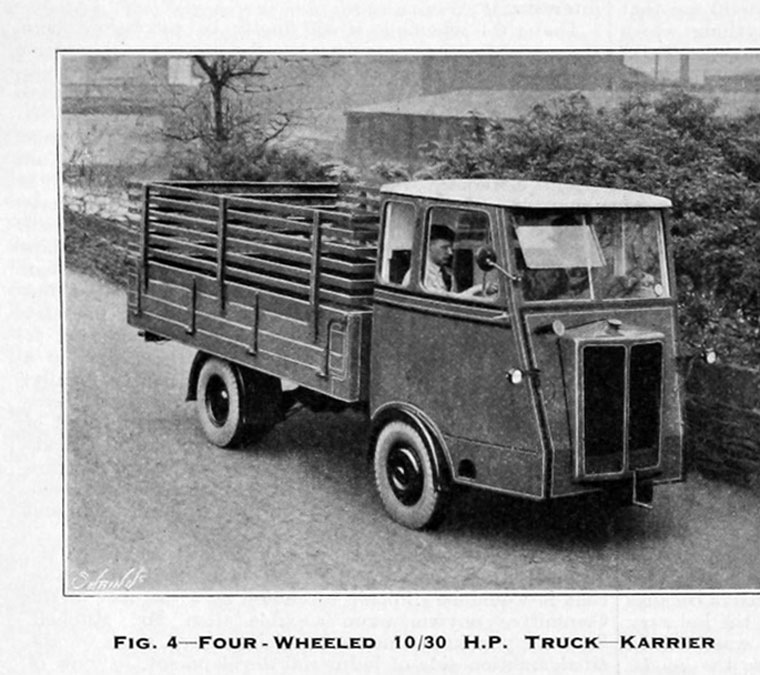
In 1929, Karrier started production of the “Colt” three-wheeler as a dustcart chassis for Huddersfield Corporation. In 1930, this was developed into the “Cob” tractor to haul road trailers for the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. The “Cob” was similar to the Scammell Mechanical Horse. In the mid-1930s, the “Cob” range was supplemented by the four-wheel “Bantam”.
Takeovers and mergers
Rootes Group
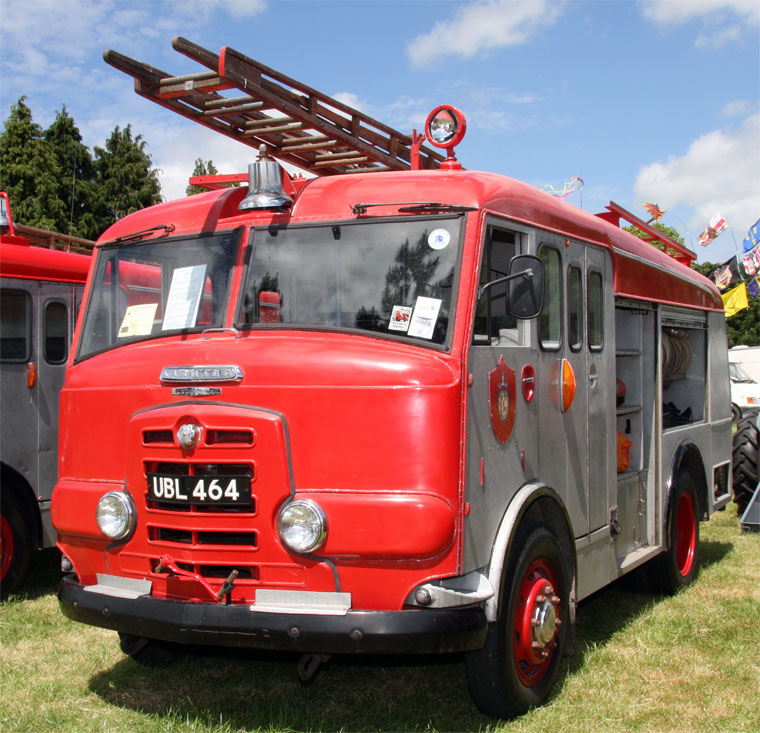
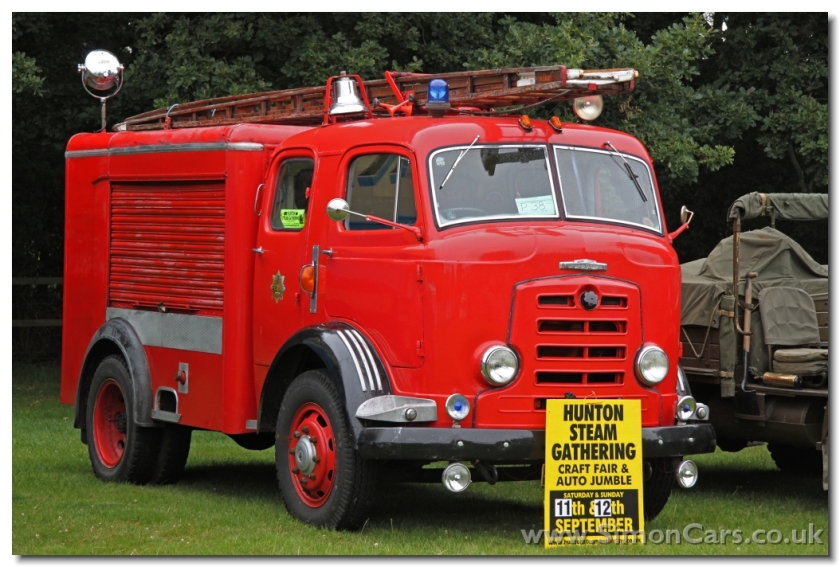
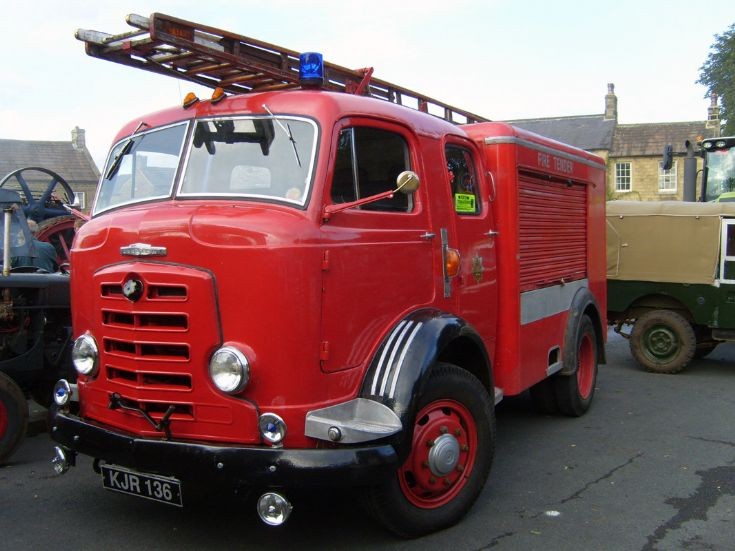
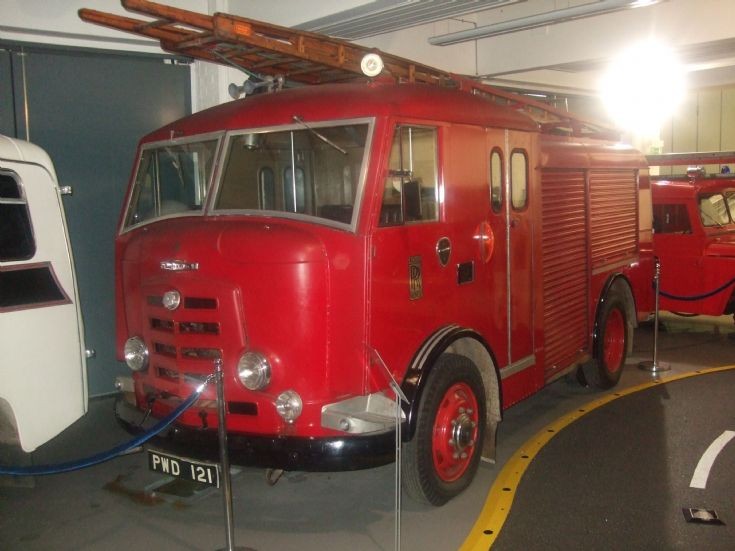
After takeover bids in 1934, the Rootes Group acquired Karrier and moved production to Luton, closing the Huddersfield operation. In the late 1950s and 1960s, some Karrier vehicles were fitted with the iconic Rootes TS3 two-stroke opposed piston diesel engine. Other engines used in this period include Humber Hawk 4- cylinder petrol engines (L-Head and OHC), Humber Super Snipe 6-cylinder (L-Head and OHV) and Perkins Diesels.
At Luton, the only designs carried over from the previous era were the three wheeler and the six-wheel trolleybus chassis.
The trolleybus business became integrated with that of Sunbeam following its absorption into the Rootes group. In 1946 the trolleybus operations and the Wolverhampton trolleybus line was sold to Brockhouse Ltd, who in 1948 sold it to Guy Motors.
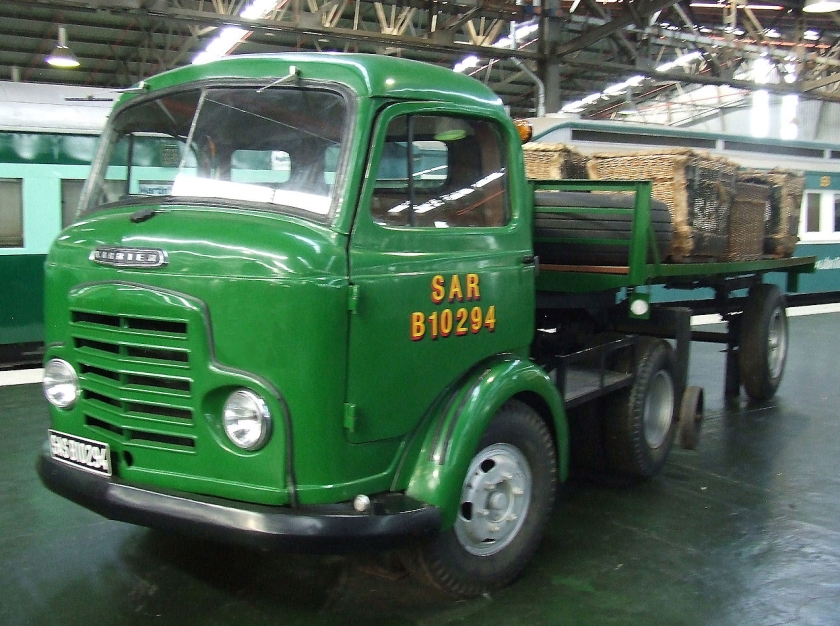
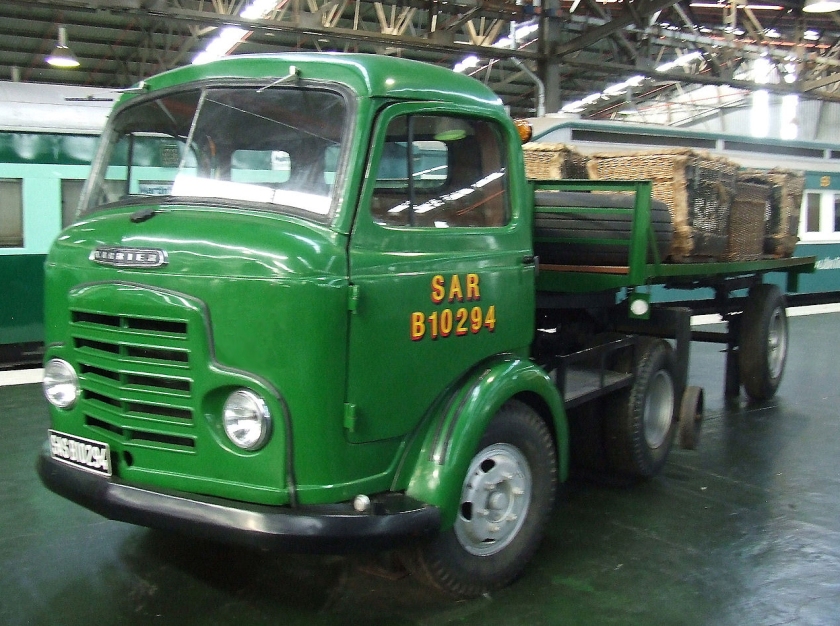
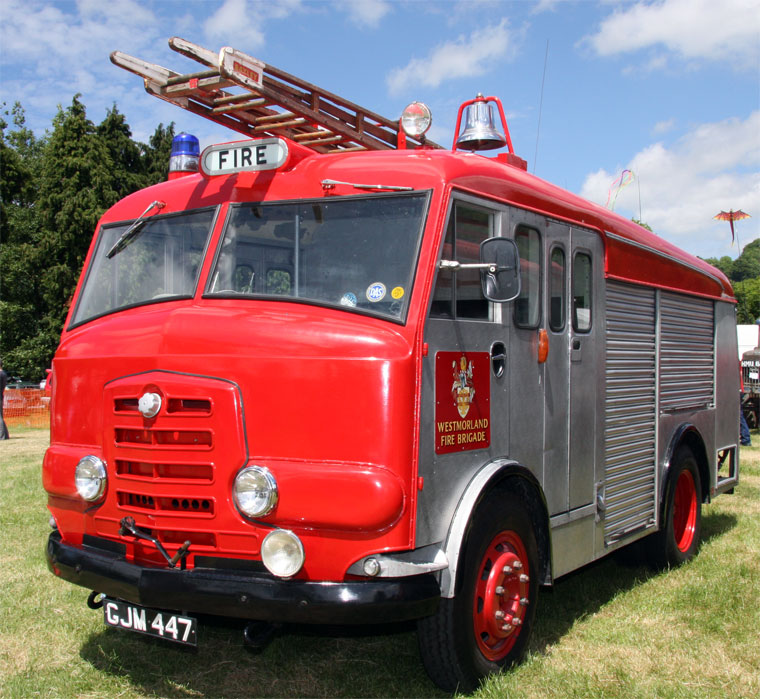
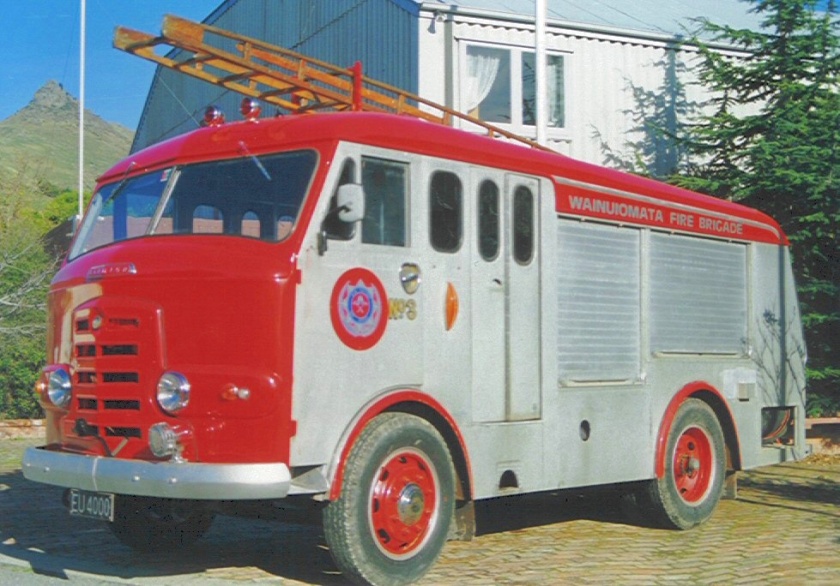
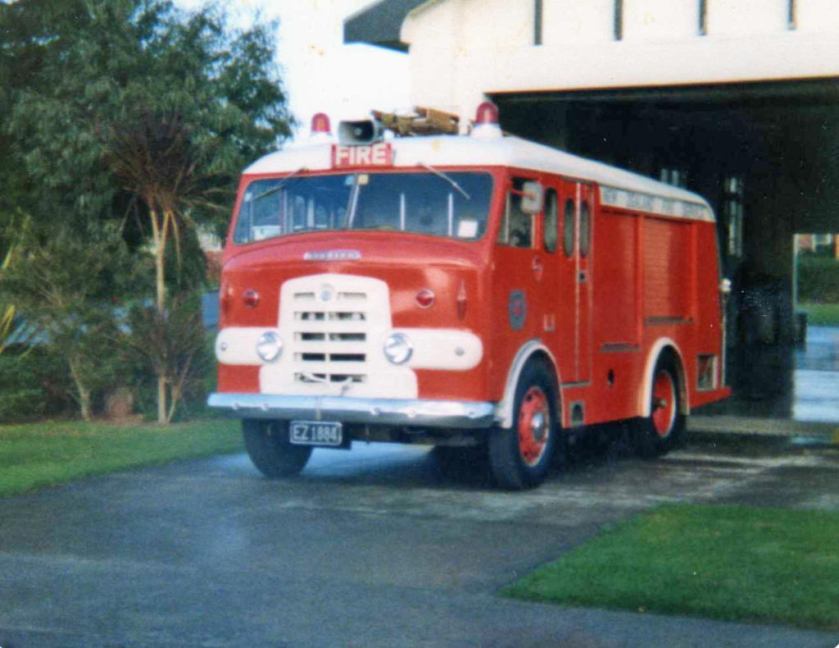
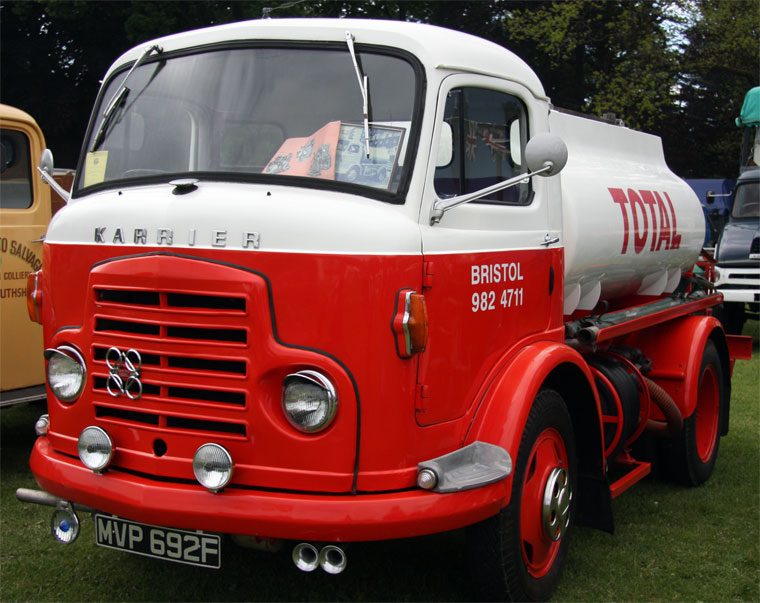
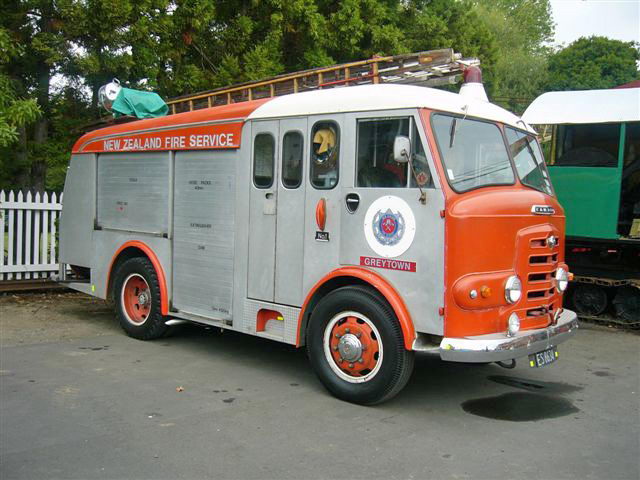
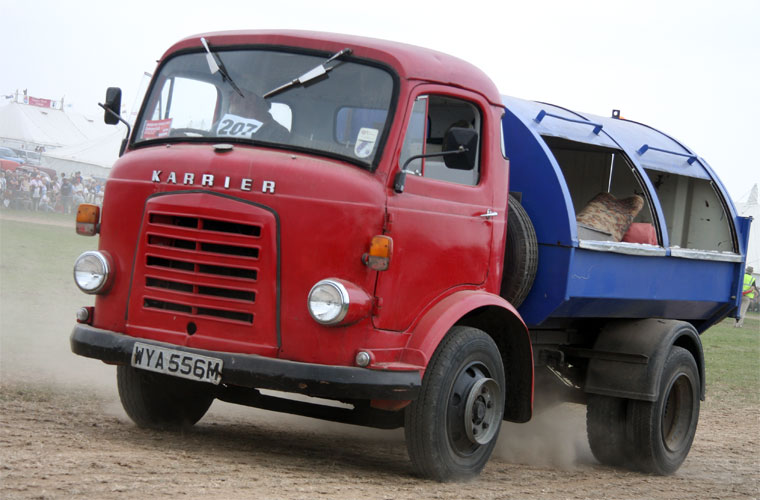
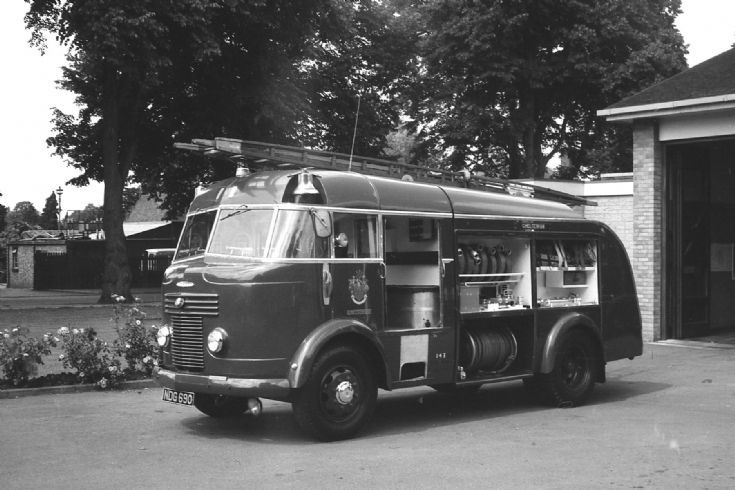
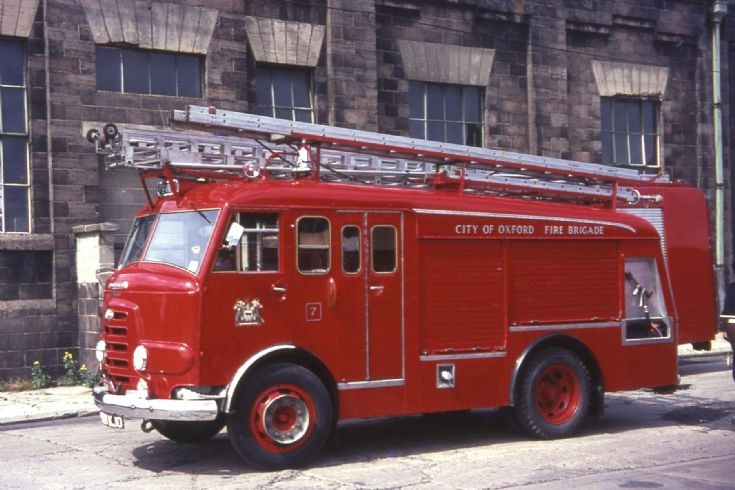
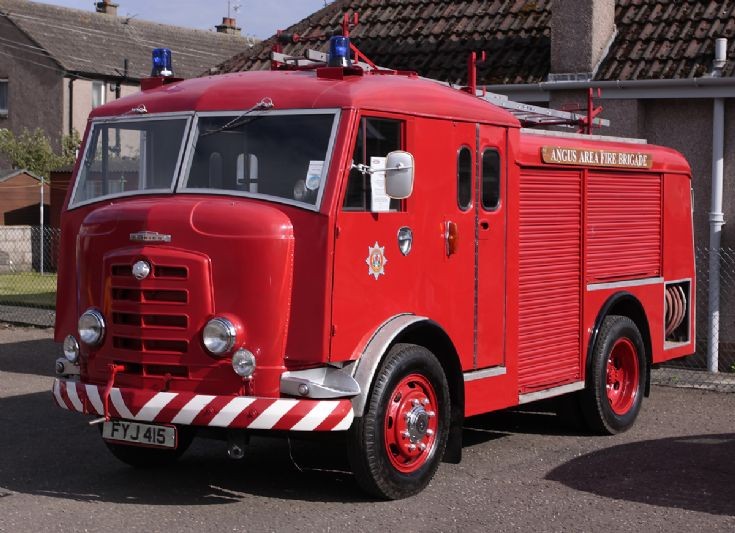
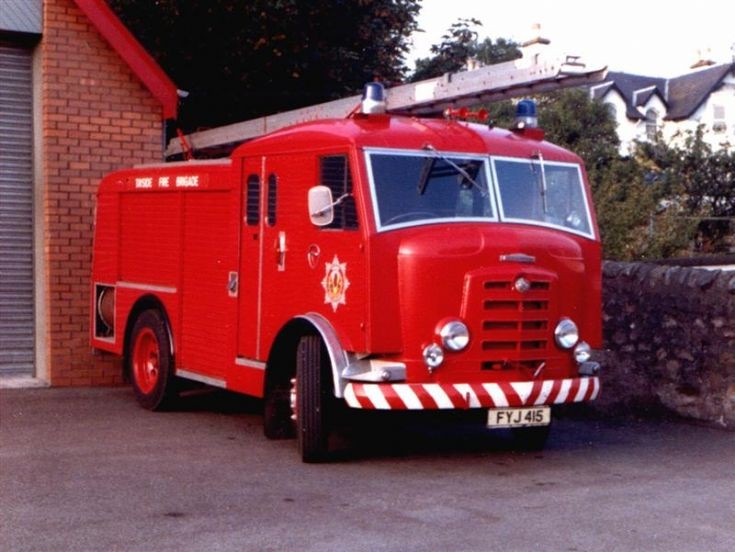
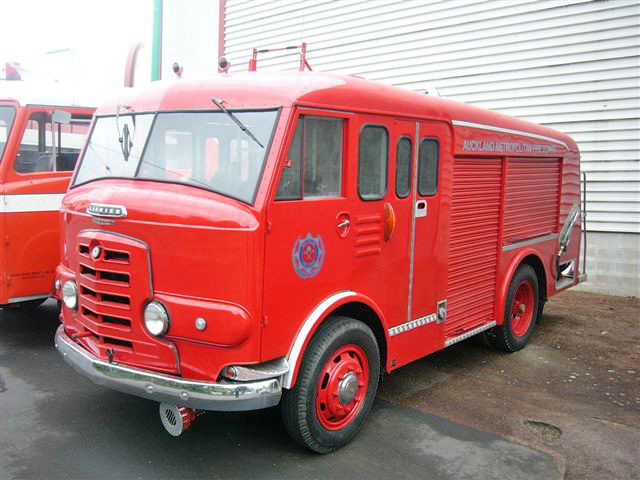
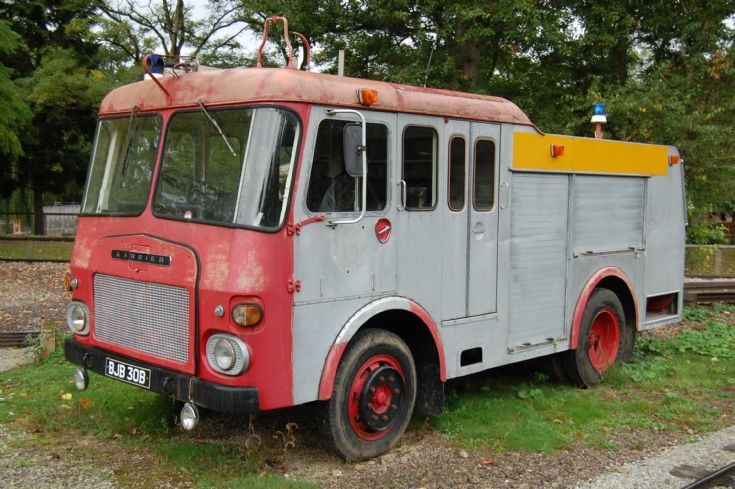
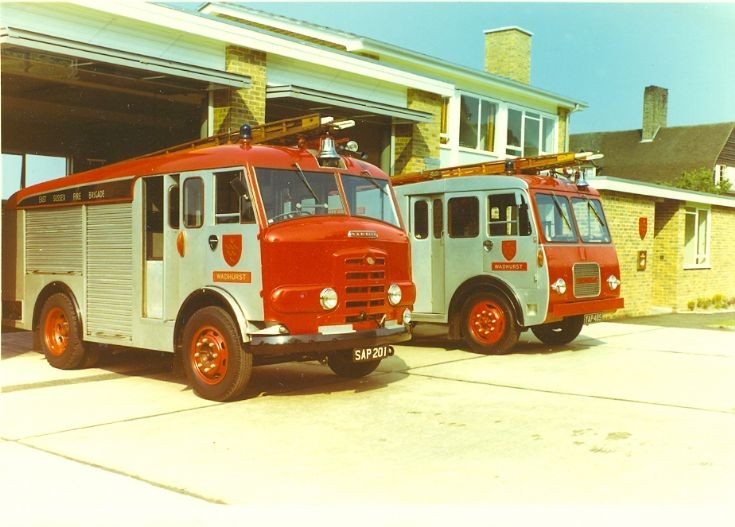
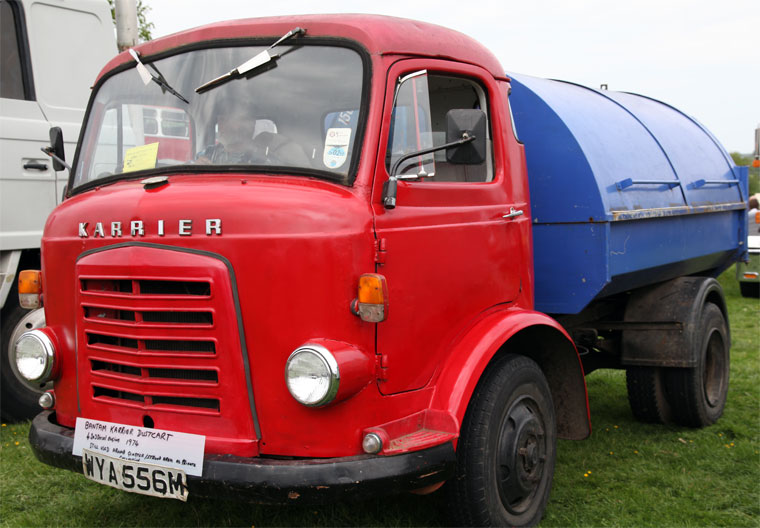
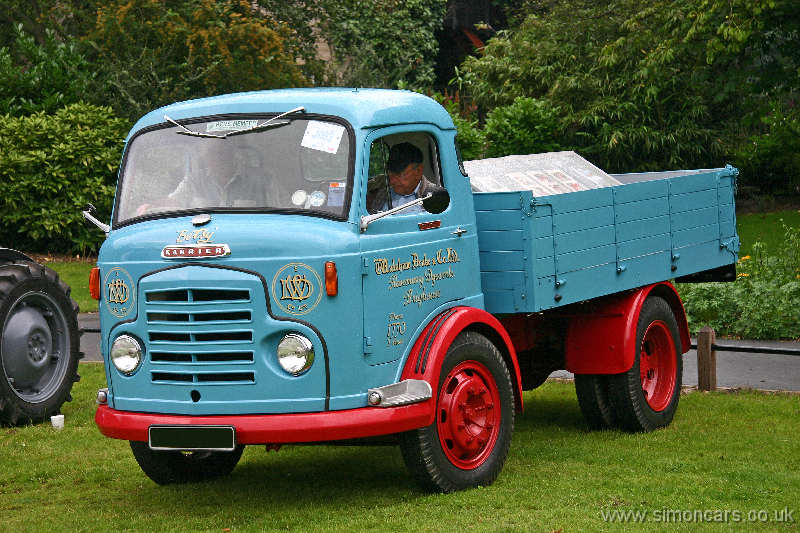
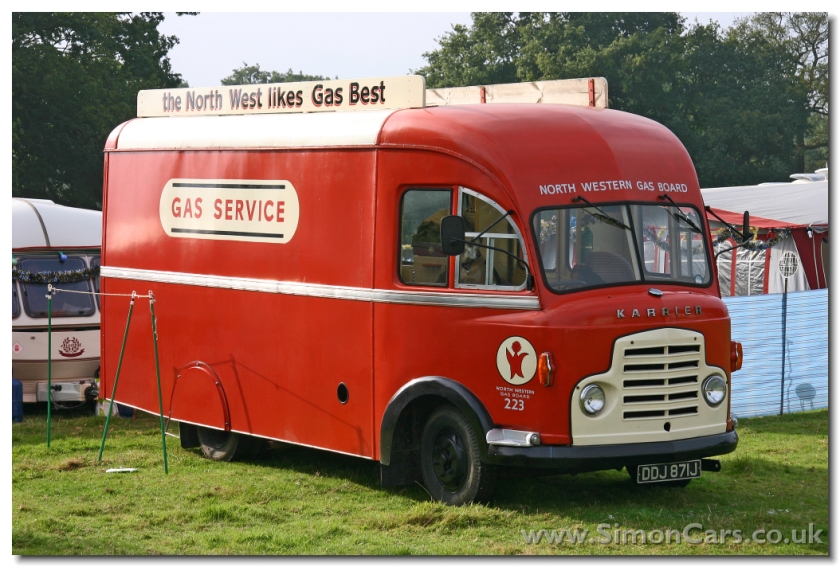
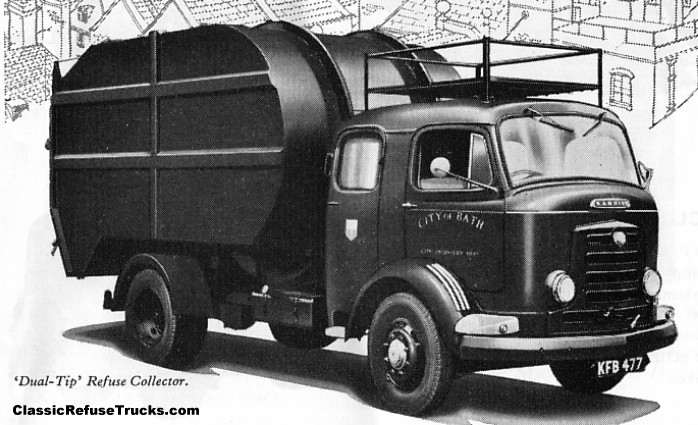
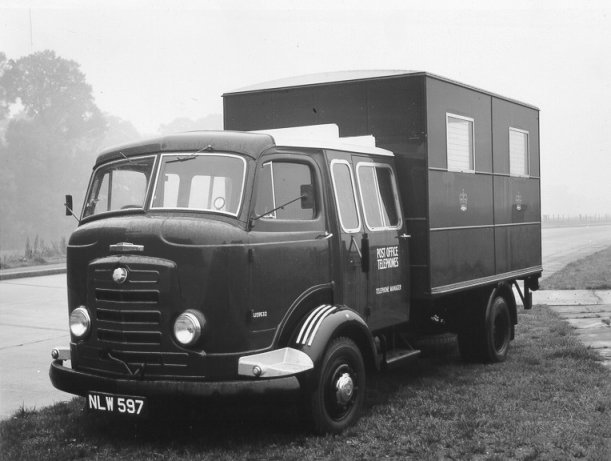
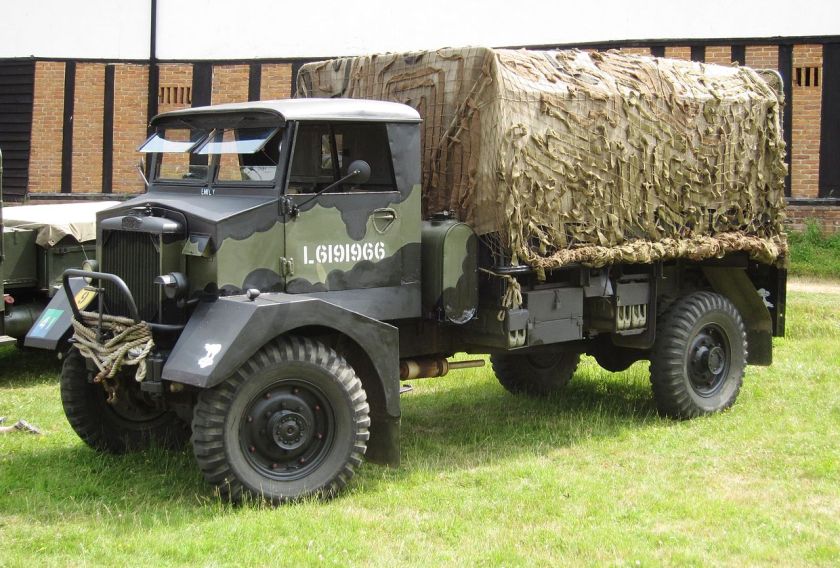
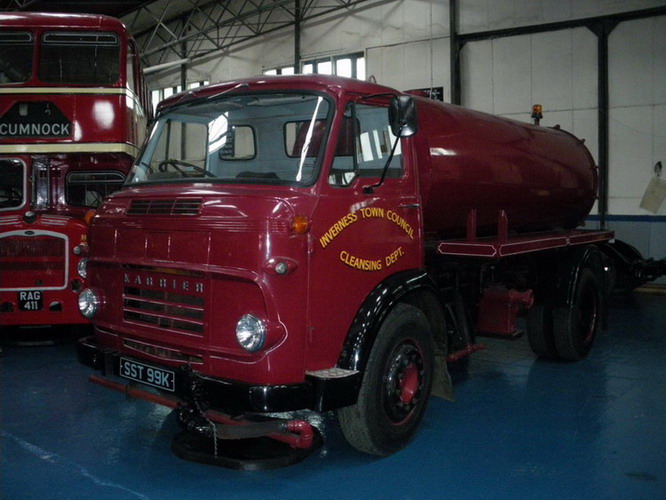
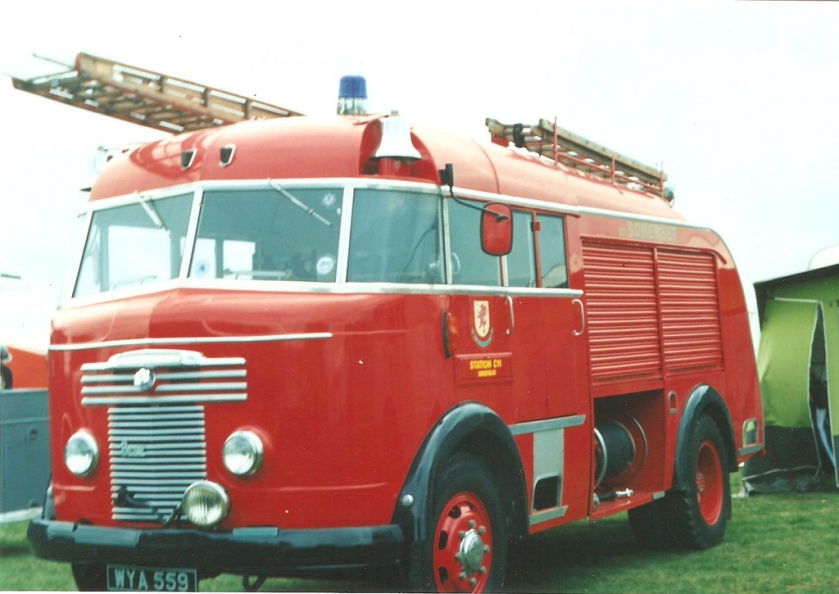
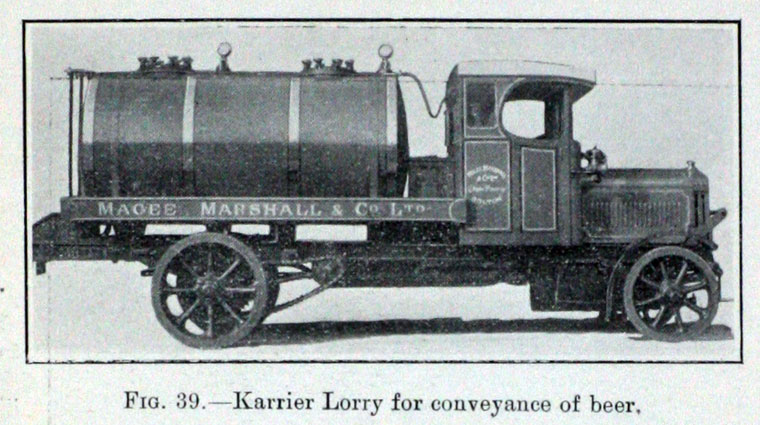
Under Rootes ownership, Karrier trucks were generally smaller size than their sister, Commer brand, with “Bantam” models using 13-inch and “Gamecock” models using 16-inch wheels, to give lower loading height. Partly because of this, they were particularly popular with local authorities for varied applications, including highway maintenance tippers, refuse collection vehicles and street lighting maintenance tower wagons. Karrier trucks and chassis were also popular with airport operators and airlines for baggage handling trucks, water bowsers and toilet servicing.
Dodge (UK)
The Dodge Brothers company came to the UK in 1922 and began importing United States Dodge knock-down kits to build in the UK at a production line in Park Royal, London. Eventually, production was moved to the Chrysler plant at Kew; Dodges built there were known as “Dodge Kews”. During the Second World War this factory was part of London Aircraft Production Group and built Handley Page Halifax aircraft assemblies.
In 1965, production moved to Dunstable where Commer, Dodge (UK) and Karrier were all brought together.
Chrysler Europe
By 1970, the Rootes Group had been taken over (in stages) by Chrysler Europe, with support from the British Government which was desperate to support the ailing British motor industry. The Dodge brand (also used by Chrysler in the USA) began to take precedence on all commercial models. The last vestige of Karrier was probably in the Dodge 50 Series, which began life badged as a (Chrysler) Dodge but with a Karrier Motor Company VIN (vehicle identification number) plate.
Peugeot and Renault
Chrysler eventually gave up on UK operations, selling the business to Peugeot. The new owner had little interest in heavy trucks and the factory was then run in conjunction with Renault Véhicules Industriels, (then part of Renault though now Volvo). The combined company used the name Karrier Motors Ltd, although the vehicles took on Renault badges and were sold through Renault Trucks dealers. Renault had been keen to secure a UK manufacturing operation for engines for its own models, and did relatively little to market or develop the British designs, favouring its existing French range such as the Renault Master. The end of the Karrier name could not be far off; eventually, Renault severed ties with Peugeot and introduced a Renault Truck Ind. or Renault Vehicles Ind. VIN plate (RVI).
The Karrier trademark is still in the possession of Peugeot, and it is not uncommon for vehicle marques to be reinstated.
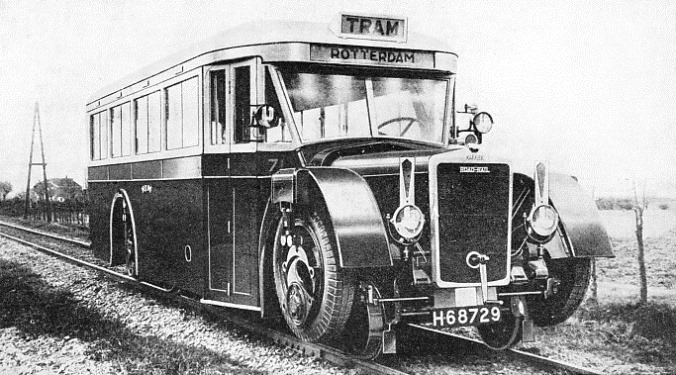
Ro-Railer
Karrier’s Ro-Railer was a hybrid single decker bus capable of running on both road and rail. It was introduced in 1932 and tested by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway but it was not a success and was not perpetuated. One of the few operational bus rail systems is to be found in Adelaide (Australia) called the O-Bahn Busway.

Karrier Motors started life in 1904 in Hudersfield as Clayton and Company. In 1907, they started making Karrier cars, and in 1920 changed their name to Karrier Motors Ltd; they evolved into truck and bus chassis builders, with municipalities being major companies.
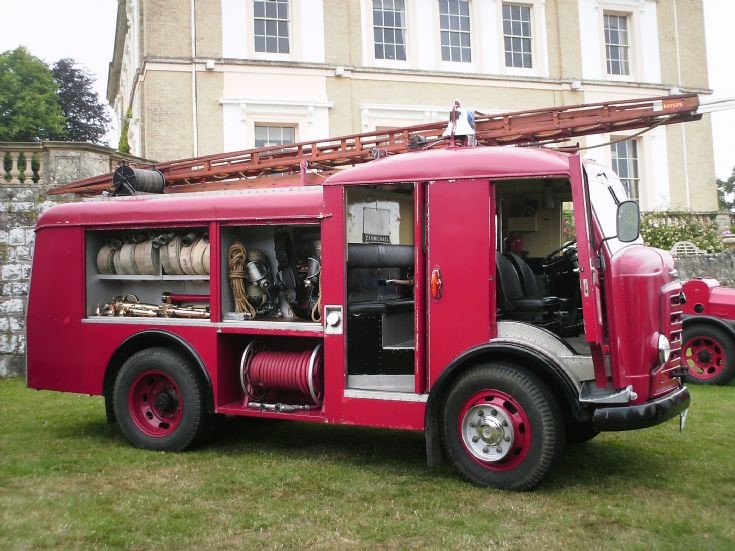
Karrier’s early vehicles were designed to be tough, no-frills vehicles, built to have large load spaces, short length, and a powerful engine to tackle Yorkshire hills. The first public service vehicle to climb Porlock Hill, Somerset, was a Karrier bus with 21 passengers and a 50 horspeower engine.
Early on, Karrier, like Commer, produced a design for World War I trucks, and many were built before 1914; during the war, 2,000 more were made for the military. After the war, Karrier gained a new factory and a new range of vehicles, and by 1924 was making 17 different models; pneumatics were first sold in 1924 on a 25-cwt chassis, and in 1926, the first purpose-built passenger chassis was made. The chassis were progressively improved, gaining pneumatic tires and having excess weight excised.
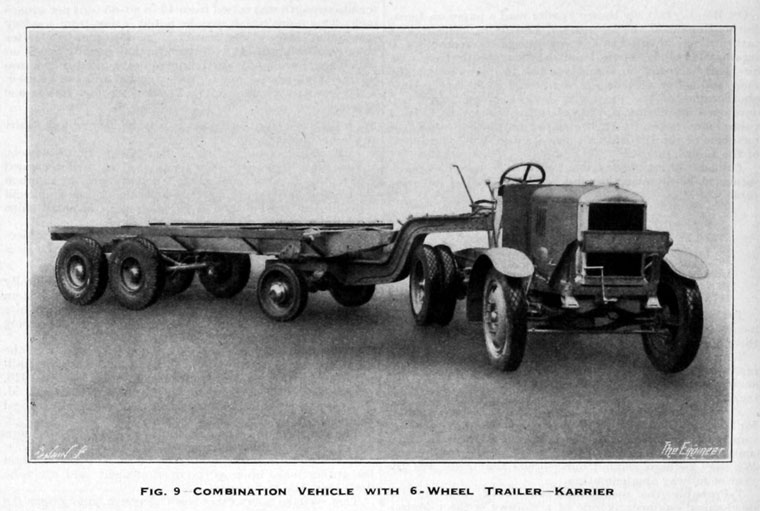
During the late 1920s, Karrier build numerous six-wheel chassis, two of which were the first vehicles of any kind to make a circuit of Australia, running for 22 weeks through 11,000 miles of harsh terrain, running on schedule. In 1927, the Super Safety Six Wheel Coach was launched; in 1928, the Karrier-Clough Six Wheel Trolleybus followed. The KWF6, a rigid six-wheeler engineered for use “in the colonies” and for hard road work, had an eight-ton payload with single sets of wheels on each of three axles.

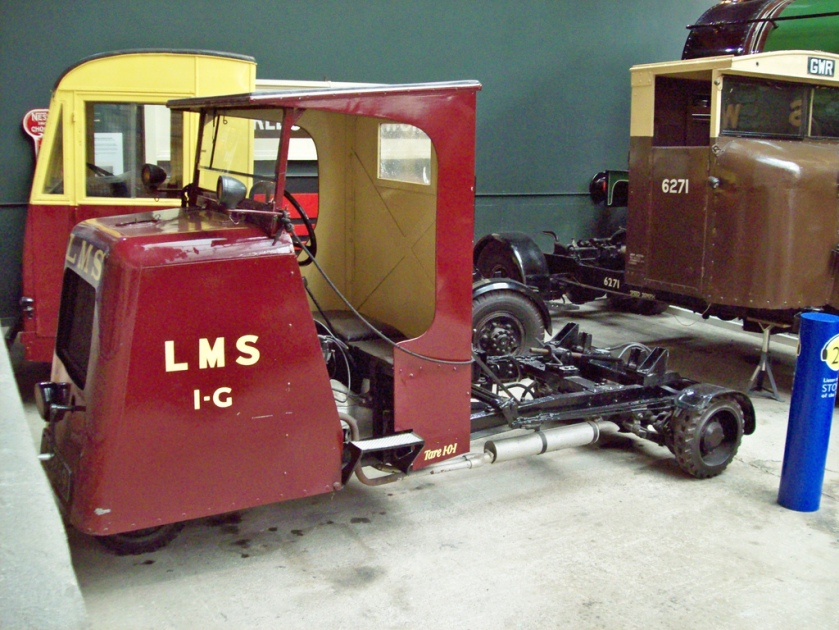
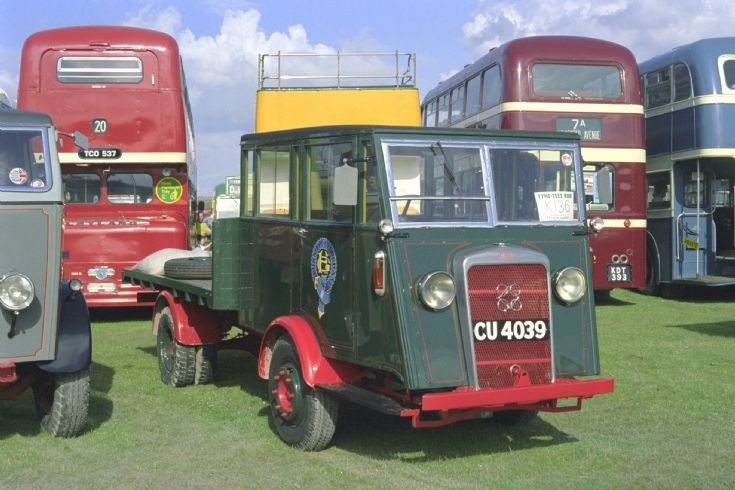
In 1930, Karrier produced a “mechanical horse” design, the Karrier Cob, engineered jointly with the London Midland & Scottish Railway for package delivery; it was powered by a two-cylinder Jowett engine, and could couple with horse-drawn trailers with the shafts removed. The London and North Eastern Railway had the same idea, and turned to Scammell Lorries, which developed a similar concept but with an automatic couple/uncouple system for trailers; Scammell appears to have first used the term “mechanical horse,” in 1934 (they would later use Perkins diesels, followed by the same Leyland OE160 used by late Karrier Bantams).
The Colt, launched in 1931, was a similarly designed tractor version, a two-ton three-wheel tractor, also powered by the Jewett horizontally opposed flat two-cylinder engine, with the “Colt Major” providing four cylinders.
Karrier also created the “road railer,” which had one set of wheels for roads and another for railroad tracks, and later developed a two-ton truck called the Bantam, a good seller particularly with parcel carriers such as British Rail. Its coupling was compatible with the Scammell system.
Karrier was, after a couple of takeover bids, acquired by Rootes Group in 1934. In Rootes’ standard fashion, production was quickly moved to Luton, where a new assembly area was built, and Hudersfield was closed; the model range was reduced to avoid competition between Commer and Karrier, and shared components were sought out. Karrier was now focused on three items, the Cob and Colt three-wheel “mechanical horses” (just three Cobs are known to survive), the Bantam (which could also be used as a mechanical horse), and the CK3 and CK6 chassis of three and six tonnes for municipal use. There were no visible similarities between the two truck brands, hiding their common owner. (Mechanical horses were lightweight, low-powered tractors usually used for local delivery. Their appearance could be similar to standard chassis-cab trucks, though many had three wheels.)
The Bantam started out with just 9 hp, raised to 18 hp via a Humber engine after Rootes took it over.
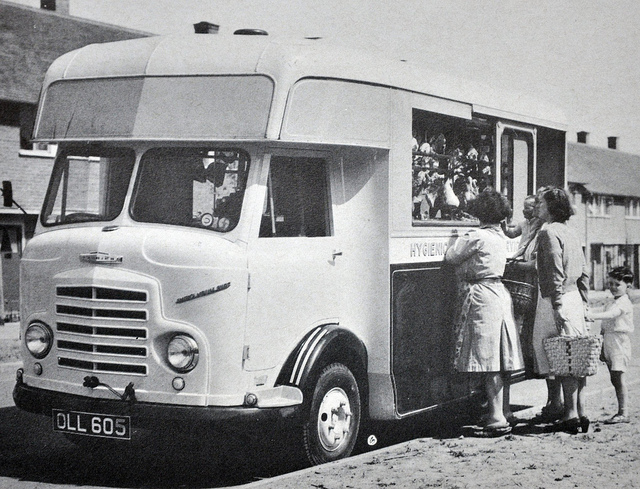
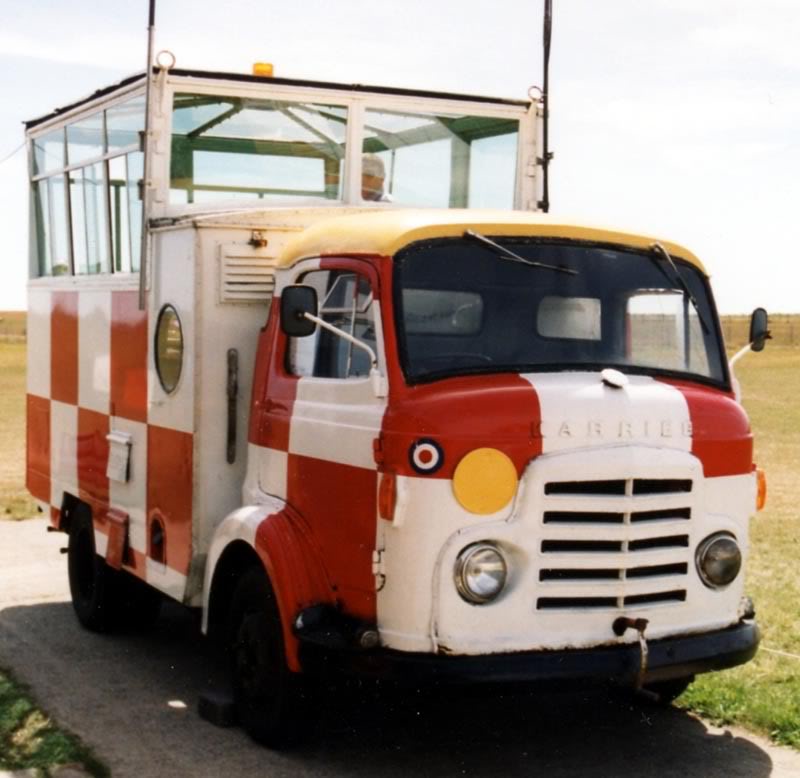
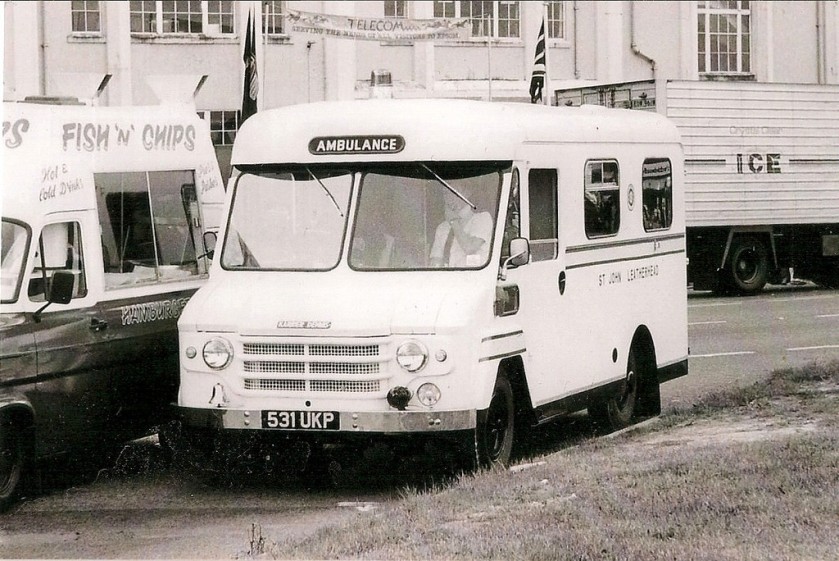
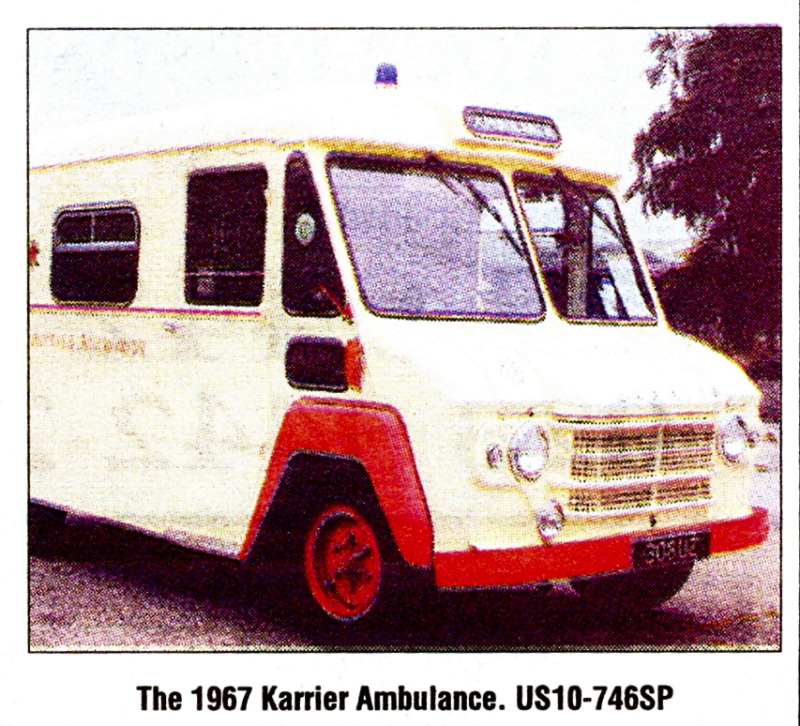
By 1939, over 600 municipalities used Karrier vehicles; the company had close relationships with aftermarket body builders, who made garbage collectors, tower wagons, and gully emptiers, as well as a left-hand-control road sweeper (a Karrier branded item based on a Commer chassis) and ambulance (also branded by Karrier but based on a Commer van).
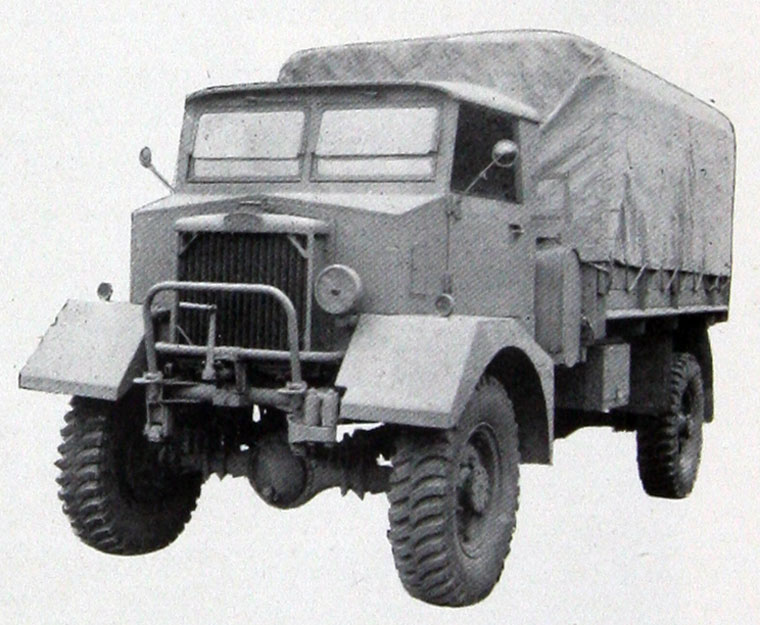
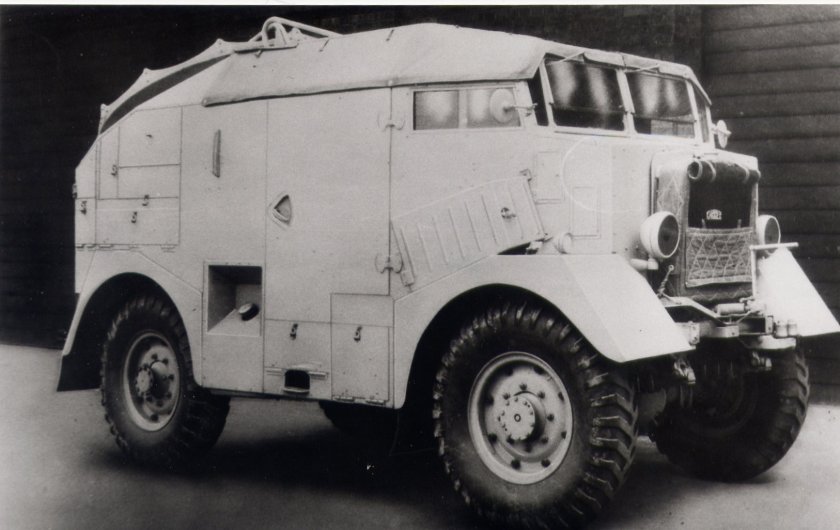
During World War II, there were separate designs for the two trucks; Karrier made cross-country four and six wheeled trucks. Overall, 10,000 Karrier trucks were used by the military during the war.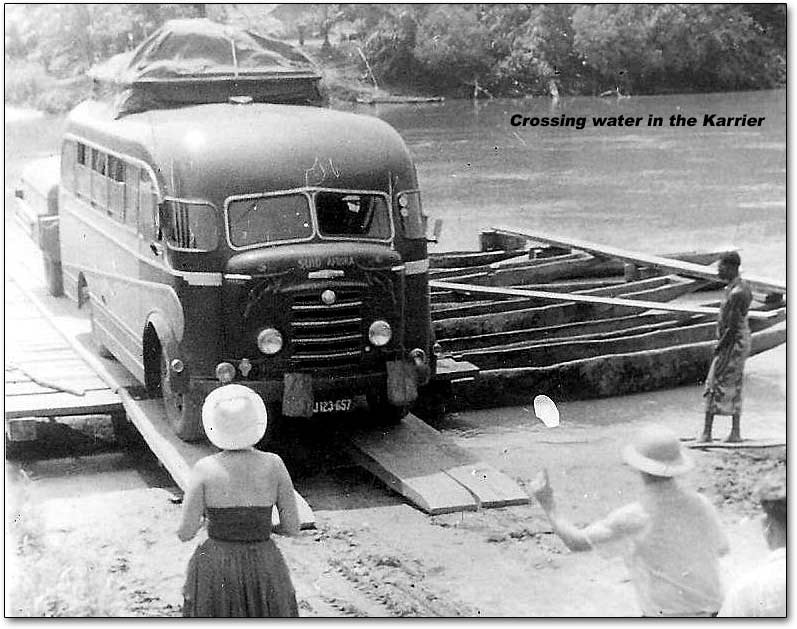
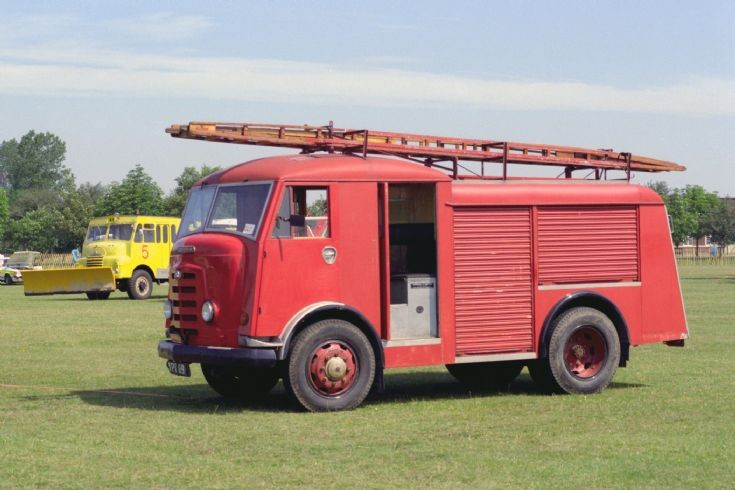
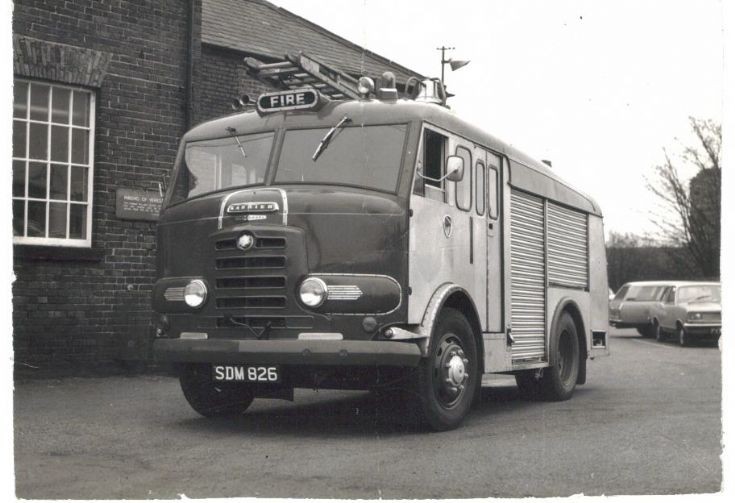
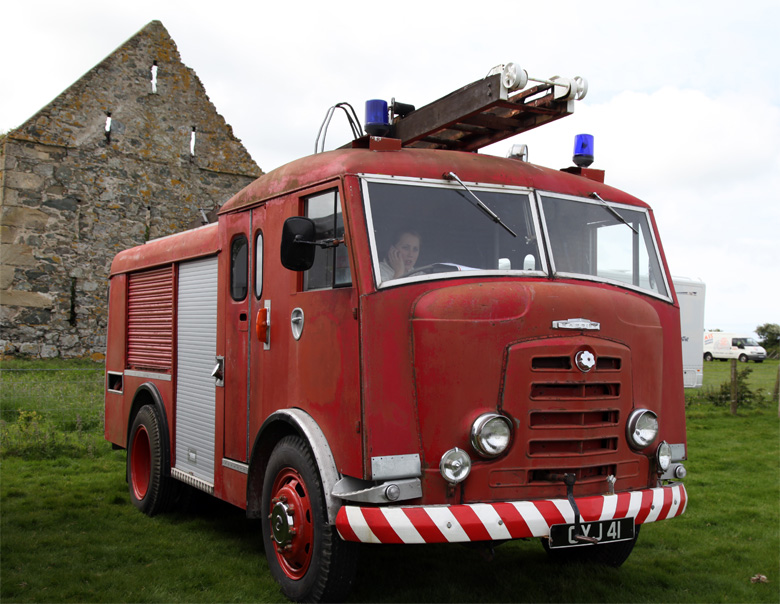
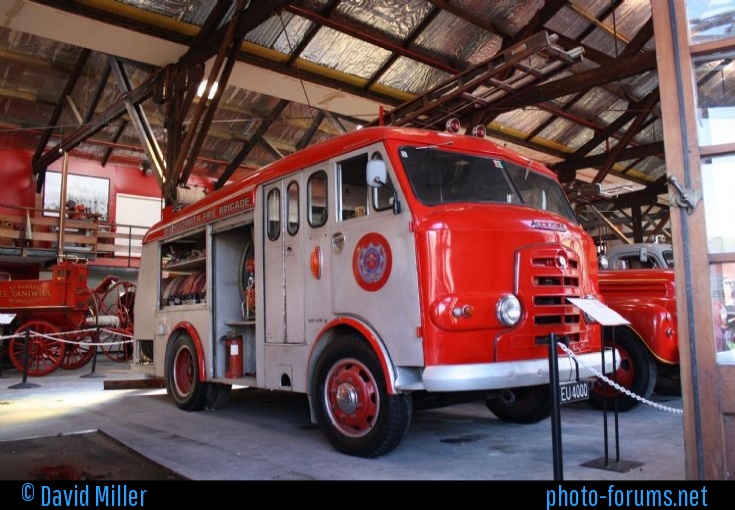
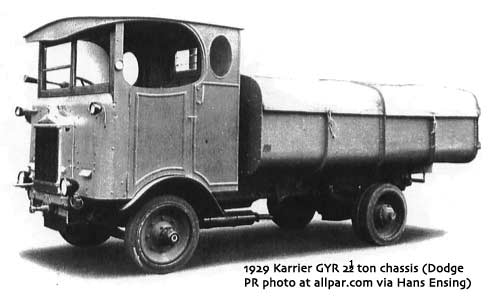
Around 1949, the Karrier Bantam switched to a cast aluminum raidator shell, replacing pressed metal. In 1952, the Bantam was updated with a new cab and Perkins diesel engine, and the CK3 was replaced by the Gamecock (seen above on a historic journey from South Africa to London); this had a new cab similar to Commer’s forward control cabs. The Karrier Bantam lasted through 1970, using a 3-ton coupling gear.

Bigger garbage trucks demanded bigger chassis, and Karrier supplied its Transport Loadmaster based on the Commer QX. A new engine, the TS3, was launched in 1954 by Rootes, using three cylinders and six pistons, designed as a military multi-fuel diesel engine but available in relevant Karriers.
A major success was the Spacevan, launched in 1960 as the 1500, renamed PA, then renamed PB, and later given its final name. Sold as both a Commer and Karrier, the Spacevan had a diesel early on, with automatic transmissions coming in 1965 and a 1-ton payload version coming in 1962. The Spacevan was a major success, and was restyled in 1978.

In 1965, due to increased demand, production moved to Dunstable, where Commer / Dodge and Karrier were all brought together (Luton was refitted as a transmission plant.) The Dodge badge was used more and by the mid-1970s, it was on all Commer / Karrier / Dodge vehicles. By then, Rootes Group had been acquired by Chrysler.
The 50 series was the result of subsidies by the British goverment in 1975/76, giving Dodge / Karrier / Commer a boost in developing a 3.5 to 7.5 tonne range of vehicles to help keep the UK truck building business on an even keel. It came out in 1979, badged as a Dodge but with a Karrier nameplate, just in time for Peugeot’s acquisition of Chrysler Europe, which included Rootes and Simca. In January 1980, all Commer / Karrier / Dodge vehicles officially became Talbot. Peugeot had no interest in truck building and sold it on to Renault in 1981; but for 1980, the 50 series was still badged as a Dodge under the Talbot name.
In 1983, it switched to being sold as a Dodge under the Renault name, and in 1985 the Renault logo joined the nameplate; but the Dodge name was retained until 1987, when the trucks were replaced by the New 50 series, badged as Renaults only. Due to poor sales, the entire line was shut down in March 1993, with the line becoming the UK distribution center for French-built tractor units. The production line was taken away in 1994 by a Chinese group, and presumably Dodge medium duty trucks are now being produced in China. (For more details, see dodge50.co.uk.)
Models
- K Type (1920-1931) 3/6 tons
- CYR Low loading garbage truck
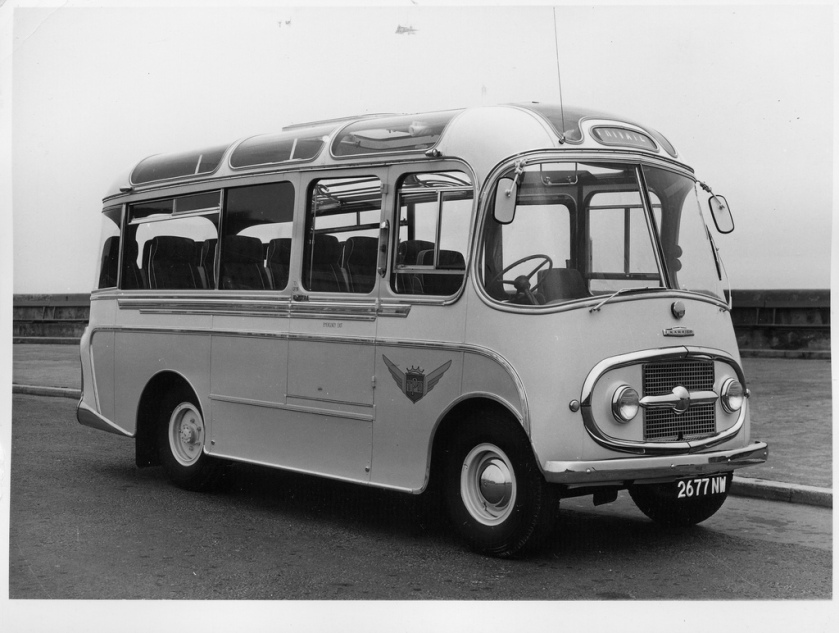
- H Type (1922- ) 20-26 seat bodywork.
- C Type (1923- ) Dorman engine.
http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/W._H._Dorman_and_Co
- Z Type (1924- ) 14 seater one-ton
- ZA (1929- ) 1.5-ton
- KL (1925- ) passenger range with a low-height chassis and pneumatic tyres.
- WL (1925- ) first six-wheeler
- KW6/KWF6 8-ton six-wheeler
- CL6 (1926) carried 32 passengers. Around 50 of these were produced.
- Cob (1931- ) 3-ton
- Cob Major 4-ton
- Road Railer Additional wheels for use on tracts
- Colossus (132- ) 12-ton six-wheeler
- CK (1935-1952)
- Bantam
- CK3 3-ton
- CK6 6-ton
- Gamecock (1952- )
For Karrier Buses look
http://myntransportblog.com/2014/04/24/buses-more-karrier-huddersfield-west-yorkshire-uk/