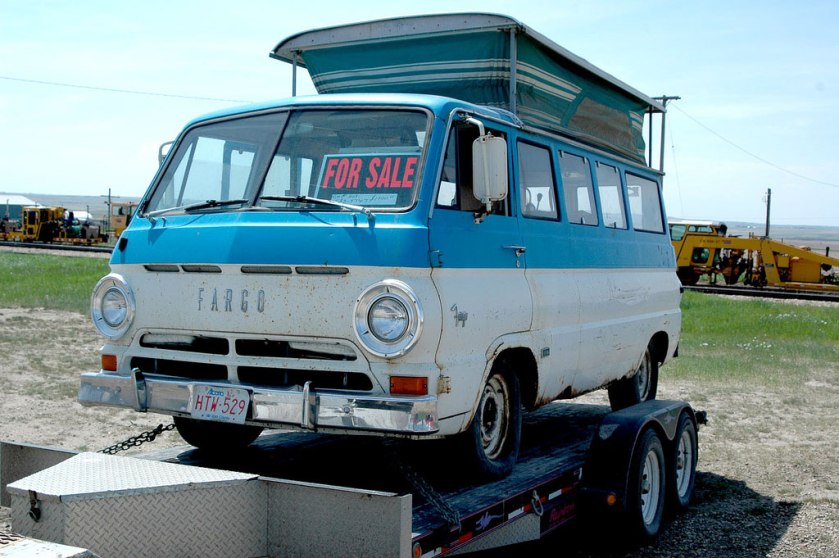
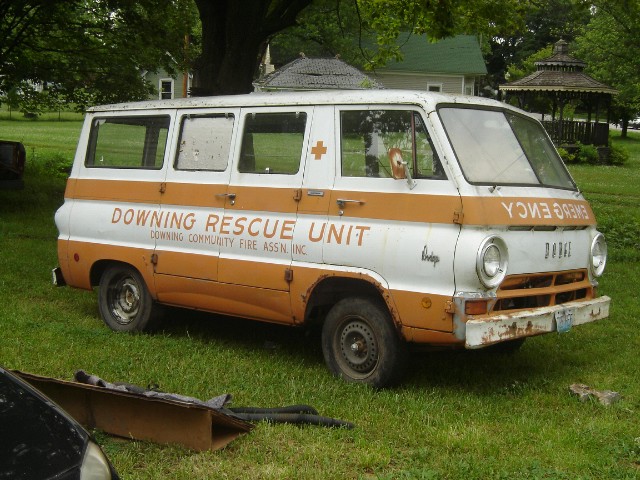
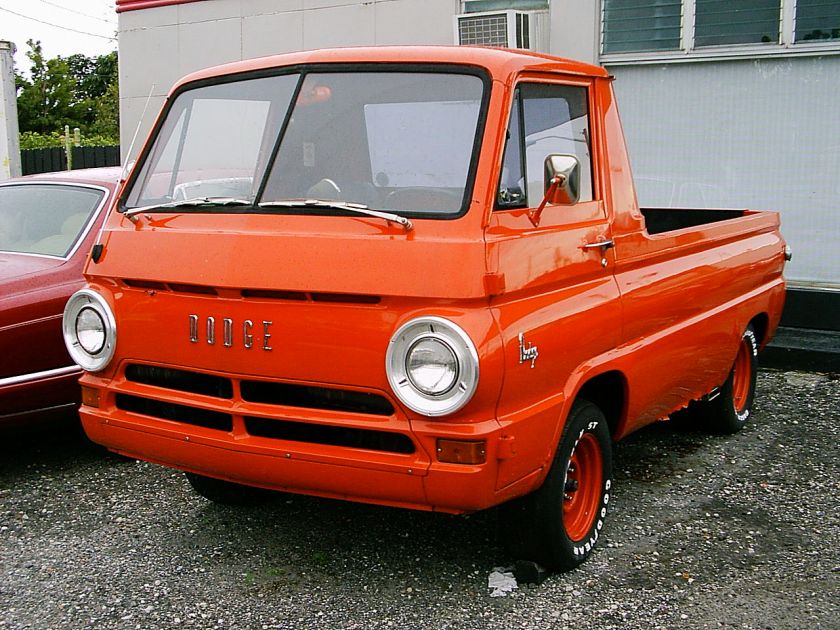
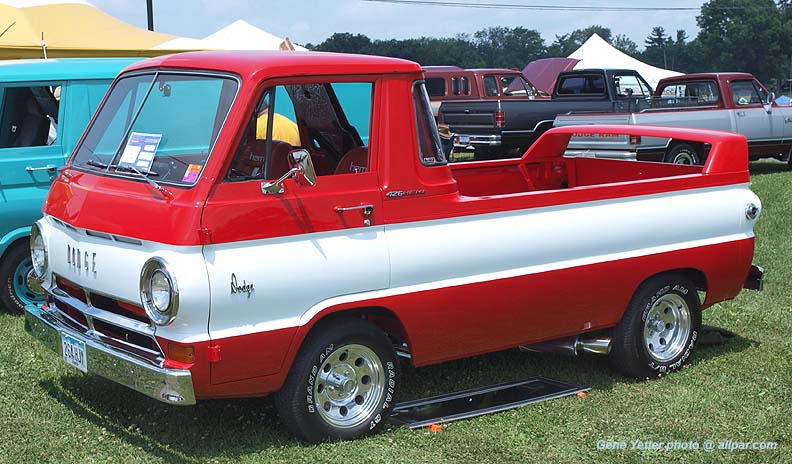
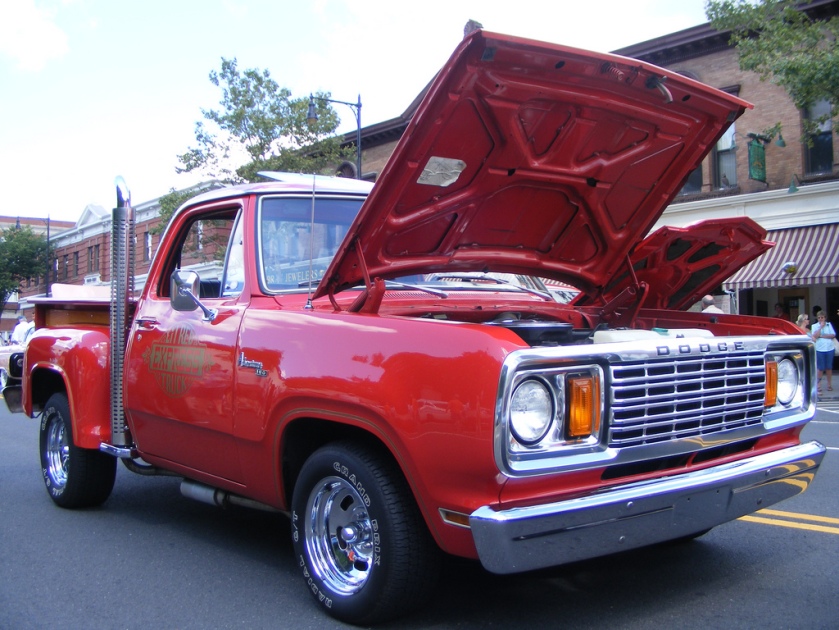
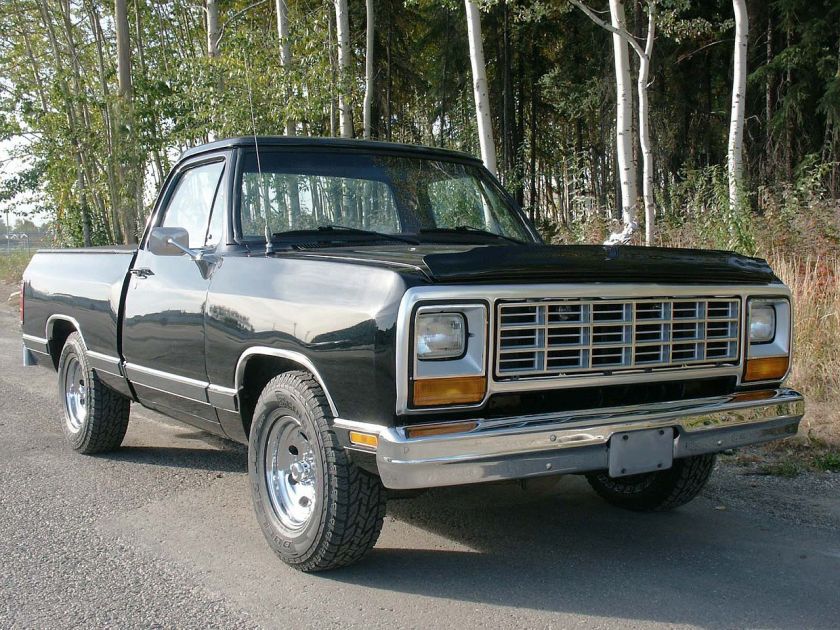
for Dodge Buses and Schoolbuses:
http://myntransportblog.com/2013/12/29/buses-dodge-brothers-detroit-usa/
Past models
- 100 “Commando” (1970–1980)
Dodge 100 “Commando”
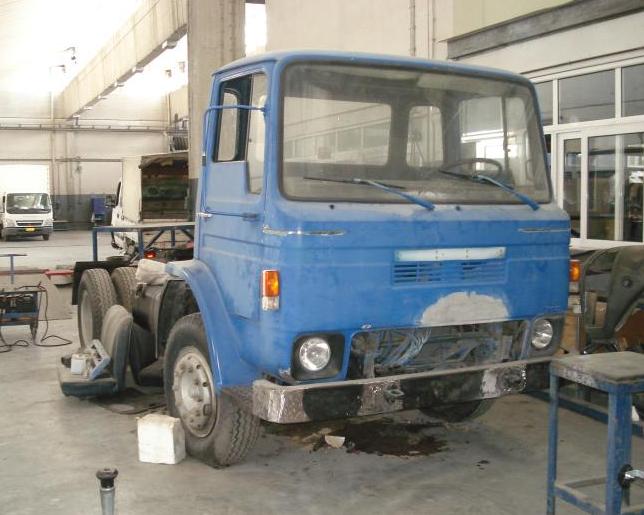
The Dodge 100 “Commando” trucks were 7.5–28 short tons (6.8–25.4 t) trucks built by Dodge in Britain, primarily in the 1970s and 1980s. A previous Dodge 100, known informally as the “parrot-nose” or “Kew Dodge”, had been produced in the 1950s at a factory in Kew, London.
History and development
Originally developed by Commer, the range was first built as a concept in 1965-66, to replace the Commer VC and VE range with 8–24 short tons (7.3–21.8 t) gross vehicle weight (GVW). As Chrysler Europe acquired a controlling interest in Commer’s owner, the Rootes Group, the truck design and name were changed to complement the Dodge 500 trucks.
Drivetrains
The Dodge 100 was intended to use a Rootes diesel engine, but noise regulations ruled out the reliable but noisy Rootes units. In the end, naturally aspirated and turbocharged four- and six-cylinder Perkins diesel engines (locally made in the UK) were used for lighter weights, with the Mercedes-Benz OM352 offered as a premium engine (due largely to the reputation of Mercedes in Europe, where Perkins was relatively unknown). Also Valmet DSA diesels were installed for some limited market areas. Four-, five-, and six-speed synchromesh manual transmissions from Rootes were used, while rear axles were a mixture of Rootes Groups’ own hypoid design and Eaton Corporation‘s single- and two-speed axles. The chassis used a special alloy for greater strength and lighter weight.
Final capacity ranged from 7.5–16 short tons (6.8–14.5 t) GVW for full vehicles and 24/28 tons GCW for tractors.
Renault
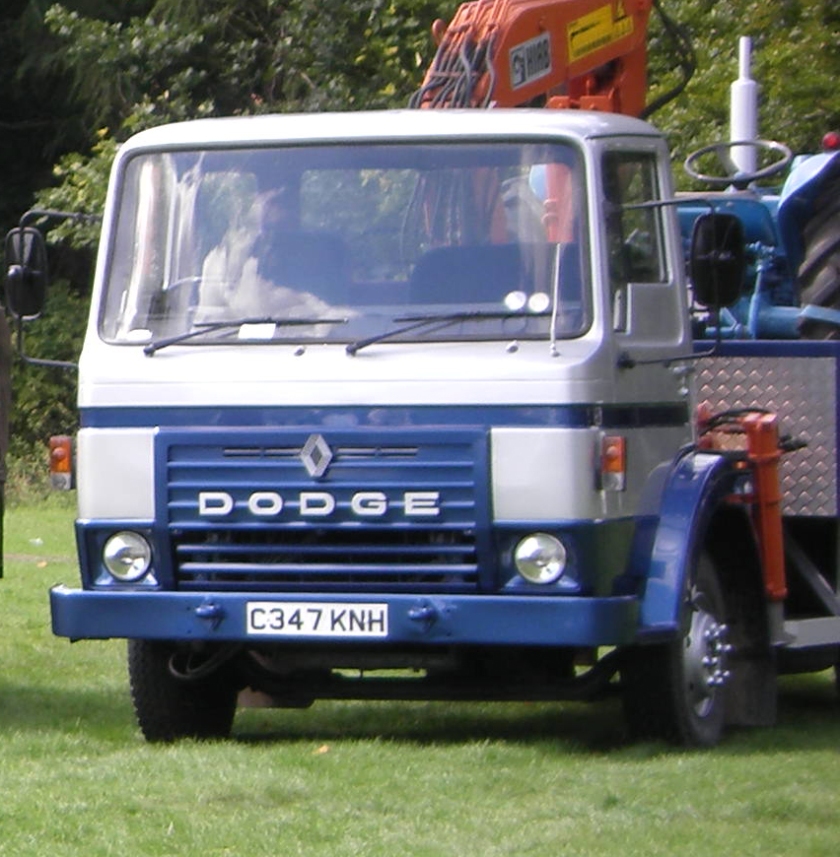
The 100 Series was in production for around 15 years in most areas of the world (though not in the United States, due to the costs that would be involved in meeting local regulations). It was sold as a Commer, Dodge, DeSoto, Fargo, and Renault (by Renault Trucks). A Mark 2 version upgraded the engine and made other minor refinements. Eventually the Dodge 100 was eliminated by Renault, which had acquired the former Rootes Group truck operations after the car operations were purchased by Peugeot, though a Renault version of the Dodge 100 was built for a time; by 1987, it was being marketed as simply the Renault Commando. Renault later switched production at the former Rootes factory to Renault’s own bus and truck engines.
Dodge 50 Series
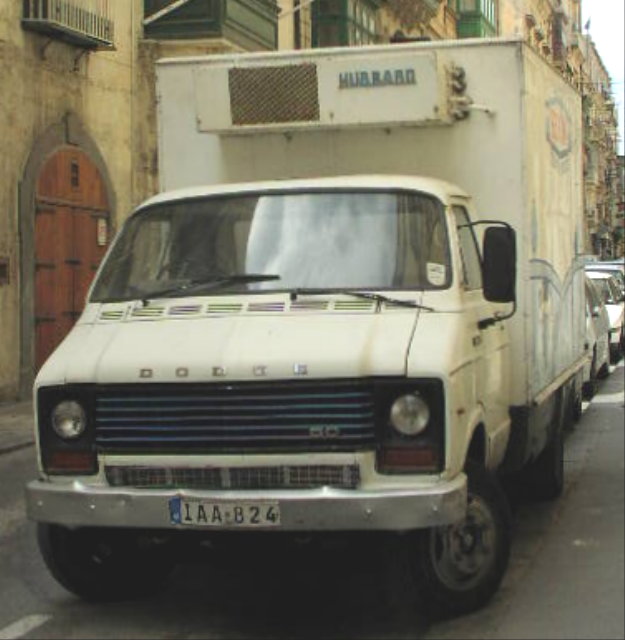


The Dodge 50 Series, later known as the Renault 50 Series were light commercial vehicles produced in the UK by Chrysler Europe and later Renault Véhicules Industriels (at that time part of Renault, now Volvo) between 1979 and 1993.
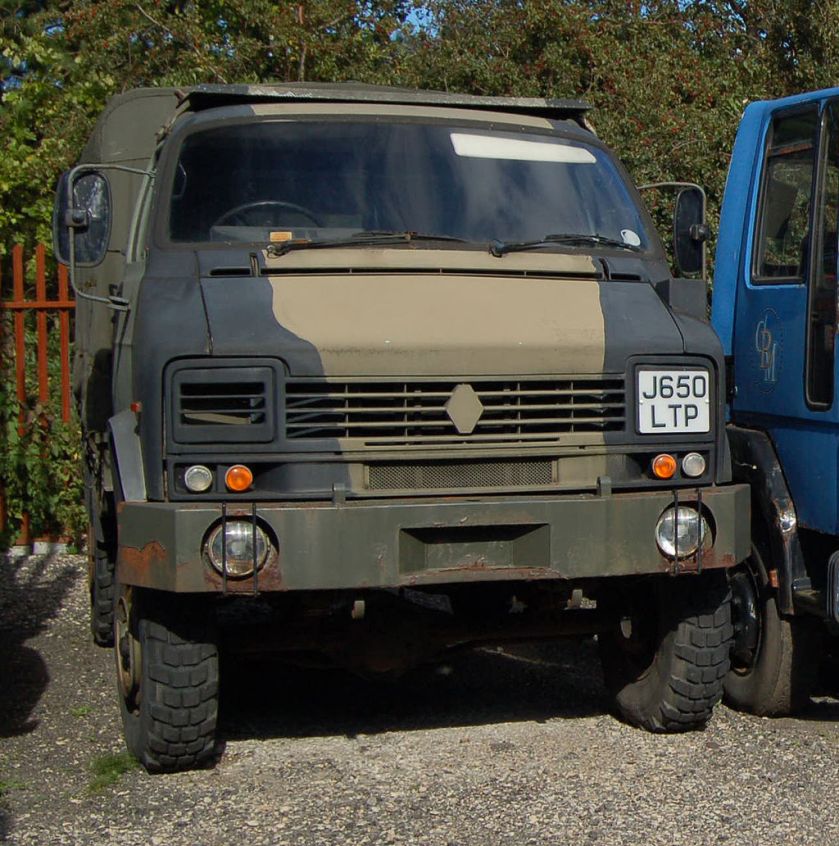
The 50 series included a wide range of chassis and body configurations, including two distinctly different cab designs, and spanned the 3,500–7,500 kg (7,700–16,500 lb) revenue weight range. Various engines were offered, including the Perkins Phaser and 4.236, and there was also a four-wheel-drive version, the RB44, built by Reybolds Boughton (now known as Boughton Engineering).
Versions
Bodybuilding companies converted many into various configurations from tipper trucks to buses. Many were built as “chassis cabs” to have box bodies fitted; these were widely used by utility companies in the UK. They often came fitted with compressors and generators. Gradually this kind of vehicle fell out of favour, partly due to reliability issues relating to combining plant equipment with the vehicle drivetrain. The vehicle is otherwise toughly built. The utility companies today favour smaller vans with towed generators. The four-wheel-drive version saw some use with the British army since it was one of very few British-built trucks of the class, and it could carry considerably more stores and equipment than even the largest Land Rover models.
Chrysler received financial assistance from the British Government which was desperate to support the ailing British motor industry. However, having inherited various struggling car and commercial vehicle marques (and factories) from the Rootes Group, notably the commercial marques Commer and Karrier, in addition to various French concerns, Chrysler Europe struggled to return a profit. In 1978, Chrysler pulled out of their European operations altogether, selling them to Peugeot. The cars and small vans became known as Talbots.
Peugeot takeover
However, Peugeot had little interest in commercial vehicles and the factory for the heavier models was run in partnership with Renault Véhicules Industriels, who sought a UK production site for engines for their existing Renault-branded models. They continued to manufacture the 50 Series, along with the small Dodge (formerly Commer) Spacevan, and the large Dodge 100 / Commando 2 Series of 7,500–23,000 kg (16,500–50,700 lb) trucks. The transition to Renault branding was slightly muddied by some vehicles bearing both a Dodge name and a Renault-diamond badge.
Renault 50
By 1987, the 50 Series had been updated and was badged as the Renault 50 Series or Desoto 50 Series in Bermuda; the UK incarnation of the Dodge marque ceased to be used for new vehicles. (Chrysler maintained an entirely separate Dodge brand in the U.S., and in 2006 began re-introducing Dodge car models from the USA into the UK market.) Renault continued to manufacture the 50 Series until 1993, but it was never a great sales success, even being forced to compete with other Renault products, in the form of the Master van, which Renault favoured in its export markets.
In 1994, Renault — keen to clear the factory for large-scale engine production — sold the production tooling to a Chinese manufacturer. The 50 series is still being produced in China under a different name, details are scarce but there are two pictures of them with accompanying text from the website of the company who performed the transition (link to website in external links)
The vehicle is still a common sight on British roads, having become a popular choice for conversion to live-in vehicles including professionally built campers and workshops. There are also a number still in service as horseboxes, and a few remain in active service with the army. There is a friendly community amongst the owners and users of these vehicles.
See also
Dodge 500
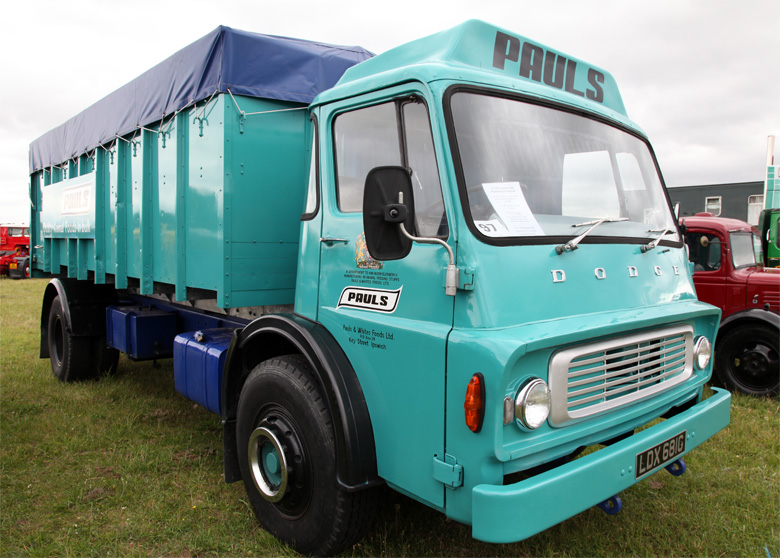
The Dodge 500 was a heavy duty truck introduced in 1964 and built in the United Kingdom by Dodge. It replaced Dodge UK’s earlier 300 series cab over trucks.
History and development
Popular in Britain, and also used in some export markets, the Dodge 500 was also sometimes badged as a DeSoto or Fargo. The trucks were sold as a cab and chassis and the operators arranged for the purchase of the bodies or trailers. Later this range came to be known as the “K”-series.
The 500 Series was developed in the early 1960s, with styling by Ghia and engineering by Rootes Group in Kew, England. The suspension used leaf springs in front and rear with optional rear auxiliary springs. The truck was diesel powered, with forward control and a tilt cab; it was launched in December 1964. Customers obtained the trucks in primer and painted them. The cabs were noted for their styling, roominess and comfort, visibility of the road, and engine placement with minimal intrusion into the cab.
Payload capacities ranged up to 11 short tons (10.0 t) for two-axle units, up to 16 short tons (15 t) for three-axle units, or a gross combined vehicle weight of up to 67,000 lb (30,000 kg) for the tractors. Those desiring lighter capacity trucks were directed to the Dodge 100.
With the help of the supplier, a special high tensile steel alloy was developed to lighten the frame. Tubular and channel section cross members were bolted to the frame side-members. Spring hanger brackets were also bolted to the frame, utilizing the cross members where possible. Cummins and Perkins diesel engines were used.
Buyers had a choice of a Cummins diesel — V6 or V8 — producing 130–170 hp (97–127 kW) and 248-328 pound-feet of torque, or a locally made Perkins diesel with 120 hp (89 kW) and 260 lb·ft (353 N·m) of torque. These were known to be reliable powerplants. An existing time-tested manual transmission was used.
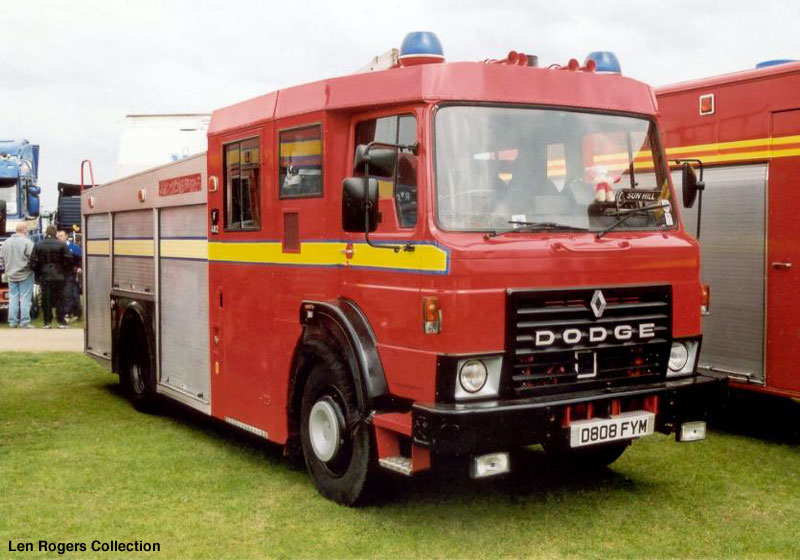
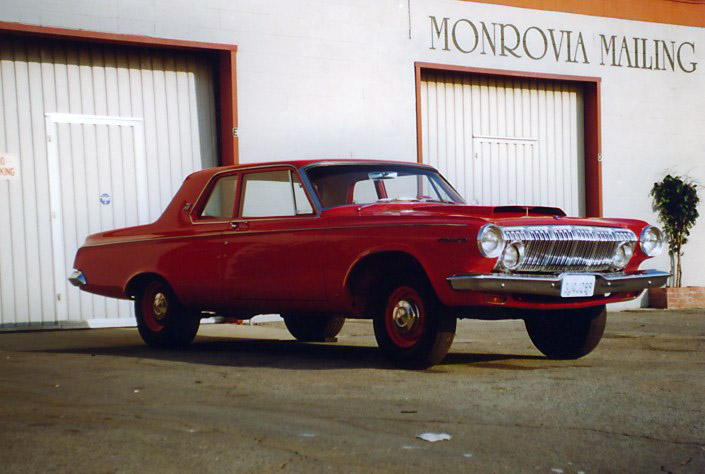
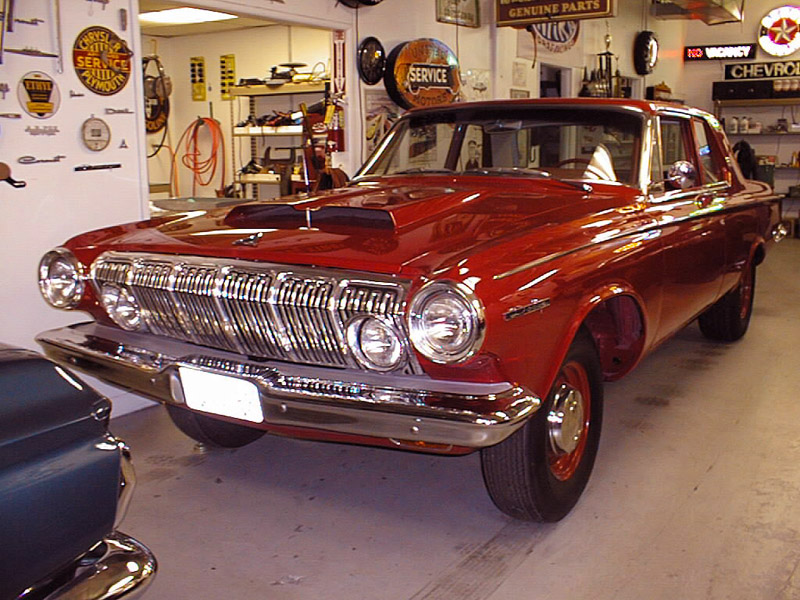
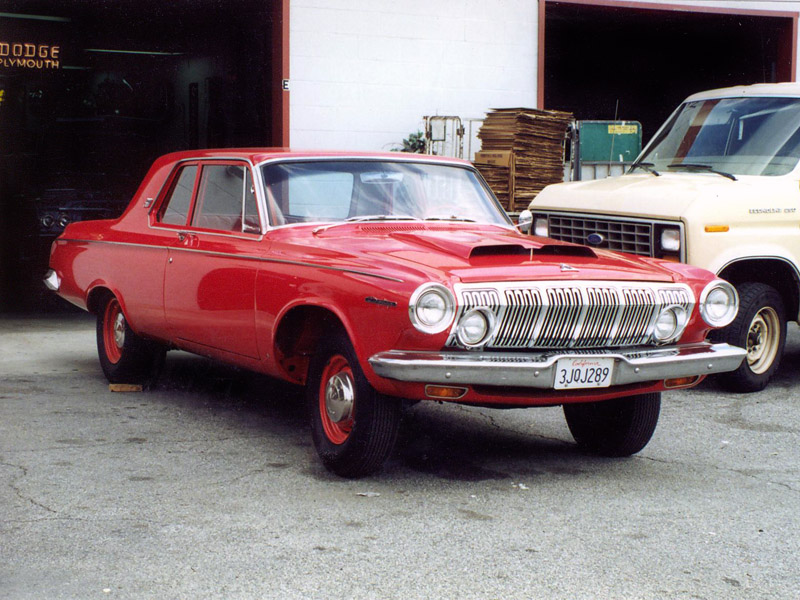
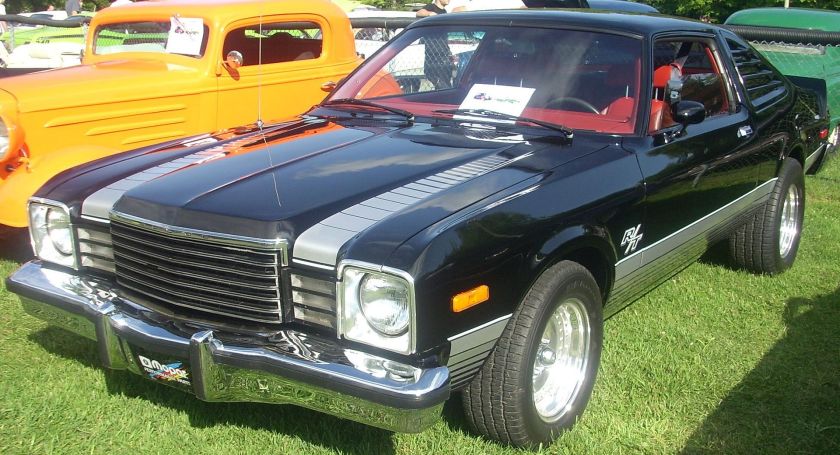
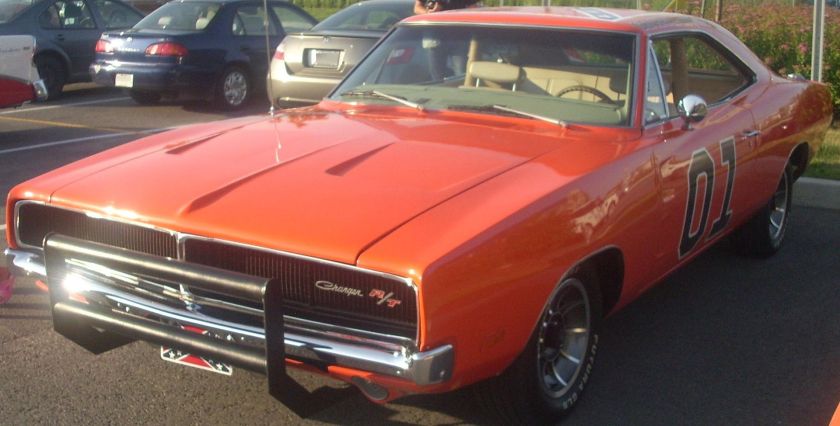
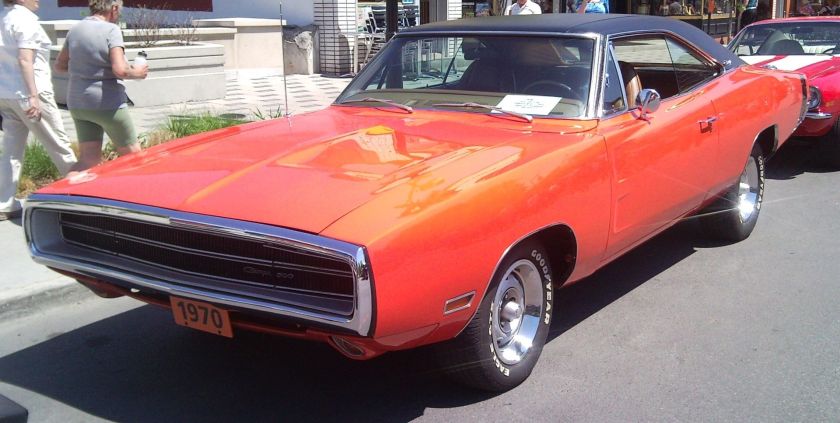
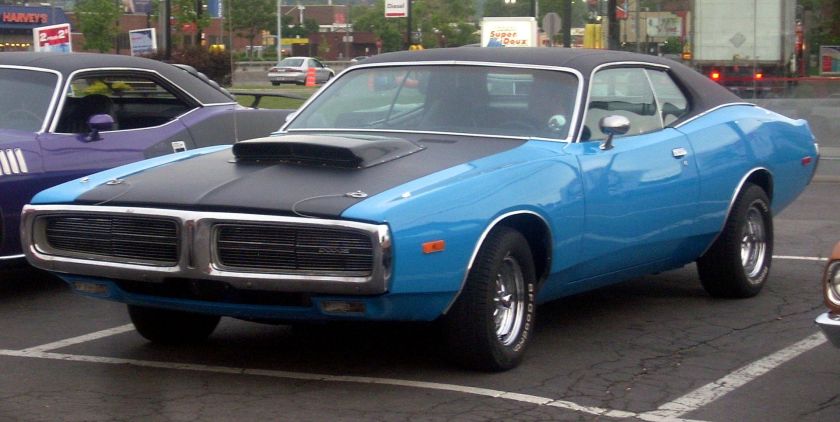
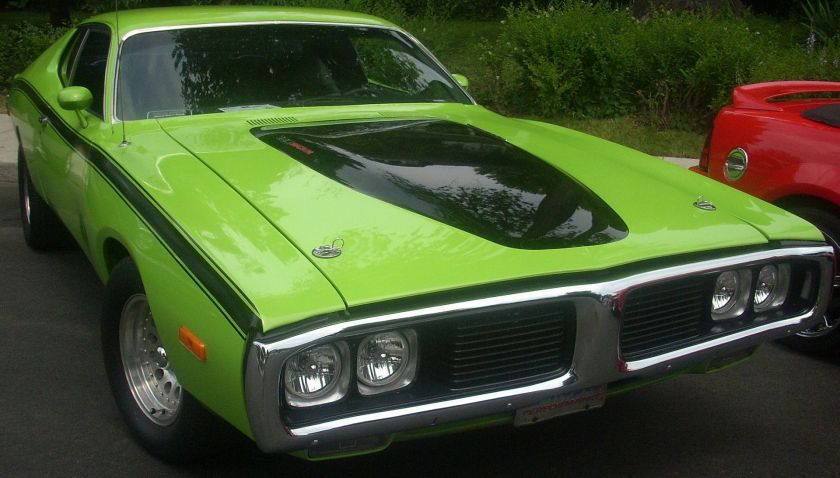
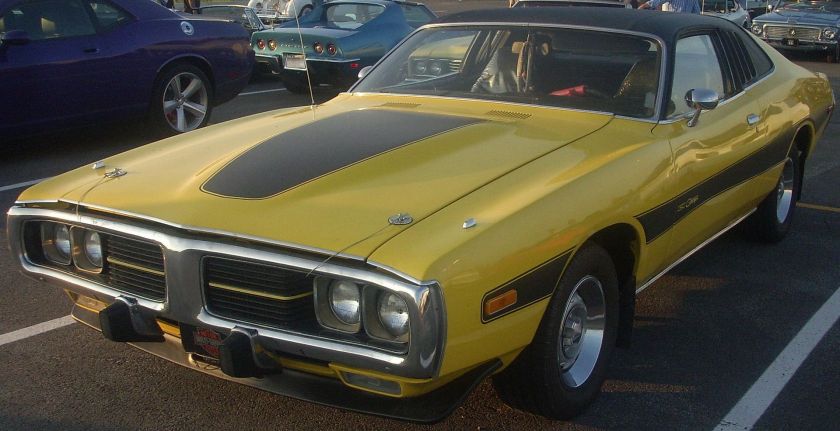
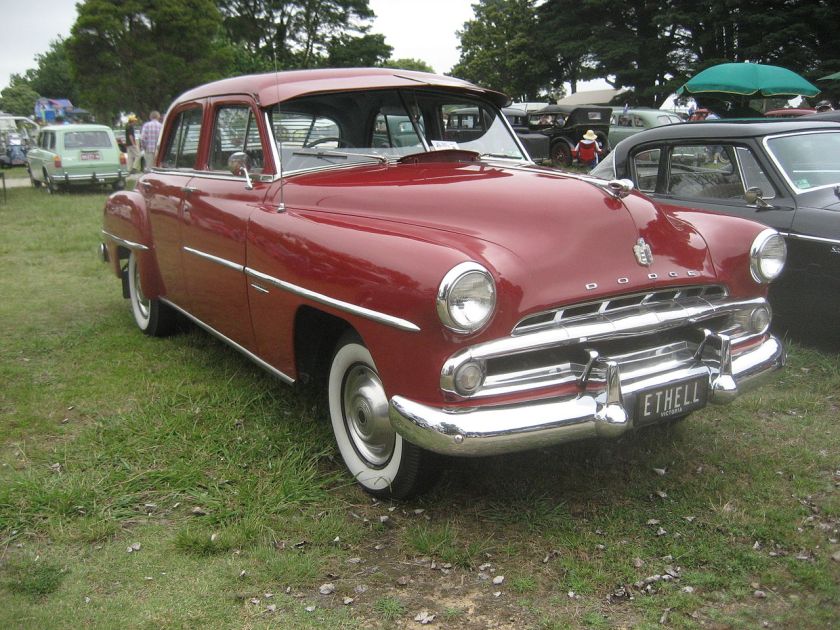
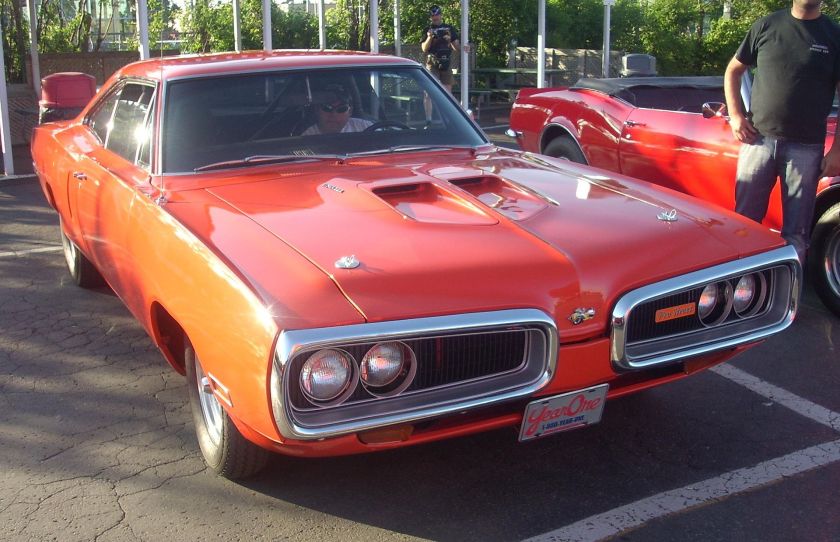
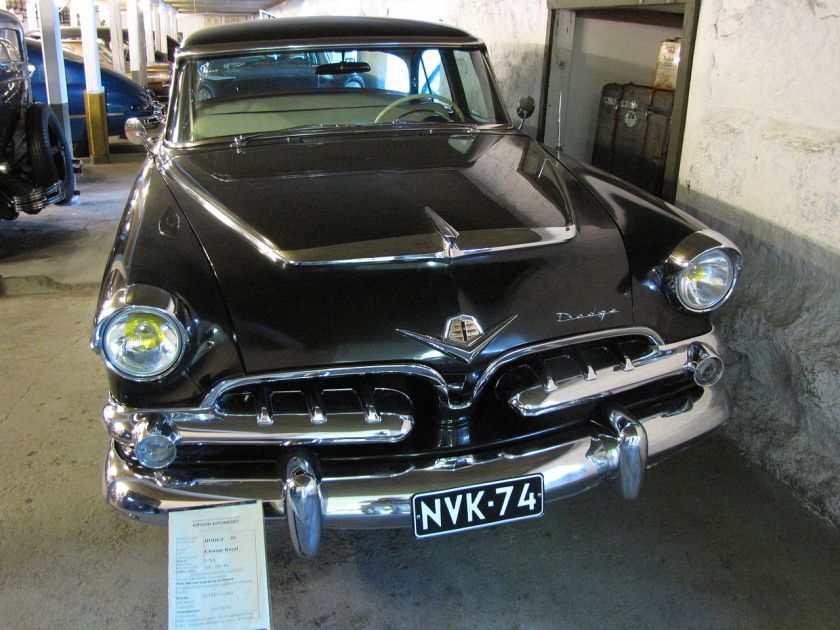
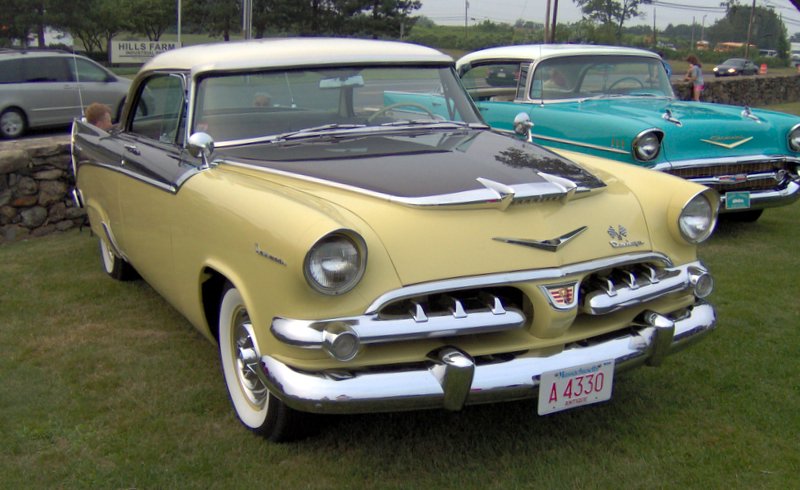
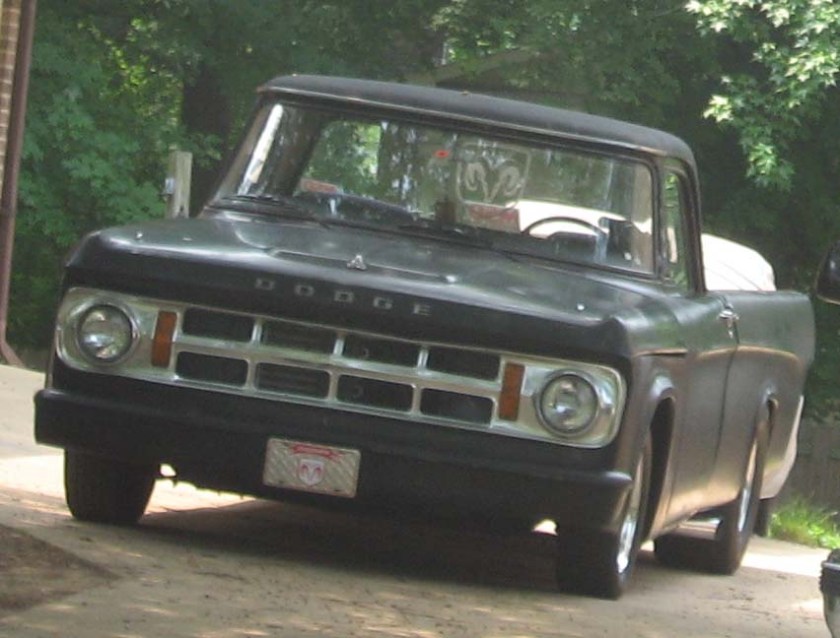
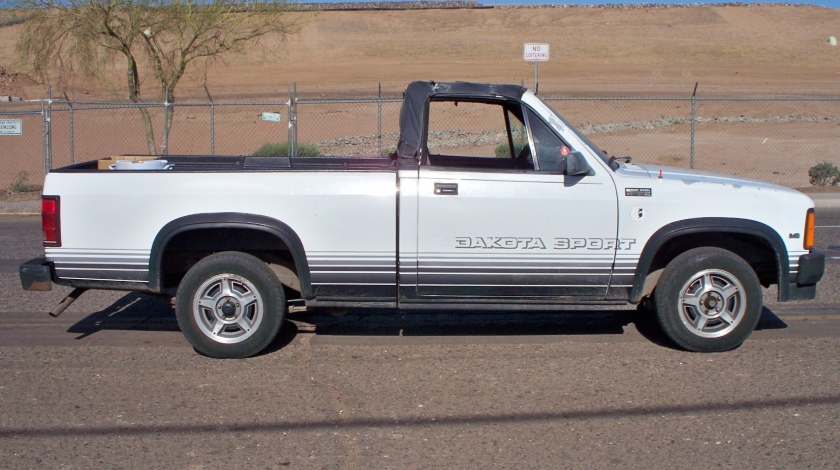
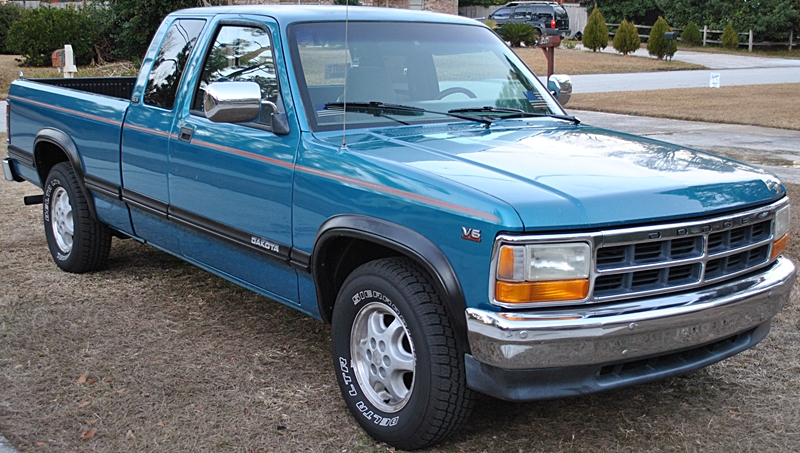
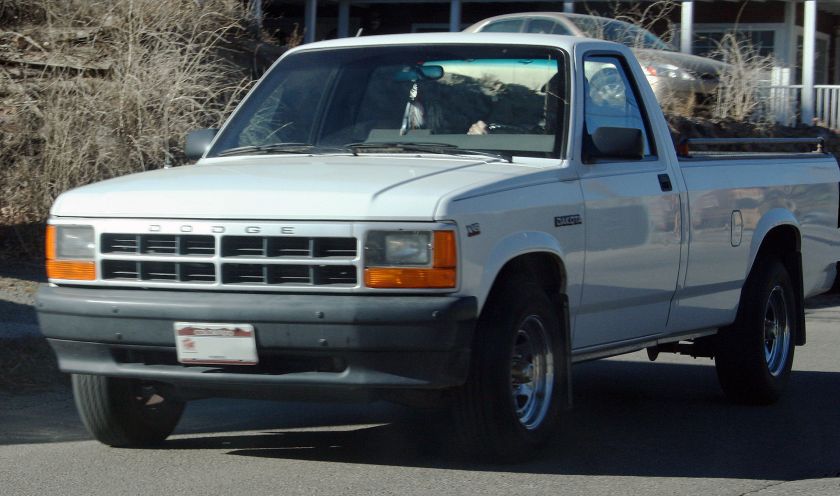
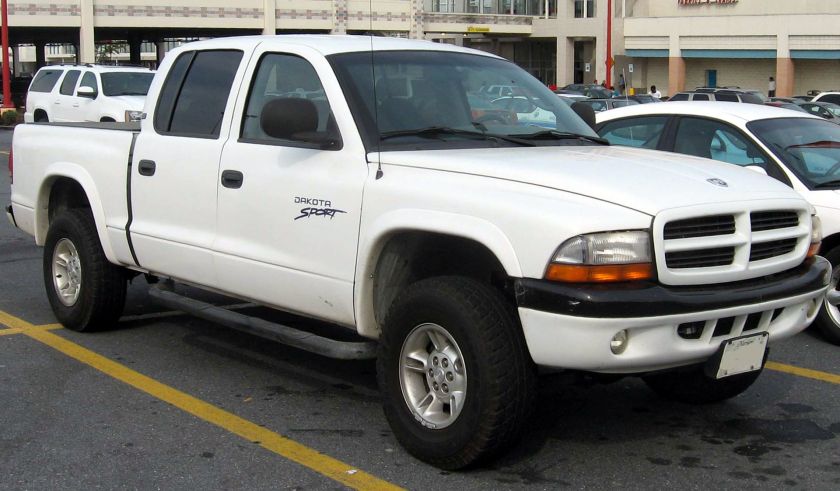
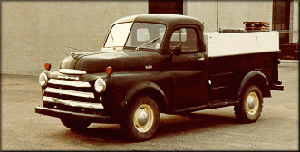
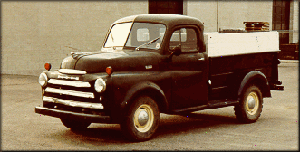
Dodge Commando © Len Rogers Collection
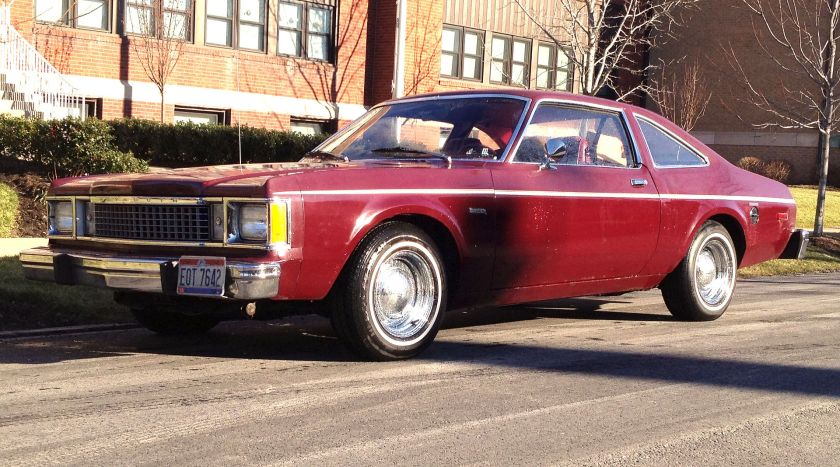
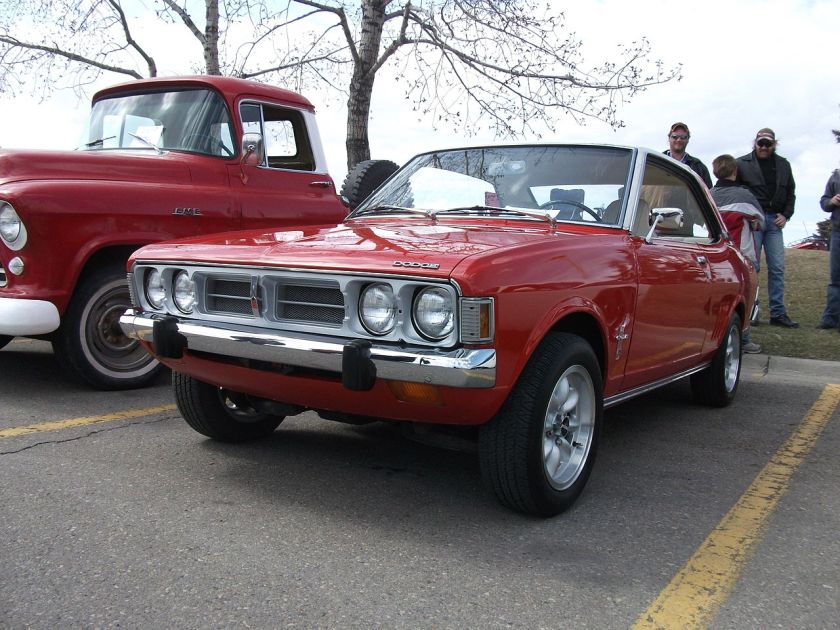
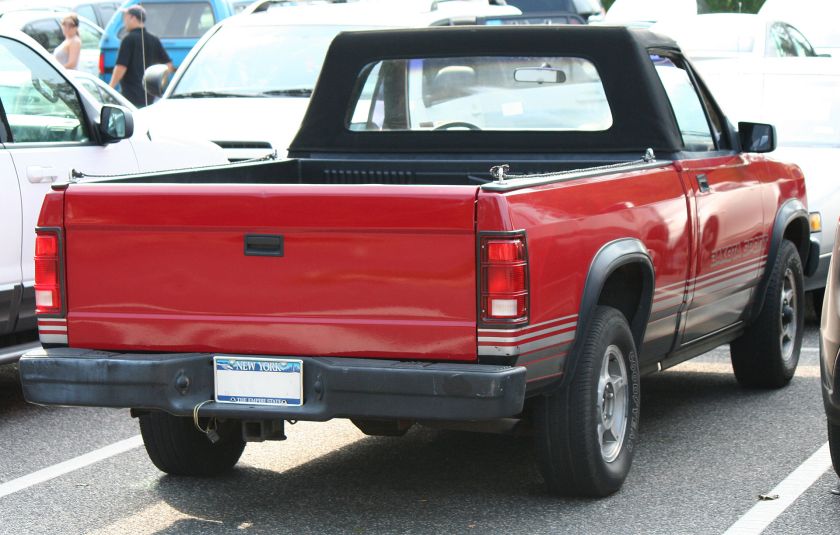
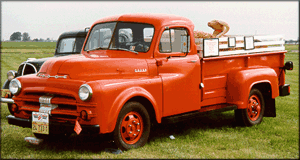
Dodge Horsebox
330 (1963–1964)
Dodge 330
| Dodge 330 | |
|---|---|
 
1963 Dodge 330 (model)
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Dodge |
| Production | 1962-1964 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full size |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | FR |
| Platform | B-body |
| Related | |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 3,022.6 mm (119 in) |
| Length | 5,285.7 mm (208.1 in) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Polara |
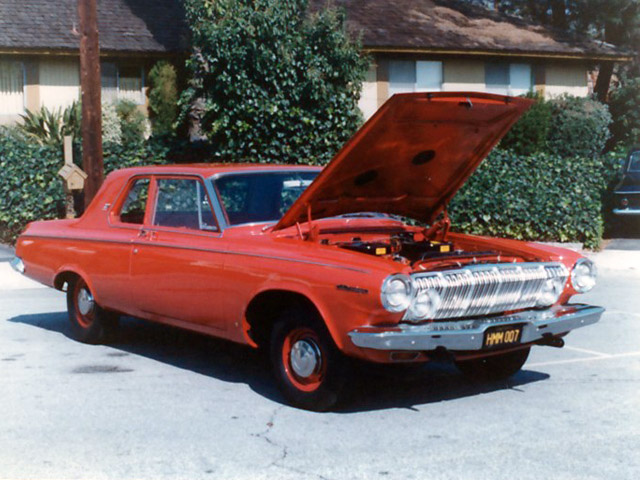
The Dodge 330 was a Full Size automobile sold by the Dodge division of the Chrysler Corporation in 1962, 1963, and 1964, based on the B-body. The coupe often used a 6-cylinder engine. The car was available as a 2dr Sedan or 4dr Sedan. Base motor was the 225 Slant-Six. The 318 2bbl, 361 2bbl, 383 2bbl, 383 4bbl, and 426 4bbl were optional. As an intermediate trim level above the Dart, it came standard with a cigarette lighter, front foam cushions, and rear arm rests. The car rode a 119″ wheelbase and was 208.1 inches long along with the higher trimmed 440 and Polara. In 1965, full sized Dodge’s got bigger on the new C Body with 121 in (3,073 mm) wheelbase, and the 330 and 440 were both replaced by the new, bigger Polara. The 880 now took the Polara’s former place in the lineup.
The Dodge 330 Max Wedge was a 330 2 door sedan powered by the 426 Max Wedge with dual 4 Barrel Carburetors and 425 hp (317 kW). It was available in both years, mostly ordered as a super stocker for the race tracks. Civilian versions are rare today.
Dodge/1963_Dodge/1963_Dodge_Standard_Size_Brochure”. Oldcarbrochures.com. Retrieved 2011-11-20.
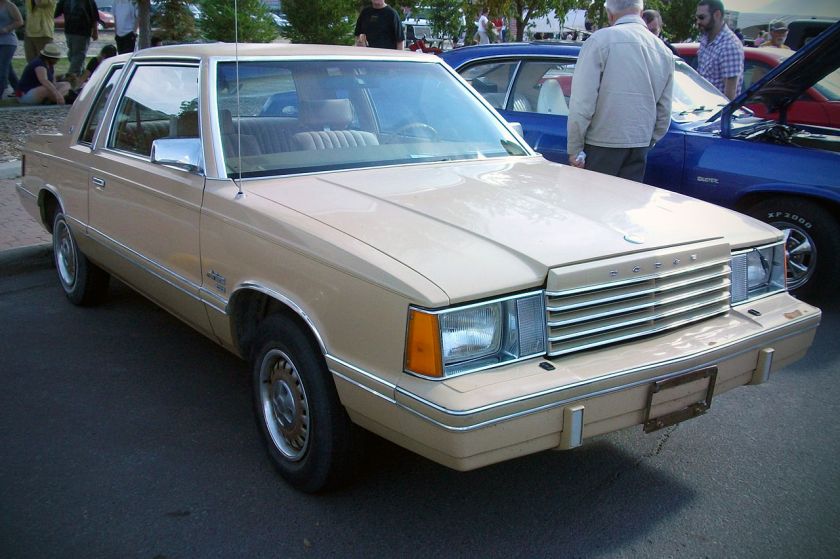
- 400 (1982–1983)
Dodge 400
| Dodge 400 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1981–1983 |
| Model years | 1982–1983 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 2-door convertible 2-door coupe 4-door sedan |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Platform | K-body |
| Related | Chrysler LeBaron Chrysler Town & Country Dodge Aries Plymouth Reliant |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.2 L K I4 2.6 L Mitsubishi G54B I4 |
| Transmission | 3-speed A413 automatic 3-speed A470 automatic |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Aspen |
| Successor | Dodge 600 |
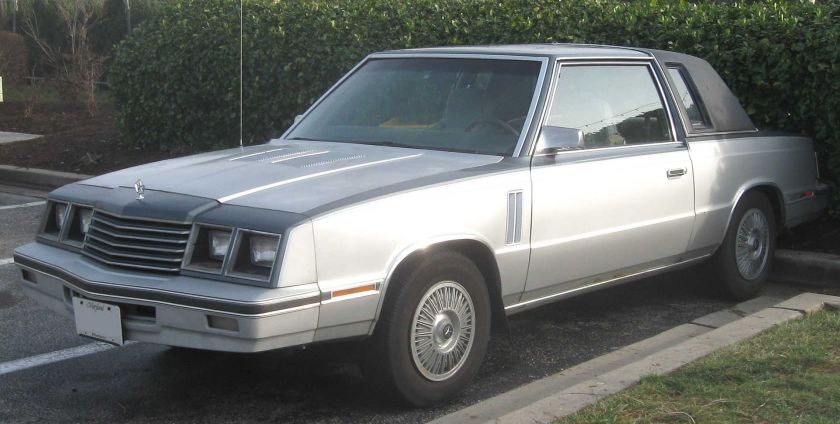
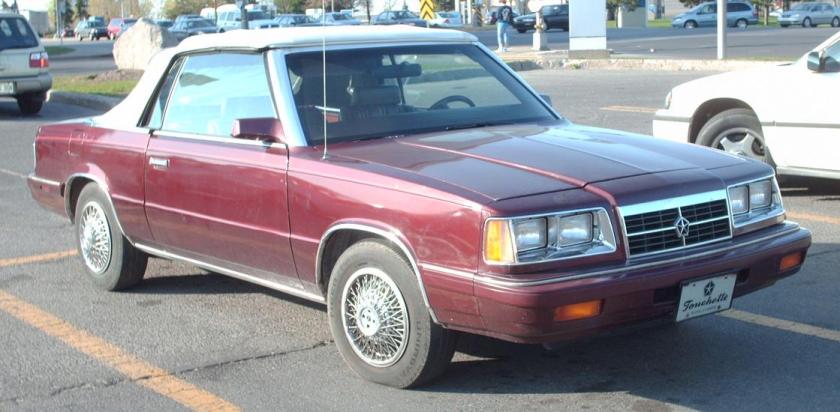
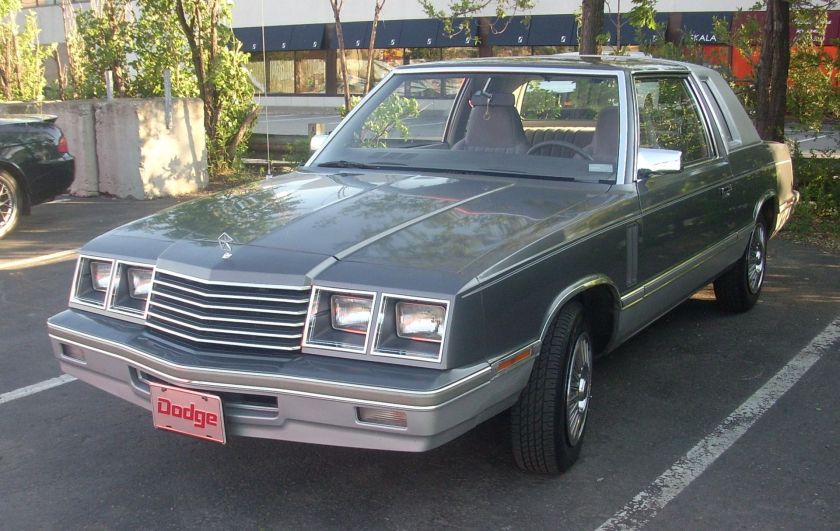
The Dodge 400 was Dodge‘s second K-car in the early 1980s. It was similar to the Chrysler LeBaron of the same era. The 400 was introduced for the 1982 model year, yet was renamed and added to the midsize Dodge 600 lineup just two years later.
1982
The 400 was intended to be a more upmarket version of the Aries. It was available in three bodystyles: two-door coupe or convertible and a four-door sedan.
This was Dodge’s first convertible since the 1971 Challenger and the first domestically-manufactured convertible since 1976, when Cadillac had phased out the Eldorado convertible.
Chrysler’s chairman Lee Iacocca believed he could revive interest in convertibles, which at the time were no longer part of any major manufacturer’s range, except Volkswagen.
The 400 was available in two trim levels: base and LS. Engine choices were limited to a 2.2 L I4 engine or an optional Mitsubishi-sourced 2.6 L “Silent Shaft” 4-cylinder. The convertible came with the Mitsubishi-sourced engine as standard.
31,449 vehicles were produced.
1983
There were no major changes made for 1983 other than the LS trim being omitted from the lineup. Production figures for 1983 were 25,952 vehicles.
During 1983, the 400 sedan was replaced by the Dodge 600. The coupes and convertibles were rebadged as Dodge 600 from 1984.
Dodge 600
| Dodge 600 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called |
|
| Production | 1983–1988 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 2-door convertible 2-door coupe 4-door sedan |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Platform | E-body (sedan) K-body (convertible and coupe) |
| Related | Chrysler E-Class Chrysler New Yorker Plymouth Caravelle |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | 5-speed A520 manual 5-speed A525 manual 3-speed A413 automatic 3-speed A470 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 103.3 in (2,624 mm) |
| Length | 185.2 in (4,704 mm) |
| Width | 68.0 in (1,727 mm) |
| Height | 53.1 in (1,349 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge 400 |
| Successor | Dodge Spirit (Canada) Dodge Dynasty (United States) |
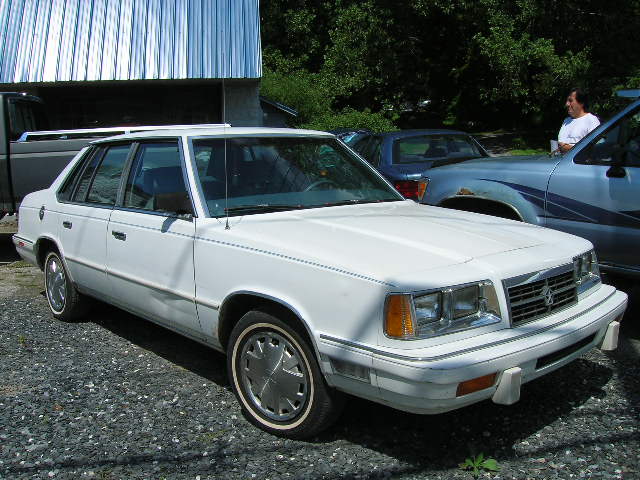
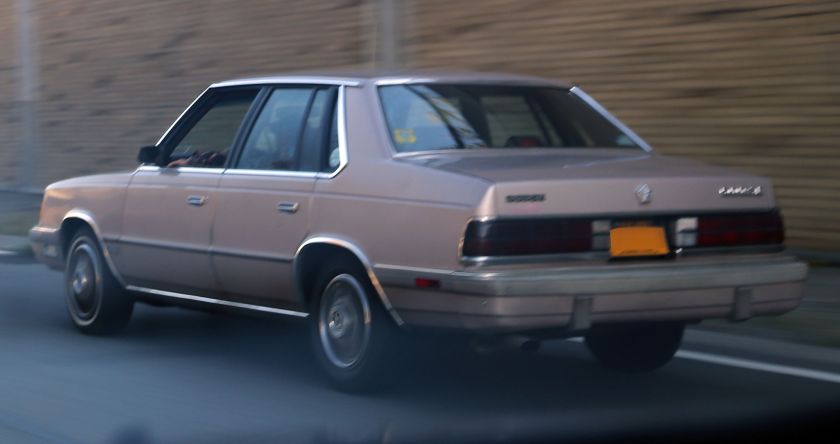
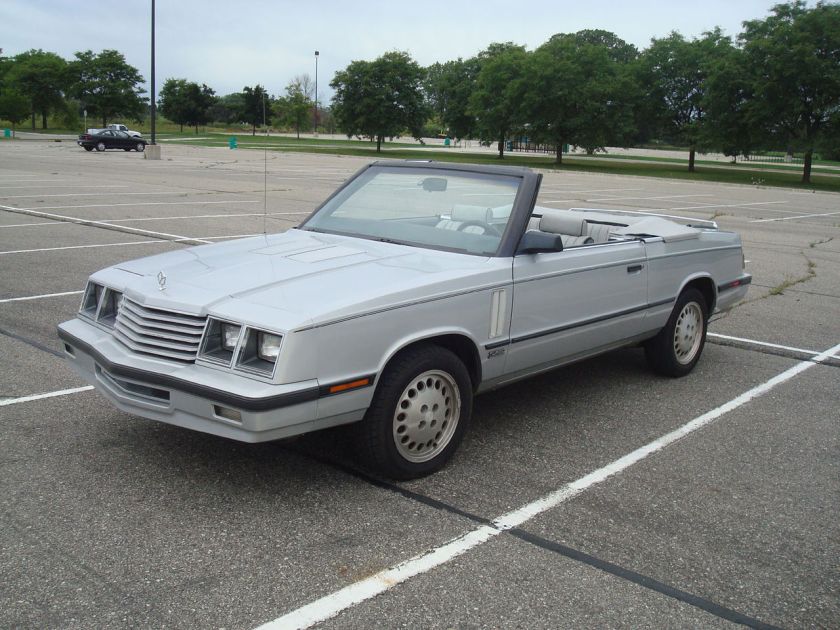
The 600 was Dodge‘s version of the Chrysler E-Class luxury car of the 1980s. It was introduced in 1982, as a 1983 model, as a small mid-size car on the Chrysler E platform and was discontinued after the 1988 model year. It was Chrysler‘s answer to the GM A-body, whereas the M-body Dodge Diplomat would compete with full-size cars. It replaced both the 400. (Dodge 600 coupes and convertibles were, essentially, rebadged 400s.) Like the preceding 400, it slotted between the Aries and Diplomat.
Debut
The 600 was intended to be Dodge’s answer to the European sedans of the day. Its numerical name and rear-end styling was designed to evoke thoughts of Mercedes-Benz models, however it fell more in line with North American contemporaries such as the Chevrolet Celebrity, Pontiac 6000 and the Ford Fairmont (the 600 actually resembled the Dodge Mirada more than any European car). It debuted as a four-door sedan, available in two trims: Base and ES (“Euro/Sedan”). Power was provided by Chrysler’s 2.2 L 4-cylinder engine, with the Mitsubishi-built 2.6 L 4-cylinder available as an option.
|
Sales of the 600 nearly doubled in its second year. This was in large part due to the addition of the former 400’s coupe and convertible body styles to the 600’s range (which continued to stay on the K platform). Like most midrange-to-upscale K-car derivatives, digital dashboards and the Electronic Voice Alert were options.
ES Turbo
Mid-way into 1984 Dodge introduced a sporty new “ES Turbo” package for convertibles. It featured Chrysler’s new 2.2 L 142 hp (106 kW) Turbocharged engine (which also became an option on sedans and coupes) and a special sport-tuned “ES” suspension. The interior came with standard leather seats, digital dashboard, and four-spoke steering wheel (redesigned in 1985). Visual exterior cues differentiate ES models from base convertibles by way of blacked-out trim (replacing much of the chrome), 15-inch “pizza” style aluminum wheels, “ES” decklid badges, Turbo fender badges, and functioning dual hood vents.
Sales of the ES Turbo were initially slow, with only 1786 copies being sold for the 1984 model year. Output increased to 5621 for 1985, then eased to 4759 for 1986, after which the model was discontinued along with all 600 convertibles. Base price for the 1986 ES Turbo convertible was $14,856.
Midlife changes and end of production
| Production | |
|---|---|
| Year | Units |
| 1983 | 33,488 |
| 1984 | 61,637 |
| 1985 | 58,847 |
| 1986 | 59,677 |
| 1987 | 40,391 |
| 1988 | 55,550 |
| Total | 309,590 |
Several changes were made to the 600 in 1985. The 600 sedan was moved to a longer wheelbase and the former base and ES trims were dropped, replaced by a new SE trim. This was due in part to the new Lancer, which would have competed directly with the 600 (the 5-speed manual transmission was no longer offered as well, in an attempt to keep competition between the Lancer and 600 to a minimum). The coupe and convertible remained relatively unchanged except for minor trim and interior changes. The only significant advancement was the replacement of the 2.2 L engine’s two-barrel Holley electronic feedback carburetor by an electronic throttle-body fuel injection system.
The sedan’s base trim returned in 1986, while all 600s were given new, restyled front and rear fascias (the front in particular adopted the now familiar “crosshair” grille, dropping the Mirada-inspired horizontal slats). The 2.6 L engine was replaced by a larger 2.5 L version of the Chrysler 2.2 L.
The 600 was nearing its end. The coupe and convertible were dropped for 1987, while the sedan would only last another year, ending production in 1988. The 600 was replaced by the 1988 Dynasty(badged as a Chrysler in Canada, whereas the Canadian successor is the Dodge Spirit).
- A100 (1964–1970)
Dodge A100
| Dodge A100 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Fargo |
| Production | 1964–1970 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact pickup truck Compact van |
| Body style | 2-door pickup truck 2-door van |
| Layout | MR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 170 cu in (2.8 L) Slant-6 I6 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6 I6 273 cu in (4.5 L) LA V8 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | SWB: 90 in (2,300 mm) LWB: 108.0 in (2,743 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge B-series |
The A100 line was a model range of American compact vans and trucks manufactured and marketed from 1964–1970 by Chrysler Corporation for the Dodge marque in the United States and the Fargo marque in Canada.
The A100 competed with the Ford Econoline and Chevrolet Van, as well as the Volkswagen Type 2. The range included a pickup truck and van, both with a “forward control” design. The implementation of situating the driver on top of the front axle with the engine near the front wheels is called internationally a “cab over” vehicle. The nose was flat, with the engine placed between the driver and passenger, who sat above the front axle. The unibody vehicles used a short, 90 in (2,300 mm) wheelbase. An A108 was also available from 1967–1970, with a longer 108 in (2,700 mm) wheelbase. The A108 was popular with camper conversion companies. A substantially modified, Hemi-powered A100 wheelstanding exhibition pickup called the “Little Red Wagon” driven by Bill “Maverick” Golden was a popular drag strip attraction in the 1960s through the early 2000s.
Engines
- 1964-1966 170 in³ (2.8 L) Slant-6 I6, 101 hp (75 kW)
- 1970 198 in³ (3.2 L) Slant-6 I6, 125 hp (93 kW)
- 1964-1970 225 in³ (3.7 L) Slant-6 I6, 145 hp (108 kW)
- 1965-1966 273 in³ (4.5 L) LA V8
- 1967-1970 318 in³ (5.2 L) LA V8, 210 hp (160 kW)
L-Series trucks
From 1966-1971, Dodge built L-Series medium-duty Cabover Engine trucks based on the A-100.
Dodge A100 in popular culture
The Dodge A100 was featured in the American television series That 70’s Show episode Red’s Last Day. It also appeared in the movie Cars as the character Dusty Rust-eze.
Gallery
-
Dodge A100 Pickup
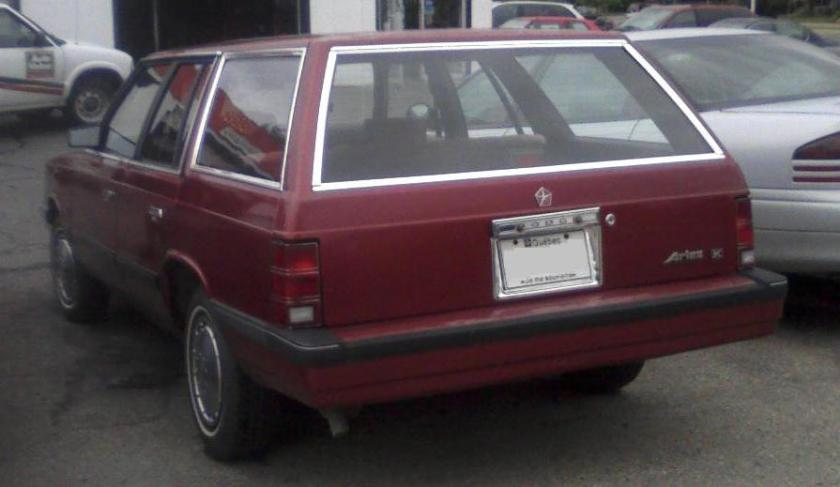
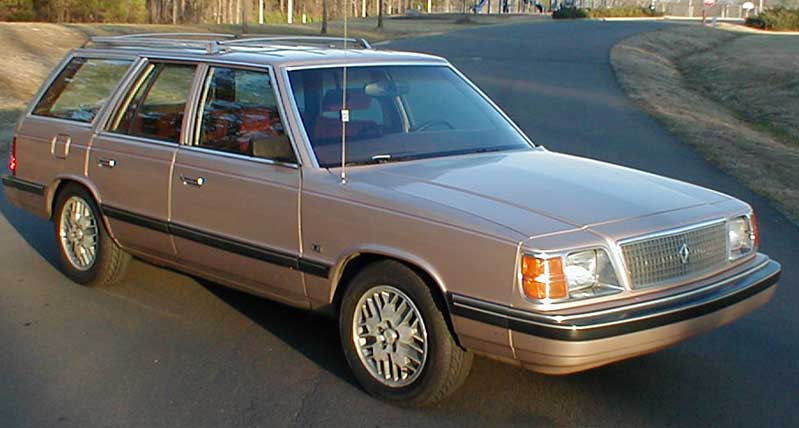
- Aries (1981–1989)
Plymouth Reliant
| Plymouth Reliant Dodge Aries |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1981–1989 |
| Assembly | Newark, Delaware (Newark Assembly), United States Detroit, Michigan (Jefferson Avenue Assembly), United States Toluca, Mexico (Toluca Car Assembly) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupe 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | K-body |
| Related | Chrysler LeBaron Chrysler Town & Country Dodge 400 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | 4-speed A460 manual 5-speed A465 manual 5-speed A520 manual 5-speed A525 manual 3-speed A413 automatic 3-speed A470 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 100.3 in (2,548 mm) Wagon: 100.4 in (2,550 mm) |
| Length | 178.6 in (4,536 mm) Wagon: 178.5 in (4,534 mm) |
| Width | 68.0 in (1,727 mm) |
| Height | Sedan: 52.9 in (1,344 mm) Coupe: 52.5 in (1,334 mm) Wagon: 53.2 in (1,351 mm) |
| Curb weight | 2,300 lb (1,043 kg) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Aspen / Plymouth Volaré |
| Successor |
|
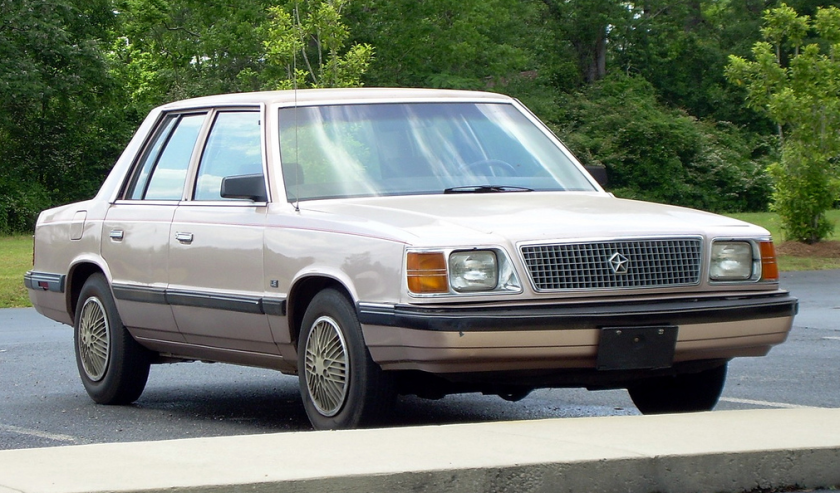
The Plymouth Reliant and Dodge Aries were introduced for model year 1981 as the first “K-cars” manufactured and marketed by the Chrysler Corporation. As Rebadged variants, the Reliant and Aries were manufactured in Newark, Delaware, Detroit, Michigan, and Toluca, Mexico — in a single generation.
The Reliant replaced the Plymouth Volaré/Road Runner. The Aries replaced the Dodge Aspen. Though similar in overall size to a compact car, the Reliant’s interior volume and six-passenger seating gave it a mid-sizedesignation from the EPA.
Ford and Chrysler would compare the K cars with the Fairmont and Tempo. The Aries was sold as the Dart in Mexico.
The Reliant and Aries were selected together as Motor Trend magazine’s Car of the Year for 1981 — and sold almost a million (Aries) and 1.1 million units (Reliant).
History
The Aries and Reliant debuted in 1981, with Chrysler added a small “K” emblem to the rear of each, shortly after their introduction. The Reliant was available as a 2-door coupe, 4-door sedan, or as a 4-door station wagon, in three different trim lines: base, Custom and SE (“Special Edition”). Station wagons came only in Custom or SE trim. Unlike many small cars, the K cars retained the traditional 6 passenger 2 bench seat with column shifter seating arrangement favored by many Americans. The Reliant was powered by a then-new 2.2 L I4 SOHC engine, with a Mitsubishi “Silent Shaft” 2.6 L as an option (curiously this engine also featured hemispherical combustion chambers, and all 1981 models equipped with it featured “HEMI” badges on the front fenders). Initial sales were brisk, with the both Reliant and Aries each selling over 150,000 units in 1981.
Changes for 1982 included a new hood ornament (changed from either a Plymouth “frog legs” hood ornament or a Dodge badge mounted flat on the hood to an upright Chrysler Pentastar), roll-down rear door windows vs. the former stationary glass with rear quarter pop-outs, a counterbalanced hood, and black painted valve cover on the 2.2L engine (vs. the former blue). In 1984, the hood ornament was removed and the Chrysler Pentastar moved to the grille. Also, the tail lights received chrome trim, and the interior received a padded dash and new black instrument cluster with round gauges. The first major changes occurred in 1985, when the K’s received a new front fascia, featuring either a new egg-crate or crosshair grille (for the Plymouth and Dodge, respectively) and a new rear fascia featuring five-section taillights. A new trim line, the top-tier LE (“Luxury Edition”), was added (it also replaced the Custom trim level on the wagon).
Powertrain changes for 1986 included replacement of the 2.2 L engine’s carburetor by a new throttle-body electronic fuel injection system, while a new 2.5 L four-cylinderengine, also fuel-injected, was added to the option list, replacing the Mitsubishi 2.6 L. The four-speed manual transmission – previously offered as standard equipment – was dropped.
The Reliant underwent only minor changes throughout the rest of its production run. The SE trim line was dropped after 1986, while the LE and base trim remained the only trims till the end of production. The base trim line was renamed America in 1988, offered as relatively inexpensive, basic transportation. 1988 was the last year for station wagons. The Aries and Reliant were replaced by the Dodge Spirit/Plymouth Acclaim, with the sedan and two-door only being sold for 1989.
Overview
The Reliant and Aries were downsized replacements for the six-passenger Volare and Aspen, which in turn were modernized version of the original Valiant and Dart compact cars of the 1960s. Based on experience gained with subcompact Omni/Horizon of 1978, the roomier K-cars set out to build a family sized car with a front-wheel drive design powered by a four cylinder engine. They were offered as 2 and 4 door notchback sedans and wagons and retained six-passenger seating on two bench seats. While the Chevrolet Citation introduced front-wheel drive in the 1980 model year to replace the Nova, its unusual styling and problems with recalls hampered its success. They achieved nearly a million in sales between the two original nameplates before being rebadged and upgraded, not counting the numerous stretched, sporty or minivan derivatives. Ford would not replace its family-sized Fairmont with a front-wheel drive design until the 1986 Ford Taurus, while cars like the Chevrolet Cavalier and Ford Tempo would be marketed as upscale compacts rather than family sedans.
After their introduction, the Reliant and Aries were marketed as the “Reliant K” and “Aries K”. A small “K” badge was also added after the word “Reliant” to the rear of the car. The Reliant and Aries were Motor Trendmagazine’s Car of the Year for 1981.
After launcd in 1981, sales of the Reliant and Aries got off to a bad start; this can be attributed to Chrysler’s inadequate preparation. Early advertisements for the K-cars promoted the low $5,880 base price. Rather than honoring that by producing a sufficient amount of base models, Chrysler was producing a larger number of SE and Custom models. When consumers arrived at Plymouth (and Dodge) dealers, they were shocked to find that the Reliant they were planning on purchasing would end up costing hundreds or thousands of dollars more. As a result of this, Chrysler corrected their mistake and began building more base models. After this, sales of the Reliant skyrocketed.
The Reliant was available in standard “base”, mid-level SE, and high-end Custom (later renamed LE) trim levels. Unlike the coupe and sedan, the station wagon was not available in base trim. “Custom/LE” Reliant wagons came standard with exterior woodtone siding, although it could be deleted if the buyer wanted it to be. All models except base could be ordered with front bucket seats rather than the standard bench.
6-passenger seating
The Aries and Reliant were classified by the EPA as mid-size and were the smallest cars to have 6-passenger seating — with a 3 seat per row setup, similar to larger rear-wheel drive cars such as the Dodge Dart and other front-wheel drive cars such as the Chevrolet Celebrity. Chrysler marketed the car as being able to seat “six Americans.”
Changes through the years
Changes for 1982 included a revised hood ornament (changed from a Plymouth logo to a Chrysler Pentastar), roll-down rear door windows vs. the former stationary glass with rear quarter pop-outs, a counterbalanced hood, a Pentastar trunk medallion, and black painted valve cover on the 2.2L engine (vs. the former blue). Changes for 1983 were limited to a blacked out grille. In 1984, the hood ornament was removed and the Chrysler Pentastar moved to the grille; the Mercedes Benz-styled grille used on the Reliant was modified. Also, the tail lights received chrome trim, and the interior received a padded dash and new black instrument cluster with round gauges. For 1985, the Reliant received a substantial restyle, with new, rounder front and rear fascias. This included new head & tail lights and a new grille that was the same height as the headlights (rather than going all the way up to the hood as with previous model years). The base engine was a transverse mounted Chrysler designed 2.2 L (135 cid) inline-four engine with an electronic two-barrel carburetor (later replaced by a fuel injection system in 1986), rated at 82 hp (61 kW). Transaxles were a 4-speed floor shift manual or a 3-speed automatic with either a floor or column shift. A Mitsubishi motor was optional, and cars so equipped for 1981 were badged as 2.6 HEMI. Reliants equipped with this engine accelerated 0–60 mph in the 13-second range. The Mitsubishi 2.6 L G54B engine was a popular option, but driveability and reliability problems led to the Mitsubishi engine being replaced by a fuel-injected Chrysler 2.5 L I4 for 1986. For 1987, the coupe’s fixed rear windows got a small pivoting vent at the trailing edge of the rear doors. Also for 1987, the base model was renamed America in the U.S (this was later done to the base models of the Horizon and Sundance). After 1987, only minimal changes were made through the end of the production run.
The last Reliant rolled off the assembly line on December 9, 1988. The 1989 Reliant was a carryover from the 1988 model year. Only the America trim was available on these models. No station wagon models were sold in 1989. The Reliant was replaced by the Acclaim for 1989, with the coupe replaced by the Plymouth Laser liftback.
- Aspen (1976–1980)
Dodge Aspen
| Dodge Aspen | |
|---|---|

Dodge Aspen Coupe
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Plymouth Volaré, Dodge Dart, Chrysler Valiant Volaré |
| Production | 1976–1980 |
| Assembly | Hamtramck, Michigan, United States Bogotá, Colombia Mexico City, Mexico |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | F-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6 I6 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 |
| Transmission | A230 3-speed manual A833 4-speed manual A904 3-speed TorqueFliteautomatic A998/A999 3-speed TorqueFliteautomatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 108.7 in (2,761 mm) (coupe)112.7 in (2,863 mm) (sedan & wagon) |
| Length | 198.8 in (5,050 mm) (coupe) 201.2 in (5,110 mm) (sedan & wagon) |
| Width | 73.3 in (1,862 mm) |
| Height | 53.3 in (1,354 mm) (coupe) 55.3 in (1,405 mm) (sedan)55.7 in (1,415 mm) (wagon) |
| Curb weight | 3,200 lb (1,500 kg) (base coupe) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor |
|
| Successor | |
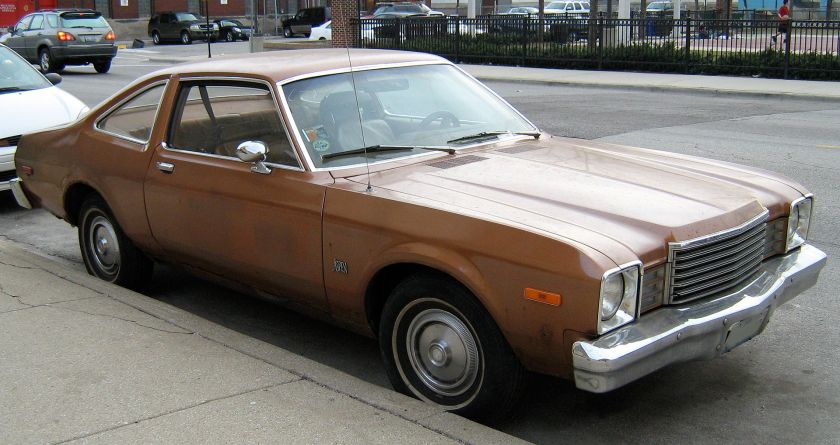
The Dodge Aspen, produced from 1976 to 1980, was a compact car from Chrysler Corporation‘s Dodge division; its Plymouth–branded counterpart was the Volaré (“volare” is Italian, and it means “fly, soar, fly by, fall off, or pass quickly”). It was launched as a two-door coupe, a four-door sedan, and a unique-for-the-segment station wagon. By the end of their production run, the Aspen and Volaré would be considered intermediate cars.
The Dodge Aspen and Plymouth Volaré were introduced in the fall of 1975 as 1976 models, and were collectively named Motor Trend’s “Car of the Year” for 1976. They were the successors to the A-body Plymouth Valiant, Duster, and Dodge Dart. The Dart, Valiant, and Duster were sold alongside the Aspen and Volaré for part of the 1976 model year, then discontinued.
The Aspen and Volaré were produced for 5 model years, 1976 through 1980. For 1981, they were replaced by the smaller front-wheel-drive K-cars — the Dodge Aries and Plymouth Reliant — and the M-body Dodge Diplomat and Plymouth Gran Fury, which were very similar in structure, size, and engineering to the F-body Aspen and Volaré.
The Aspen and Volaré were designed to be somewhat more luxurious than the A-body models, at least in the most expensive models. The new cars also continued the A-body pattern of different wheelbases forcoupés versus the sedans and wagons. Aspen and Volaré 2-doors had a 108.7-inch (2,760 mm) wheelbase. Sedans and wagons got a 112.7-inch (2,860 mm) wheelbase.
Production history
The vehicle was wind-tunnel tested to be aerodynamically sound in its fuel conservation potential as the complete aerodynamics development program included a wide range studies from drag reduction to crosswind stability, wind noise and ventilation performance. The effects of this testing resulted in softened front end contours, removal of drip troughs and helped shaped internal air flow ducting. Body engineering in the Aspen was executed using computer technology; unit body engineering was conducted by use of clear plastic stress models that showed up stress points before any sheet metal was formed. Weight reduction to provide maximum fuel economy was achieved through use of thinner glass, lighter weight side door beams and high-strength, low-alloy brackets and reinforcements that were four times as strong as conventional mild steel. A reduced number of stampings resulted in better panel fits and fewer welds. The Aspen had improved visibility and compared with other Dodge compacts, the Aspen provided a total glass area increase of 25% on two-door models and 33% on sedans.
Wheel alignment adjustments such as caster and camber could be made by removing plates over the wheel housings. The new isolated tranverse suspension system was a substantial departure from the longitudinal torsion bars Chrysler had introduced in 1957 and used on all models since that year, until the release of the F-bodies. The transverse (side-to-side) bars weren’t as geometrically favorable but saved space and weight. In addition, the new front suspension system was touted as giving a “big car ride” as the suspension had a low, or softer, fore and aft compliance which allowed the wheel to move rearward instead of straight up and down when the tire encountered an object, dampening the blow and rolling with the condition of the road. The two parallel torsion bars and an anti-sway bar were mounted forward of the front wheels, integrated into a spring-strut front suspension. These components were attached to a K-shaped structural crossmember. The K-shaped crossmember was isolated from the unitized car body by four rubber mounts. This transverse torsion bar suspension was also incorporated into the M- and J-body cars. The conventional leaf spring rear suspension was also rubber-isolated, so there was no metal-to-metal path through which road noise or vibration can be transmitted to the body; even the steering column was isolated.
Recalls
The Aspen and Volaré are perhaps best known within the industry for a series of product recalls, caused by defects, that nearly bankrupted Chrysler and led to permanent changes in the organization’s management and in North American automobile production.
In 1978, Chrysler recalled every 1976 and 1977 Aspen and Volaré for possible replacement of the front fenders, which were prematurely rusting. Many cars got new fenders, painted in the proper color. Galvanized sheet metal was phased in for the body, along with full inner front fender liners made of polyethylene (plastic) to solve the rust problem once and for all. A large number of powertrain changes, particularly in ignition and fuel delivery, were also made to improve driveability. After 1977, F-bodies had few problems with rusting or quality control.
Marketing
R. M. “Ham” Schirmer, manager of Dodge car and corporate advertising for Chrysler, said that the Aspen name originated from the codename Aspen-Vail when the project for it and the Plymouth “sister car” began in 1971. “Aspen is a very pleasant name, ” Schirmer said, “people think of the outdoors, but not necessarily skiing when they hear it. . . It won’t inhibit where we want to position the car because it’s basically neutral. ” Nonetheless, Chrysler sponsored the 1976 Dodge Aspen Team K2 Freestyle and opened up World Pro Skiing’s seventh season in Aspen, Colorado as the Dodge Aspen Cup running courses on Aspen Highlands and Aspen Mountain. In print and media actor Rex Harrison was spokesman for the Aspen, whose advertising campaign was inspired by the “Ascot Gavotte” scene in Harrison’s My Fair Lady. A patter song was spoken in rhythm, by Harrison, as “Unbelievable.” Singer Sergio Franchi was the spokesman for the Volaré and sang the pop song Volare, with altered lyrics, in TV and radio commercials. The accent mark used in the car’s name is not in the Italian word or the song title; Volaré commercials described it as an “accent on quality”; incidentally, “volaré” in Spanish with the accent translates as “I will fly”.
Aspen R/T
The Aspen R/T coupe model offered features including wider E70x14 tires, Rallye wheels, grille blackout treatment, body striping, and ‘R/T’ decals and medallion. A 360 V8 option, with a net 170 hp (130 kW) and 280 lb·ft (380 N·m) of net torque, was along with the Overdrive-4 transmission unavailable in California as the engine delivered an average fuel economy of 15.2 mpg-US (15.5 L/100 km; 18.3 mpg-imp). In a Motor Trend road test, a 360 R/T turned in a standing quarter mile (~400 m) at 17.4 seconds at a speed of 86.1 miles per hour (138.6 km/h). In an exercise normally reserved for quicker sports cars, the R/T made a 60 to 95 mph (97 to 153 km/h) run in 13.8 seconds. The R/T was about as quick from zero to sixty miles per hour as the 1977 Camaro Z28 and Corvette L82, both with four barrel 350 engines. The Aspen was a bit slower by the clock but faster through the traps in the quarter mile than all of the other three from GM. The Plymouth version was the Volaré Road Runner.
Station wagons
Station wagons were available in both model lines, all featuring liftgates with fixed rear windows. These models had a cargo volume of 71.9 cubic feet (2.04 m3) and load capacity of 1,100 lb (500 kg), which was 100 lb (45 kg) less than the intermediate and standard size Chrysler wagons. The liftgate opening was nearly 4 ft (1.2 m) wide and 27.6 in (70 cm) high. With the rear seat folded down, the cargo area was 74 in (190 cm) long at the belt line and 43.2 in (110 cm) wide between the wheel houses. Premium station wagons in either the Aspen SE or Volaré Premier series featured simulated woodgrain on its exterior side panels. On Aspen SEs, the woodgrain was framed in simulated blond (painted metal) wood-look trim. On the Premiers, the side panels were trimmed in stainless steel frames accented in matte black. Aside from the brand badging and grilles unique on each brand, this station wagon trim element remains one of the few visual clues that differentiated the Aspen from the Volaré. Side covers of the cargo area were made of one-piece injection molded polypropylene. Covered, lockable stowage compartments of 1.5 cu ft (0.042 m3) capacity were provided in these panels; these compartments were standard on the Aspen SEs and optional on the low-line wagons.
1976
The first year of the Aspen was met with much fanfare and sales. The replacement for the venerable Dart, the Aspen would share the same engines and three-box body style with its predecessor, but not much else.
The Aspen was dubbed “the family car of the future”. Available as a 2-door coupé, 4-door sedan or 4-door station wagon, it came in three trim levels – base, Custom and SE (Special Edition). Coupes featured frameless door glass but a thick “B” pillar was used, replacing the popular hardtop body style of the Dart. The performance R/T package came only on the coupe and featured a 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 standard or an optional 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 with either a 2- or 4-barrel carburetor. The 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant Six was standard across the line, and was available in most states with a choice of 1- or 2-barrel carburetion. Total production was 189,900 (Aspen) and 255,008 (Volaré).
1977
Nothing much changed for the Aspen’s second year. A new T-top was added to the coupé’s option list this year. The R/T package added a “Super Pak” option. This consisted of front and rear spoilers, wheel opening flares and louvred rear windows. A new stripe kit was also added as well. An R/T equipped with this package became a “Super R/T”. The Volaré was Canada’s top selling car this year. Total production was 266,012 (Aspen) and 327,739 (Volaré).
1978
The Aspen went through numerous changes for 1978. The three trim lines were consolidated into one. The Custom and Special Edition lines were still available but were now reduced to option packages. The Aspen also received a new front fascia, similar to the Volaré, while the Volaré’s grille was restyled with an eggcrate pattern. Chrysler added a “Duster” trim package in an attempt to bolster waning sales, relying on the popularity of the time-tested 1970–1976 A-Body of the same name. There were new performance packages, the Super Coupe and Kit Car. Both packages used the same performance exterior add-ons as the “Super Pak”, now renamed the “Sport Pak”, but came in different colors as well as different options.
The Super Coupe came with GR60x15 Goodyear GT radial tires mounted on 15×8 wheels, a heavy-duty suspension with rear sway bar, a matte black finish on the hood and came only in one color – Sable Tan Sunfire Metallic. Special three color (orange, yellow and red) stripes separated the body color from the matte black colors. Only 531 were built.
The Kit Car, made in honor of NASCAR legend Richard Petty, was supposed to look as much like a race car as possible. The wheels had no hubcaps, the wheel opening flares had a bolted on look, and even the windshield had metal tie downs just like the race cars. Unlike a race car, the Kit Car came standard with an automatic transmission. A special addition was a decal kit with large door mountable “43” decals and 360 decals for the hood. These decals were shipped in the trunk either to be installed by the dealer or by the owner. Most people however, left them in the trunk. It only came in one color – a special two-tone red. The Kit Car would prove to be one of the rarest Aspens ever built, as only 145 were ever built.
A new Sunrise package, similar to the Volaré Duster package, was also new for 1978. This was available only on the coupé, and consisted mainly of new stripes and louvred rear windows.
Wider tail light lenses with amber turn signals replaced the Plymouth Valiant/Duster-styled lenses on both Aspen and Volaré coupés and sedans. Total production came to 166,419 (Aspen) and 217,795 (Volaré).
1979
Not much would change for the Aspen in its second to last year of production. The only readily visible change was the replacement of the amber rear turn signals with red ones again. The 1978 option packages continued into 1979, with the exception of the Super Coupe and Kit Car. A new 85 mph (137 km/h) speedometer, new colors and a diagnostic connector for the engine were added. The station wagon was available as a “Sport Wagon” with special stripes, a front airdam, and wheel arch flares. Total production came to 121,354 (Aspen) and 178,819 (Volaré).
1980
For its last year of production, the Aspen and Volaré gained a new front end with rectangular headlamps, and shared the hood, fenders and front bumper with the Dodge Diplomat. Special Edition and Premier packages were available, while the Special Edition package was now only available on the sedan and coupe. The less popular “Duster” trim package was also available for the 1980 model year. The R/T package was installed only on 285 Aspens for this year before the Aspen name as well as the R/T badge would be discontinued. Total production came to 67,318 (Aspen) and 90,063 (Volaré). The 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 was dropped this year, leaving the 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 as the top engine—even for the R/T. Power from the 318 dropped from 140 horsepower (104 kW) at 4,000 rpm to 120 horsepower (89 kW) at 3,600 rpm in two barrel models. Four barrel models actually increased from 140 horsepower (104 kW) (non-California) at 4,000 rpm to 155 horsepower (116 kW) at 4,000 rpm. The 225 cu in (3.7 L) inline six-cylinder remained the base engine. The “Super Six” two barrel option was dropped, leaving the Holley 1945 single barrel set up as the sole choice. The “slant-six” produced 90 horsepower (67 kW) at 3,600 rpm. The Dodge Aspen was replaced with the front-wheel drive Dodge Aries for the 1981 model year.
Around the world
Between 1977 and 1979, the small Swiss specialty automaker Monteverdi built a modified version of this car, called the Sierra, intended to compete in Europe’s luxury car market.
The Dart name (rather than Aspen) was applied to Dodge-branded F-body cars in Mexico and Colombia, corresponding to the local Chrysler-branded F-body cars badged as Valiant Volaré. The Mexican F-body Volarés were not marketed as Plymouth, because that brand was dropped after 1969. Chrysler de México also sold cheaper versions of the American K-cars -Plymouth Reliant and Dodge Aries- (in 1982–1987) and Plymouth Caravelle (1988) as Chrysler Volarés. As a matter of fact, the 1988 Chrysler Volaré E (an inexpensive version of the 1988 Plymouth Caravelle with a 1986–1988 Plymouth Reliant front end attached to it) served as Mexican Highway Patrol (“Policía Federal de Caminos” in Spanish) units from 1988 to 1990. They got a Chrysler Turbo II 2.2L engine and 3-speed automatic transmission (shifter on the dash, like US patrols) and were known in Mexico as “Turbo-patrols”.
The Volaré also became known as the Volaré “Duster” in Canada.
After the F-body
The F-body cars were withdrawn from production worldwide after 1980, but spawned two platforms, the Chrysler J platform and the Chrysler M platform. The Aspen model name was revived in 2007 for the Chrysler Aspen luxury sport utility vehicle (SUV).
- Avenger (1995–2000; 2008–2014)
Dodge Avenger
| Dodge Avenger | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer |
|
| Production | 1995–2000 2007–2014 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
The Dodge Avenger is a front-wheel drive, mid-size sedan, built by the Chrysler Corporation for the Dodge marque is listed as #21 in the most affordable midsize cars as of 2014. The Dodge Avenger made its North American debut in 1995 as a two-door coupe, which was produced until 2000. It was re-introduced to the market as a four-door sports sedan starting in 2008. The 2014 model year marked the last production for the Avenger after the release of its replacement, the 2015 Chrysler 200.
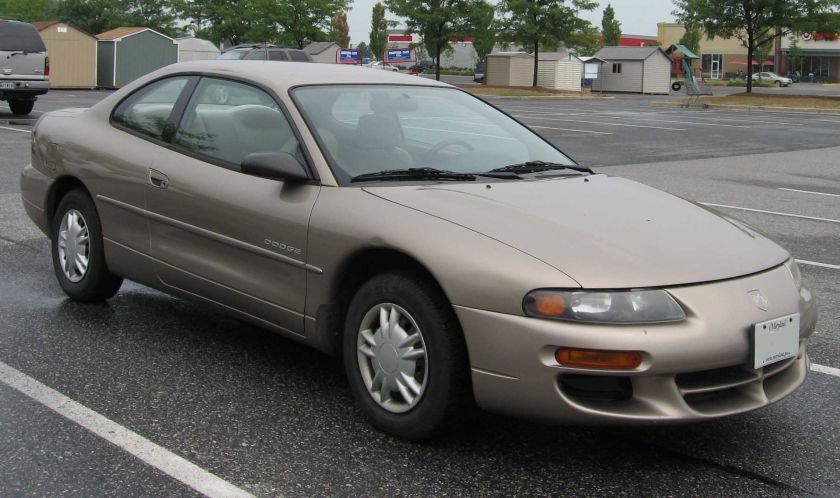
Dodge Avenger Coupe (1995–2000)
| Dodge Avenger Coupe | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Chrysler Sebring coupe |
| Production | 1995–2000 |
| Assembly | United States: Normal, Illinois(Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler FJ platform |
| Related | Eagle Talon Mitsubishi Eclipse |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.0 L 420A I4 (gasoline) 2.5 L 6G73 V6 (gasoline) |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 4-speed Ultradrive 41TE automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 103.7 in (2,634 mm) |
| Length | 190.2 in (4,831 mm) (1998–2000) 187.2 in (4,755 mm) (1995–97) |
| Width | 69.1 in (1,755 mm) (1998–2000) 68.5 in (1,740 mm) (1995–97) |
| Height | 53.0 in (1,346 mm) (1998–2000) 51 in (1,295 mm) (1995–97) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Stealth, Dodge Daytona |
| Successor | Dodge Stratus coupe |
Introduced as a two-door coupe in North America, the Dodge Avenger was built from 1995 to 2000 in a similar size and price class as the Dodge Daytona, which was discontinued in 1993. The Avenger, along with the similar Chrysler Sebring coupe, was built by Diamond Star Motors (DSM), a joint venture between Chrysler Corporation and Mitsubishi Motors, on a version of the Mitsubishi Galant platform (which also spawned the similar Mitsubishi Eclipse). Mitsubishi purchased Chrysler’s share of the joint venture in 1995. Avengers and Sebring coupes built from 1995 to 1996 both have DSM markings in their engine compartments.
The Avenger was built on a 103.7 in (2,634 mm) wheelbase and used either a 2.0 L inline-four engine (the Chrysler 420A) or a Mitsubishi-designed 2.5 L V6. The four-cylinder was coupled to either a five-speedmanual transmission, shared with the Mitsubishi Eclipse and Eagle Talon, or a four-speed automatic. The V6 engine was only available with the A604 transmission. The Avengers featured a fully independent double wishbone suspension and variable speed rack and pinion steering.
Changes
ABS was used in all ES models to 1999. In 1997, the front fascia, trunklid, and rear bumper were changed; 16-inch wheels were standard, and the license plate was moved from the decklid to the rear bumper. In 2000, the V6 and automatic transmission combination was made standard on all Avengers, and ABS was made an “option” for ES models. The four-cylinder engine was dropped for 2000.
Trims
- 1995–2000 – “Highline” base model (V6 among other options made standard in 2000)
- 1995–2000 – ES
From 1997, a “Sport Appearance Package” was made available on Base model. This package included 16″ wheels, a deck lid spoiler, along with other standard and optional features.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1995 | Initial introduction – replaces the Daytona. A DOHC 16-valve 2.0 L I4 engine (140 hp, 130 lb·ft (176 N·m) of torque) is standard. A SOHC 24-valve 2.5 L V6 engine and an automatic transmission (155 hp, 160 lb·ft (217 N·m) of torque) are made optional on the ES. Fog lamps and ABS are also optional on the ES. |
| 1996 | Power and torque ratings for the V6 are increased (163 horsepower, 170 lb·ft (230 N·m). torque), ES Coupes had new seat fabric. |
| 1997 | Sport model introduced (in addition to the base and ES). The Avenger Sport package consisted of exclusive 16-inch aluminum wheels and a body-color spoiler. New front and rear fascias are added. Added a body-color rear spoiler, P215/50HR17 tires, and 17-inch cast aluminum wheels for the ES. The V6 is also standard for the ES, as well as rear disc brakes. |
| 1998 | An on-board recycling vapor recovery system, cafe latte exterior color and a black and gray interior color combination are added. |
| 1999 | Next generation driver and front passenger airbags are added, as well as a new exterior color: Shark Blue. The V6 engine and automatic transmission are standard on all models in mid-year, as well as several options. |
| 2000 | Last year for the Avenger. V6/automatic drive train are standard. ABS an option on ES models. Gained a number of standard features that had previously been optional, including power windows and locks. Base models added cruise control and 4-wheel disc brakes. ES coupes now come with standard leather upholstery, keyless remote entry, and a power driver’s seat. |
In 2000, the Avenger was discontinued and replaced by the Dodge Stratus coupe for 2001. This model was also made at the former Diamond Star plant by Mitsubishi, using the Eclipse platform and architecture, though the Stratus sedan was engineered and built by Chrysler.
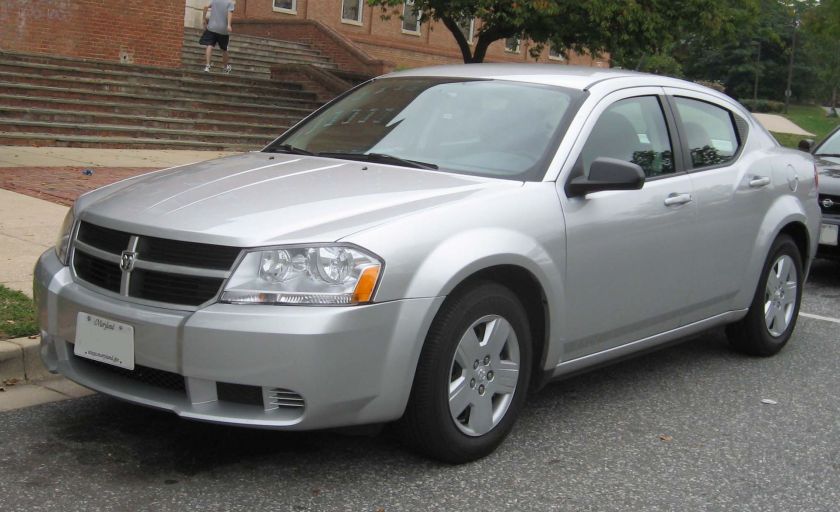
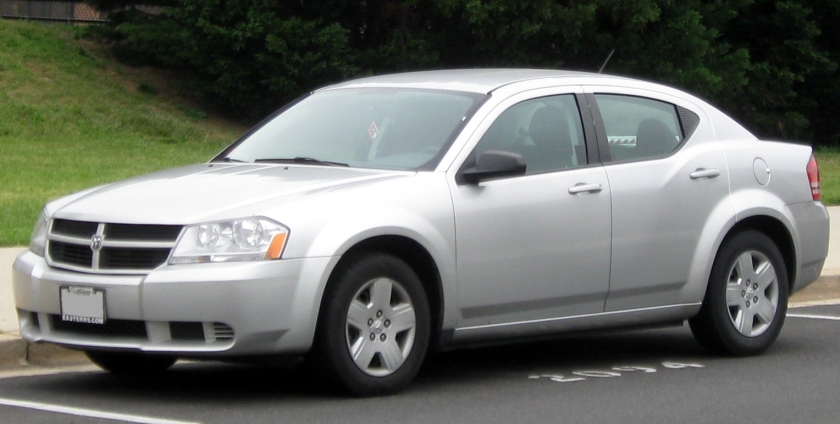
Dodge Avenger sedan (2007–2014)
| Dodge Avenger sedan | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Dodge GTS (Mexico) |
| Production | February 2007– December 2013 |
| Model years | 2008–2014 |
| Assembly | United States: Sterling Heights, Michigan (Sterling Heights Assembly) Mexico: Chihuahua (2013-2014)ine = 2.0 L World I4(gasoline) 2.0 L VW I4 (t/c diesel) 2.4 L World I4 (gasoline) 2.7 L EER V6 (gasoline) 3.5 L EGF V6 (gasoline) 3.6 L Pentastar V6 (gasoline) |
| Designer | Ryan Nagode |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive / all-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler JS platform |
| Related | |
| Powertrain | |
| Transmission |
|
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 108.9 in (2,766 mm) |
| Length | 190.9 in (4,849 mm) |
| Width | 71.8 in (1,824 mm) |
| Height | 58.9 in (1,496 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Stratus |
| Successor | Chrysler 200 |
The Dodge Avenger name returned in February 2007 as a MY2008 model as a sedan to replace the Dodge Stratus, whose coupe version had replaced the original Avenger in 2001. According to some reports, the Avenger, along with the redesigned Chrysler Sebring, shares a DaimlerChrysler/Mitsubishi Motors platform called JS which used the Mitsubishi GS as a starting point, then was heavily modified. The base engine in theSE and SXT trim levels is the 2.4 L GEMA I4 naturally aspirated “World Engine”, a joint venture between DaimlerChrysler, Mitsubishi and Hyundai. Additional engines include an optional 2.7 L V6 in the SXT and a standard 3.5 L V6 in the R/T trim level. In addition to the 2.4 L “World Engine” and the V6s, export vehicles were offered with the 2.0 L naturally aspirated “World Engine”, as well as a 2.0 L turbocharged diesel (Pumpe-Düse) made by Volkswagen. As a 2008 model, the Dodge Avenger came to showrooms in February 2007.
Features on the new Avenger include optional heated/cooled cup holders as well as Dodge’s new “Chill Zone”, a feature that comes standard on all Avenger models, which can store up to four 12-US fl oz cans in the glove box and chill them to 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Like its Dodge Journey stablemate, the Avenger’s exterior was styled by Chrysler’s Ryan Nagode. The interior was styled by Ben S. Chang.
The Avenger replaced the Charger as Dodge’s car in NASCAR in 2007 for Car of Tomorrow races. It got its first win with former Formula One driver Juan Pablo Montoya in the2007 Toyota/Save Mart 350 at the Infineon Raceway.
The Avenger was officially unveiled at the Paris Motor Show on September 28, 2006 as a concept car. It was launched in Europe and was sold in the United Kingdom, filling a gap in the Chrysler range that was left by the Neon’s demise four years earlier. It was also launched in Australia, although with only the 2.4 L engine.
In the United Kingdom, it has been discontinued, although sales continued in the Republic of Ireland and in Western Europe until late 2009 following Fiat’s takeover of Chrysler Group. This new version continued with SE, SXT trim levels and is not badged the same way as North American or the South American versions. The Avenger competed directly with the Chevrolet Malibu and Ford Fusion, with the 2007 and later Chrysler Sebring being aimed at the higher priced American cars such as the Mercury Milan, Pontiac G6 and Saturn Aura.
In the US, the Avenger was launched with a 30 second television ad, “Tuned Up,” that debuted Sunday, March 4, 2007 during NHL hockey, an ad in which a lab technician discovers he can play Smoke on the Waterby Deep Purple on the Avenger’s transmission. Another television spot likened the Avenger to the “superhero” vehicle for the everyman, depicting a driver piloting his Avenger through Gotham-like streets and alleys, speaking to the MyGig entertainment system in distinctly Batman-reminiscent tones, to arrive home, pull into a two-car garage and open the rear door to a sleeping child in the rear car-seat.[7]
Revisions
In the 2009 model year, like its Caliber, Charger, Grand Caravan, Journey & Nitro models, the “AVENGER” badge at the trunklid’s left was pushed to the right to make way for “DODGE” at the left.
Changes for 2011
For 2011, the Avenger received its first major overhaul since its 2008 re-introduction. Exterior changes include slightly revised sheet metal with a new crosshair grille displaying the new Dodge logo on the lower right corner of the grille, a sleeker bumper cut design, and standard LED combination tail lights. Changes to the interior are more noticeable with a completely redesigned dashboard and instrument panel featuring an available 6.5-inch navigation/media center screen. Higher-quality soft-touch plastics for dashboard, door, and trim panels replaces the old materials, which were criticized for their poor fit and finish quality, as well as being unpleasant to the touch. The seats receive better cushioning and higher-grade upholstery. Two-tone interior color combinations will be available.
Mechanically, the 2011 Avenger came standard with the existing 173 hp (129 kW) 2.4 L GEMA I4, although it was now paired with a six-speed automatic as well as the option of the previous four-speed. Also available is the new 3.6 L Pentastar V6, which generates 283 hp (211 kW) and 260 lb·ft (350 N·m) of torque. The suspension was heavily revised to improve handling and ride quality. Trim level designations were also new, with existing trims being replaced by Express, Mainstreet, Lux and Heat models.
The Dodge Avenger was ranked the “Most American Made” sedan by The Kogod Made in America Auto Index in 2013. The Dodge Avenger also has an overall rating of 6.7
Trims
- SE: (2007–2009, 2012–2013)
- SXT: (2007–2010, 2012–2013)
- SXT Plus: (2012)
- R/T: (2007–2010, 2012–2013)
- R/T AWD: (2007–2009)
- Express: (2011)
- Mainstreet: (2011)
- Lux: (2011)
- Heat: (2011)
Total American sales
| Calendar Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 2007 | 83,804 |
| 2008 | 61,963 |
| 2009 | 38,922 |
| 2010 | 50,923 |
| 2011 | 64,023 |
| 2012 | 96,890 |
| 2013 | 93,842 |
| 2014 | 51,705 |
Safety
The 2008-2013 Avenger, also sold as the Chrysler Sebring from 2008-2010, and the Chrysler 200 from 2011-2013, receives an overall “Good” rating with no significant injuries. In the small overlap test, also conducted by the IIHS, the car received an overall “Acceptable” rating, due to marginal dummy kinematics and slight intrusion into the passenger compartment. In the side test, the Avenger earns a “Good” rating, however, rib fractures would be possible for the driver. In the roof strength evaluation, it earns a “Good” rating, as well as its head restraints and seats. The Avenger earned the “Top Safety Pick” award in 2010, 2011, 2012, 2014, and earned the “Top Safety Pick+” award for 2013.
Discontinuation
Production of Dodge Avenger ended on December 20, 2013 as, with remaining 2014 model year vehicles produced in 1Q 2014. It was in export production for Canadian market until 1 July 2014, and sold in Canada as a 2014 model until stock depletion.
Chrysler plans to replace the Avenger with the newly-introduced 2015 Chrysler 200 starting mid-2014, and to lure the appropriate clientele range towards slightly more-price, but much more offering luxury sedan variant.
Motorsport
The first-generation Dodge Avenger body style was widely used in the National Hot Rod Association, but came to the most prominence being driven by Darrell Alderman, and Scott Geoffrion, during their run from 1994–2000, as the celebrated Dodge Boys. The car was also used for the 1994 and 1995 incarnations of the International Race of Champions. The second-generation Dodge Avenger was used in the 2007 NASCAR Nextel Cup Season as the Car of Tomorrow model from Dodge. In 2008, the Dodge CoT was changed back to the Charger.
- B Series (1948–1953)
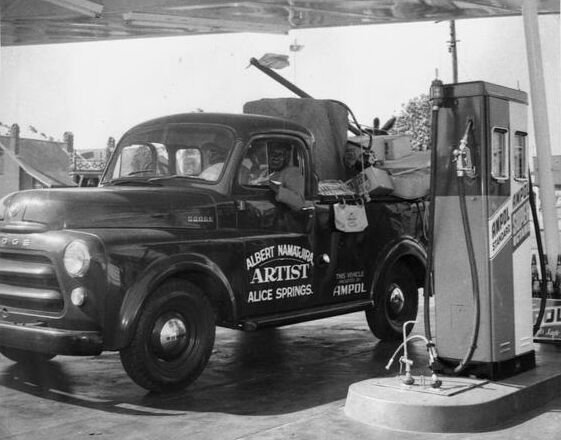
Dodge B Series
| Dodge B-Series | |
|---|---|

Dodge B-Series, with a C-Series grille.
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Model years | 1948-1953 |
| Assembly | Los Angeles, California Stockton, California Warren, Michigan |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size pickup truck |
| Body style | 2-door pickup truck |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 116 in (2,900 mm) 108 in (2,700 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge C Series |
Chrysler‘s Dodge division has used the B Series name on two different vehicles, a pickup truck and a van.
Pickup truck
The B-series pickup trucks were sold from 1948-1953. They replaced the prewar Dodge Truck and were replaced by the Dodge C Series in 1954. The B Series trucks came in several different variants. The B1-B were ½ ton trucks standard with a 95 hp (71 kW) flathead-straight-six engine while the B1-C were ¾ ton trucks with a standard 108 hp (81 kW) flathead-straight 6 engine. It also came in several other variants such as the B1-T and B1-V which were semi-truck cabs and vans, respectively. A woodie version, the “Suburban”, was also available from outside companies.
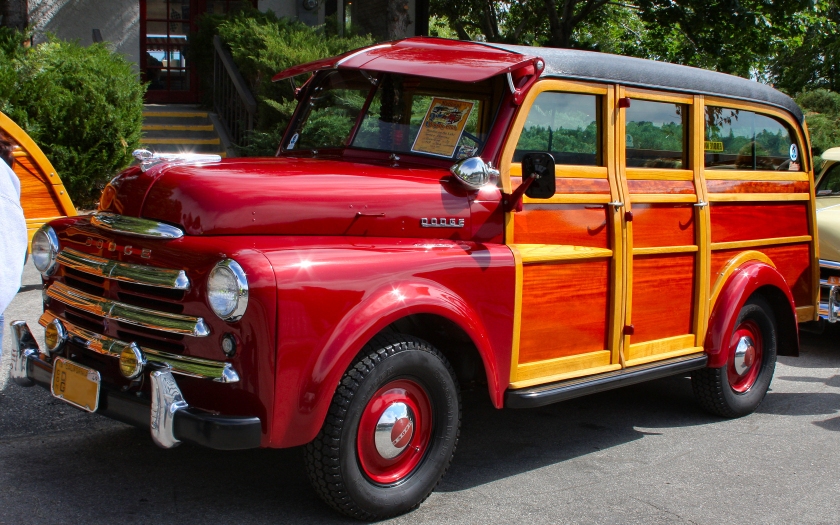

The B Series trucks featured a high-visibility “pilot-house” cab with optional rear quarter windows. The engine was shifted forward and the front axle moved back on the frame for better weight distribution as well as a shorter wheelbase, moving from 116 in (2,900 mm) to 108 in (2,700 mm). The cargo bed sides were made higher to increase capacity by 40%. The redesigned cab could seat three people, with 2.5 in (64 mm) more height, 6 in (150 mm) more width and 3 in (76 mm) additional in length. The cab was mounted on rubber mounts for an improved ride. Another innovation for the time was the use of cross-steering arrangement, giving the trucks a 37° turning radius. The cargo box space was increased over previous models and overload springs made optional on all variants to increase hauling capacity. In 1950, more new features were added as the 3-speed manualshift lever was relocated to the steering column instead of on the floor. A fluid drive standard transmission, with 3 or 4 speeds, became an available option. The front end and dashboard/gauge layout were redesigned for 1951.
1953 was the last year of the Pilot-house, but brought many new changes. The Truck-O-Matic transmission, a fully automatic transmission was available for ½ and ¾ton models. A longer 7 ft 6 in (2.29 m) bed became available, which would increase the wheelbase to 116 in (2,900 mm). And the new wide “step-style” rear fenders were added, which would continue to be used by Dodge up until the 1980s.
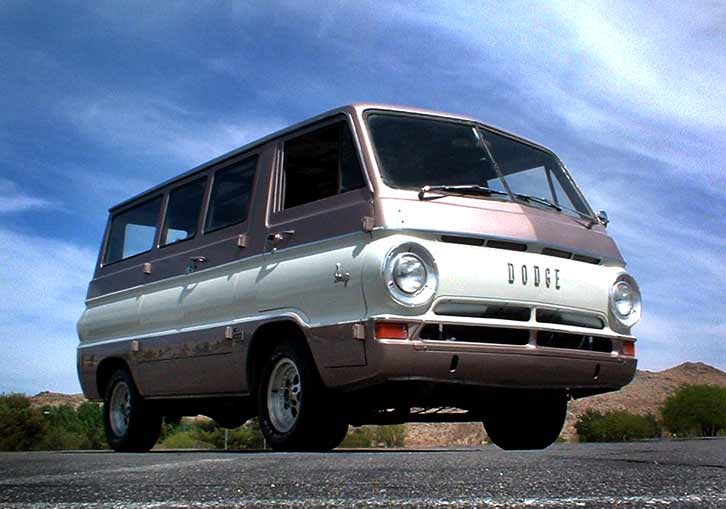
Van
The B Series also refers to full-sized vans made by the Dodge division of Chrysler Corporation from 1970 (as early 1971 models) through 2003. During that time, they were originally numbered B100, B200, and B300; the numbers were later upped by 50 (B150, etc.) and finally multiplied by 10 (B1500, B2500, B3500) in the mid-1990s. The actual names were Dodge Sportsman, Dodge Tradesman, Dodge Van, at first; they later changed to Ram Van, Ram Wagon, and, briefly. There was also a Kary Van extended height model.
The cargo and passenger vans used the same frame and powerplants (both 6- and V8 engines), but the passenger vans had seats for up to 15 passengers (on the extended length, long-wheelbase Maxivans), dual air-conditioning systems (in later years), and large windows on both sides. The 15-passenger vans are today commonly used by military, commuters, church groups, scouts, urban camping, and some corporations. Throughout their run, two wheelbases were used: 109 in (2,800 mm) and 127 in (3,200 mm), with an extended length version based on the 127 in (3,200 mm) wheelbase. Engines ranged from the 198 in³ Slant Six (available only in 1970-71), to the 440 in³ V8 (only briefly available in the late 1970s), with factory compressed-natural-gas 318 in³ (5.2 L) engines available from around 1995 onwards, to fleet buyers only. A popular Kary Van (basically a factory-built cube van, instead of upfitted by an aftermarket company), which extended the cargo area height to 6 ft 2 in (1.88 m), was added in 1972. A sliding door was made optional in 1974; that same year, the original stamped aluminum grille was also replaced with a molded plastic part. A one-piece rear door and hard-service interior were made optional in 1975.
For many years, Dodge was the sales leader for vans, including conversions for tradespeople, ambulances, school buses, and campers, working with numerous upfitters to provide alternatives for customers. However, in 1979, the RV market crashed, and Dodge stopped making RV chassis; their van sales also dropped roughly in half. After that, upgrades to the “B-vans” came more slowly, especially as the vans’ utility was in some ways duplicated by the company’s own popular Plymouth Voyager and Dodge Caravan minivans.
In 1988, a 239 in³ (3.9 L) V6 originally developed for the Dodge Dakota mid-size pickup replaced the 225 in³ (3.7 L) Slant Six, and throttle body injection was given to the 318 V8. The 360 in³ (5.9 L) V8 gaining fuel injection and a roller camshaft in 1989. In 1990, rear wheel antilock brakes were made optional, along with a heavy-duty four-speed automatic transmission.
In 1992, the V6 and 5.2L V8 engines were fitted with sequential multiple-port fuel injection (SMPI) and a “barrel”-type intake manifold, which boosted power dramatically, and the outboard positions of the rear seat gained three-point belts. In the same year, compressed natural gas 5.2 L engines became optional for fleet buyers. The 5.9 L received the new intake and SMPI for 1993.
Numerous changes to the drivetrain, body, and suspension were made after 1993, as Dodge tried to make the vans more competitive, leading to a fairly sizeable redesign in 1998, which added numerous features, made the vans more driveable and safer, and added power to the 5.9 L V8 engine. More, and also substantial, changes were made for the 2000 model year, but little was changed from then until the final vans. Dodge stopped making the vans in June 2003, citing the expense of meeting future safety standards and slow sales. The Pillette Road plant in Windsor, Ontario which made the vans was closed down and later demolished.
- C Series (1950–1960)
Dodge C Series
| Dodge C Series | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Production | 1954-1960 |
| Assembly | Warren, Michigan, United States Los Angeles, California, United States (until 1955) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size pickup truck |
| Body style | 2-door pickup |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 241 cu in (3.9 L) V8 315 cu in (5.2 L) V8 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 331 cu in (5.4 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 2-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 108 in (2,743 mm) 116 in (2,946 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge B Series |
| Successor | Dodge D Series |
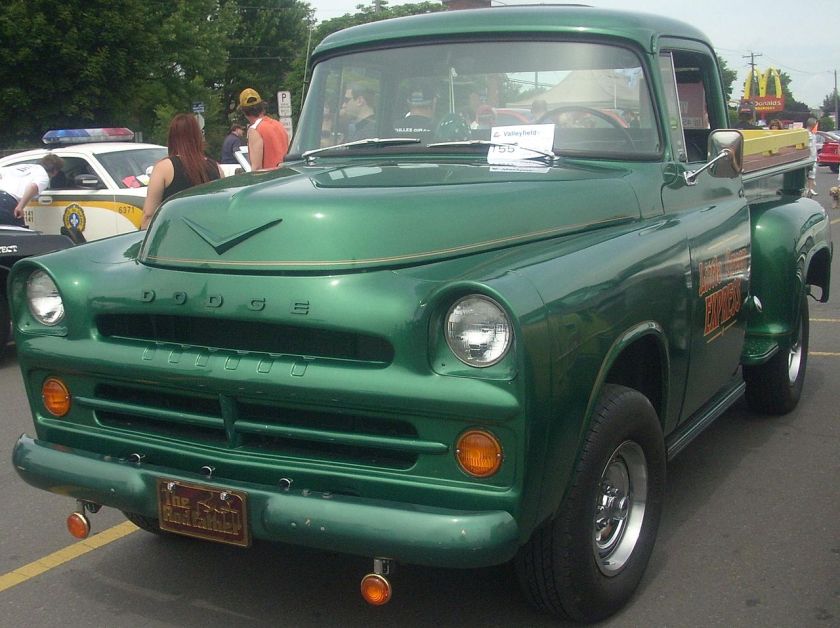
The C Series was a line of pickup trucks sold by Chrysler‘s Dodge division from 1954 to 1960. It replaced the Dodge B Series of trucks and was eventually supplanted by the Dodge D Series, introduced in 1961.
Unlike the B Series, which were closely related to Dodge’s prewar trucks, the C Series was a complete redesign. Dodge continued the “pilot house” tradition of high-visibility cabs with a wraparound windshield introduced in 1955. A two-speed “PowerFlite” automatic transmission was newly available that year.
Chrysler called the Hemi-powered Dodge trucks “Power Giant” in 1957, and introduced power steering and brakes, a three-speed automatic, and a 12-volt electrical system.
A flat-sided (and thus wider) “Sweptline” cargo box came in 1959. The company also adopted the standard pickup truck numbering scheme, also used by Ford and GM at that time. Thus, the ½ ton Dodge was now called the D100. A traditional separate-fender body “Utiline” version was also built which had a GVWR of 9,000 lb (4,100 kg).
Engines (light-duty):
- 1957-1960; Flathead I6, 120 hp (89 kW)
- 1969; 241 in³ Red Ram V8, 133 hp (99 kW)
- 1959; 331 in³ FirePower V8, 172 hp (128 kW)
- 1957-1959; 315 in³ Red Ram V8, 204 hp (152 kW)
- 1959; 318 in³ A-type V8, 200 hp (150 kW)
Medium-Duty/Heavy-Duty C Series
Since it still utilized the older cab design, the C Series name was continued for Dodge’s line of medium- and heavy-duty trucks (better known as the LCF Series) through the 1975 model year, long after most of Dodge’s other trucks had moved to the newer D Series designation.
External links
- Caliber (2006–2012)
Dodge Caliber
| Dodge Caliber | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Dodge |
| Production | August 2006–November 2011 |
| Model years | 2007–2012 |
| Assembly |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact car |
| Body style | 5-door hatchback |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive / all-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler PM/MK platform |
| Related | |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 103.7 in (2,634 mm) |
| Length | 173.8 in (4,415 mm) |
| Width | 68.8 in (1,748 mm) |
| Height |
|
| Curb weight | 3,052 lb (1,384 kg) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Neon |
| Successor | Dodge Dart (PF) |
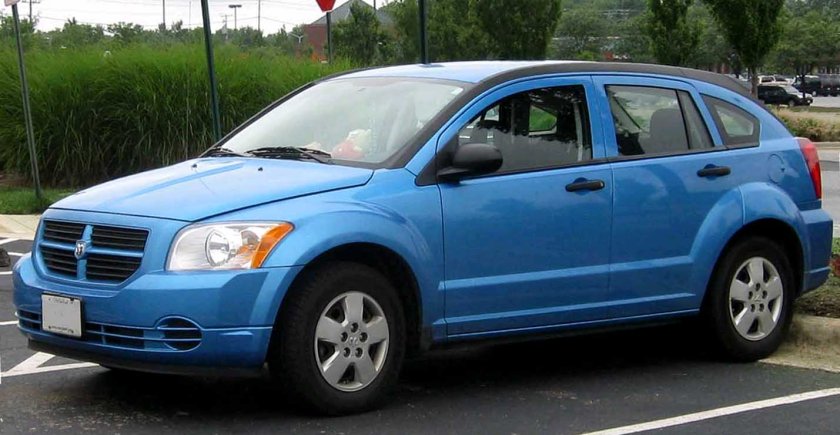
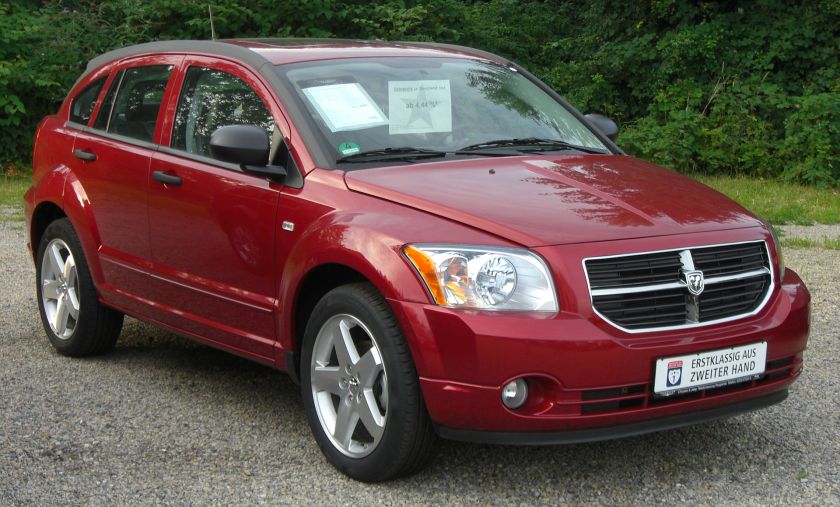
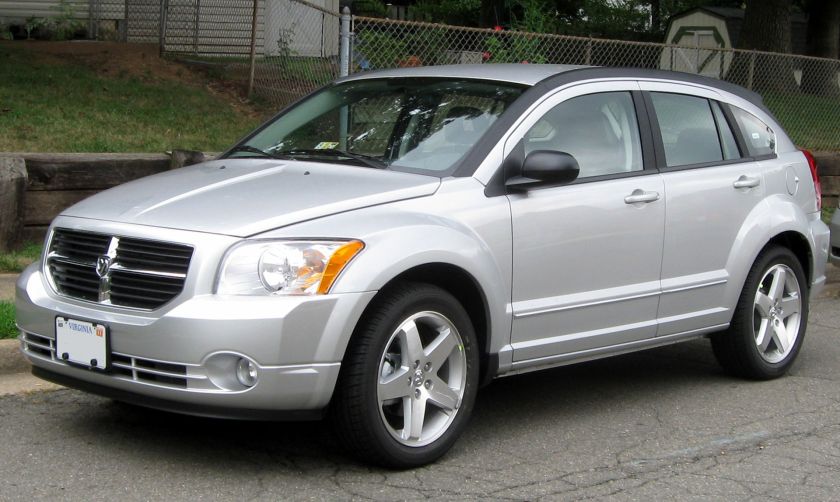
The Dodge Caliber is a compact car that was produced by the Dodge division of Chrysler from model years 2007 to 2012. It replaced the Neon, which Chrysler had discontinued in 2005. The Caliber went on sale in March 2006 as a five-door hatchback; but with its appearance, it is sometimes considered a station wagon or a crossover. The Caliber was the smallest and the least expensive vehicle in the brand’s line-up until the 2013 Dodge Dart (PF) succeeded it.
Overview
The Caliber concept was revealed at the 2005 Geneva Motor Show and featured styling elements derivative of larger Dodge vehicles (notably Dodge Magnum), such as a crosshair grille, rough border angles, and flared fenders. The pre-production version showed some improvements over the concept model and has debuted on January 10, 2006 at the North American International Auto Show, with dealership availability starting in April.
The Caliber was built at the Belvidere Assembly (Illinois) plant, where its predecessor was produced. The Caliber was developed and released solely as a five-door hatchback during its run.
The Caliber was an important vehicle for Chrysler in its quest to expand globally. The Caliber was one of Dodge’s first modern offerings in Europe and in Asian markets such as Japan and Singapore, as it established new distribution channels there. It was also introduced in China in 2008 as Dodge’s second modern vehicle offering in that market. Dodge vehicles were last officially sold in China during the World War II era. The introduction of the Caliber had marked the return of the Dodge brand to Australia, for the first time since the early 1970s.
The Caliber in Japan joined the Chrysler PT Cruiser in 2007, as the PT Cruiser was offered since 2001, but as with previous Chrysler products sold in Japan, the width dimension exceeded Japanese Governmentdimension regulations, and Japanese consumers were liable for annual taxes for driving a larger car which affected sales. As Chrysler products were considered large to the Japanese market, Chrysler offered products that offered spacious interiors with four doors and one piece liftgates to broaden their appeal to the Japanese as a compromise for paying the annual tax for large vehicles.
The marketing plan for the first year of the Caliber’s production included 20% of the budget going towards online marketing, a blitz of print ads, and TV commercials.[4] The Caliber was a reasonable sales success despite various criticisms” as Dodge’s entry-level model.
Features
The Dodge Caliber offers a continuously variable transmission (dubbed CVT2 by Dodge) sourced from Jatco (a Nissan subsidiary), the second DaimlerChrysler model to employ this technology after the Mercedes-Benz A-Class. It uses a four-cylinder 1.8-2.4 L World gasoline engine, designed jointly by Chrysler, Mitsubishi, and Hyundai.
The car features an optional electronically controlled all-wheel drive system with variable torque at speeds of 25 to 65 mph (40 to 105 km/h) for optimal handling.
The Caliber rides on a heavily modified GS platform, co-designed with Mitsubishi Motors. The modified GS platform is now called the JS platform by Chrysler for mid-size cars and PM/MK for compact cars. It shares a portion of the platform with the Mitsubishi Lancer, but is most similar to the Jeep Compass and Jeep Patriot. The Caliber wheels have a 5-hole pattern with a 114.3 mm bolt circle.
Safety
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) gave the Caliber an overall Good score in frontal crash testing. The Dodge Caliber was standard with side curtain airbags, but torso side airbags were optional. The IIHS had scored the Caliber Marginal overall in their side impact test. However, that Caliber was not equipped with the optional torso side airbag.
Models
Three models were available at the Caliber’s launch, with a fourth available in mid-2006.
SE
The base SE model features front-wheel drive and a 1.8 L 148 hp (110 kW) World I4 attached to a Magna Drivetrain T355 5-speed manual transmission. A 2.0 L 158 hp (118 kW) version of the engine paired with the CVT2 transmission was available as an option.
The standard configuration for the SE lacks air conditioning, power windows, door locks, or mirrors. The grille surround is body-colored, while that of all other models is chromed. Canadian SXT and R/T models feature body color grilles instead of chrome grilles. The Caliber SE doesn’t have a tachometer or assist handles, 15 in (38 cm) steel wheels with wheel covers are standard. Some options were not available on the SE.
For 2011, this model was named Express, reverting to SE for 2012. For 2012, the CVT transmission option was dropped only for the SE, leaving the five-speed manual transmission as the only available transmission option for the SE. The CVT continued to be offered in the SXT and SXT Plus models for 2012.
SXT
The SXT has the same engine choices as the SE but many more features are available as standard. Air conditioning is standard equipment at this level, including the Chill Zone beverage cooler inside the front lower glove compartment. The gauge cluster gains a tachometer and an (optional) trip computer. The driver’s seat adds height adjustment, the passenger seat folds flat for load-carrying, and the rear seats recline. Power windows, locks, mirrors, and remote keyless entry are included. The grille is chromed and 17 in (43 cm) steel wheels are standard, with 17 in (43 cm) aluminum wheels as an option. The cargo area light includes a removable and rechargeable flashlight while the front dome light incorporates two reading lamps.
Some Dodge publications mention a SXT Sport Wagon model, while others (e.g. the Dodge website) list a SXT “E” package with identical features. This consists of 17 in (43 cm) aluminum wheels, color-keyed cloth seat inserts, color-matched instrument panel trim, along with fog lamps.
The UK SXT Sport model has 18 in (46 cm) alloy wheels, color-keyed cloth seats and instrument panel, and a 9-speaker audio system as standard; early UK models did not have the chrome grille. The UK SXT Sport was available with a Volkswagen 2.0 L diesel engine mated to a six-speed manual transmission.
For 2011, the Heat, Uptown, and Mainstreet were three available trim levels of the Caliber, reverting to SXT and SXT Plus in 2012.
R/T[edit]
The R/T model has a 2.4 L 172 hp (128 kW) version of the World engine, equipped with the CVT2 transmission, and programmed with an ‘AutoStick’ feature giving six simulated fixed ratios in a clutchless manual mode in addition to the standard CVT ‘Drive’ mode. All-wheel-drive was an option on the R/T model until 2009, but with automatic transmission only. Eighteen-inch aluminum wheels were standard, while chromed versions were optional. At launch, the CVT2 with all-wheel drive was the only powertrain combination available for the R/T. A front-wheel drive variant with the T355 5-speed manual transmission commenced production in late summer 2006.ABS was standard, and the suspension and steering systems were tuned for performance.
Externally, the R/T is distinguishable by body-color/chrome door handles (replacing black on other models), a chrome side molding, chromed exhaust tip, and front fog lights as standard, as well as R/T badging.
Internally, the car came standard with color-keyed fabric seat inserts, while leather seats were an option as on the SXT. Color-keyed instrument panel trim was also standard, as well as a leather-wrapped steering wheel with audio controls and speed control, and a cargo area cover (all options on the SXT).
The R/T model was discontinued in 2010.
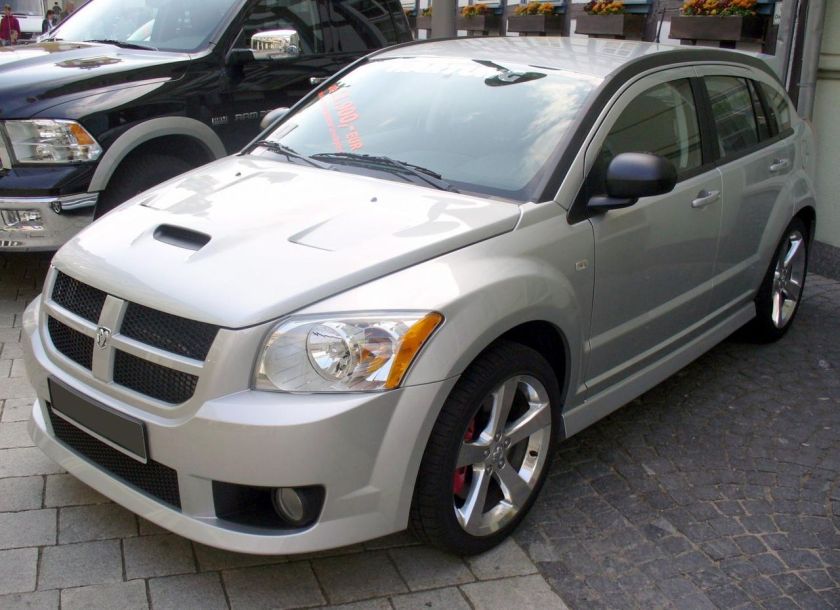
SRT4
The SRT4 model that was introduced at the Chicago Auto Show in February 2006, was a replacement for the original Neon-based SRT-4 produced by Chrysler’s Street and Racing Technology group.
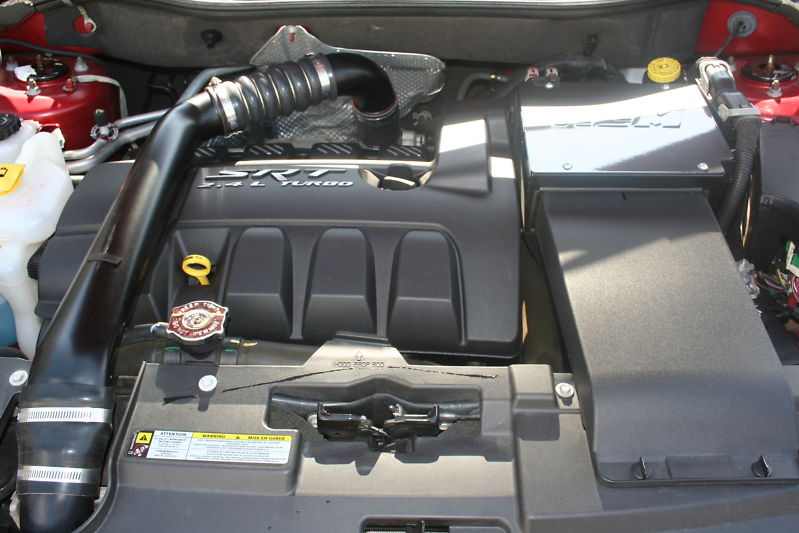
It was a hatchback set to compete with the Volkswagen GTI and the Mazdaspeed3. It featured a 2.4 L DOHC 16V turbocharged I4 with dual variable valve timing (DVVT). The engine produces 285 hp (213 kW) at 6,400 rpm, and 265 lb·ft (359 N·m) of torque at 5,600 rpm using the Mitsubishi TD04HL4S-20 turbo. Edmunds.com tested a Caliber SRT4 on a chassis dynamometer and obtained 281 hp (210 kW) and 261 lb·ft (354 N·m) of torque at the wheels. Edmunds called the manufacturer’s rating conservative; putting more power to the road than cars costing twice as much. This engine is mated to a Getrag six-speed manual transmission, and utilizes a front-wheel drive drivetrain. The Caliber SRT4 utilizes a MacPherson strut front suspension, and a multilink rear suspension. The SRT4 came with large 13.4 in (34 cm) vented front disc brakes (from the Dodge Charger Police Pack version) with dual-piston calipers and 11.9 in (30 cm) rear single-piston disc brakes. It also featured four-wheel ABS, with electronic assistance. The wheels are 19 in (48 cm), five-spoke, SRT-stamped, painted aluminum and equipped with Goodyear RSA 225/45R19 tires. Package options included polished aluminum wheels, Goodyear Eagle F1 Supercar tires, SIRIUS satellite radio with Kicker SRT livin’ loud audio, EVIC with performance pages, security alarm, and optional paint colors.
The SRT4 model of the Caliber was available through 2009.
Engines
| Model | Year | Engine type | Power | Torque | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE, SXT | 2007–2009 | 1.8 L World I4 | 148 bhp (110 kW) | 125 lb·ft (169 N·m) | 5-Speed Manual, FWD |
| 2007–2011 | 2.0L World I4 | 158 bhp (118 kW) | 141 lb·ft (191 N·m) | CVT2 (2007–present), 5-Speed Manual (2010–2012), FWD | |
| Diesel | 2006–2007 | 2.0 L I4 turbo (from Volkswagen 140hp TDI BKD) | 138 bhp (103 kW) | 229 lb·ft (310 N·m) | Europe & Australia only, FWD (without DPF) |
| Diesel | 2008–2011 | 2.0 L I4 turbo (from Volkswagen 170hp TDI BMR) | 168 bhp (125 kW) | 229 lb·ft (310 N·m) | Europe & Australia only, FWD (with DPF) |
| R/T | 2007–2011 | 2.4 L World I4 | 172 bhp (128 kW) | 165 lb·ft (224 N·m) | AWD: CVT2 (2007–2008), FWD: CVT2/5-Speed manual (2007–2011) |
| SRT-4 | 2008–2009 | 2.4 L World I4 turbo (“Warhawk”) | 285 bhp (213 kW) | 265 lb·ft (359 N·m) | 6-Speed Getrag Manual, FWD |
Total U.S. sales.
| Calendar Year | Sales |
|---|---|
| 2006 | 92,224 |
| 2007 | 101,079 |
| 2008 | 84,158 |
| 2009 | 36,098 |
| 2010 | 45,082 |
| 2011 | 35,049 |
| 2012 | 10,176 |
| 2013 | 45 |
Updates
2009
For the 2009 model, the Caliber underwent a minor facelift. The plain plastic black-colored door handle available on base models were replaced by painted car-colored handles previously available only on R/T. In addition, the trunk lid was reduced in weight and simplified in opening. In the interior, all panels were made black instead of grey. The “DODGE” badge that was on top of the Ram logo at the middle was shifted to the left, while “CALIBER” badge was moved to the right from the left, both equal in font size. The car model title, previously indicated on the right, was moved to the bottom right of the gate lid.
2010
The 2010 model year was unveiled at the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show, featuring a refreshed interior design composed of metallic outlines and parts of glass to suppress the abundance of plastic materials on previous models, as well as the addition of an 8-way power drivers seat, heated mirrors, and an automatic climate control system previously available only on R/T. The dashboard also features the relocation of the glove box due to many customer complaints, which now occupies the spot over the radio panel and comprises a “push-open” lock instead of the previous “squeeze-and-pull” opening mechanism.
The 1.8 L engine was dropped from the SE and SXT models, and the SRT-4 model is discontinued. European market models receive a new 2.2 L diesel engine with 163 hp (122 kW) and 236-pound-force-foot (320 N·m) of torque that provides a combined city and highway fuel efficiency of 40.6 miles per US gallon (5.79 L/100 km; 48.8 mpg-imp).
For the North-American markets, the models were renamed and re branded, with SE becoming “Main Street”, SXT — “Heat” and R/T — “Rush”. Two more models were launched in 2010: a luxury all-included variant “Uptown” and a base variant “Express” in which the black plastic handles returned. “Express” was the only model not to feature the automatic climate control as an option, the “Main Street” featured speed control, anti-lock brake system and electronic stability control, which were previously unavailable as options for SE. All models except “Express” featured 17-inch wheels.
2011
The 2011 model brought six new paint schemes, standard stability control except on Express models, Sirius traffic when equipped with a navigation system, 18-inch chrome-clad wheels available on Uptown models (17″ painted are standard), updated steering except on Express models, and new shocks and a thicker rear anti-roll bar on Rush and Heat models. The Caliber and the Nitro were the only two cars in the Dodge vehicle line-up to still feature the Ram logo on both fascia, rear and the steering wheel. The Dodge Nitro also featured driver and passenger’s floor mats. The logo was removed from the mats in Calibers with the 2009 model.
2012
For the 2012 model year, the models were renamed back to SE, SXT, and SXT Plus. The Plus version includes all the SXT items and 18-inch aluminum wheels with performance tires, as well as a 6-way power adjustable driver seat.[15]
Reception
In October 2013, Top Gear magazine placed the Caliber on its list of “The 13 worst cars of the last 20 years”, describing the car as “Kind of like Kid Rock in car form, although marginally less annoying.”
Discontinuation
The 2010 Caliber was the last model sold in Europe. The 2011 model ended production on November 23, 2011 in United States, with the remainder being sold as the 2012 model year Caliber in both U.S. and Canada. A successor called the Dart, based on the Alfa Romeo Giulietta‘s platform, went on sale in June 2012 as the compact vehicle in Dodge’s lineup.
- Charger (B-body) (1966–1978)
Dodge Charger (B-body)
| Dodge Charger | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1966–1978 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 2-door coupe |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | B-body |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Magnum |
The Dodge Charger is a mid-size automobile produced by Chrysler. The 1966–1978 Chargers were on the Chrysler B platform.
Origin of the Dodge Charger
During the early-1960s, automakers were exploring new ideas in the personal luxury and specialty car segments. Chrysler, fast to enter the specialty car market, selected their Dodge Division to enter the marketplace with a bigger model to fit between the “pony car” Ford Mustang and the “personal luxury” Ford Thunderbird. The intention was to use the B-body for a sporty car with fastback look while sharing as much of their existing hardware as possible.
The fastback Charger was introduced in mid-season of the 1966 model year “in retaliation to the AMC Marlin, Ford Mustang, and Plymouth Barracuda“, but even though based on the existing Coronet, “it was style-wise a complete departure from the Dodge’s mainstream cars.” The 1965 Rambler Marlin, along with the Dodge Charger that arrived during the 1966 model year, were “the two cars set the standard for radical fastback design in American mid-size automobiles.” According to Richard M. Langworth, “because it was an intermediate like the Rambler Marlin, the Charger could have been an aesthetic disaster, but long side windows prevented its sweeping roof from looking too heavy.”
Burt Bouwkamp, Chief Engineer for Dodge during the 1960s and one of the men behind the Dodge Charger, related his experience during a speech in July 2004.
- Lynn Townsend was at odds with the Dodge Dealers and wanted to do something to please them. So in 1965 he asked me to come to his office – for the second time. He noted that one of the Dodge Dealer Council requests was for a Barracuda type vehicle. The overall dealer product recommendation theme was the same – we want what Plymouth has. The specific request for a Mustang type vehicle was not as controversial to Lynn. His direction to me was to give them a specialty car but he said ‘for God’s sake don’t make it a derivative of the Barracuda‘: i.e. don’t make it a Barracuda competitor.
- So the 1966 Charger was born.
- “We built a Charger ‘idea’ car which we displayed at auto shows in 1965 to stimulate market interest in the concept. It was the approved design but we told the press and auto show attendees that it was just an “idea” and that we would build it if they liked it. It was pre-ordained that they would like it.”
First generation
| First generation | |
|---|---|
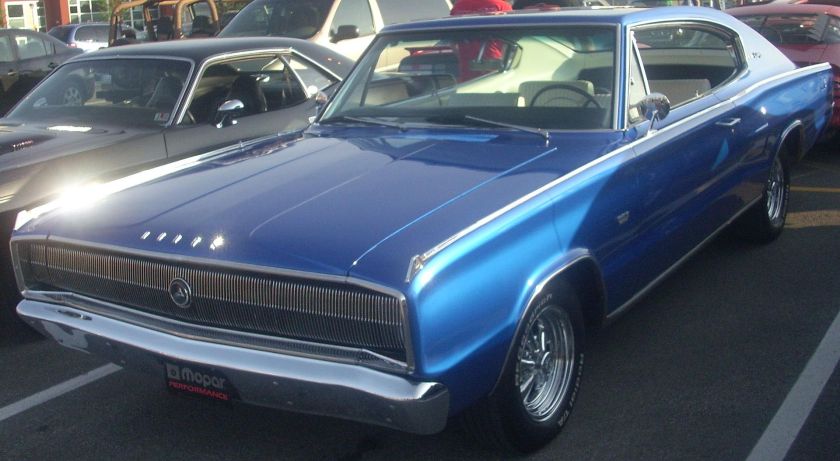 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1966–1967 |
| Assembly | United States: Detroit, Michigan(1966) Hamtramck, Michigan (1967) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Dodge Coronet Plymouth Belvedere Plymouth Satellite Plymouth GTX |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.2 L) 2bbl A V8 (1966) 318 cu in (5.2 L) 2bbl LA V8 (1967) 361 cu in (5.9 L) 2bbl B V8 (1966) 383 cu in (6.3 L) 2bbl B V8 (1967) 383 cu in (6.3 L) 4bbl B V8 426 cu in (7.0 L) 2×4bbl Hemi RB V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) 4bbl RB V8 (1967) |
| Transmission | A230 3-speed manual A833 4-speed manual TorqueFlite 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 117.0 in (2,970 mm) |
| Length | 203.6 in (5,170 mm) |
| Width | 75.8 in (1,930 mm) |
A “mid-1966 surprise was Dodge’s Coronet-based Charger fastback.” Sharing its chassis and front-end sheet-metal with the mid-sized Dodge Coronet, the Charger “still looked a lot like a Coronet or AMC’s conceptually similar Rambler Marlin … [and] substantially more expensive than either. The Charger with a $3,100 base price “was immediately paired up in the automotive press with American Motors’ year-old Marlin, another fastback specialty machine that came in at around $2,850” and some called the Charger “a good-looking Marlin.”
The Charger’s interior was different from all other cars with its back seats that folded down and created a station wagon or camper usefulness. “The Charger didn’t begin with the performance/ muscle car image, though you could get a Hemi with it.” The Charger evolved into possibly the top Chrysler-made muscle car.
The 1966 and 1967 model years of the Charger are also the only Dodge cars that displayed the Fratzog Emblem on the grill as well as the trunk hatch.
1966
On January 1, 1966, viewers of the Rose Bowl were first introduced to the new “Leader of the Dodge Rebellion”, the 1966 Charger. The Charger’s debut also followed by a half model year the introduction of a new street version of the 426 cu in (7.0 L) Chrysler Hemi engine. With the Charger, Dodge had a new model to build a performance image to go along with this engine.
Designed by Carl “CAM” Cameron, the Dodge Charger introduced a fastback roofline and a pot-metal “electric shaver” grille. The grille used fully rotating headlights (180 degree) that when opened or closed made the grille look like one-piece unit. Hidden headlamps were a feature not seen on a Chrysler product since the 1942 DeSoto. In the rear of the new Dodge, the fastback design ended over a full-width six-lamp taillight that featured chromed “CHARGER” lettering.
Inside, the standard Charger featured a simulated wood-grain steering wheel, four individual bucket seats with a full length console from front to rear. The rear seats and rear center armrest pad also folded forward while the trunk divider dropped back, which allowed for generous cargo room. Numerous interior features were exclusive to the Charger including door panels, courtesy lights, as well as premium trim and vinyl upholstery. The instrument panel did not use regular bulbs to light the gauges, but rather electroluminescence lit the four chrome-ringed circular dash pods, needles, radio, shifter-position indicator in the console, as well as clock and air conditioning controls if equipped. The dash housed a 0 to 6000 rpm tachometer, a 0 to 150 mph (240 km/h) speedometer, as well as alternator, fuel, and temperature gauges as standard equipment.
Engine selections consisted of only V8s, though a straight-six engine became standard by 1968. 1966 transmissions included a three-speed steering-column mounted manual with the base engine, a console mounted four-speed manual, or three-speed automatic. In 1966, four engines were offered: the base-model 318 cu in (5.2 L) 2-barrel, the 361 cu in (5.9 L) 2-barrel, the 383 cu in (6.3 L) 4-barrel, and the new 426 Street Hemi. Only 468 Chargers were built with the 426.
Total production in 1966 came to 37,344 units for the mid-model year introduction.
In 1966, Dodge took the Charger into NASCAR in hopes that the fastback would make their car a winner on the high-banks. However the car proved difficult to handle on the faster tracks because its body generatedlift. Drivers would later claim that “it was like driving on ice.” To solve this problem Dodge installed a small lip spoiler on the trunk lid that improved traction at speeds above 150 mph (240 km/h). This was made a dealer-installed option in late-1966 and in 1967 because of NASCAR rules (with small quarter panel extensions in 1967). The 1966 Charger was the first U.S. production vehicle to offer a spoiler. David Pearson, driving a #6 Cotten Owens-prepared Charger, went on to win the NASCAR Grand National championship in 1966 with 14 first-place finishes.
1967
The 1967 model year Charger received minor changes. Outside, new fender-mounted turn signals were introduced and this would serve as the main external identifier between a 1966 and 1967 Charger. A vinyl roof became available. Inside, the full length console was eliminated to satisfy customer complaints about the difficulty for entry and exit from the back seats. It was replaced with a regular sized console. Bucket seats were standard, but a folding armrest/seat and column shifter was an option allowing three people to sit up front.
The 440 “Magnum” was added and the 361 cu in (5.9 L) V8 was replaced by a 383 cu in (6.3 L) engine. The 440 was rated at 375 bhp (280 kW) with a single 4-barrel carburetor. The 318 two-barrel “LA” Chrysler LA engine was now the base engine with wedge-shaped combustion chambers, unlike the previous 1966 polyspherical (or “poly”) design, it was rated at 230 bhp (170 kW). The 383 4-barrel rated at 325 bhp (242 kW) and the 426 Street Hemi rated at 425 bhp (317 kW) remained as options. A mere 27 Chargers were built with the 426 engine.
Sales of the 1967 Chargers dropped to half of the previous introductory half-year with a total of 15,788 units. According to automotive historian Patrick Foster, both the AMC Marlin and the very similar looking first generation Dodge Charger “flopped on the market as sporty car buyers were showing their preference for compact pony cars.”
Second generation
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
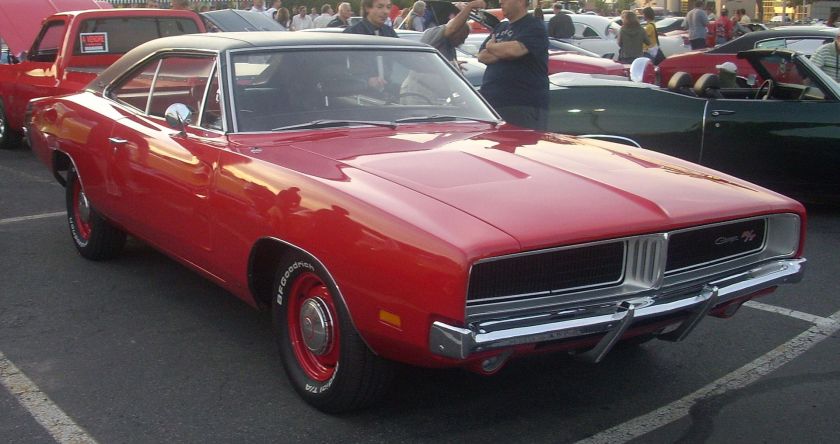 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1968–1970 |
| Assembly | United States: Detroit, Michigan Hamtramck, Michigan Los Angeles, California St. Louis, Missouri |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Dodge Coronet Plymouth Belvedere Plymouth Satellite Plymouth GTX Plymouth Road Runner |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) 1bbl I6 (1969-70) 318 cu in (5.2 L) 2bbl LA V8 383 cu in (6.3 L) 2bbl B V8 383 cu in (6.3 L) 4bbl B V8 426 cu in (7.0 L) Hemi 2×4bbl RB V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) 4bbl RB V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) 2×3 RB (1970) |
| Transmission | A904 3-speed automatic A727 3-speed automatic A230 3-speed manual A833 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 117 in (3,000 mm) |
| Length | 208 in (5,300 mm) (1968) 207.9 in (5,280 mm) (1969-70) |
| Width | 76.7 in (1,950 mm) (1968-69) 76.6 in (1,950 mm) (1970) |
| Height | 53.2 in (1,350 mm) (1968-69) 53.0 in (1,350 mm) (1970) |
1968
The entire B-body lineup for 1968 was redesigned and the Charger was further differentiated from the Dodge Coronet models. Designer Richard Sias developed a double-diamond coke bottle profile with curves around the front fenders and rear quarter panels. Front and rear end sheet metal was designed by Harvey J. Winn. The rear end featured a “kick up” spoiler appearance, inspired by Group 7 racing vehicles. On the roof, a “flying buttress” was added to give the rear window area a look similar to that of the 1966-67 Pontiac GTO. The Charger retained its full-width hidden headlight grille, but a vacuum operated cover replaced the electric motor rotating headlights. The previous full-width taillights were replaced with dual circular units at the direction of Styling Vice President, Elwood P. Engel. Dual scallops were added to the doors and hood.
Inside, the interior was new with a conventional fixed rear seat replacing the folding bucket seat design. The conventional trunk area included a vinyl mat, rather than the previous model’s carpeted cargo area. The center console in the front remained, but there was no center armrest. The tachometer was now optional instead of standard and the electroluminescent gauges disappeared in favor of a conventional design.
The standard engine was the 318 cu in (5.2 L) 2-bbl V8, until it was replaced in mid-year with a 225 cu in (3.7 L) slant-six. The 383-2 and 383-4 remained unchanged. A new high-performance package was added, the R/T (“Road/Track” with no ‘and’ between Road and Track). The R/T came standard with the previous year’s 440 “Magnum” and the 426 Hemi was optional.
In 1968, Chrysler Corporation began an ad campaign featuring a cartoon bee with an engine on its back featuring models called the “Scat Pack”. The Coronet R/T, Super Bee, Dart GTS, and Charger R/T received bumble-bee stripes (two thin stripes framing two thick stripes). The stripes were standard on the R/Ts and came in red, white, or black, but could be deleted at no extra cost.
The 1968 model year Charger sales increased to 96,100, including over 17,000 Charger R/Ts.
1969
There were two different 383 engines available in 1969: 2-barrel and 4-barrel. The 2-barrel was rated at 290 hp. The four barrel engine was rated at 330 hp and was identified by the “pie tin” on the air cleaner as “383 / FOUR BARREL”. The 330-hp engine was unique to the Charger model in 1969. While this engine was available with an un-silenced air cleaner option, it differed internally from the 335-hp 383 “Magnum”. In 1969 the B-series engines were all painted turquoise with the exception of the 383 four speed, 440 Magnum and 426 hemi which were painted Street Hemi Orange. The 335-hp 383 Magnum engines were also painted Street Hemi Orange. The 383 Magnum motor was used in Road Runners and Super Bees, but did not appear in a Charger body until 1971. Differences between the 330-hp 383 4-barrel and 335-hp 383 magnum were mostly internal. Both versions used the Carter AVS carb and the larger exhaust manifolds from the 440 magnum engines, but the magnum had a windage tray in the oil pan. The cams shaft profiles were different, as were the valve springs.
The 1969 model year brought few modifications. Exterior changes included a new grille with a center divider and new longitudinal taillights both designed by Harvey J. Winn. A new trim line called the Special Edition (SE) was added. This could be available by itself or together with the R/T, thus making an R/T-SE. The SE added leather inserts to the front seats only, chrome rocker moldings, a wood grain steering wheel, and wood grain inserts on the instrument panel. A sunroof was added to the option list, but was ordered on only 260 Chargers. The bumble bee stripes returned as well, but were changed slightly. Instead of four stripes, it now consisted of a wide stripe framed by two smaller stripes. In the middle of the stripe, an R/T cutout was placed. If the stripe was deleted, a metal R/T emblem was placed where the R/T cutout was. Total production was around 89,199 units.
The television series The Dukes of Hazzard (1979–1985) featured a 1969 Dodge Charger that was named The General Lee. “The General” sported the Confederate battle flag painted on the roof and the words “GENERAL LEE” over each door. The windows were always open, as the doors were welded shut. The number “01” is painted on both doors. Also, when the horn button was pressed, it played the first 12 notes from the de facto Confederate States anthem “Dixie“. The car performed spectacular jumps in almost every episode, and the show’s popularity produced consumer interest in the car.
Charger 500
In 1968, the NASCAR inspired Charger R/T failed to beat the Ford cars (the Ford Torino Talladega and the Mercury Cyclone Spoiler II) on the high-banks oval-tracks. Wind tunnel tests showed the tunneled rear window caused lift and the gaping mouth induced drag. As a result, Dodge made the rear window flush with the rest of the roof and put a 1968 Coronet grille in the front.
The original Charger 500 prototype was a 1968 Charger R/T with a 426 Hemi and automatic transmission. The prototype was painted in B5 Blue with a white stripe, as well as a white interior. The Charger 500 was one of three models introduced in September 1968. Standard engine was the 440 Magnum, but factory literature claims the 426 Hemi was standard. The Charger 500 had the Torqueflite standard and the same equipment standard as the R/T.
A total of 500 Charger 500s were made, of which only 67 had the 426 Hemi engine; 27 with a 4-speed and 40 with an automatic transmission.
Charger Daytona
Dodge was not satisfied with the results of the Charger 500. The car was not enough to beat the other aerocars on the NASCAR circuit. After months of research and development, including at the aftermarket shop, Creative Industries, the Dodge Charger Daytona was introduced on April 13, 1969. It quickly received over 1,000 orders.
Chrysler made many attempts at improving the aerodynamics of the 500 by adding noses rumored to be up to 23 in (580 mm) long. The Charger Daytona finally received an 18 in (460 mm) nose. The full size Charger Daytona was tested with an 18 in (460 mm) nose at the Lockheed-Martin Georgia facility. The test was a success and the project was greenlighted. The nose piece was only part of the innovation. The Charger Daytona also received a 23 in (580 mm) tall wing in rear. This wing was bolted through the rear quarter panels and into the rear subframe. Although proven to be less effective than shorter wing designs, the tall wing was considered necessary to avoid interfering with operation of the trunk lid. The tall wing also helped out in an unintended way, by giving the car directional stability due to its deeply splinted sides.
The Charger Daytona engineering model was tested on the Chelsea, Michigan Chrysler Proving Grounds on July 20, 1969. Driven by Charlie Glotzbach and Buddy Baker, it was clocked at 205 mph (330 km/h) with a small 4-bbl. carb. The Charger Daytona’s nose made 1,200 pounds of downforce and the wing made 600 pounds of downforce. The Dodge styling department wanted to make changes to the Charger Daytona as soon as they saw it, but was told by Bob McCurry to back off; he wanted function over finesse.
The Charger Daytona introduced to the public had a fiberglass nose without real headlamps and a wing without streamlined fairings. The media and public loved the car, but were mystified by the reverse scoops on the front fenders. The PR representatives claimed it was for tire clearance. Actually, they reduced drag 3%.
The Charger Daytona came standard with the 440 Magnum Engine with 375 hp (280 kW) and 480 lb·ft (650 N·m) of torque, A727 Torqueflite Automatic Transmission, and a 3.23 489 Case 8 3/4 Chrysler Differential. Optional was the 426 Hemi with 425 hp (317 kW) and 490 lb·ft (660 N·m). The 426 Hemi was also available with the no cost option of the A833 4-Speed Manual. Only 503 Charger Daytonas were built, 433 were 440 Magnum 139 4-Speed and 294 Torqueflite; 70 were 426 Hemi power, 22 4-Speed and 48 Torqueflite.
In the end, the Daytona was brought down by the decision to make the 1970 Plymouth Superbird the only Chrysler winged car for the model year. While Daytonas were raced through the 1970 season, only one Daytona was raced until 1971 (in the 1971 Daytona 500) when NASCAR decreed that engine displacement of wing cars would be limited to 305 cu in (5.0 L). That particular car, driven by Dick Brooks finished in seventh place.
1970
In 1970, the Charger was changed slightly. This would be the last year of the 2nd generation Charger and featured a large wraparound chrome bumper and the grille was no longer divided in the middle. New electric headlight doors replaced the old vacuum style. The taillights were similar to those used in 69, but 500 and R/T models came with a new more attractive taillight panel. On the R/T, new rear-facing scoops with the R/T logo were mounted on the front doors, over the door scallops. A new 440 or HEMI hood cutout made the option list for this year only.
Dodge painted the hood scallop inserts black and put the silver engine callouts on top. New “High Impact” colors were given names, such as Top Banana, Panther Pink, Sublime, Burnt Orange, Go Mango and Plum Crazy (sometimes nicknamed “Statutory Grape”). The 500 returned for another year, but as a regular production Charger.
Interior changes included new high-back bucket seats, the door panels were also revised and the map pockets were now optional instead of standard. The ignition was moved from the dash to the steering column (as with all Chrysler products this year), and the glove box was now hinged at the bottom instead of the top as in 1968-69. The SE “Special Edition” trim option added luxury features and was available in as the 500 SE and R/T SE models. The all new pistol grip shifter was introduced, along with a bench seat, a first for the Charger since its debut.
A new engine option made the Charger’s list for the first time, the 440 Six Pack. With three two-barrel carburetors and a rating of 390 hp (290 kW), it was one of the most exotic setups since the cross-ram Max Wedge engines of the early 1960s. The Six Pack was previously used on the mid-year 1969 Dodge Super Bee and Plymouth Road Runner. Despite this new engine, production slipped again to 46,576 mainly due to the new E-body Dodge Challenger pony car, as well as rapidly increasing automobile insurance rates. In the 1970 NASCAR season, the 1970 Charger had ten wins, more than any other car, including the 1969 Dodge Charger Daytonas and Plymouth Superbirds, thus giving Bobby Isaac the Grand National Championship.
Third generation
| Third generation | |
|---|---|
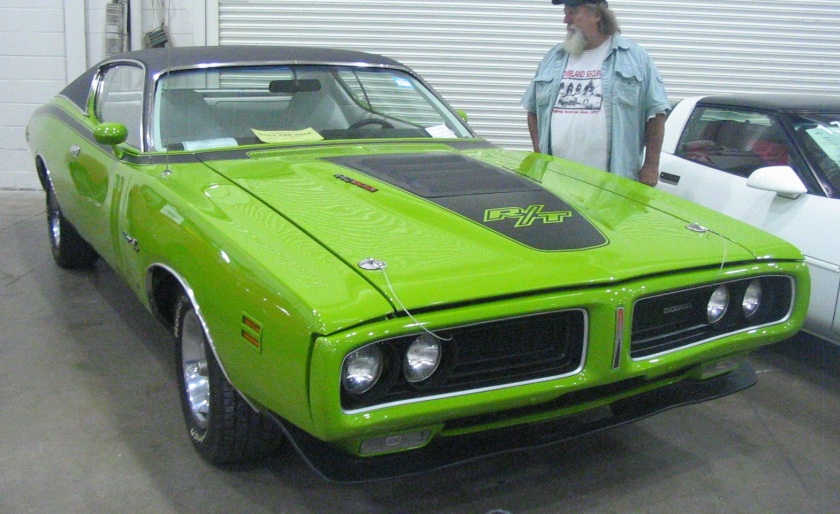

1971 Dodge Charger
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1971–1974 |
| Assembly |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 115.0 in (2,921 mm) |
| Length | 205.0 in (5,207 mm) |
| Height | 53.0 in (1,346 mm) |
1971
The 1971 model year introduced a new third generation Charger that was characterized by a new split grille and more rounded “fuselage” bodystyle. The interiors were like those of the E-body and were now shared by the Plymouth B-body, the Plymouth Satellite Sebring and Road Runner. The hidden headlights were now optional. A rear spoiler and a “Ramcharger” hood were new options. This hood featured a pop-up scoop mounted above the air cleaner controlled by a vacuum switch under the dash. On Plymouth Road Runners it was called the “Air Grabber” hood, and it was previously used on the Coronet R/T and Super Bee.
Dodge also merged its Coronet and Charger lines. From 1971, all four-door B-bodies were badged as Coronets and all two-door B-bodies as Chargers. Thus for one year only, the Charger Super Bee became part of the Charger lineup. From 1971 to 1974, Charger models used the Coronet’s VIN prefix of “W”.
The Dodge Super Bee made the move from the Coronet line to the Charger line for 1971 only, after which this model was discontinued. Several other models were carried over from 1970, including the 500, R/T, and SE. Sales of the R/T declined due in part to higher insurance costs. A total of 63 Hemi versions were built, and 2,659 were built with other engines that year. Increasing insurance rates, combined with higher gasoline prices, reduced sales of most muscle cars and 1971 was the last year of availability for the 426 Hemi “Elephant engine” in any car. The 1971 model year was the last for the 440 Six-Pack engine (although some early Dodge literature (August 1971 press) stated that this engine was available for 1972. However, a few factory installed six-pack Chargers and 6BBl Road Runners were built early in the production run). In the Super Bee’s final year, the 340 became a $44 option over the standard, low-compression 383 .
The “Hi-Impact” colors were discontinued after the 1971 model year; with a 1971-only “Citron Yella”.
1972
The 1972 Charger introduced a new “Rallye” option to replace the R/T version. The SE was differentiated from other 1972 Chargers by a unique formal roof treatment and hidden headlights. The 383 engine was replaced with a lower compression 4-barrel 400, while the 440 engine were still available, rated at net 280 hp (209 kW; 284 PS) rating instead of the previous 350 hp (261 kW; 355 PS) gross values. The ratings went down as the net horsepower measure was more realistic. Also beginning in 1972, all engines featured hardened valve seats to permit the use of regular leaded or unleaded gasoline rather than leaded premium fuel as in past years due to tighter emissions regulations. Though the 440+6 (designating a triple 2-barrel carb setup and 310 bhp (231 kW; 314 PS) was listed in the early 1972 sales literature, it was found in the August 1971 testing that this engine would not meet the new and more stringent 1972 emissions laws. The low-compression 4-barrel 440 Magnum 280 hp (209 kW; 284 PS) with a 4-barrel carburetor became the top engine, and the optional Pistol-Grip 4-speed Hurst manual shifter could be coupled to the 340, 400, and 440 Magnum engines. The Ramcharger hood scoop was discontinued, as well as elimination of optional lower geared performance rear axle ratios and extra heavy duty suspensions. It was also the final year for the Dana 60 differential, and was available only in combination with the 440/4 speed, heavy duty suspension, and the 3.54:1 rear axle ratio.
The only remaining “Hi-Impact” color choices were “Hemi Orange” (EV2) and “Top Banana” (FY1), the latter was available under different names through 1974.
1973

For 1973, the Chargers received new sheet metal (though at first glance only the rear roof “C-Pillars” looked different) and were in fact longer, wider, and slightly taller than the 1971-72 cars. Also new were vertically slatted taillights and new grills. Hidden headlights were dropped, even as an option. The 318 was still standard, with the 340 (available only on the Rallye), 360 (2-barrel only), 400 (low power 2-barrel/single exhaust and high performance 4-barrel/dual exhaust) and 440 remaining as options. The SE models had a new roof treatment that had a “triple opera window” surrounded by a canopy-style vinyl roof. All other models had a new quarter window treatment, discontinuing its AMC Gremlin-style window in favor of a more conventional design. Total sales this year were around 108,000 units, the highest ever for the 1971-74 Charger generation, though more than 60 percent of the cars had the non-high performance engines. The 1973 Chargers, and all Chrysler products, were equipped with 5 mph bumpers, front and rear.
1974
The 1974 model year saw only minor changes that included new color choices, a softer grain pattern on interior surfaces, and a slight increase in the size of the rubber bumper tips. The 340 option was dropped and the 360 4-bbl replaced the 340 as the small block performance engine. All other engine options remained the same. Several performance rear end ratios, including a 3.23 “Sure Grip” rear end were still available. A four speed transmission was still an option except with the 440 engine. Emphasis now turned to luxury instead of performance with higher sales for the SE model. The Charger, was no longer considered a performance model as it turned into a personal luxury car. The muscle car era came to a close, and the 1974 Dodge Charger would be the final year. The 1974 also came with a 360 cu in (5.9 L) 2-bbl V8, with a K in the fifth symbol in the vehicle identification number.
The 1971-74 Chargers were campaigned in NASCAR, with Buddy Baker, Bobby Isaac, Dave Marcis, and Richard Petty scoring several wins. Richard Petty won 25 races with this body style between 1972 and 1977 as NASCAR allowed the Chargers to run a few years longer than normal, as Chrysler did not have anything else to replace it. A 1974 bodied Charger driven by Neil Bonnett scored Dodge’s last NASCAR victory (until 2001) at the December 1977 Los Angeles Times 500. Richard Petty has proclaimed this body style as his favorite car that he ran during his career.
Fourth generation
1975
| Fourth generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1975–1978 |
| Assembly | United States: Detroit, Michigan Hamtramck, Michigan St. Louis, Missouri |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Dodge Coronet Chrysler Cordoba Plymouth GTX Plymouth Fury |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 3-speed manual 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 115.0 in (2,921 mm) |
| Length | 216.0 in (5,486 mm) |
| Height | 52.0 in (1,321 mm) |
In 1975, the Dodge Charger and Chrysler Cordoba shared the same all new body based on the B platform. The Chrysler Cordoba had replaced the Plymouth Satellite Sebring. The Charger SE (Special Edition) was the only model offered. It came with a wide variety engines from the 318 cu in (5.2 L) “LA” series small block V8 to the 400 cu in (6.6 L) big block V8. The standard engine was the 360 cu in (5.9 L) small block. Sales in 1975 amounted to 30,812. Because of the extreme squareness of the bodystyle, NASCAR teams were forced to rely on the previous years (1974) sheetmetal for race-spec cars. In order for Dodge to be represented, NASCAR allowed the 1974 sheetmetal to be used until January 1978, when the new Dodge Magnum was ready for race use. In 1976 a Dodge Charger was one of two NASCAR stock cars to compete in the 24hrs at LeMans, having been modified with head-lamps, tail-lamps and windshield wipers. It was driven by Herschel and Doug McGriff and sponsored by Olympia Beer, earning the nickname “Oly Express”.
1976
In 1976, the model range was expanded to four models; base, Charger Sport, Charger SE and the Charger Daytona. The base and Sport models used a different body than the SE and Daytona, and were essentially a rebadging of what had been the 1975 Dodge Coronet 2-door models — and available with a 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant Six, which was not offered on the SE and Daytona. The Charger Daytona was introduced as an appearance package with either the 360 or 400 engine. Sales increased slightly to 65,900 units in 1976.
1977
In 1977, the base Charger and Charger Sport were dropped as this body style became part of the newly named B-body Monaco line, and only the Charger SE and Charger Daytona were offered. Sales dropped to 36,204.
1978
In 1978, its final year as a B-Body, only 2,735 Chargers were produced. Charger sold in the same market segment as the Magnum that also was a B-body car.
- (Shelby) Charger (L-body) (1983–1987)
- Colt (1971–1994)
Dodge Colt
| Dodge Colt | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi Motors |
| Also called | Plymouth Champ Plymouth Colt Eagle Summit Plymouth Cricket |
| Model years | 1971–1994 |
| Assembly | Kurashiki, Okayama, Japan |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact (1971–1979) Subcompact (1979–1994) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge/Plymouth Neon Eagle Summit (For sedan, U.S. only) |
The Dodge Colt and the similar Plymouth Champ and Plymouth Colt, were subcompact cars sold by Dodge and Plymouth from 1970 (MY1971) to 1994. They were captive imports from Mitsubishi Motors, initially twins of the rear-wheel drive Galant and Lancer families before shifting to the smaller front-wheel drive Mitsubishi Mirage subcompacts in 1979. With the 1994 introduction of the Dodge/Plymouth Neon, Chrysler felt no need to continue selling captive imports under these badges, although the Eagle Summit (also a Mirage clone) continued to be available until 1996.
First generation
| First generation | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Colt Galant Mitsubishi Galant Plymouth Cricket (CDN) |
| Production | 1971–1973 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 2-door hardtop (pillarless coupe) 4-door sedan 5-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L 4G32 I4 |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,420 mm (95 in) |
Introduced in 1970 as model year 71, the first generation Dodge Colt was a federalized first generation Mitsubishi Colt Galant. Available as a two-door pillared coupe, two-door hardtop, 4-door sedan, and 5-door wagon, the Colt had a 1,597 cc (97.5 cu in) four-cylinder engine. The unibody layout was traditional, front engine and rear-wheel drive withMacPherson struts in front and a live rear axle. Standard transmission was a four-speed manual, with a three-speed automatic being an option. The engine initially produced 100 hp, but this dropped to 83 in 1972 when stricter emissions standards took effect. For 1973 a sporty GT hardtop coupe was added, featuring rally stripes, sport wheels and a center console amongst other features. The Dodge Colt was originally intended to be Chrysler’s answer to the AMC Gremlin, Ford Pinto and Chevrolet Vega but because it came from Mitsubishi and was not a true Chrysler product, the first Colts actually competed more directly with Japanese imports, such as the Toyota Corolla and Datsun 510.
Second generation
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Galant Chrysler Galant/Valiant Galant (AUS) Plymouth Colt (CDN) Plymouth Cricket (CDN) |
| Production | 1974–1977 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | FR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,420 mm (95 in) |
Based on the underpinnings of the first generation model, Galant sedans and coupes received a new, somewhat rounder body in 1973, while wagons continued with the old body and new nose. The new version, with single headlights rather than the doubles of the previous generation, became the 1974 Dodge Colt in the US, available in the same bodystyles as the first one. The base engine also remained the same, but a larger G52B “Astron” engine became optionally available (standard in the GT coupe). This one developed 96 hp at 5,500 rpm. Ratings varied from 79-83 hp for the smaller one and 89-96 hp for the larger engine in different publications.
A four-speed manual or three-speed automatic remained available, but for 1977 a five-speed became available (standard in the GT and Carousel coupes). The Carousel, introduced in 1975 along with larger bumpers, was more luxurious and carried a blue and white paintjob. For 1977, the “Silent Shaft” version of the smaller engine became available, and was fitted as standard equipment in GT and Carousels. The introduction of the new Dodge Colt “Mileage Maker” meant there was a mix of second and third generation models in 1977. Second generation 2-door hardtops and wagons continued alongside 2- and 4-door “Mileage Makers”. The wagon was also available with an “Estate” package, including wood grain applique and adjustable reclining seats.
Third generation
| Third generation “Mileage Maker” | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Lancer Plymouth Colt |
| Production | 1977–1979 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L 4G32 I4 |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,340 mm (92 in) |
| Third generation wagon | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Galant Sigma Chrysler Sigma Mitsubishi Sigma, Colt Sigma |
| Production | 1978–1981 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 5-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Related | Mitsubishi Galant Lambda Dodge Challenger |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 2,515 mm (99 in) |
The third generation Dodge Colt was effectively made up of two lines: coupes and sedans were of a smaller, Lancer-based series, while the Wagons were based on the new Mitsubishi Galant Sigma. In late 1976, for the 1977 model year, the smaller A70-series Mitsubishi Lancer became the Dodge Colt, with two-door coupe and four-door sedan bodies. While the wheelbase was only slightly shorter than that of the second generation Colt, overall length was down from 171.1 to 162.6 inches (4,346 to 4,130 mm). The new Colt was also referred to as the Dodge Colt “Mileage Maker” to mark it as different from its larger predecessor. Second generation Coupe and Wagon versions remained for the 1977 model year.
The engine was the familiar 4G32 iteration of Mitsubishi’s Saturn engine family, of 1,597 cc and still with 83 hp at 5,500 rpm. A “Silent Shaft” (balance shaft) version of this engine along with a five-speed manual transmission (instead of the standard four speeds) were part of a “Freeway Cruise” package, which also included a maroon/white paintjob. For ’78 power dropped to 77 hp with the introduction of the “MCA-Jet” high-swirl system.
For 1978 a new, larger Dodge Colt Wagon arrived, a rebadged Mitsubishi Galant Sigma. It came with the same 1.6-litre MCA-Jet four as the smaller sedans and coupes, but a 2.6-litre, 105 hp (78 kW) Astron engine was an option. While the last year for the Lancer-based Colts was 1979, the wagon lingered on alongside the front-wheel drive Mirage-based fourth generation until 1981 when it was effectively replaced by the domestic Dodge Aries K wagon.
Fourth generation
| Fourth generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Mirage/Colt Mitsubishi Lancer Fiore Plymouth Colt Plymouth Champ |
| Production | 1978–1984 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback 5-door hatchback |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.4 L 4G12 I4 1.6 L 4G32 I4 1.6 L 4G32T turbo I4 |
From late-1978 for model year 1979, the Dodge Colt and Plymouth Champ nameplates were applied to the front-wheel-drive Mitsubishi Mirage imports into North America. The Colt and Champ (Plymouth Colt after 1982) was a 3-door hatchback, and came in Standard or Custom equipment levels. These imports used a 70 hp Mitsubishi Orion 4G33 1.4-liter overhead-cam, four-cylinder engine at first, which received the highestUnited States Environmental Protection Agency fuel economy rating in its debut year. This engine was joined by the 1.6-liter 4G32 Saturn engine (80 hp) at the end of the year. There were three manual transmissions and one automatic transmission available. There was a KM110 four-speed manual transmission, or a novel “Twin Stick” (Mitsubishi Super Shift) version of the transmission that used a two-speed transfer case to give 8 forward and 2 reverse speeds. There was also the option of a KM119 five-speed manual transmission or a TorqueFlite three-speed automatic transmission.
| Colt US Sales[5] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | 3-door | 5-door |
| 1979 | 60,521 | — |
| 1980 | 83,711 | — |
| 1981 | 84,144 | — |
| 1982 | 52,355 | 22,675 |
| 1983 | 46,479 | 27,192 |
| 1984 | 44,724 | 19,657 |
For 1982 a five-door hatchback joined the lineup. The names of the equipment levels changed to “E” and “DL”. At some point claimed power dropped to 64 and 72 hp respectively for the small and large engines, while the 1.6 was only available with the automatic transmission. In August 1983, for the 1984 model year (which was to be the last year of this model of Colt), the GTS Turbo model arrived along with a naturally aspirated GTS package. Unique for North America – the turbocharged Colt/Mirages sold elsewhere had a 1.4-litre engine – this used the fuel-injected 1.6-litre 4G32T engine also seen in the next-generation Colt, providing 102 hp (76 kW) at 5500 rpm and considerable performance. It, too, featured the eight speed Twin Stick transmission and also received ventilated brakes in front. Both GTS models, available with three-door bodywork only, received a larger 13.2 US gal (50 L) gas tank rather than the E and DL’s 10.6 US gal (40 L) tank.[9] They also featured a sporty appearance with uprated suspension, blacked out trim details, and a sizable front air dam.
Fifth generation
| Fifth generation | |
|---|---|

1987-1988 Dodge Colt three-door
|
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Mirage Mitsubishi Colt Mitsubishi Lancer Eagle Vista (CDN) Plymouth Colt |
| Production | 1984–1988 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Front engine, front-wheel drive /four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 4/5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 93.7 in (2,380 mm) |
| Length | Hatch: 157.3 in (3,995 mm) Sedan: 157.3 in (3,995 mm) |
| Width | 63.8 in (1,621 mm) |
| Height | 50.8 in (1,290 mm) |
In 1984, the fifth generation Dodge/Plymouth Colt appeared (model year 1985). A carbureted 68 hp 1468 cc four was the base engine, while the upscale Premier four-door sedan and GTS Turbo models received the 4G32BT turbocharged 1.6-litre already seen in the last model year of the previous Colts. A first for FWD Colts was the availability of a three-box sedan body, though this was no longer available after 1986. From 1988 (and lasting until 1991), this car was also marketed as the Eagle Vista in Canada. There was also a five-door minivan/station wagon called the Dodge/Plymouth “Colt Vista”; this was simply a rebadged Mitsubishi Chariot.
Early cars have small rectangular headlights in black inserts, while later models received more aerodynamic, flush-fitting units. The lowest priced model was the “E” (for Economy), followed by the “DL” and topped by the turbocharged (but shortlived) Premier and GTS Turbo.
The Colt Wagon, while never available with the turbocharged engine, did receive a more powerful 1,755 cc engine in the four-wheel-drive version. Unlike the FWD version, the DL 4×4 was not available with an automatic transmission. While the Hatchback Colts were replaced for 1989, the Colt Wagon continued to be available until the 1991 introduction of the Mitsubishi RVR-based Colt Wagon, which also replaced the Colt Vista. This car was also marketed as the Eagle Vista Wagon in Canada.
Sixth generation
| Sixth generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Mirage/Lancer Plymouth Colt Eagle Summit |
| Production | 1989–1992 |
| Assembly | Kurashiki, Okayama, Japan(Hatchback) Normal, Illinois (Sedans) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback 4-door sedan |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.5 L 4G15 I4 1.6 L 4G61 I4 1.6 L 4G61T turbo I4 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 4-speed manual 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 93.9 in (2,385 mm) |
| Length | 158.7 in (4,031 mm) |
| Width | 65.5 in (1,664 mm) |
| Height | 52.0 in (1,321 mm) |
In 1989, the Eagle Summit joined the array of nameplates describing the Mitsubishi Mirage.
Since the demise of the Dodge Omni/Plymouth Horizon in 1990, the Colt was the only subcompact in the Dodge and Plymouth lineups. The Colt sedan was not sold in the United States for the sixth generation (though it was sold in Canada), as it would be replaced by the Dodge Shadow/Plymouth Sundance liftbacks in the Dodge/Plymouth lineup for 1989. In Canada only the Eagle Vista, a carryover model that replaced the Colt sedan continued when the Colt underwent a redesign. The sedan bodywork was available to American consumers as an Eagle Summit however, and the Dodge/Plymouth Colt sedans returned for 1993-94 as a variant of the next generation Eagle Summit. The Dodge/Plymouth Colt, Eagle Summit, and Mitsubishi Mirage of this generation used a 1.5 or 1.6-litre inline-four engine.
A model powered by the 1.6-litre 4G61T 135 hp (101 kW) turbocharged four-cylinder was produced for the 1989 model year only. There are a rumored 1500 of these special editions to have been produced. The engine was only offered in the Mirage and the Colt GT Turbo, which were distinguished by their ground effects and spoilers (although these parts were also available for a price as add-ons to other model ranges) and by their extra features not normally found on base model ranges such as power seats, power windows, power locks, and power mirrors, special colored interior and seats, as well as a 150 mph/9000 rpm gauge cluster. The Turbo Colt/Mirage Turbo was one of Car and Driver magazine’s Ten Best for 1989. A naturally aspirated version of this engine was available for the following years Colt GT, with power down to 113 hp.
Power of the 1.5-litre 4G15 was up to 82 hp (61 kW) thanks to multi-point fuel injection. Top speed was 160 km/h (99 mph).
The Colt Wagon was redesigned in 1991, now based on the RVR, and continued in production until the 1996 model year.
Seventh generation
| Seventh generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Mitsubishi Mirage Eagle Summit Plymouth Colt |
| Production | 1993–1994 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 3-door van (see Mitsubishi RVR) |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Related | Mitsubishi Lancer |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.5 L 4G15 I4 1.8 L 4G93 16V I4 |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 3/4-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | Sedan: 98.4 in (2,499 mm) Coupe: 96.1 in (2,441 mm) |
| Length | Sedan: 174.0 in (4,420 mm) Coupe: 171.1 in (4,346 mm) |
| Width | Base: 66.1 in (1,679 mm) ES: 66.5 in (1,689 mm) |
| Height | Sedan: 51.4 in (1,306 mm) Coupe: 51.6 in (1,311 mm) |
The seventh generation of the Colt was the same as Plymouth’s version, and also the same as the Eagle Summit. As usual, they were all simply badge-engineered versions of the Mitsubishi Mirage/Lancer. The two-door coupe bodystyle was unique to the North American market, where hatchbacks are generally unpopular and space is rarely a concern. There was no hatchback version of the seventh generation Dodge/Plymouth Colt. Originally available in Base and GL versions, the ES (with supposedly more sporting intentions) was added later.
1.5 and 1.8 litre four-cylinder engines were used, with the larger engine originally only available to four-door Colts. While the sporting variants offered in the sixth generation were not renewed, the two-door ES was available with the more powerful sixteen-valve SOHC 1.8 for the 1994 model year. The smaller engine has 92 hp (69 kW) while the larger version has 113 hp (84 kW). The previous Colt Wagon (Mitsubishi RVR) continued to be sold until 1996, while the Dodge Colt was replaced by the new Neon after the 1994 model year.
Sports
Not unlike the related Mirage, the Colt and other similar vehicles were well utilized in rallying, both in the United States and abroad. The Colt was the most widely utilized of these variants, appearing in events through the 1970s and 1980s. A Colt was run to a third-place finish in the first ever Sno*Drift rally in 1973, and repeated the feat the following year, as well as a third time in 1982.
Related versions
The Plymouth Cricket nameplate was used (in addition to Dodge Colt) on Galants sold in Canada between mid-1973 and 1975, after Chrysler stopped using the Plymouth Cricket name for a rebadged Hillman Avenger-based model sourced from the United Kingdom (and sold across North America between 1971 and 1973).
The Plymouth Arrow was offered from 1976 to 1980 as a rebadged version of the Mitsubishi Lancer Celeste, not to be confused with the rebadged Mitsubishi truck sold as the Plymouth Arrow starting in 1979.
- Coronet (1949–1959, 1965–1976)
Dodge Coronet
| Dodge Coronet | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1949–1976 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size (1949–1959) Mid-size (1965–1976) |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Monaco (Downsized) |
The Coronet was a full-size car from Dodge in the 1950s, initially the division’s highest trim line but, starting in 1955, the lowest trim line. In the 1960s, the name was transferred to Dodge’s mid-size entry.
First generation (1949–1952)
| First generation | |
|---|---|
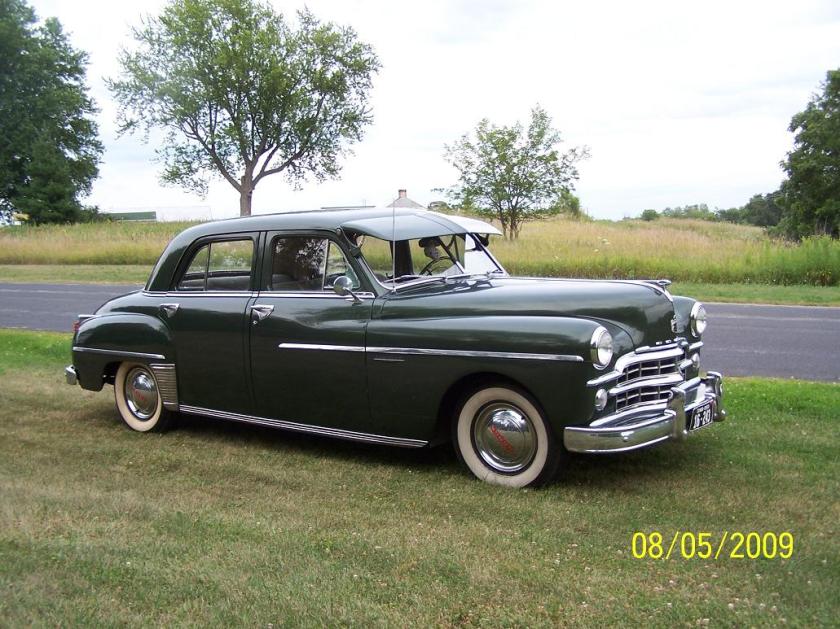 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1949–1952 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 2-door hardtop 4-door sedan 4-door limousine (8 passenger) 4-door station wagon |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 230 cu in (3.8 L) 103hp I6 |
| Transmission | “Gyromatic or Fluid drive” |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 123.5 in (3,137 mm) |
| Length | 203.6 in (5,171 mm) (1949) 202.8 in (5,151 mm) (1950) |
| Width | 74″ |
1949
The Dodge Coronet was introduced with the division’s first postwar body styles. Lower trim lines were the Wayfarer and Meadowbrook. The only engine for Dodge was a 230-cubic-inch (3,800 cc) flat-head straight six cylinder engine with a single barrel Stromberg carburetor, producing 103 horsepower (77 kW) (gross). The stock Dodge Coronet was a smooth running car, and the six-cylinder engine could power the car to 90 miles per hour (140 km/h)+ . A limited production model was a four-door, eight passenger limousine, an extended version of the stock Dodge Coronet. One of the most notable features of the first-generation Coronet was a three-speed, fluid-driven transmission that was operated by a foot pedal on the floor. It required no shifter. It had full instrumentation.
1950
Dodge received a facelift for 1950 but like the 1949 models were still divided into Wayfarer, Meadowbrook and Coronet lines. The 1950 models can be identified easily by the new grille design which featured 3 heavy horizontal bars. The upper and lower bars formed a stylish oblong shape. Within this oblong grille was a thick center bar with parking lights on each end and a large chrome plaque in the center bearing the Dodge crest. The 8-passenger sedan’s length was 216.8 inches.
1951–1952
Dodge received yet another facelift in 1951 but this time the cars remained virtually unchanged for two model years. Busy manufacturing military vehicles for use in Korea, they chose not to dedicate valuable resources to completely redesign civilian vehicles. Still divided into Wayfarer, Meadowbrook and Coronet lines through 1952, by 1953 the Wayfarer line had been discontinued. The grille of the 1951–52 model was similar in shape to the 1950 grille, but with the elimination of the thick vertical center bar and the addition of six vents running horizontally between the top and center bars, a whole new look was achieved. The Coronet Diplomat was Dodge’s first hardtop-convertible, featuring a pillarless steel roof styled after the contemporary Chrysler Newport. The speedometer was now circular, and the other four gauges were rectangles.
Second generation (1953–1954)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Model years | 1953–1954 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupe |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 241 cu in (3.9 L) V8 230 cu in (3.8 L) I6 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual Gyrol fluid Drive Gyro-Torque Drive |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 119 in (3,023 mm) |
| Length | 201.4 in (5,116 mm) |
1953
For 1953, the Coronet was totally redesigned. It gained an optional 241 cu in (3.9 L) “Red Ram” Hemi Engine and set over 100 land speed records at the Bonneville Salt Flats. The windshield became one-piece. Electric windshield wipers were standard, while the radio cost $83.
1954
The Dodge Royal line was added above the Coronet in 1954. Dodge was putting more luxury into all of its models which included the Meadowbrook, Coronet and new Royal lines. Still, styling changes for 1954 were modest. The chrome molding on the hood lip was wider than on the 1953 models and a large chrome upright in the center of the grille replaced the five vertical dividers used previously. It still came with full instrumentation. 1954 saw Chrysler’s first fully automatic transmission, two-speed PowerFlite, offered as an extra-cost option on all Dodges.
Third generation (1955–1956)
- See also 1955 Dodge
The 1955 Coronet dropped to the lower end of the Dodge vehicle lineup, with the Wayfarer and Meadowbrook names no longer used and the Dodge Custom Royal added above the Dodge Royal, Dodge Lancer,Dodge La Femme . Bodies were restyled with help from newly hired Virgil Exner to be lower, wider, and longer than the lumpy prewar style, which in turn generated a healthy boost in sales over 1954. Power came from either a 230 cu in (3.8 L) Chrysler Flathead engine straight-6, now producing 123 hp (92 kW) Two v8 were offered 270 cu in (4.4 L) Polyspheric (poly or semi-hemi) heads V8 175 hp (130 kW) and Hemi engine 315 cu in (5.2 L) (the “Hemi“) Power windows were new. Wheelbase was 120 inches. They were 212.1 inches long. A number of trim lines were available:
- 2- or 4-door station wagon — The Coronet wagon used the Suburban name and had the V8 or Six.
- hardtop coupé — The V8 Coronet Lancer
- 2- or 4-door sedan — V8 or Six
- 2-door sedan — V8 or Six
- 4-door, eight-passenger limousine
1956 (:See also Plymouth Fury) was the last year of this body style before the change in 1957, the only differences offered in 1956 from ’55 were trim packages and the new Dodge D-500. The D-500 was the first Dodge factory high performance made in honor of the (D-500-1) “Super Stock” model with the only external clues being discreet crossed checkered flags and “500” lettering on its hood and lower rear deck it was also available for order from the dealer on Coronet models, including station wagons and two-door sedans. The standard D-500 trim included a 315 cid V8 with hemispherical heads (unlike other Dodge V8s ( List of Chrysler engines) which used Polyspheric heads), a unique camshaft, valve lifters, pushrods, carburetor, ignition, and pistons. With a compression ratio of 9.25:1, four-barrel Carter WCFB carburetor, and dual-point distribution, peak horsepower was 260 bhp (190 kW) while torque was a solid 330 lb·ft (450 N·m). The D-500 also received an upgraded suspension with very stiff front coil springs; heavy duty Oriflow shock absorbers, with the same valving specified for Dodge police cars, were mounted in the springs. Similar units were used in the rear. Overall height of the D-500 was 1.5 inches (38 mm) lower than its standard Dodge counterpart. The D-500 came standard with 15×5.5 inch wheels with 7.60×15 inch tubeless tires. New for safety were safety door locks. The D-500-1 (the first 500 made required by NASCAR, was intended for NASCAR competition. The D-500-1 had an even stiffer suspension than the D-500. Under the hood, the engine received larger valves (about 18% larger), a full-race camshaft, and a double log intake manifold that used two four-barrel Carter WCFB carburetors and a shaved deck for 8.25:1 compression. This all added up to 285 bhp (213 kW). It was the fastest car that year from the factory.
Fourth generation (1957–1959)
- See also 1957 Dodge
1957 saw the debut of the new D-501, which replaced the D-500 from the year before as the top Coronet. The D-501 received Chrysler’s proven 354 cid Hemi V8, which were actually left over engines from the 1956 Chrysler 300B production. Camshafts from the 1957 Chrysler 392 cid engines were installed in the 354 V8s for added kick. Topped with a pair of Carter four barrel carbs and sporting a 10.0:1 compression ratio, the new engine put out 340 bhp (250 kW). Other changes included the addition of the Torsion-Aire Ride (torsion bar) front suspension and a heavy duty suspension with heavy duty shock absorbers and a heavy duty leaf sprung rear. A 3.73:1 rear axle was standard with the three-speed manual transmission, but automatic cars received a 3.18:1 rear axle. There were 13 optional rear axles available, ranging from 2.92:1 through 6.17:1. The D-501 received 7.60×15 tires wrapped around 15×8 inch wheels. Brakes were impressive 12-inch (300 mm) diameter drums. Only 101 D-501s were produced. A padded dash was optional.
The 1958 and 1959 Coronet, Royal, and Custom Royal used a DeSoto chassis but had less ornate trim. Power came from the 230 cu in (3.8 L) “Getaway” L-head straight-6 or the 325 cu in (5.3 L) “Red Ram” V8. In 1959 a Silver Challenger model was also offered on the Coronet line. This was a six-cylinder or V-8 model available only in silver paint and only on a two-door body. It came with many extra features at no cost, such as wall-to-wall deep pile carpeting, premium white wall tires and wheel covers, luxury fabrics and upgraded interior and electric windshield wipers. The car grew to 217.4 inches long.
The Dodge Custom Royal was also assembled by Chrysler Australia from early 1958 to 1960.
Fifth generation (1965–1970)
| Fifth generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1965–1970 |
| Assembly | Highland Park, Michigan, United States Los Angeles Assembly, Maywood, California |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 2-door hardtop 2-door convertible 4-door sedan 4-door station wagon |
| Platform | B-body |
| Related | Plymouth Belvedere Plymouth Savoy Dodge Charger Plymouth GTX Plymouth Road Runner |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6 I6 273 cu in (4.5 L) LA V8 318 cu in (5.2 L) A V8 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 361 cu in (5.9 L) B V8 383 cu in (6.3 L) B “Magnum” V8 426 cu in (7.0 L) Hemi V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) RB “Magnum” V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 4-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 116.0 in (2,946 mm) Wagon: 117.0 in (2,972 mm) |
| Length | 209.7 in (5,326 mm) |
1965–1967
After brief absence, the Coronet name was attached to the former full-size models in 1965 to become Dodge’s intermediate-sized car. The 1965 models were basically refreshed Dodge Polaras in the same B-body style offered in 1963 and 1964, riding on a 117 wheelbase. For 1965, Dodge sold slightly over 209,000 units, making the Coronet the most popular model sold by Dodge that year. Trim levels initially were base Coronet including a Deluxe version, Coronet 440 and Coronet 500. The base Coronet and Deluxe were available as two-door sedans, four-door sedans and station wagons. For 1965 only, Dodge also sold only 101 units of a modified wheelbase version of the base Coronet two-door sedan and 440 hardtop used for NHRA drag racing. The model known as A990 came with a racing version of the 426 Hemi engine. The car A990 was stripped of all features and included base bucket seats from Dodge’s truck-van line of vehicles. The altered wheelbase eventually became commonly known as Funny Cars because of their stretched front clips. Front seat belts and padded dash were standard. The middle of the Coronet line-up was the 440 and was available as a two-door hardtop, convertible or station wagon. The 440 designation did not indicate engine displacement as commonly assumed. The nomenclature was a carryover theme from the 1963–64 Polara series. The top of the Coronet line-up was the Coronet 500 and was available only as a two-door hardtop or convertible in 1965. Slightly over 33,300 units were sold in 1965 and included as standard, a V8 engine (273 cubic inches), exterior trim and badging, bucket seats, padded dash and chrome floor console. Coronets were manufactured at Chrysler’s Los Angeles assembly plant and at Lynch Road assembly plant in Detroit. Engines offered for 1965 included the base 225 Slant-Six, 273, 318 (Polyhead), 361 (the last year for this big block engine was 1966), 383 and 426 in multiple HP choices. Sales brochures list the 413 (its last year offered) as available, but no records exist of this engine commonly used in Imperials, being installed in Coronets for 1965. A tachometer was optional.
There would be no Coronet 500 wagon until 1968. Coronet received a redesign in 1966, and a facelift in 1967. Trim levels initially were base Coronet, Coronet 440 and Coronet 500. In 1966, the Coronet Deluxe was introduced, fitting between the base Coronet and the Coronet 440. The Coronet R/T was introduced in 1967. The Coronet R/T was available as a two-door hardtop or convertible. Standard engine was Chrysler’s largest, the 440-cid V-8, it was tweaked to 375 bhp and christened the Magnum. The only engine option was the 426-cid Hemi, now in its second year in “Street” trim and again rated at 425 bhp. It added $908. Transmission choices were Mopar’s excellent heavy-duty three-speed TorqueFlite automatic or a four-speed manual.
When the 426ci Hemi was made available to the general public for the 1966 model year, it could be ordered in any Coronet model or trim level. No Hemi-powered Coronet wagons have been verified, but a few Coronet Deluxe four-door sedans are known to exist. A total of just 136 Coronet 500 Street Hemis were built for 1966. Beginning in 1967, Chrysler decided that the Hemi should be available only in their badged muscle cars: the Dodge Charger and Coronet R/T and the Plymouth Belvedere GTX. The top engine option for the rest of the Coronet line was supposed to be the 383 ci 4 bbl V8. Despite this, some Hemi-powered 1967 Coronet Deluxe two-door sedans were produced. There is also one Hemi-powered 1967 Coronet 440 two-door hardtop known, and One Hemi-powered 1967 Coronet 500 two-door hardtop known, which is not among the 55 WO23 Super Stock cars produced for Dodge drag racers.
1968–1970
The Coronet and similar Plymouth Belvedere received complete redesigns in 1968, as did the Dodge Charger, which shared the B-body platform. There was a mild facelift in 1970. Trim levels initially included the base Coronet, Coronet Deluxe, Coronet 440, Coronet 500 and Coronet R/T. The Coronet Super Bee was introduced in early 1968 as a companion to the Plymouth Road Runner. In keeping with Dodge’s position as a step above Plymouth, the Super Bee shared the Charger’s Rallye instrument cluster and the Coronet 440’s rear finish panel.
As in 1967, the 440ci RB V8 was only available in the Coronet R/T in 1968. The 426ci Hemi V8 was supposed to be limited to the R/T and Super Bee, but two 1968 Coronet 440s are known to have been built with this engine.
In mid-1969, the A12 package was introduced on the Super Bee. It included a 390 hp (291 kW) version of the 440 with three 2bbl Holley carburetors on an aluminum intake manifold, a black fiberglass lift-off hood secured with metal pins, heavy-duty suspension and 15″ steel wheels with no hubcaps or wheel covers. The hood had an integrated forward-facing scoop which sealed to the air cleaner assembly and bore a decal on each side with the words “SIX PACK” in red letters, “Six Pack” being the name used for the 6-bbl induction setup when installed on a Dodge (Plymouth went with “440 6bbl” on the A12 Road Runners). The A12 Super Bee could be had with most Super Bee options, with the exception of air conditioning and tire-wheel packages. The A12 option was a 1969-only package, but the 440 6bbl returned in 1970 as an optional engine on both the Super Bee and the Coronet R/T.
The base Coronet and Deluxe were available as 2-door coupes, 4-door sedans or station wagons. The base Coronet was dropped in 1969, leaving the Deluxe as the lowest trim level through 1970.
The Coronet 440 convertible was dropped for 1968, but a 2-door coupe was added along with the 2-door hardtop, 4-door sedan and station wagon. This would remain the lineup through 1970.
Coronet 500 retained its 2-door hardtop, convertible and 4-door sedan through 1970. A Coronet 500 station wagon made its debut in 1968, continuing through 1970. Simulated woodgrain trim was standard on the Coronet 500 wagon.
The Coronet R/T 2-door hardtop and convertible continued through 1970.
The Super Bee was only available as a 2-door coupe or 2-door hardtop. Chrysler did display a convertible with Super Bee stripes at car shows in 1968, but never offered it as a production model. Some enthusiasts have created “phantom” Super Bee convertibles by adding the appropriate trim and stripes to Coronet 500 convertibles.
The Dodge Super Bee was a limited production muscle car from Dodge division produced from 1968–1971. The original Super Bee was based on the Dodge Coronet, a 2-door model only and was produced from 1968–1970. It was Dodge’s low-priced muscle car, the equivalent to Plymouth Road Runner, and was priced at $3,027. Available with Hemi engine, this option increased by 33%, only 125 models were sold with this engine option. The Super Bee included a heavy-duty suspension, an optional Mopar A-833 four-speed manual transmission, with high performance tires, and a stripe (with the bee logo) wrapped around the tail. The name “Super Bee” was derived from the “B” Body designation given Chrysler’s midsized cars which included the Coronet.
A “six-pack” (three two-barrel carburetors) version of the 440 engine was added to the list mid-year. This engine was between the standard engine and the Hemi as a $463 option. The 1969 model year gave customers several engines to choose from, the base 383 hp (high performance), 440 six pack, and the 426 Hemi V8. The 440 Magnum (4bbl) was not available as an option, it was reserved for the Coronet R/T.
In 1970, the Super Bee was given a different front end look that consisted of a dual ovaled grill that was referred to as “bumble bee wings”, this new look turned off many buyers. Despite the new looks, the engines, as well as the “ramcharger” hood (that carried over from 1969 model), sales plummeted for the 1970 model. In 1970, Dodge also produced four Super Bee convertibles; the whereabouts of the four cars are unknown.
Sixth generation (1971–1974)
| Sixth generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1971–1974 |
| Assembly | Highland Park, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 4-door station wagon |
| Related | Plymouth Belvedere Plymouth Savoy Dodge Charger Plymouth GTX Plymouth Road Runner |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6 I6 318 cu in (5.2 L) 318 LA V8 383 cu in (6.3 L) B “Magnum” V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) B V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) RB “Magnum” V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 118.0 in (2,997 mm) |
| Length | Sedan: 207.0 in (5,258 mm) Wagon: 213.4 in (5,420 mm) |
| Width | Sedan: 77.7 in (1,974 mm) Wagon: 56.4 in (1,433 mm) |
| Height | Sedan: 53.7 in (1,364 mm) Wagon: 63.4 in (1,610 mm) |
1971–1972
The new Coronet was a twin of the four-door Plymouth Satellite and featured more flowing styling. It was offered only as a sedan and station wagon, the related and also restyled Dodge Charger covering the coupe market. Slight alterations of the front grille, headlights, and taillights followed in 1972. Sales of the Coronet were fairly low from this point onwards, with around 80–90,000 produced each year through 1973 (compared with 196,242 as recently as 1968), due both to the fuel crisis and to a proliferation of Dodge and Plymouth models, and the growing effect of overlap with the other Chrysler Corporation brands.
1973
In addition to the usual changes in grille, lights, and interior, Dodge introduced its “TorsionQuiet” system of additional silencers and rubber vibration insulators, providing a much smoother ride and a quieter interior.
1974
The front and rear fascias were redesigned, most notably the rear bumper, which met the 1974 DOT requirements. The sedan bodystyle would be the basis of the later Coronets (and its twin, the Plymouth Fury) until the 1978 model year.
Seventh generation (1975–1976)
| Seventh generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1975–1976 |
| Assembly | Highland Park, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 4-door station wagon |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6 I6 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) B V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | Sedan & Wagon: 118.0 in (2,997 mm) Coupe: 115.0 in (2,921 mm) |
| Length | Sedan: 217.9 in (5,535 mm) Coupe: 213.8 in (5,431 mm) Wagon: 225.6 in (5,730 mm) |
| Width | Sedan: 77.7 in (1,974 mm) Coupe: 77.4 in (1,966 mm) Wagon: 79.2 in (2,012 mm) |
| Height | Sedan: 53.9 in (1,369 mm) Coupe: 52.6 in (1,336 mm) Wagon: 56.5 in (1,435 mm) |
- Custom (1946–1948)
1942 dodge-custom-series-club-coupe-d-22-1942
1946 Dodge Custom
- Custom 880 (1962–1965)
Dodge Custom 880
The Dodge Custom 880 was an automobile sold under the Chrysler Corporation‘s Dodge brand from 1962 through the end of the 1965 model year. It was brought to market quickly to remedy Dodge’s vulnerability in the mid-price fullsize field, as well as to help fill the void in Chrysler’s lineup left by the discontinuation of DeSoto in 1961.
Origins
| Dodge Custom 880 | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Model years | 1962–1965 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 361CID 265 hp (198 kW) 265hp OHV V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 3-speed Torqueflite automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 122 in (3,099 mm) |
| Length | 213.5 in (5,423 mm) |
The Custom 880 was a quick solution to consumer demand for a full-size Dodge passenger car during the 1962 model year.
The 1962 Dodges introduced in the fall of 1961 had their origins in a rumor heard by a Chrysler executive that Chevrolet was planning to downsize their full-sized automobiles for the 1962 model year. Not wanting Chrysler to play catch-up, and wanting to beat Chevrolet at its own game, Plymouth and Dodge designs were placed in an emergency downsizing program that took the previously approved full-size designs and shrank them to smaller vehicles that would compete head-to-head with the rumored smaller Chevrolet.
But to Chrysler’s shock and dismay, Chevrolet’s 1962 full-size lineup emerged slightly larger than the 1961 models, with the mid-range Chevrolet Bel Air (on a 119 in (3,000 mm) wheelbase) growing a .5 in (13 mm) longer in its body, although the car weighed 45 lb (20 kg) less than its 1961 predecessor. The rumored “small Chevrolet” turned out to be the new Chevy II compact, which was intended to bolster Chevy’s position where the Corvair had faltered in that segment of the market.
The “full-size” Dodge Polara and Dart that emerged for 1962 were built on a 3 in (76 mm) shorter (116 in (2,900 mm)) wheelbase and were 7 in (180 mm) shorter overall than the comparable Chevrolet, placing Dodge in the precarious position with consumers of not offering a true full-sized automobile. Ford also brought their new intermediate- or mid-size Fairlane and Mercury Meteor to market for 1962 with a 115 in (2,900 mm) wheelbase. They were roughly the same size as the new standard-size Dodges, which made the new Mopars intermediates by default.
Compounding the size issue were the designs themselves, which did not translate well from their full-size origins to what amounted to intermediate size. In the rush to shrink the cars, the proposed curved side glass was deleted in favor of flat glass, which blunted the effect of the graceful curve of the body sides. They also reduced the total glass area, which made the cars look smaller as well.
An unpopular design for second year in a row — the 1961 models had awkward-looking “reversed” tailfins and a pinched grille, among other unusual features — combined with the cars’ smaller overall size, threatened Dodge’s viability enough that Chrysler was forced to move immediately to stem Dodge’s financial and market share losses.
1962
Without lead time sufficient to develop an all new full-sized Dodge, Chrysler approved the sharing of the full-size body used by the Chrysler Newport and the non-letter 300 series. The models were differentiated by mating a modified 1961 Dodge Polara front clip to the Newport’s definned rear quarter panels and passenger compartment. This body sharing allowed Dodge to launch the car in January 1962.
The only visible cue at the front of the car that was different from the 1961 Dodge was the addition of Dodge’s new three-pointed “Fratzog” emblem in place of the stylized star bar from the 1961 Polara. From the rear, the 1962 Custom 880 was identical to the Chrysler Newport except for Dodge badging.
The model name Custom 880 was derived from Dodge’s numerical sub-model naming structure that was also used on the Dart and sportier models of the Polara, although the model designation was not physically present on the car. Only “Dodge” badges on the rear quarter panels and decklid of the car were applied. A six-way power seat was optional.
For the short 1962 run, the Custom 880 was available as a four-door sedan, two- or four-door hardtop, a two-door convertible, and a choice of six- or nine-passenger station wagons which featured Chrysler’s hardtop styling.
Despite its late arrival, the Custom 880 proved to be a success. A total of 17,500 vehicles were produced, earning sales that Dodge would have otherwise lost.
1963
For 1963, the Custom 880 returned with a full offering of body styles, and a new base model, simply named the 880. Chrysler-branded cars were redesigned for 1963, leaving the 880’s body unique to Dodge, although the car was still produced alongside the now totally different Chrysler.
In what must have been near-record time, Dodge designers created an entirely new look for the car ahead of the cowl, fronted by a new convex grille in the shape of a very long oval. Straighter front fenders flanked a hood with a depressed central section featuring the Dodge name in block letters above the grille. Designers cleverly integrated the new Chrysler’s front bumper into the design as well.
At the rear there was less change, although the car received restyled taillights. Set in heavy chromed housings, they were mounted to the carryover quarter panels and imparted a Dodge familial appearance to the rear, as one of Dodge’s styling hallmarks of the time was round taillights.
The new base-model 880 station wagons utilized the pillared body in both six and nine passenger models, while the Custom-series wagons featured the pillarless hardtop design. With Chrysler no longer using the body and its interior trim elements, Custom 880s were better appointed than they had been during the 1962 model year.
A total of 28,200 vehicles were produced for 1963, of which 5,600 were station wagons.
1964
The 880 and Custom 880 received their most significant and final redesign of the 1960 body for 1964. This time, the rear body contours were squared up somewhat, with new decklids, wraparound rectangular taillights, and new quarter panels. Four-door models received a new roofline, although this was actually the same as had been used on the Chrysler New Yorker until 1962. Regardless, it did impart a fresh appearance. The grille was also updated, this time featuring a concave design with a central horizontal break spanning the distance between the headlights.
Custom 880s received stainless steel rocker panel trim, foam-padded seats, and a grooved stainless steel panel that spanned the distance between the taillights. The Customs, as the top of the 880 line, also received better interior appointments than the base models.
Because of tooling expenses, station wagon bodies — which were also shared with Chrysler models — did not receive all of the changes applied to non-wagon models. Most notably, wagons continued to feature the heavy rear horizontal blade stamping first seen on the 1961 Plymouth wagons. The station wagons continued in both pillared (880) and hardtop (Custom 880) models, although this would be the final year for the hardtop wagon — Dodge and Chrysler being the last American automotive brands to offer the style. Station wagons also received rectangular taillights that wrapped around the sides of the vehicle.
All 880s and Custom 880s received a revised instrument cluster layout, replacing the previous design which had been in use with little change since 1961. An oil pressure gauge was standard. Front leg room was 41.9 inches.
The 880 and Custom 880 received favorable press reviews, especially for their redesign. Evidently, the public also agreed, as they bought 31,800 vehicles, a record for the model.
1965
| Dodge Custom 880 1965 | |
|---|---|
| Layout | FR |
| Powertrain | |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 4-speed manual TorqueFlight |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 121″ |
| Length | 212.3″ |
| Width | 79″ |
1965 marked the first time that Elwood Engel‘s influence on Chrysler’s corporate overall design themes was fully expressed, although he had joined the company in 1961. Gone were the relatively extreme curves and angles that were a legacy from the final Virgil Exner-styled cars. Engel’s design philosophy, which was encouraged by Chrysler chairman Lynn Townsend, took Chrysler’s products in the direction of rectilinear geometric angles; rectangular and trapezoidal shapes dominated Dodge’s fullsize designs for the year.
The introductions of the 1965 models also allowed Chrysler to rectify its 1962 mistake and reintroduced a full-sized Dodge Polara to the public. The “new” Polara took the position formerly held by the 880, with the Custom 880 taking the top trim level. The sporty new Dodge Monaco, which was available only as a two-door hardtop, was the top-of-the-line model produced by Dodge in 1965 and was designed to compete against the Pontiac Grand Prix. An AM/FM radio and a 7-position tilt steering wheel were optional.
All big Dodges, 880, Monaco, and Polara, now featured the same body and styling. Gone was the 1961 Chrysler design. All Custom 880s came with the standard features found in the Polara and added foam-padded seats and stainless steel window frames on station wagons and sedans. Hardtops and convertibles featured all-vinyl interiors. Custom 880s also featured a pillared six-window “town sedan” body that was unavailable in the Polara series. The series also featured the first Dodge-brand “wood” trimmed station wagon since the early 1950s, a look achieved through the use of Di-Noc appliqué framed in stainless steel trim. A total of 23,700 Custom 880s, all with V8 engines, were built during the model year.
End of the line
Dodge discontinued the Custom 880 nameplate at the end of the 1965 model year in the United States. In an effort to move its top full-size series upscale for 1966, the division adopted the Monaco name for all of the former Custom 880 models, with the exception of the six-window sedan, which was discontinued. The original Monaco hardtop added the 500 label for ’66, and was still promoted as a competitor to the Pontiac Grand Prix.
Production figures
Combined Dodge 880 and Custom 880 annual production figures rounded to the nearest 100:
- 1962, 17,500
- 1963, 28,200
- 1964, 31,800
- 1965, 23,700
- Total: 101,200
- Custom Royal (1955–1959)
Dodge Custom Royal
| Dodge Custom Royal | |
|---|---|
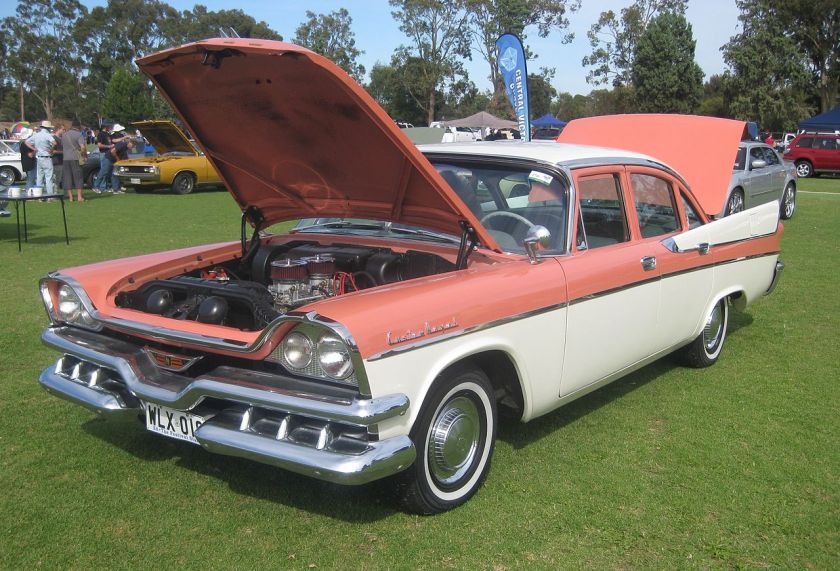

1957 Dodge Custom Royal 4-Door Sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Dodge |
| Production | 1955–1959 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door hardtop 4-door hardtop 2-door convertible |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Polara |
The Dodge Custom Royal is an automobile which was produced by the Dodge division of the Chrysler Corporation in the United States for the 1955 through 1959 model years. In each of these years the Custom Royal was the top trim level of the Dodge line, above the mid level Dodge Royal and the base level Dodge Coronet.
Australian production
The Custom Royal was assembled by Chrysler Australia at its Mile End plant in South Australia from early 1958 utilizing CKD kits imported from Detroit. It was offered only as a four-door sedan.
- D Series (1961–1993)
Dodge D Series
| Dodge D Series | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Also called | Dodge Ram (1981–1993) Dodge W-Series (4×4 models) Dodge Power Ram (4×4 models from 1981–1993) |
| Production | 1961–1993 |
| Assembly | Warren, Michigan, United States Buenos Aires, Argentina |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size pickup truck |
| Body style | 2-door truck 4-door truck |
| Layout | Front engine, rear-wheel drive /four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler AD platform |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge C Series |
| Successor | Dodge Ram (newer platforms have “D” prefixed in its identity) |
The D Series was a line of pickup trucks sold by the Dodge division of American automaker Chrysler from 1961 to 1980. After 1980, the trucks were renamed the Dodge Ram and the same basic design was retained until the 1994 introduction of a completely redesigned Ram. The D Series shared its AD platform with the Dodge Ramcharger/Plymouth Trailduster twins.
1961–1964
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1961–1964 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 170 cu in Slant-6 I6 225 cu in Slant-6 I6 426 cu in RB V8, 365 hp (272 kW) and 470 lb·ft (637 N·m) gross 318 cu in A V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed push button automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 114 in (2,896 mm) (short bed) 122 in (3,099 mm) (long 8 ft (2,438 mm) bed) |
The body offered the then-traditional step-style bed, with distinct fenders as an option.
The D Series used the familiar Chrysler Slant-6 engine in displacements of 170 cu in, 198 cu in, and 225 cu in as the base models, depending on the year. (The 198 was relatively rare, available as the base engine only from 1969–1973.) All of Chrysler’s larger engines, with the notable exception of the Chrysler Hemi engine were available as factory options.
Another innovation was the introduction of an alternator rather than a generator for electrical power. A three-speed automatic transmission was a major advance—the truck used a two-speed automatic less than a decade earlier.
Yet another innovation, a “Crew Cab” (four-door) body style was introduced in 1963, a first for a factory pickup. Prior crew cabs were custom conversion jobs. A “Club Cab” was also available for 1973, providing transverse seating for either a single third passenger or two small third and fourth passengers (most often, the Club Cab was used as extra cargo space).
The first generation of the D-series was manufactured in Argentina. They were given the Dodge and Fargo brands, as Dodge D-100 and Fargo De Soto. The trucks were produced by the Argentinian subsidiary Chrysler-Fevre Argentina S.A.
Custom Sports Special and High Performance Package
1964 saw the introduction of the sporty Custom Sports Special. The Custom Sports Special included bucket seats, console, carpeting and racing stripes. The optional High Performance Package could be ordered with a CSS truck or by itself on a base model truck complete with Chrysler’s big 426 cu in wedge-head V8. This engine produced 365 hp (272 kW) and 470 lb·ft (637 N·m)—in-line with the muscle car revolution that was then sweeping Detroit. The High Performance Package also included the LoadFlite automatic transmission, a 6000 rpm-rated Sun tachometer with heavy-duty gauges, power steering, dual exhaust and rear axle torque rods (traction bars) sourced from 1961 Imperials. Custom Sports Special trucks were produced from 1964 to 1967. The High Performance Package was only offered from 1964 to early 1966.
1965–1967
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1965–1971 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 170 cu in Slant-6 I6 225 cu in Slant-6 I6 318 cu in A V8 273 cu in LA V8 383 cu in RB V8, 258 hp (192 kW) and 375 lb·ft (508 N·m) gross 318 cu in LA V8, 160 hp (119 kW) |
| Transmission | 3-speed dash mounted or column mounted lever shifted automatic |
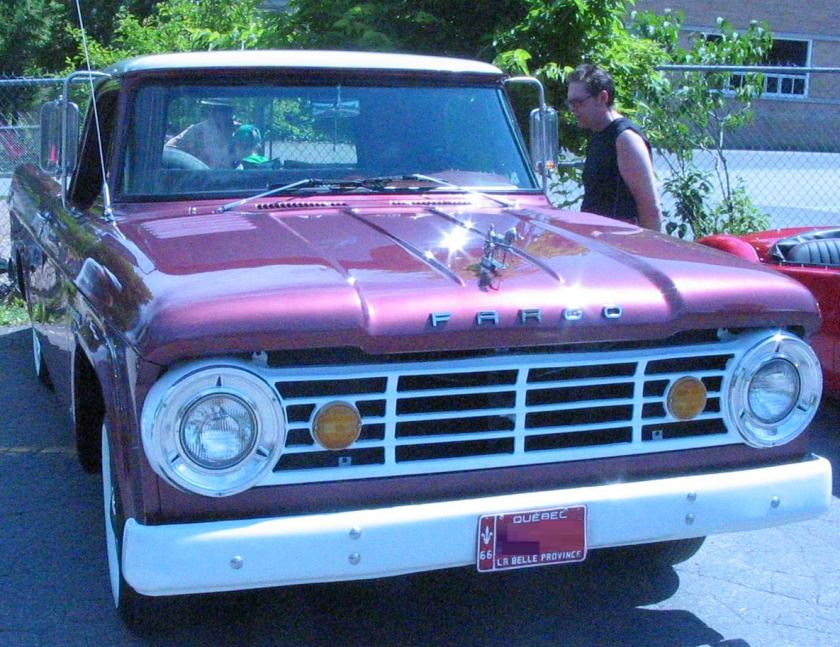

The D Series was redesigned for 1965. Updates included a wider tailgate and the replacement of the A series engines with the updated LA series. In 1967, the D Series trucks received big-block 383 2-barrel engines as a standard option.
From 1965 until the early 80s, the D series were assembled by the Automotive Equipment Group (מכשירי תנועה בע”מ) in Israel at a new factory located at Nazareth-I’llit (תעשיות רכב נצרת-עלית), using straight-4 and -6 gasoline engines with manual transmission. This factory also produced the Jeep Wagoneer SUV for the Israeli army, and UK Ford Escort and Ford Transit vehicles for the civilian market. The D Series were made both for the civilian market and for the Israeli army. The models were D100 & D200 light trucks, D500 truck, and the D600 truck with the straight-6 engine and having on-demand four-wheel drive. There was also a bus version made (mainly for army use). This bus was a 20-seat bus built on the chassis of the D500 truck using the straight-4 engine with front & rear hydraulic doors, complete D500 front end & hood, and D500 dashboard.
1968–1971
The 1968 models received a new front grille—two rows of four holes each. A new Adventurer trim package replaced the old Custom Sports Special; basically, it included a padded front seat with vinyl trim (either full bench or buckets with console) and carpeting, plus other hallmarks such as extra chrome trim and courtesy lighting.
By 1970, the Adventurer would be expanded into three separate packages: the base Adventurer, the Adventurer Sport and the top-line Adventurer SE. The Adventurer SE included such things as a chrome grille, wood trim on the dashboard, the padded vinyl front seat with color-keyed seatbelts, full courtesy lighting, extra insulation, dual horns, full carpeting, luxury door panel trim, a vinyl-embossed trim strip ran along the sides of the truck, full wheel discs and a woodgrain-insert panel on the tailgate. The 1970 models also featured a new four-section grille (two rows of two holes each).
“The Dude”
In August 1969, the “Dude Sport Trim Package” was released. This was essentially the D100 already in production, with an added black or white body-side “C” stripe decal; a Dodge Dude decal on the box at the rear marker lamps; tail lamp bezel trim; and dog dish hub caps with trim rings. The Dude’s tailgate was unique, featuring a Dodge decal on a flat tailgate surface, without the typical tailgate’s embossed logo. The Dudes were only offered in the 1970 and 1971 model years and only 1500 to 2000 Dudes were produced.
1972–1980
| Third generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1972–1980 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Transmission | 3-speed column shifted Automatic transmission |
A redesign of the D Series for 1972 that lasted until 1980 introduced a more rounded look, similar to the 1973–1987 GM C/K series. This redesign for the third generation, that spanned until 1993 with minor changes, included new features such as an independent front suspension and pocketed taillights (the distinctive reverse on top lights were recessed to .25 in (6.4 mm) to avoid damage in loading docks and confined spaces). Styling cues, such as the scalloped hood and rounded fenderwells, were similar to the rounded, smooth look of the 1971 Plymouth Satellite. These trucks were built with a considerable amount of galvanized steel to resist rust and corrosion making them very durable. Because of this, today these trucks make great restoration projects.
Dodge pioneered the extended cab pickup with the introduction of the Club Cab with the 1972 models. This was a two-door cab with small rear windows which had more space behind the seats than the standard cab, but not as long as the four door Crew Cab. 1972 also saw the introduction of the 440 cu in engine as an option for the light trucks.
The 1972 D Series was made famous in the television show Emergency!, where it was the featured paramedic rescue squad vehicle for the entire seven seasons of the popular show.
Notable models produced during this era were the 1978–1979 Li’l Red Express, the Warlock, the Macho Power Wagon, the Macho Power Wagon Top Hand, Macho Power Wagon Palomino, and the Adventurer . The colors of the Dodge Macho Power Wagon Palomino were the same as a Palomino horse. (Note: All Li’l Red Express Trucks were Adventurers, though not vice versa). Another rare model is the Midnight Express which was available for the 1978 model year only. This truck was equipped much like the Li’l Red Express with exhaust stacks, wheels, and gold pinstriping. The Midnight Express was painted black instead of red and featured a “Midnight Express Truck” decal on the door. Most Midnight Express trucks were powered by the 440 engine, instead of the 360 like the Li’l Red Express. All of these trucks were considered “lifestyle” pickups and were marketed to an audience that wanted specialty, personal use trucks.
The 1978 models also saw the introduction of the first Diesel powered Dodge pickup truck. Available as an economy choice in the light duty trucks was Mitsubishi’s 6DR5 4.0 L inline 6-cylinder naturally aspiratingdiesel, rated at 105 hp (78 kW) at 3500 rpm, and ~230 N·m (~169 lb·ft) at 2200 rpm. The diesel used standard Dodge manual and automatic transmissions via specially made adapter plate which had the LA V8 bolt pattern. This rare factory option, VIN code H, was the result of fuel crisis and the collaboration of Chrysler and Mitsubishi. The engine, while being trustworthy and having far better economy than any other engine in the Dodge lineup at the time, suffered from its low power output and was considered to be underpowered by American standards, even though it was previously used in the Japanese 3.5-ton cab-over Mitsubishi T44 Jupiter Truck and in industrial applications. Because of the low sales it was phased out quickly and as a result it became practically a single year specialty.
Thousands of D Series trucks entered military service as the M880 series CUCV.
1981–1993
This final generation was face lifted in 1981 when the D Series was a rebadge as the Dodge Ram pickup around when Lee Iacocca took charge of the ailing Chrysler Corporation. Such things including an embossed “DODGE RAM” name on the tailgate along with other obvious changes like the grille and hood, the taillights, and the entire interior. More subtle was the addition of a “shoulder” line reminiscent of the GM competition. Beginning in 1981, even more corrosion-resistant steel was used in the construction of the trucks. This body style continued until 1993 and many of these vehicles are still on the road. Many body panels are interchangeable for all models from 1972–1993, so it is not uncommon to see a “hybrid” with, as an example, a 1978 grille mounted with a 1974 hood and a 1991 cab. Sometimes the bed is swapped with a moving truck style box for models like these. In most jurisdictions, the year is dictated by the year of the truck’s chassis regardless of the body which has been bolted to it. Also kept was the Utiline step-side model that had the same truck bed that dated back to the 1940s. This was dropped during this last era of the W/D Dodge trucks.
A narrower range of engines was offered: the base power plant was the 225 cu in (3.7 L) slant-6, now with top-fed hydraulic tappets, and the 318 cu in (5.2 L) and 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA-series V8s. The slant-6 was supplanted by the 3.9 L (237 cu in) V6 for 1988; in 1992 it and the V8s became Magnum engines. The 6BT 5.9 L (360 cu in) 12-Valve Cummins B Series diesel engine became an option in 1989.
Sales were good during the Sweptline era and into the late 1970s. A combination of stagnant styling nearly two decades old plus brand loyalty primarily to Chevrolet and Ford during the 1980s and 1990s reduced sales volume for the first generation Dodge Ram. A wholly new Dodge Ram was released for the 1994 model year.
Dodge Dakota
| Dodge Dakota | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler (1987–1998; 2007–2011) DaimlerChrysler (1998–2007) |
| Production | 1987–2011 |
| Assembly | Warren, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size pickup truck |
| Layout | Front engine, rear-wheel drive /four-wheel drive |
The Dodge Dakota is a mid-size pickup truck from Chrysler‘s Ram (formerly Dodge Truck) division. From its introduction through 2009, it was marketed by Dodge. The first Dakota was introduced in 1986 as a 1987 model alongside the redesigned Dodge Ram 50. The Dakota was nominated for the North American Truck of the Year award for 2000. The Dakota has always been sized above the compact Ford Ranger andChevrolet S-10 but below the full-sized pickups such as Dodge’s own Ram. It is a conventional design with body-on-frame construction and a leaf spring/live axle rear end. The Dakota is the first mid-size pickup with an optional V8 engine. One notable feature was the Dakota’s rack and pinion steering, a first for work trucks. Dakotas have been used by police and fire departments, as off-road vehicles, patrol trucks, or even brush trucks.
First generation (1987–1996)
| First Generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1987-1996 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door pickup truck 2-door convertible 2-door extended cab |
| Related | Shelby Dakota |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.2 L (134 cu in) K I4 2.5 L (150 cu in) K I4 2.5 L (150 cu in) AMC I4 3.9 L (238 cu in) LA/Magnum V6 5.2 L (318 cu in) LA/Magnum V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 4-speed automatic 5-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 111.9 in (2,842 mm) 123.9 in (3,147 mm) 130.9 in (3,325 mm) (ext. cab) |
| Length | 1987–1990: 185.9 in (4,722 mm)/204.4 in (5,192 mm) 1989–1990 Club Cab: 211.1 in (5,362 mm) 1991–93: 184.2 in (4,679 mm)/202.7 in (5,149 mm) 1991–93 Club Cab: 203.2 in (5,161 mm) 1994–96: 195.3 in (4,961 mm)/213.8 in (5,431 mm) 1994–96 Club Cab: 214.3 in (5,443 mm) |
| Width | 1987–88: 68.4 in (1,737 mm)/68.1 in (1,730 mm) 1989–1996: 69.4 in (1,763 mm) |
| Height | 1987–1990: 64.2 in (1,631 mm)/67.1 in (1,704 mm) 1989–1993 Club Cab: 64.7 in (1,643 mm) 1991–93 Club Cab 4WD: 67.7 in (1,720 mm) 1994–96 4WD: 67.3 in (1,709 mm) 1994–96 Club Cab 4WD: 68.5 in (1,740 mm) 1994–96 2WD: 65.0 in (1,651 mm) 1994–96 2WD Club Cab: 65.6 in (1,666 mm) |
The Dodge Dakota was conceived by Chrysler management as the first mid-sized pickup combining the nimble handling and fuel economy of a compact pickup with cargo handling capacity approaching that of full-sized pickups. To keep investment low, many components were shared with existing Chrysler products and the manufacturing plant was shared with the full-sized Dodge D-Model. The name Dakota means “friend” or “ally” in the Sioux language, though it could have also referred to The Dakotas states North Dakota and South Dakota.
The first generation of the Dakota was produced from 1987 through 1990. It was slightly updated for the 1991 model year. Straight-4 and V6 engines were offered along with either a 5-speed manual or 4-speedautomatic transmission. Four-wheel drive was available only with the V6. Both six and eight-foot beds were offered. Fuel injection was added to the 3.9 L V6 for 1988 but the output remained the same.
In 1988, the Sport package was added as a mid-year release. Exterior colors came in Black, Bright White and Graphic Red. Available in both 2wd and 4×4, the Sport included:
- AM/FM Stereo radio with cassette player
- Carpeted logo floor mats
- Center armrest bench seat
- Charcoal/Silver Deluxe Cloth interior with fold-down arm rest
- Color-keyed leather-wrapped sport steering wheel
- Deluxe wipers
- Dual remote control outside mirrors
- Floor Carpet
- Gauge Package
- Mopar Air Dam with Bosch Fog Lamps
- Mopar Light Bar with Bosch Off-Road lamps (4×4 only)
- Unique bodyside tape stripes
- Euro-style black out grille and bumpers
- Sliding rear window
- 3.9 L V6 engine
- 15″ aluminum wheels (5 bolt: 5 x 4.5in / 5 x 114.3 mm)
The N-body platform was the result of operational efforts by Harold K. Sperlich, who was in charge of Chrysler’s Product Planning in the early 1980s; in which Japanese-inspired compact pickups of the time lacked the size and features necessary to meet the demands of American buyers. In the late-1970s, Chrysler was still recovering from their near-bankruptcy and resources were in short supply. Sperlich challenged the N-Body team to search for all opportunities to reuse existing components to create the Dakota. The resulting highly investment-efficient program enabled Chrysler to create an all-new market segment at low cost. Key individuals involved in making this product a reality included Glenn Gardner, Glen House, Robert Burnham, Don Sebert, Jim Hackstedde, and Clark Ewing. The basic Dakota vehicle was ultimately used as a foundation to create the Dakota extended cab version and the Dodge Durango SUV.
1989 saw the unusual Dakota convertible. The first American convertible pickup since the Ford Model A, it featured a fixed roll bar and a simple manual top. Roughly 2,482 were sold that first year. Another important addition that year was Carroll Shelby‘s V8-powered Shelby Dakota, his first rear-wheel drive vehicle in two decades.
An extended “Club Cab” model was added for 1990, still with two doors. This model allowed the Dakota to boast capacity for six passengers, even though the rear seat was best suited for cargo or children and shorter adults.
In 1991, the front of the Dakota received a new grille and hood which extended the engine compartment to better fit the optional 170 hp (127 kW) 5.2 L V8, which was inspired by the earlier Shelby Dakota V8 option. By 1992, the standard square sealed beam glass headlamps were phased out for the aerodynamic style molded plastic headlamps attached to the grill components. It was equipped with halogen lights, making 1991 the only year for a unique front-end for the Dakota, though it is mechanically possible to fit sealed beams on 1992 to 1996 model years as this model year was an overlap between new grille introduction and new headlamp introduction. Also debuting in 1991 were six-bolt wheels (replacing the earlier five-bolt wheels) based on Dodge’s marketing attempting to differentiate the Dakota from competing manufacturers’ trucks and the upcoming introduction of the redesigned Ram. 1991 was also the first year for an optional driver side airbag (made standard in 1994) and the last year for the Dakota convertible.
In order to fulfill the Dodge division’s commitment to the American Sunroof Company (who were responsible for the modifications to these trucks), production of the “drop top” Dakota was extended into the 1991 model year. Production was extremely limited, with just 8 produced in total, making them the most rare of all Dakotas. Unlike the previous years, colors and options varied more than before as the manufacturer picked each of these trucks in a somewhat random fashion. No advertising was given to these trucks, and they do not appear in sales literature. This is most likely due to the fact that the majority of them were pre-sold (sold before getting to their dealer lots).
Both of the V-configuration engines were updated to Magnum specs the next year, providing a tremendous power boost. Along with the introduction of the Magnum engine came multi-port electronic fuel injection (EFI). The EFI computer (called a PCM by Chrysler) was partially responsible for the improved performance. The new engine/computer combination produced about 230 hp (172 kW)
1994 saw a few minor changes, with the most notable being the addition of a driver’s side airbag, located in a new, two spoke design steering wheel (also found in the Ram). Other changes included the discontinuation of the “SE” and “LE” trims. In following with the all-new Ram full-sized pickups, the top end trim was renamed to “SLT”, with these models (along with select others) wearing the new chrome finished, styled 6-bolt steel wheels styled similar to the 5-bolt type found on the larger Ram. Other changes included revisions to color and overall trim options. SRS airbags were also added for 1994. A CD player became optional, as did a combination cassette player and CD player unit. Leather seats were also available on LE models. New alloy wheels were available.
In 1996, the first generation’s final year, the base K-based 2.5 L SOHC I4 engine option was out of production and had been considered vastly underpowered compared to the competition, so Dodge replaced it with another 2.5 L I4 engine; this being of American Motors heritage with an OHV valvetrain and rated at 120 hp (89 kW). This was the only major change for 1996, and the AMC 2.5 L would also be carried over as the base engine in the new, larger 1997 model.
Li’l Red Express Dakota & Dakota Warrior
Two special editions of the first were constructed with step-side beds. Both were constructed by L.E.R. Industries of Edwardsburg, Michigan. The step-side beds were constructed out of fiberglass and galvineel. Wooden bed rails were also available.
The Li’l Red Express Dakota was made to resemble the original Express, which was based on the Dodge D-Series. It featured the classic-looking step-side bed and also had dual vertical exhaust stacks just behind the cab, which were purely cosmetic (though they could be made to be functional). The Dakota Warrior was made to resemble the Warlock trucks of the late 1970s. Warriors featured the same custom bed as the Dakota Express, but lacked the vertical exhaust stacks. Both the Express and Warrior Dakotas had a graphics package made to resemble those of the original Express and Warlocks, respectively.
Production numbers for the Express and Warriors were very low, in the hundreds. The rarest of those came with the 5.2 L Magnum V8 engine, which was only an option during 1992, the final year of Express and Warrior production.
Engines
- 1987–1988 – 2.2 L (135 cu in) K I4, SOHC, 97 hp (72 kW)
- 1987–1991 – 3.9 L (238 cu in) LA V6, 125 hp (93 kW)
- 1989–1995 – 2.5 L (150 cu in) K I4, 99 hp (74 kW)
- 1991 – 5.2 L (318 cu in) LA V8, 170 hp (130 kW)
- 1992–1993 – 3.9 L (238 cu in) Magnum V6, 180 hp (130 kW)
- 1992–1993 – 5.2 L (318 cu in) Magnum V8, 230 hp (170 kW)
- 1994–1996 – 3.9 L (238 cu in) Magnum V6, 175 hp (130 kW)
- 1994–1996 – 5.2 L (318 cu in) Magnum V8, 225 hp (168 kW)
- 1996 – 2.5 L (150 cu in) AMC I4, 120 hp (89 kW)
Second generation (1997–2004)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
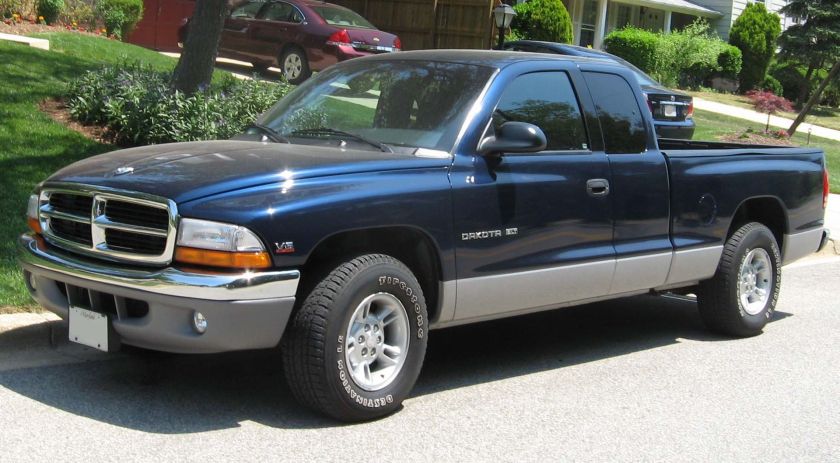 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1997–2004 (North America) 1998–2001 (Brazil) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door pickup truck 4-door pickup truck |
| Related | Dodge Durango |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.5 L PowerTech I4 2.5 L 425 OHV I4 Diesel 3.9 L Magnum V6 5.2 L Magnum V8 5.9 L Magnum V8 4.7 L PowerTech V8 3.7 L PowerTech V6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed 42RE automatic 4-speed 44RE automatic 4-speed 46RE automatic 4-speed 45RFE automatic 5-speed 545RE automatic 5-speed NV1500 manual 5-speed NV3500 manual 5-speed AX-15 manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 111.9 in (2,842 mm) (reg. short) 123.9 in (3,147 mm) (reg. long) 131.0 in (3,327 mm) (ext. cab) |
| Length | 1997–2001 Regular Cab: 195.8 in (4,973 mm) 1997–2001 Extended Cab & 2002-04 Quad Cab: 215.1 in (5,464 mm) 1997–2001 Club Cab: 214.8 in (5,456 mm) 2002–04: 196.0 in (4,978 mm)/215.0 in (5,461 mm) |
| Width | 71.5 in (1,816 mm) |
| Height | 1997–99 4WD: 68.0 in (1,727 mm) 1997–99 & 2002–04 Club Cab 4WD: 68.5 in (1,740 mm) 1997–2001 2WD: 65.6 in (1,666 mm)/65.3 in (1,659 mm) 2000–01 4WD: 67.9 in (1,725 mm) 2000–01 Club Cab 4WD: 68.6 in (1,742 mm) 2000–01 Quad Cab Sport 4WD: 68.8 in (1,748 mm) 2000–01 Quad Cab Sport 2WD: 66.3 in (1,684 mm) 2002–04 4WD: 67.3 in (1,709 mm) 2002–04 Club Cab 4WD: 67.4 in (1,712 mm) 2002-04 Quad Cab 4WD: 68.5 in (1,740 mm) 2002–04 2WD: 64.7 in (1,643 mm) 2002–04 Club Cab 2WD: 64.9 in (1,648 mm) 2002–04 Quad Cab 4WD: 65.6 in (1,666 mm) |
The second generation Dakota was built from 1997 through 2004. It inherited the semi truck look of the larger Ram but remained largely the same underneath. 1998 saw the introduction of the R/T model with the big 5.9 L 250 hp (186 kW) Magnum V8. At the time of its introduction, it was seen as one of the most radical in its class, not only for its styling, but for the fact it remained the only truck in its class with an available V8 engine that rivaled many V8s found in full size trucks with payloads of up to 1500 pounds.
Four-door “Quad-Cab” models were added for 2000 with a slightly shorter bed, 63.1 in (160.2 cm), but riding on the Club Cab’s 130.9 in (332.5 cm) wheelbase. The aging 5.2 L Magnum V8 was replaced by a new high-tech 4.7 L SOHC PowerTech V8. The Quad-Cab featured a full-size flip up rear seat to provide room for 3 passengers in the back or lots of dry, interior room for cargo.
In spring 1998, a new limited edition R/T package was available as an option on the Dakota Sport model. This version is considered a true street/sport truck, only available in RWD. Factory modifications such as a 250 hp 360 cid/5.9 liter V8, heavy duty 46RE 4-speed automatic transmission, performance axle, limited-slip differential, sport suspension and steering, upgraded brakes, performance exhaust, special cast aluminum wheels, monotone paint, bucket seats, and many other standard options came with the package. Chrome wheels were available on 2002 models. Some of the last models made in 2003 came with the new stampede lower body cladding package and chromed version of the original cast aluminum wheels at no extra charge. This version of the R/T Dakota was produced through 2003, with the newer 2003 R/T trucks designated as their own trimline and no longer as part of an option package on the Dakota Sport trim.
Also, in 1998 the Dakota R1 was released for production in Brazil thru the efforts of a small team known as Truck Special Programs and featured a base 4-cylinder engine and offered a 2.5L VMI turbo-diesel along with a V8, all designed around a reinforced 4 wheel drive chassis used on both 2 wheel and 4 wheel drive models. Altogether there were 28 roll-in-chassis R1 configurations designed for the Brazil market to be built at the Curitiba assembly facility as CKDs. This program was cancelled when Chrysler was purchased by Daimler.
2000 saw the introduction of the 4.7 liter V8 and 45RFE automatic transmission.
2001 saw a fairly extensive revision of the Dakota’s interior, including a completely redesigned dash, door panels and revised seats. Other minor trim revisions were made, including redesigned aluminum wheels on various models. All vehicles also got new radio options. Only the standard AM/FM radio (with no cassette deck) was discontinued, making an AM/FM radio with a cassette deck standard on all models. AM/FM stereo CD and cassette/CD variants were also available.
2002 was the final year for the four-cylinder engine in the Dakota, as Chrysler ended production of the former AMC design. Most buyers ordered the V6 or V8 engines, which were considerably more powerful and, in the case of the V6, which was made standard for 2003, nearly as fuel-efficient with a manual transmission. Also, an automatic transmission was not available with the 4-cylinder. SIRIUS Satellite Radio was also now available as an option, and revised radios with new wiring harnesses could accommodate this new feature. A CD changer radio was also available, eliminating the need for a separately-mounted unit located elsewhere inside of the truck. The driver could load up to six discs into the unit at a time, and could switch out the discs at any time, something that the driver could not do with the old unit. Radio Data System became standard equipment on some radios.
2003 was the end of the old OHV V6 and the big R/T V8; the 2004 model year vehicles were available with a new 3.7 L PowerTech V6 engine to go along with the 4.7 L V8 variant.
In 2004, the cassette deck option was discontinued, and a CD player became standard equipment on all models.
This generation was also assembled and sold in Brazil from 1998 to 2001.
The IIHS gave this generation a Poor rating in the frontal offset crash test.
Engines
- 1997–2002 – 2.5 L (150 cu in) AMC I4, 120 hp (89 kW)
- 1997–2003 – 3.9 L (238 cu in) Magnum V6, 175 hp (130 kW)
- 1997–1999 – 5.2 L (318 cu in) Magnum V8, 225 hp (168 kW)
- 1998–2003 – 5.9 L (360 cu in) Magnum V8, 250 hp (190 kW)
- 1999–2000 – 2.5 L (152.5 cu in) VM–425 OHV I4, 114 hp (85 kW)
- 2000–2004 – 4.7 L (287 cu in) PowerTech V8, 230 hp (170 kW)
- 2004 – 3.7 L (226 cu in) PowerTech V6, 210 hp (160 kW)
Third generation (2005–2011)
| Third generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Ram Dakota (2009–2011) |
| Production | 2005–2011 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door pickup truck |
| Platform | ND |
| Related | Mitsubishi Raider Dodge Durango |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 3.7 L (226 cu in) PowerTech V6 4.7 L (287 cu in) PowerTech V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed 42RLE automatic 5-speed 545RFE automatic 6-speed Getrag 238 manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 131.3 in (3,335 mm) |
| Length | 218.8 in (5,558 mm) |
| Width | 71.7 in (1,821 mm) |
| Height | Club Cab: 68.6 in (1,742 mm) Quad Cab: 68.7 in (1,745 mm) |
The redesigned 2005 Dakota still shared its platform with the new Dodge Durango SUV (which is now similar to the Ram platform). This model is 3.7 in (94 mm) longer and 2.7 in (69 mm) wider, and features a new front and rear suspension, and rack-and-pinion steering. This new generation model also reverted the wheels back to five lug wheels from the prior generation’s six lug wheels due to cost and assembly time saving measures. The Dakota is built at the Warren Truck Assembly plant in Warren, Michigan.
There was a V6 and two V8 engines available: The standard engine is a 3.7 L PowerTech V6; the two 4.7 L V8 engines are the standard PowerTech V8 and the V8 High Output or HO. The 3.7 L V6 produces 210 horsepower (160 kW) and 235 lb·ft (319 N·m) of torque. The standard-output 4.7 L V8 produces 230 hp (170 kW) and 295 lb·ft (400 N·m) of torque. The high-output 4.7 L V8 produces 260 horsepower (190 kW) and 310 lb·ft (420 N·m) of torque. Both the 3.7 L and standard output 4.7 L V8s were available with the 6-speed manual transmission in 2005 and 2006. For 2007, that option was deleted on the V8 models.
In addition to a refresh of the Dakota’s styling, this generation was not offered in a regular cab model. Only the club cab and quad cab configurations were available. 2006 saw the Dakota R/T return, however only with cosmetic modifications. Despite the “R/T” moniker which signifies “Road and Track”, the newest Dakota R/T was simply an option package, characterized by a non functional hood scoop, exclusive gauge cluster, and hockey-stick style side stripes. The package was available on both 2 and 4 wheel drive models.
The facelifted third generation Dakota was unveiled at the 2007 Chicago Auto Show. The Dakota received another facelift and interior upgrade along with a few other upgrades including built-in cargo-box utility rails, heated bench seats, best-in-class towing (up to 7,050 pounds), the largest and longest standard bed in the class, and the largest mid-size truck cab. Its new 4.7 liter V8 produces 310 hp (231 kW) and 330 lb·ft (447 N·m) of torque. The standard engine remained the 3.7 liter V6 with 210 horsepower (160 kW) and 235 lb·ft (319 N·m). of torque. Production began in August 2007.
As of 2010, the Dakota was considered a part of the Ram lineup. However, the “Dodge” emblem still existed on the tailgate, and the truck was interchangeably referred to as a Ram Dakota or Dodge Dakota. Its Mitsubishi Raider sibling was discontinued in 2009, and Chrysler was readying the Ram brand to launch in the 2010 model year, making the Ram Dakota replace the Mitsubishi Raider & Dodge Dakota.
The IIHS gave this generation a Good rating in the frontal offset crash test.
Discontinuation
The third-generation Dakota was discontinued in 2011, with the last unit coming off the assembly line on August 23, 2011, ending the truck’s 25-year run. As of 2011, according to Sergio Marchionne, the CEO of Chrysler Group, the Dakota will probably not be replaced by a similar vehicle, mostly due to declining popularity of compact trucks on the North American market (see Ford Ranger for similar outcome). Another problem was that buyers complained that the smaller pickup was not priced lower than the full-sized Ram 1500; nevertheless, there continue to be reports of the Dakota’s return since 2012. However, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles announced in September 2014 an agreement with Mitsubishi Motors to codevelop the next generation Mitsubishi L200 to be sold globally by both companies.
- (Shelby/Shelby Z) Daytona (1984–1993)
- Deluxe (1946–1948)
1946 dodge deluxe-coupe-sedan
1947 Dodge Deluxe Club Coupe
1947 Dodge Special Deluxe 4 door (Canadian)
1947 DODGE special deluxe sedan
- Diplomat (1977–1989)
Dodge Diplomat
| Dodge Diplomat | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Dodge Dart, Dodge Magnum (Mexico) Dodge Coronet (Colombia) Plymouth Caravelle (Canada; 1977–1981) |
| Production | 1977–1989 |
| Assembly | St. Louis, Missouri, United States Kenosha, Wisconsin, United States Windsor, Ontario, Canada Bogotá, Colombia |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | M-body |
| Related | Chrysler Fifth Avenue Chrysler LeBaron Dodge Aspen Chrysler New Yorker Chrysler Town and Country Plymouth Gran Fury Outside the US: Dodge Coronet Dodge Dart Plymouth Caravelle Dodge Magnum (Mexico) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant 6 I6 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed A833 manual 3-speed A727 automatic 3-speed A904 automatic 3-speed A999 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | Coupe: 112.7 in (2,863 mm) 1977–1979, 108.7 in (2,761 mm) 1980–1981, Sedan & Wagon: 112.7 in (2,863 mm) 1977–1989 (wagons through 1981 only) |
| Length | Coupe: 201.2 in (5,110 mm) 1980–83 Sedan: 206.1 in (5,235 mm) 1987–89 Sedan: 204.6 in (5,197 mm) Wagon: 205.5 in (5,220 mm) |
| Width | Coupe & Wagon: 74.2 in (1,885 mm) 1980–83 Sedan: 72.8 in (1,849 mm) 1987–89: 72.4 in (1,839 mm) |
| Height | Coupe: 53.4 in (1,356 mm) Wagon: 55.5 in (1,410 mm) Sedan: 55.1 in (1,400 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Dart |
| Successor | Dodge Monaco |
The Dodge Diplomat is an American mid-size car made from 1977 to 1989. It is essentially identical to the Plymouth Gran Fury in the U.S. market and the Plymouth Caravelle in Canada. It was also sold in Mexicobetween 1981 and 1982 as the Dodge Dart, and in Colombia as the Dodge Coronet. The Diplomat was initially offered in a coupe and sedan. In 1978, station wagons were added as replacements for the departed full-size C-body Wagons.
The Diplomat was offered with a base 225 cu in (3.7 L) straight-six-cylinder engine, in 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 form, and an optional 360 cu in (5.9 L)) Diplomat, along with its Plymouth Gran Fury/Caravelle twin, were widely favored as a police car both in the US and Canada. Aside from the 3-speed Torqueflite automatic transmission, a manual transmission was available in some years and markets on six-cylinder and 318 engines; the 360s were automatics only.
History
The Diplomat name was originally used by Dodge on 2-door hardtop models from 1950 to 1954. It was also used on the export version of the DeSoto from 1946 through 1961. Between 1975 and 1977, the Diplomat name was also used on a trim package available on the Royal Monaco two-door hardtop.
Starting with the 1977 model year, the Diplomat became a full model line, rather than as the name of a particular body style. It was a longer, fancier up-market version of the F-body Aspen. The chassis and mechanical components are identical, and doors and various other body panels are interchangeable.
The 1980 model year brought new exterior sheet metal for the Diplomat, although wagons were unchanged, from the doors back. Manual transmissions were dropped. Following the demise of the Dodge St. Regis R-body in 1981, the Diplomat remained, becoming the largest sedan in the Dodge lineup, despite technically being a mid-size car. Dodge would not market another truly full-size car (at least based upon United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) passenger volume statistics) until the Monaco debuted as a 1990 model.
By 1981, Chrysler was switching to smaller front-wheel drive designs. However, its older and larger rear-wheel drive Dodge Diplomat (as well as the Chrysler LeBaron and Fifth Avenue) continued to sell. Chrysler’s then executive vice president for manufacturing, Steve Sharf, met with officials at American Motors (AMC) to use the extra capacity at an assembly plant in Kenosha, Wisconsin to build the full-size cars. Chrysler’s tooling was moved from St. Louis to Kenosha, and over the next two and a half years, about 250,000 Chrysler and Dodge models were built by AMC at a lower cost than Chrysler could. This relationship evolved into Chrysler’s purchase of AMC in 1987.
In 1982, the coupe and station wagon were discontinued and Canada’s Plymouth version of the Diplomat came south of the border. The Plymouth Caravelle was offered in the US as the Plymouth Gran Fury. 1983 was the last year for the Slant Six, and afterwards, the only available engine was the 318-cid V8 with a two-barrel carburetor. A four-barrel 318 and a 360-cid V8 remained the optional engine choices for the police package.
For 1984, an upscale series was added to the American-market Diplomat, the SE. The SE used the Fifth Avenue’s front end with its parking lights located above the headlights. The grille insert used thin vertical bars with a wide trim strip dividing the grille vertically as well as horizontally. The SE had more exterior trim and an interior that placed the SE between the Diplomat Salon and the Chrysler Fifth Avenue.
As the 1980s progressed, fewer private customers purchased the Diplomat, and the M-body was eventually dropped during the 1989 model year. One reason behind the drop-off in sales was fuel economy. Despite lower gas prices in the mid- to late-1980s and a 2.26:1 rear-end gear ratio, the Diplomat’s carburated engine and lack of an overdrive gear on its TorqueFlite automatic transmission resulted in poor fuel economy compared with its larger competitors from Ford and General Motors, as evidenced by comparing the EPA estimates for 1986 models:
- Dodge Diplomat (5.2 L V8, 3-speed automatic): 16 city, 21 highway, 18 combined
- Chevrolet Caprice (5.0 L V8, 4-speed automatic with overdrive): 17 city, 25 highway, 20 combined
- Ford LTD Crown Victoria (5.0 L V8, 4-speed automatic with overdrive): 18 city, 26 highway, 21 combined
 1980 Station wagon 1980 Station wagon |
Late in the Diplomat’s run, the car was subject to the federal “Gas Guzzler Tax.”
Diplomats built from mid-1988 until the end of production were among the first Chrysler-built products to have a driver’s side airbag as standard equipment, some two model years before the remainder of Chrysler’s lineup (they were also among the only cars at the time to offer a tilt steering column with an airbag). Diplomats with airbags differed from earlier models in that they were also equipped with a padded, color-keyed knee blocker which extended out from beneath the instrument panel in front of the driver.
When the Diplomat and similar Plymouth Gran Fury were discontinued, it marked the last rear-wheel drive non-truck model (aside from the Dodge Viper) sold by the corporation until the Plymouth Prowler was introduced in 1997. The Diplomat’s other rear-wheel drive sibling, the Chrysler Fifth Avenue, also ended production, but the nameplate was continued on a front-wheel drive chassis. In the Dodge lineup, the Monaco became the top-of-the-line sedan.
- Dreamer (1978-1979)
dodge-d300-dreamer

- Dynasty (1988–1993)
Dodge Dynasty
| Dodge Dynasty | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Chrysler Dynasty (Canada) |
| Production | 1988–1993 |
| Assembly | Belvidere, Illinois, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | C-body |
| Related | Chrysler New Yorker |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.5 L K I4 3.0 L Mitsubishi 6G72 V6 3.3 L EGA V6 |
| Transmission | 3-speed A413 automatic 3-speed A670 automatic 4-speed A604 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 1988–1990: 104.3 in (2,649 mm) 1991–93: 104.5 in (2,654 mm) |
| Length | 192.0 in (4,877 mm) |
| Width | 1988–1990: 68.5 in (1,740 mm) 1991–93: 68.9 in (1,750 mm) |
| Height | 1988–1990: 53.5 in (1,359 mm) 1991–93: 53.6 in (1,361 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge 600 Chrysler LeBaron GTS (Canada) |
| Successor | Dodge Intrepid |
The Dodge Dynasty is a front-wheel drive sedan that was introduced in 1987 as a 1988 model to replace the 600 as Dodge‘s mid-size car. Although fairly popular, the Lee Iacocca-dictated styling was boxy and conservative compared to more aerodynamically styled competitors such as the Ford Taurus.
The Dodge Dynasty is related to the Chrysler New Yorker; both car lines were built on the Chrysler C platform in Belvidere, Illinois. It is also similar to the Chrysler New Yorker Fifth Avenue and Chrysler Imperial, which were available from 1990 to 1993 on an extended wheelbase platform of the Chrysler New Yorker. Dynasty trim levels included base and LE. Additionally, a “Brougham” package was offered on 1992 and 1993 LE models which added a padded landau roof.
A 2.5-litre inline-4 Chrysler engine, a Mitsubishi-sourced 3.0-litre V6, the 6G72 engine, and a Chrysler-built 3.3-litre V6 were available, although the 3.3 L V6 was not available until 1990. The four-cylinder came equipped with a TorqueFlite three-speed automatic transmission (the A413). The 3.0L and the 3.3L were offered solely with Chrysler’s then-new electronically controlled four-speed automatic transmission, known as the Ultradrive or A604 (List of Chrysler transmissions).
Dynasty models were all equipped with a driver’s side airbag from 1990 to 1993. A Bendix anti-lock braking system was available on all models during those years as well. The 1993 models were the only year to feature a stainless steel exhaust system and a tamper-proof odometer.
International versions
In Canada and Mexico it was marketed as the Chrysler Dynasty. The Chrysler Dynasty was identical to the 1990 Chrysler New Yorker Salon (sold in the U.S.), their only difference being their names. In Mexico, the cars were only available with the V6 engine. In Canada the four-cylinder variant was available, but seldom ordered, and it replaced the Chrysler LeBaron GTS hatchback since Chrysler Canada did not want to market the Dodge Diplomat‘s successor, the Monaco in 1990. Chrysler Canada, however, replaced the Dynasty’s predecessor, the 600 with the Dodge Spirit instead. The Chrysler Dynasty was meant to fill a void between the Chrysler LeBaron sedan and the Chrysler New Yorker, just like what the LeBaron GTS did in Canada.
- Intrepid (1993–2004)
Dodge Intrepid
| Dodge Intrepid | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation (1993–1998) DaimlerChrysler (1998–2004) |
| Also called | Chrysler Intrepid (Canada) |
| Production | 1993–2004 |
| Assembly | Canada: Brampton Assembly(Ontario) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | Longitudinal front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler LH platform |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Chrysler/Dodge Dynasty (North America) Dodge Monaco (United States) |
| Successor | Dodge Charger Dodge Magnum Chrysler 300 (Canada) |
The Dodge Intrepid is a full-size automobile available as a front-wheel drive four-door sedan that was produced for model years 1993 to 2004. It was related to the Chrysler Concorde, Chrysler LHS, Chrysler New Yorker, Eagle Vision, and also the 300M sedans. The Intrepid, Concorde, and Vision were collectively designated the LH, Chrysler’s codename for the platform which underpinned them.
The Intrepid was sold in Canada as the Chrysler Intrepid. It replaced the Chrysler Dynasty (Canada) and Dodge Monaco (United States) as Dodge’s largest car. With Dodge’s introduction to Mexico that time, it was badged as a Dodge, replacing the Dynasty when it was sold under the Chrysler brand.
Background
The Intrepid’s design goes back to 1986, when designer Kevin Verduyn completed the initial exterior design of a new aerodynamic concept sedan called Navajo. The design never passed the clay model stage.
It was also at this time that the Chrysler Corporation purchased bankrupt Italian sports car manufacturer Lamborghini. The Navajo’s exterior design was reworked and became the Lamborghini Portofino, released as a concept at the 1987 Frankfurt Auto Show. The Portofino was heralded as a design triumph, setting in motion Chrysler’s decision to produce a production sedan with the Portofino’s revolutionary exterior design, called “cab-forward“.
The cab forward design was characterized by the long, low slung windshield, and relatively short overhangs. The wheels were effectively pushed to the corners of the car, creating a much larger passenger cabin than the contemporaries of the time.
Design of the chassis began in the late 1980s, after Chrysler had bought American Motors Corporation (AMC) in 1987. During this time, Chrysler began designing the replacement for the then-new Dodge Dynasty, which was a mid-size car. Initial proposals bore resemblance to the Dynasty, but this design approach was scrapped entirely in 1988 by François Castaing, the former AMC Vice President of product engineering and development. As AMC was purchased by Chrysler, Castaing became new Vice President for Vehicle Engineering for the new company. The acquiring automaker was in desperate need to replicate the AMC and Renault corporate culture where work was conducted in an atmosphere “of constant change”. Castaing organized Chrysler’s departments into AMC-style cross-function teams, as well as incorporated the use of simultaneous engineering. Moreover, the new vehicle’s design, under Castaing’s leadership, began with the Eagle Premier platform.
The Premier’s longitudinal engine mounting layout was inherited, as was the front suspension geometry, and parts of the braking system. The chassis itself became a flexible architecture capable of supporting front or rear-wheel drive (designated “LH” and “LX” respectively).
The chassis design was continually refined throughout the following years, as it underpinned more Chrysler prototypes: the 1989 Chrysler Millennium and 1990 Eagle Optima.
The transmission was inspired by the Premier’s Audi and ZF automatics. Borrowing heavily from Chrysler’s A604 (41TE) “Ultradrive” transversely mounted automatic, it became the A606 (also known as 42LE).
The initial standard 3.3 L pushrod V6 engine engine was joined in 1990 with a 3.5 L SOHC engine with four valves per cylinder. For the second generation Intrepid R/T the block was recast in aluminum as part of a comprehensive upgrade.
First generation (1993–1997)
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1993–1997 |
| Assembly | Newark, Delaware, United States Brampton, Ontario, Canada |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Chrysler LHS Chrysler Concorde Chrysler New Yorker Eagle Vision |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 3.3 L EGA V6 3.5 L EGE V6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed 42LE automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 113 in (2,870 mm) |
| Length | 1993–94: 201.7 in (5,123 mm) 1995–97: 201.8 in (5,126 mm) |
| Width | 74.4 in (1,890 mm) |
| Height | 56.3 in (1,430 mm) |
| Curb weight | 3,318 lb (1,505 kg) |
The first generation of LH cars debuted at the 1992 North American International Auto Show in Detroit as three 1993 models: the Chrysler Concorde, Dodge Intrepid (badged as a Chrysler in Canada), and the Eagle Vision (badged as a Chrysler in Europe).
The Intrepid was available in two trim levels: base and the sportier, better-equipped ES, which added four-wheel disc brakes, 16″ wheels with better tires, and stiffer “touring” suspension damping. All Intrepids received driver and front passenger airbags, a rarity at the time, as well as air conditioning and the four-speed automatic transmission. Anti-lock brakes were optional, as was traction control and the more powerful 3.5 L SOHC engine rated at (214 hp).
The Intrepid’s launch marked a new image for the Dodge brand, which began to market itself as “The New Dodge” with a marketing campaign featuring actor Edward Herrmann, who would go on to serve as the brand’s spokesperson for the rest of the decade.
Changes were few over the Intrepid’s initial five-year production. A new variable-assist power steering rack replaced the original for 1994, allowing for easier parking while maintaining a firmer feel at speed. The touring suspension tuning was also made standard equipment in the base model this year. Anti-lock brakes were made standard in the ES in 1995, and in 1996 a new manual shift function for the automatic transmission, called Autostick, was inherited from the Eagle Vision TSi: the first transmission of its kind available in a mainstream car. In addition, Chrysler updated the Dodge Intrepid for the 1995 model year, adding the previous Dodge Ram logo, one used from 1994-2009. Each exterior treatment uses a hoodline and chrome accented daytime running lights with body colored accents. The Intrepid was often compared with theChevrolet Lumina and Ford Taurus, and to a lesser extent, the Toyota Camry and Honda Accord.[3]
Intrepids were built at American Motors‘ Brampton Assembly facility, originally established to manufacture the Eagle Premier, in Brampton, Ontario, Canada; and at the Chrysler plant at Newark, Delaware.
Engines
- 3.3 L pushrod V6
- 3.5 L SOHC V6
Second generation (1998–2004)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1998–2004 |
| Assembly | Brampton Assembly in Brampton, Ontario, Canada |
| Designer | Bob Boniface |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Chrysler LHS Chrysler 300M Chrysler Concorde |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.7 L EER V6 3.2 L V6 3.5 L EGJ V6 3.5 L EGG V6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed 42LE automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 113 in (2,870.2 mm) |
| Length | 203.7 in (5,174 mm) |
| Width | 2000–01: 74.6 in (1,895 mm) 1998–99 & 2002–04: 74.7 in (1,897 mm) |
| Height | 55.9 in (1,420 mm) |
| Curb weight | 3,422 lb (1,552 kg) |
The LH cars were redesigned for 1998 the second generation intrepid’s design was inspired by the 1996 ESX I concept car. The engines were replaced by two new all-aluminum units: a DOHC 2.7 L ( 2736 cc), 200 hp (150 kW) V6 for base models, and a SOHC 3.2 L (3231 cc), 225 hp (168 kW) V6 for the ES. A new, top-of-the-line R/T model was added in 2000, the centerpiece of which was a redesigned version of the 3.5 L (3518 cc) V6, now producing 242 hp (180 kW) and 234 hp (174 kW) for the ES. At the same time the 3.2 L was reduced to an option in the ES. 1998: The Intrepid was completely redesigned for the 1998 model year. Body shells were designed to be stronger and stiffer, as well as incorporating double-shear suspension mounts and integrated side impact protection.
- 1999: Minor changes to interior panels. The Chrysler Sentry Key theft-deterrent system disabled the ignition unless the proper key was used to start the engine.
- 2000: New variable-assist steering, and an optional 4-disc in-dash CD changer.
- 2002: The 3.5L replaced the 3.2L, and the water pump issues on the 2.7L were now resolved, New wheel covers were available for 2002. the R/T received an extra 2 hp (1.5 kW) from PCM programming changes which allowed it to have 244 hp (182 kW) on 89-octane fuel. This was also the year when DaimlerChrysler began cost-cutting that led to the deletion of various features from the Intrepid. Most notable were the deletion of the illuminated headlight switch, illuminated traction control switch, illuminated lock and window switches, door courtesy lights (replaced with red reflectors), illuminated ashtray receptacle, trunk lid liner, armrest power outlet, door emblems, driver’s seat map pocket, and the blacked-out front fascia paint scheme. Cost-cutting was one of the reasons why sales of the Intrepid started to slump.
- 2003: No major changes were made except the optional 4-disc in-dash CD changer was replaced with the optional 6-disc in-dash CD changer. The R/T was discontinued in 2003, but a new SXT model kept the 3.5 L High Output engine with an increase to a 250 hp (186 kW) rating. The SXT moniker was eventually used across the Dodge product line as a trim level. The Intrepid SXT was basically a base model Intrepid SE with the 3.5 H.O. engine taken from the R/T, with some “sportier” features such as a sunroof and spoiler. It was a value trim model actually classified as an ES (SXT), but had less features than the ES did with a more powerful engine.
- 2004: DaimlerChrysler discontinued the Intrepid after 2004 to be replaced by the new rear wheel drive LX vehicles; the 2005 Dodge Magnum and 2006 Dodge Charger. The last Intrepid rolled off the assembly line on August 28, 2003.
Fleet sales

The second generation was marketed to the commercial and government markets. Vehicles were used to make police interceptors, fire chief cars, and taxis similar to the earlier Chevrolet Caprice or Ford Crown Victoria. These packages had distinctive styling differences (such as small hub caps) and additional wiring to support strobes and flashers in the trunk compartment and in the front by the grill. These packages and some non-police (non-commercial) packages featured plastic front-end intake vents that routed air onto the rotors for additional cooling and stopping power.
Engines
- 1998–2004 – 2.7 L V6 200 hp (150 kW)
- 1998–2001 – 3.2 L V6 225 hp (168 kW)
- 2000–2004 – 3.5 L V6 234 hp (174 kW)
- 2000–2001 – 3.5 L HO V6 242 hp (180 kW)
- 2002–2003 – 3.5 L HO V6 244 hp (182 kW)
- 2003–2004 – 3.5 L HO V6 250 hp (186 kW)
Motorsport
In 2001, the Intrepid made its debut on the NASCAR circuit, signifying the return of Dodge to NASCAR competition after an 18-year hiatus. Drivers in the initial Dodge campaign included Bill Elliott, Jason Leffler, Ward Burton, Sterling Marlin, John Andretti, Buckshot Jones, Kyle Petty, Stacy Compton, Dave Blaney, and Casey Atwood. Marlin was the first to win in a Dodge, giving the marque its first victory since 1977, with Neil Bonnett driving. The Intrepid continued in NASCAR until 2006 when the Dodge Charger was only used.
Hybrid electric concepts
In the late 1990s, Chrysler used the Intrepid as a research platform for a hybrid electric vehicle in a diesel-electric configuration. Three variations were built, the Intrepid ESX, ESX II, and ESX III. The first vehicle was built in a series hybrid configuration, while the next two were considered mild hybrids. These were attempted in the time frame of 1997 to 1998.
The ESX design team set a high goal of making the vehicle capable of sipping gasoline at the rate of 80 miles per US gallon (2.9 L/100 km; 96 mpg-imp), but the eventual vehicle only achieved an estimated 55 miles per US gallon (4.3 L/100 km; 66 mpg-imp). The figure was impressive for such a vehicle. However, the car used a number of exotic materials, which made the cost excessive if it were ever to go into full-scale production. It was estimated that the car would cost $80,000, or roughly $60,000 more than a regular Intrepid. Part of this price increase was caused by the use of lead-acid batteries.
The ESX II team set a somewhat more modest goal of 70 miles per US gallon (3.4 L/100 km; 84 mpg-imp). The vehicle was made much lighter than normal by using an aluminum frame and carbon fiber composite material. This version only cost around $37,000, or about $15,000 more than a standard Intrepid. This version used nickel metal hydride batteries.
The third vehicle, the ESX III, had a target mileage of 72 miles per US gallon (3.3 L/100 km; 86 mpg-imp). It used less expensive materials, such as injection-molded thermoplastic instead of carbon fiber. The estimated cost was only about $7,500 more than a standard vehicle, which would give a total somewhere around $30,000. The ESX III used lithium ion batteries.
- La Femme (1955–1956)
Dodge La Femme
| Dodge La Femme | |
|---|---|
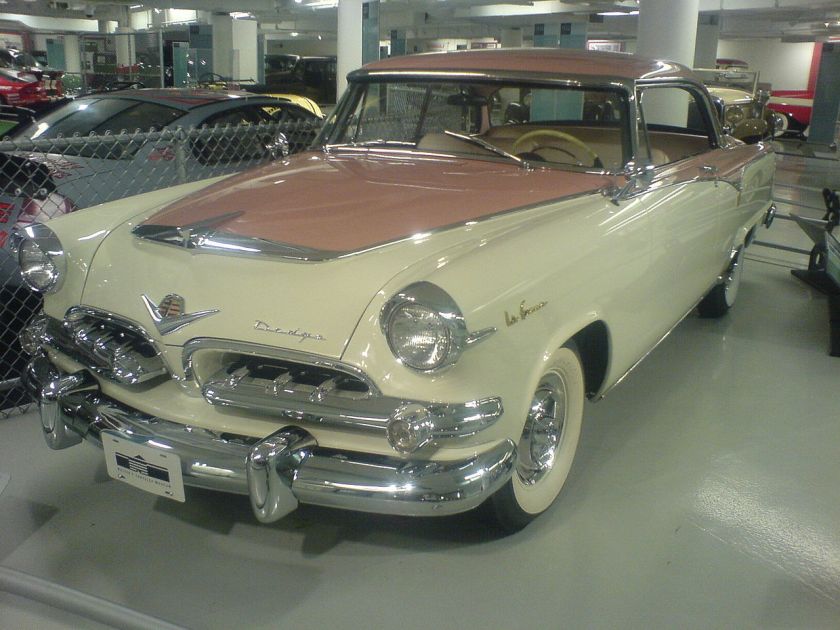

1955 Dodge La Femme
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1955–1956 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door hardtop |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Related | Dodge Coronet |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | V8 |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 120 in (3,048 mm) |
| Length | 212 in (5,385 mm) |
The Dodge La Femme was a product of the Chrysler Corporation‘s Dodge division between 1955 and 1956. The automobile was specifically designed for women. Although a marketing flop, it was later revered as a step forward in gender equality, as cars at the time were generally seen as a tool for men.
Origin
The La Femme’s raison d’être stemmed from Chrysler’s marketing department’s observation that more and more women were taking an interest in automobiles during the 1950s, and that women’s opinions on which color car to buy was becoming part of the decision making process for couples buying an automobile. The La Femme was an attempt to gain a foothold in the women’s automobile market.
The La Femme concept was based upon two Chrysler show cars from the 1954 season. Named Le Comte, and La Comtesse, each was built from a Chrysler Newport hardtop body, and each was given a clear plastic roof over the entire passenger compartment. While the Le Comte was designed using masculine colors, the La Comtesse was painted “Dusty Rose” and “Pigeon Grey” in order to convey femininity. Favorable responses encouraged Chrysler to pursue the La Comtesse concept.
1955
Dodge received the project and renamed the concept the La Femme, which began as a 1955 Dodge Custom Royal Lancer “spring special” hardtop two-door coupe, painted “Sapphire White” and “Heather Rose”. From there, the exterior received special gold-colored “La Femme” scripts that replaced the standard “Custom Royal Lancer” scripts on the cars front fenders.
The interior of the car also received attention and features. 1955 La Femme interiors were upholstered in a special tapestry material featuring pink rosebuds on a pale silver-pink background and pale pink vinyl trim. The La Femme came with a keystone-shaped, pink calfskin purse that coordinated with the interior of the car. The purse could be stowed in a compartment in the back of the passenger seat, and its gold-plated medallion faced outward. This brushed-metal medallion was large enough to have the owner’s name engraved on it.
Each purse was outfitted with a coordinated set of accessories inside, which included a face-powder compact, lipstick case, cigarette case, comb, cigarette lighter and change purse, all made of either faux-tortoiseshell plastic and gold-tone metal, or pink calfskin and gold-tone metal, and all were designed and made by “Evans”, a maker of women’s fine garments and accessories in Chicago.
On the back of the drivers seat was a compartment that contained a raincoat, rain bonnet and umbrella, all made from a vinyl patterned to match the rosebud interior fabric. Marketing brochures stated that the car was made“By Special Appointment to Her Majesty… the American Woman.”
1956
For 1956, the La Femme returned, with no less fanfare; letters to dealers from Dodge’s marketing department called the La Femme a “stunning success”. For 1956, Dodge replaced the Heather Rose and Sapphire White scheme with a Misty Orchid and Regal Orchid color scheme. The interior of the car in 1956 did not take its cue from the 1955 model, and instead featured “La Femme”-only seat patterns, headliner, interior paint and carpet. The fabrics used have proven difficult to reproduce. The seat coverings were made of a heavy white cloth with random, organic-seeming patterns of short lavender and purple loops, in a manner similar to loop-pile carpeting. The headliner cloth was heavy white fabric, with many tiny random splashes of gold paint. The carpeting was loop pile with several shades of lavender and purple. The boxes behind the seats were changed for 1956 to accommodate the rain coat, rain cap and umbrella provided with the model. Both boxes were identical this year, because there was no need to accommodate a purse, which was only offered with the 1955 La Femme.
Legacy
Dodge dropped the La Femme for 1957 and did not revisit the concept. Because the La Femme was an option package ($143), its total production was never broken out from Dodge’s production numbers, although research suggests fewer than 2,500 were made over the two-year period. At least 40 known examples exist of the 1955 version and over 20 for the 1956 version, including at least 3 verifiable D-500 optioned 1956 La Femmes.
Many theories exist concerning the low sales of the La Femme trim package. No evidence of magazine, television, radio, or other La Femme advertisements have been found since 1986. Given the large number of Dodge dealerships in the U.S. at the time, few of them received a demonstration La Femme for their showroom. Instead, single-sheet dealer pamphlets were the only clue that Dodge La Femmes were available, when other trim-special models such as the Chrysler 300 letter series, Plymouth Fury, and DeSoto Adventurer were widely promoted.
That was part II off Dodge Cars and Truck.
In Part III I hope there is place for the rest.
- Lancer (1955–1989)
- Magnum (1978–1979, 2005–2008)
- Matador (1960)
- Mayfair (1953–1959)
- Meadowbrook (1949–1954)
- Mirada (1980–1983)
- Monaco (1965–1978, 1990–1992)
- Neon (1995–2005)
- Nitro (2006–2012)
- Omni 024 (1979–1982)
- Omni (GLH) (1978–1990)
- Phoenix (1960–1973)
- Polara (1960–1973)
- Power Wagon (1945–1980)
- Ram 50 (1979–1996)
- Ram SRT 10 (2004-2006)
- Ram Van (1971–2003)
- Ramcharger (1974–2001)
- Rampage (1982–1984)
- Royal (1954–1959)
- Shadow (1987–1994)
- Sierra (1955–1956)
- Spirit (1989–1995)
- Sprinter (2004–2009)
- SRT-4 (2003–2005)
- St. Regis (1979–1981)
- Stealth (1991–1996)
- Stratus (1995–2006)
- Town Panel and Town Wagon (1954–1966)