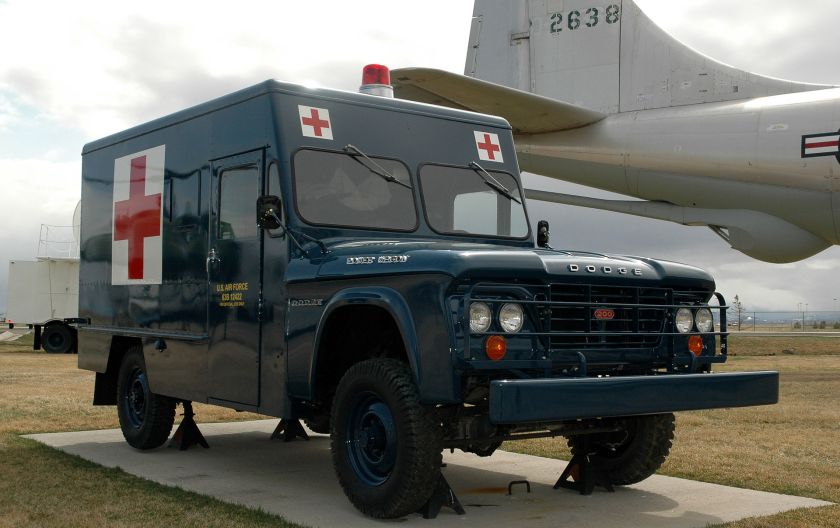
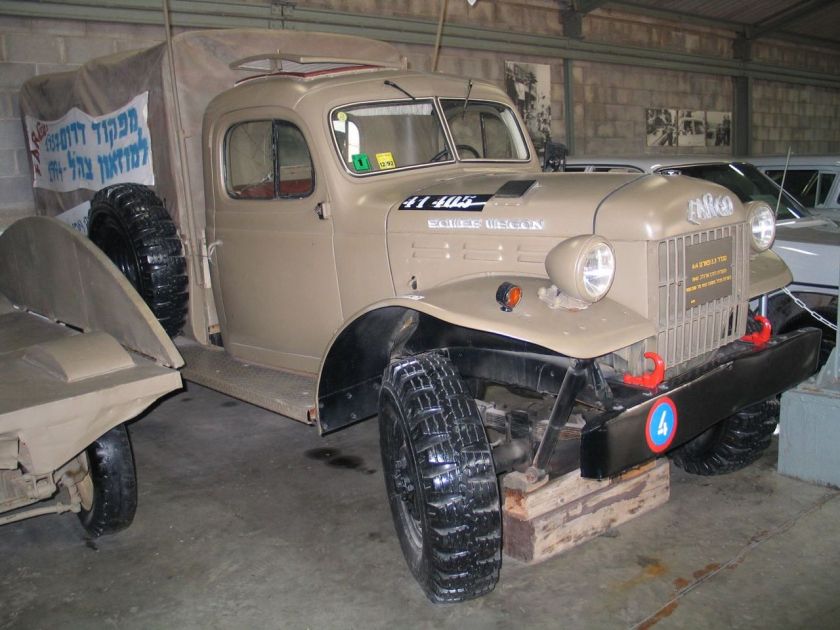
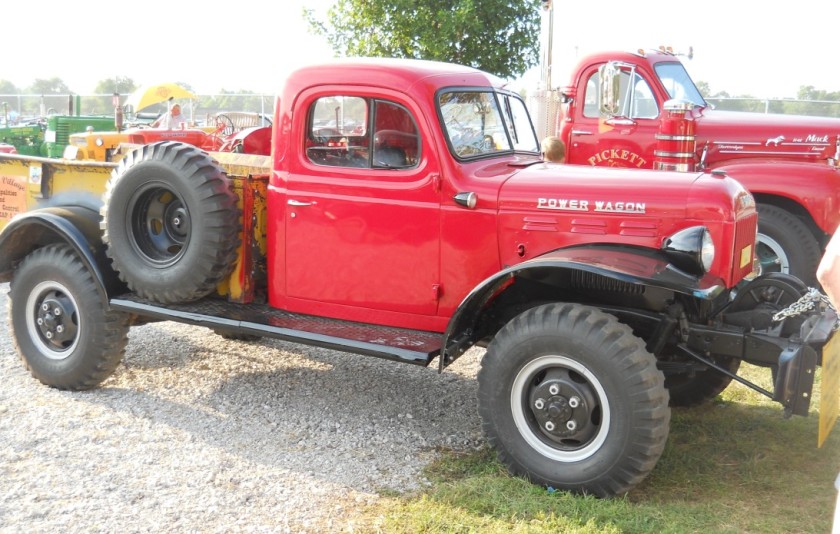
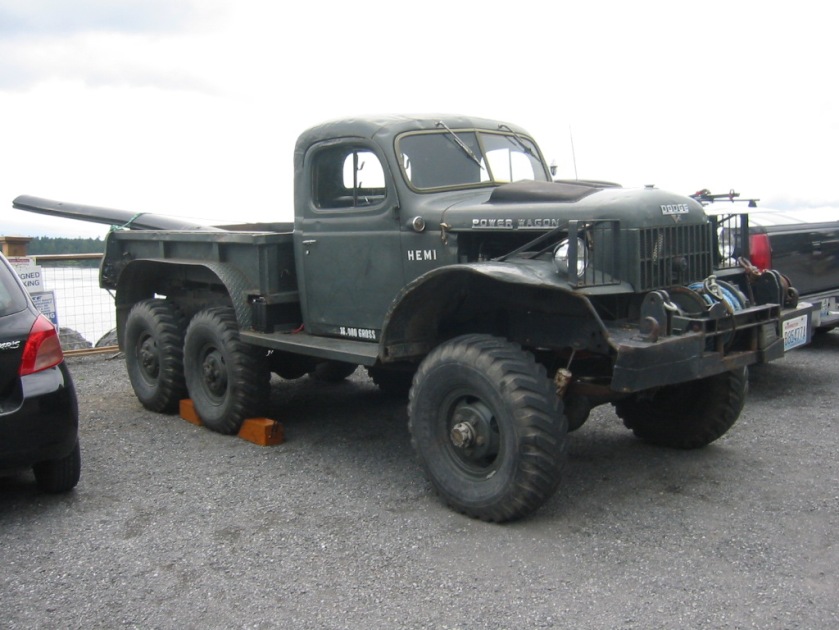
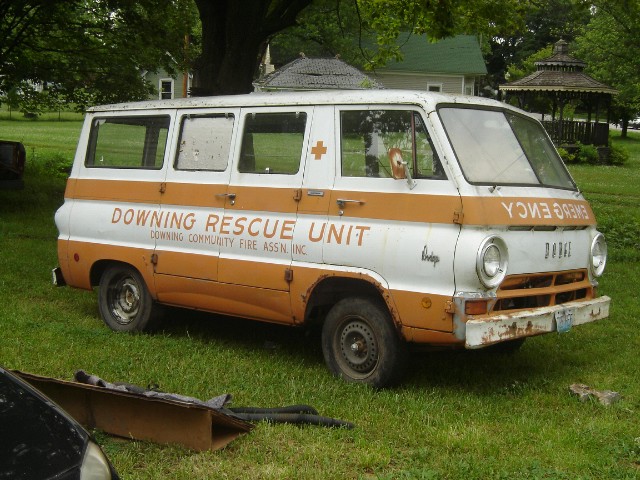
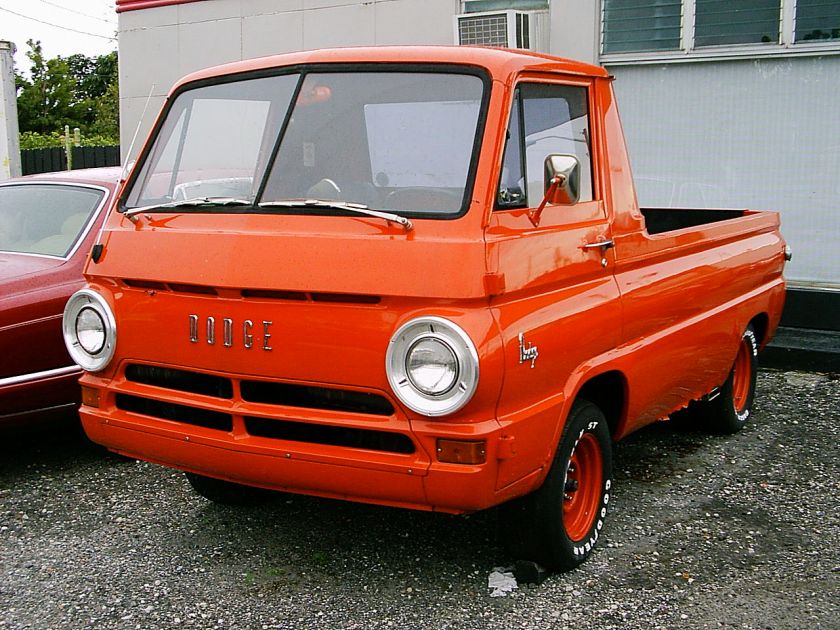
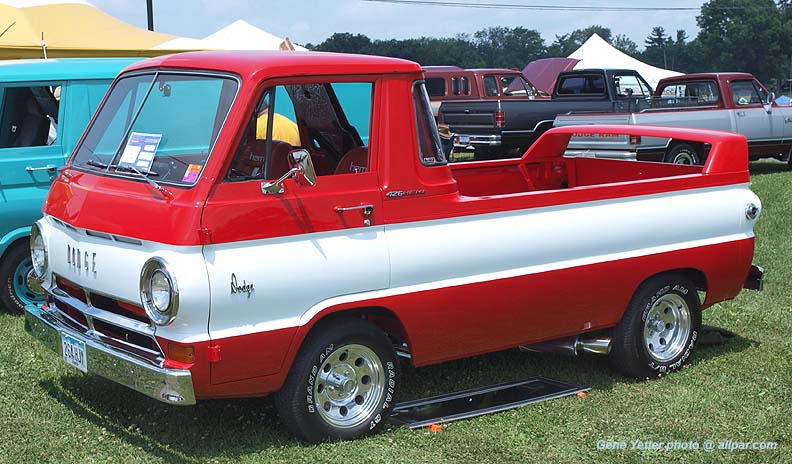
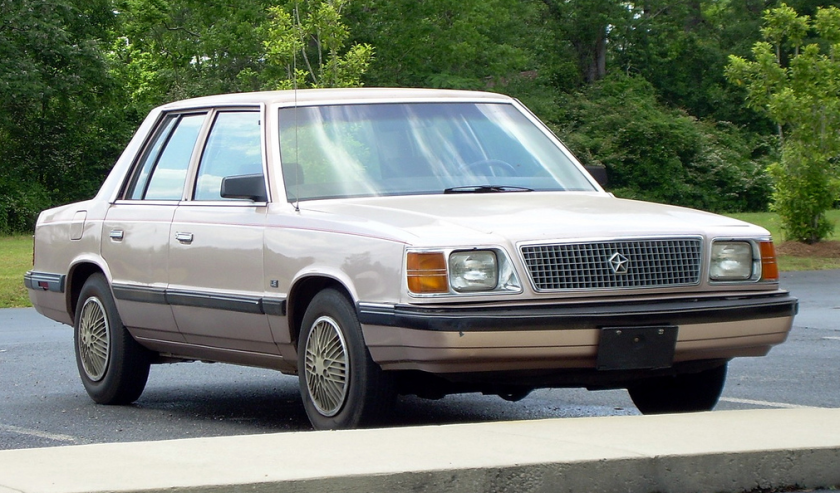
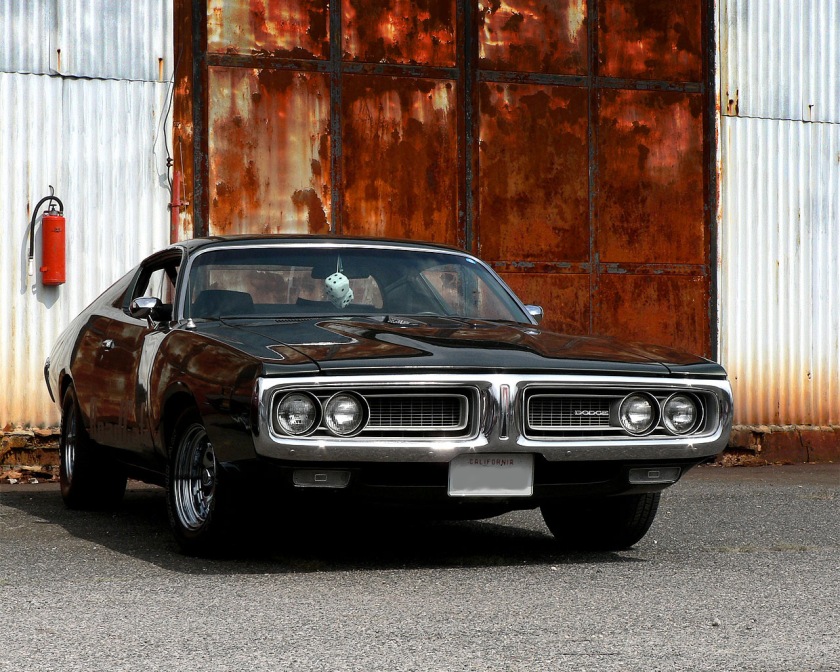
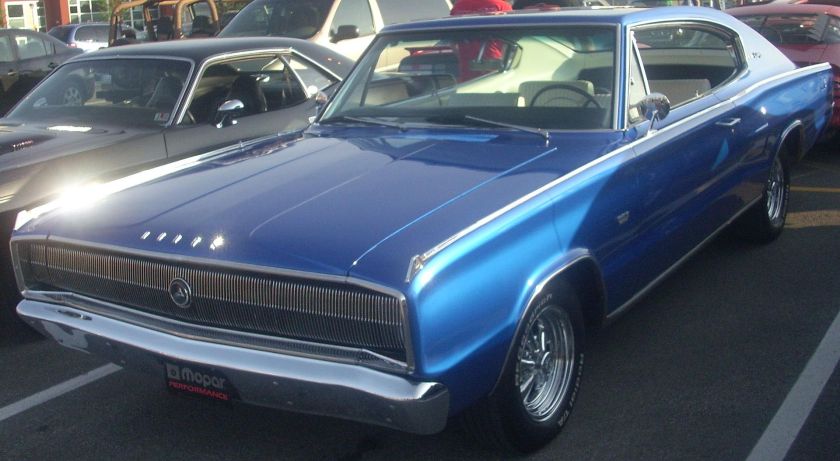
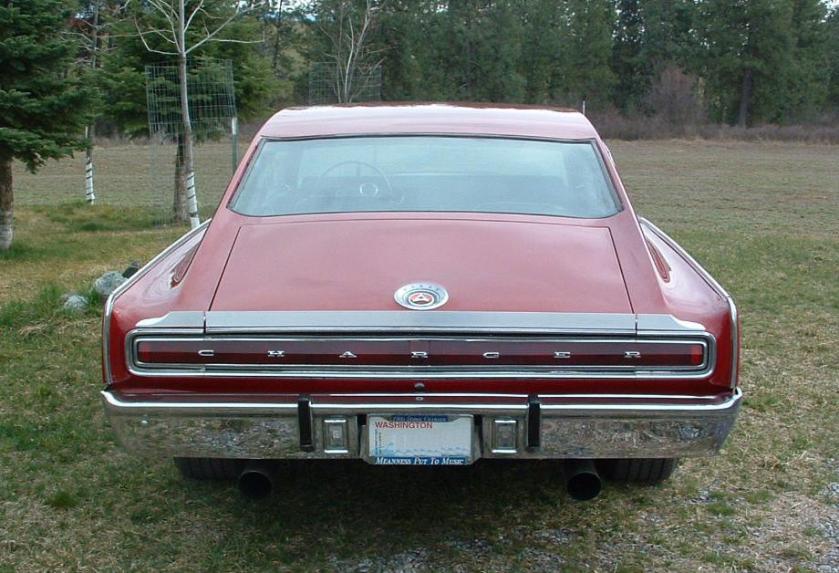
DODGE
Cars and Trucks Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA Part III
In Part III I hope there is place for the rest.
- Lancer (1955–1989)
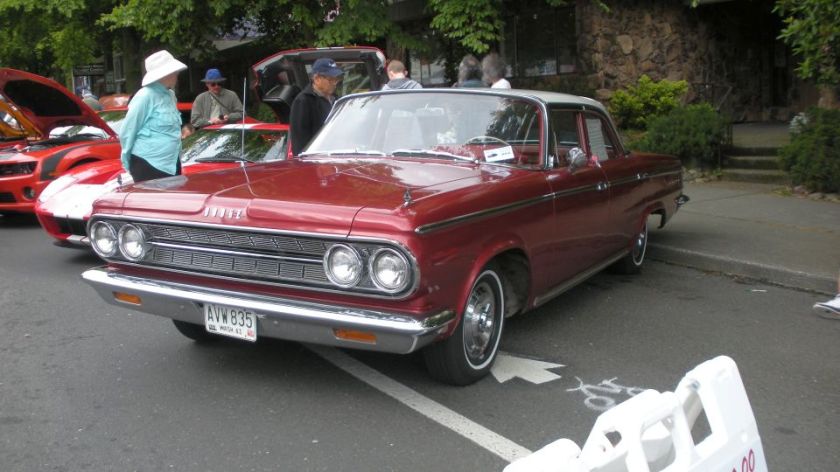
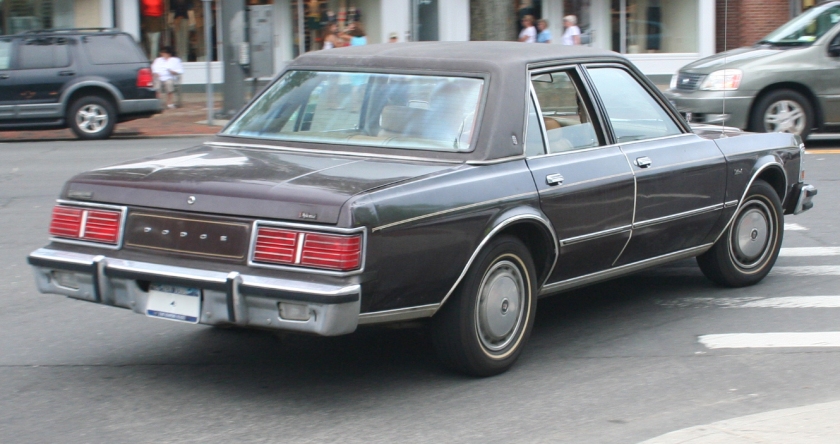
Dodge Lancer
| Dodge Lancer | |
|---|---|
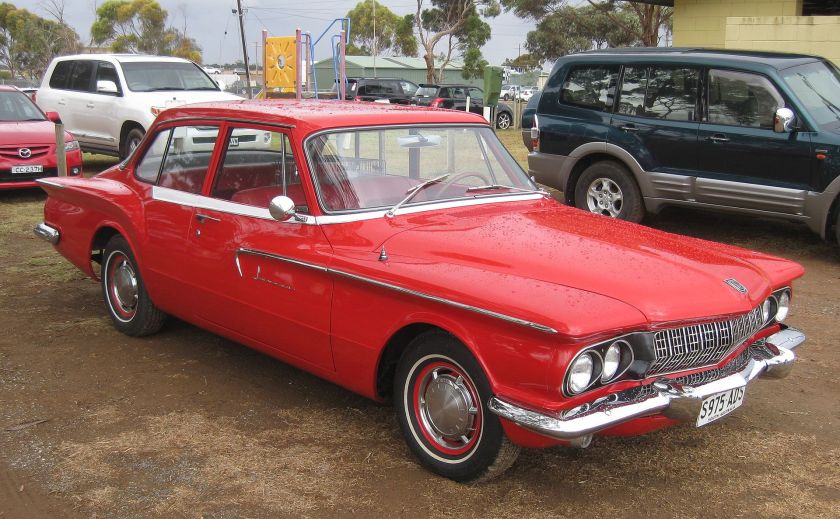

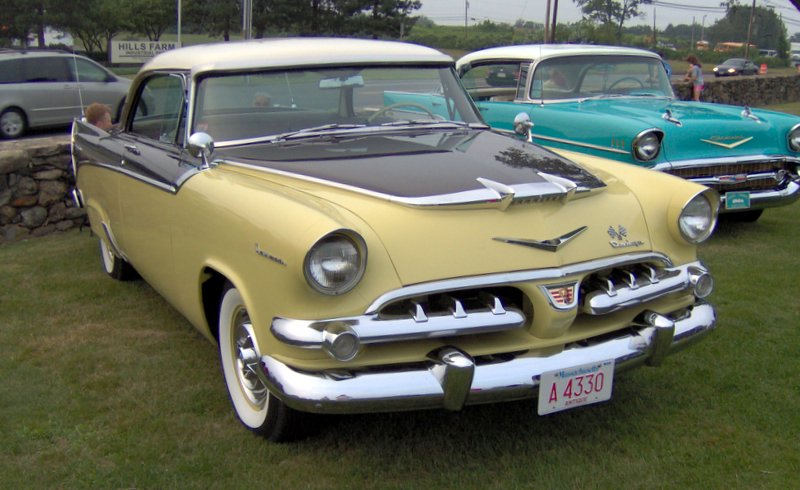
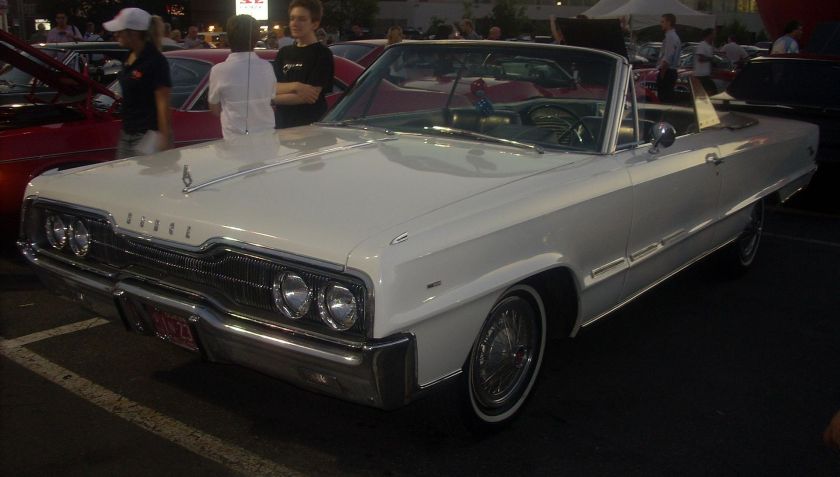
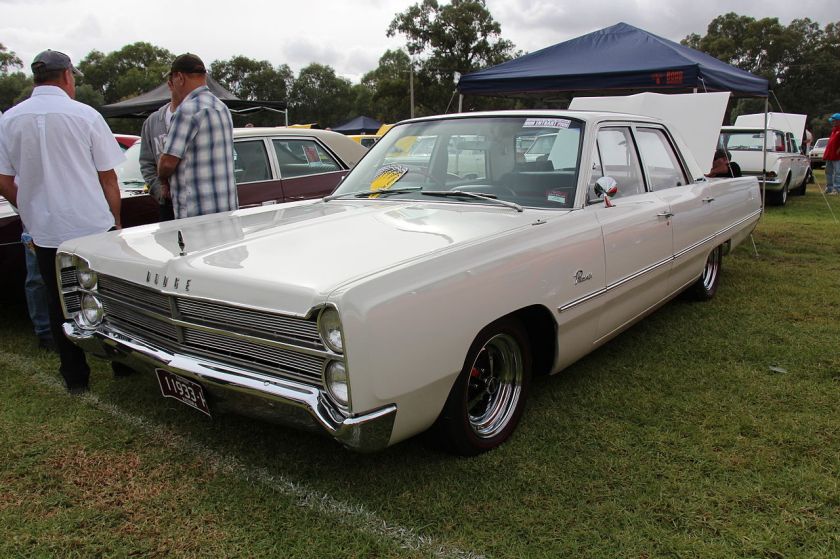
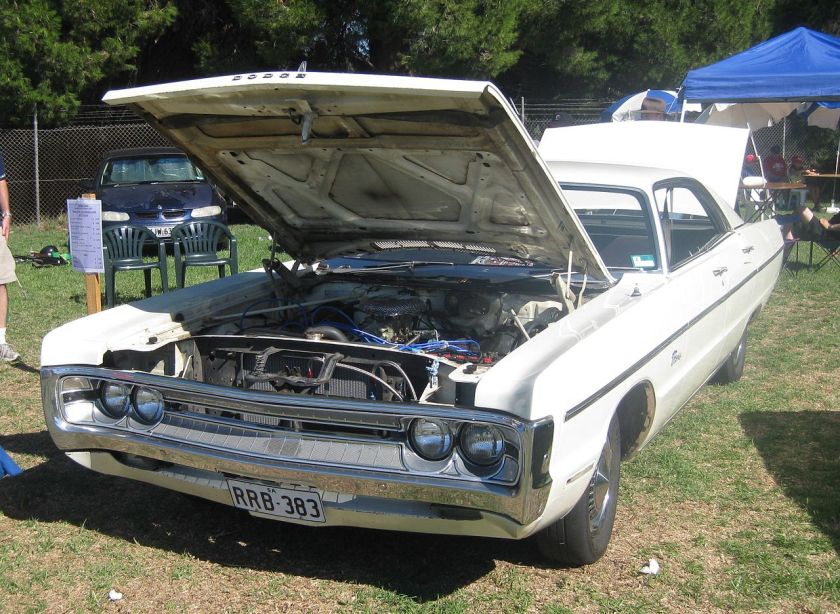
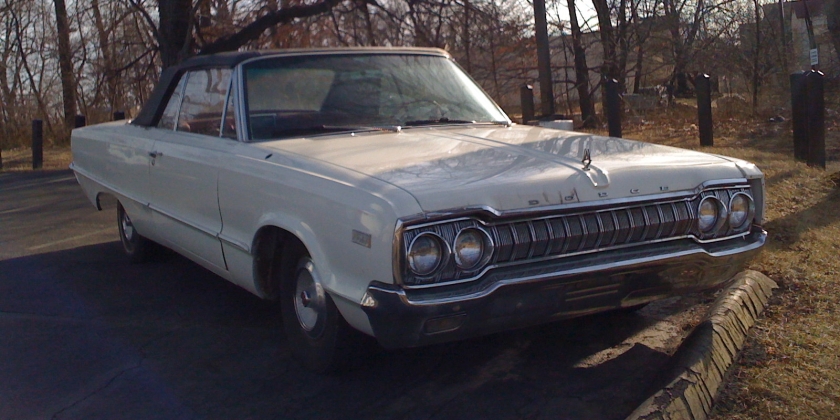
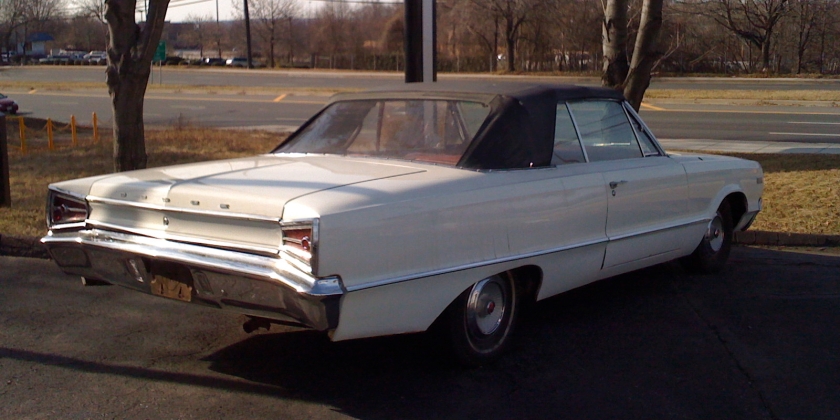
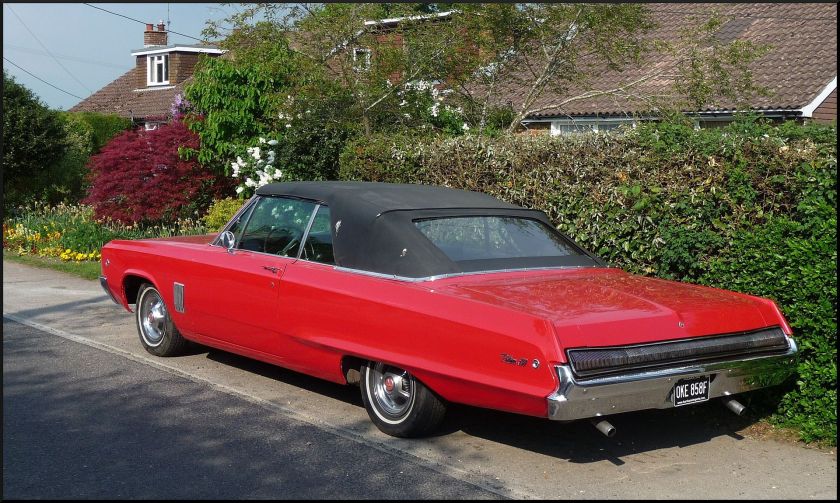
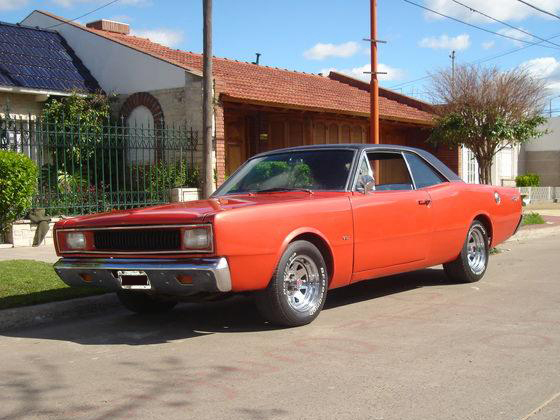
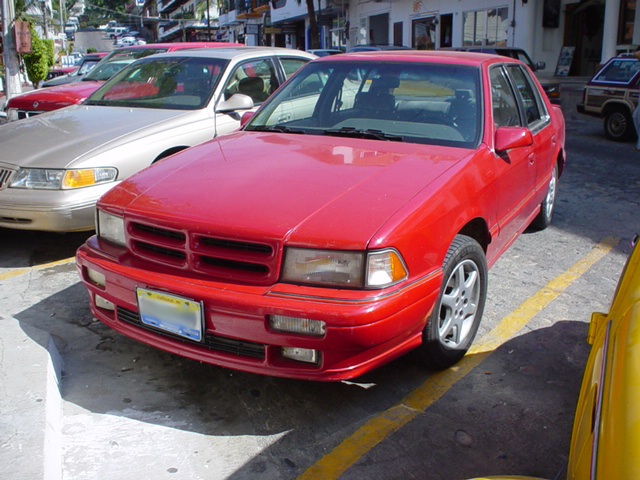
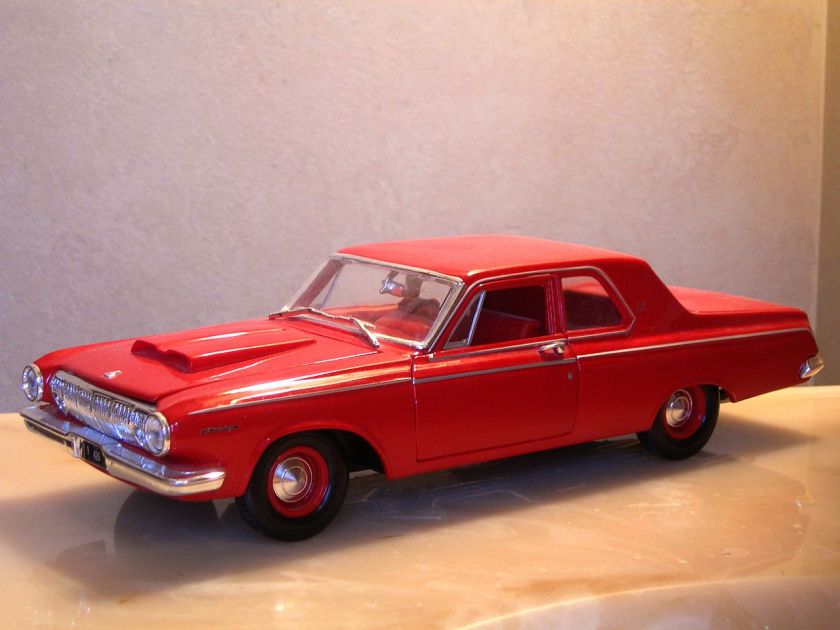
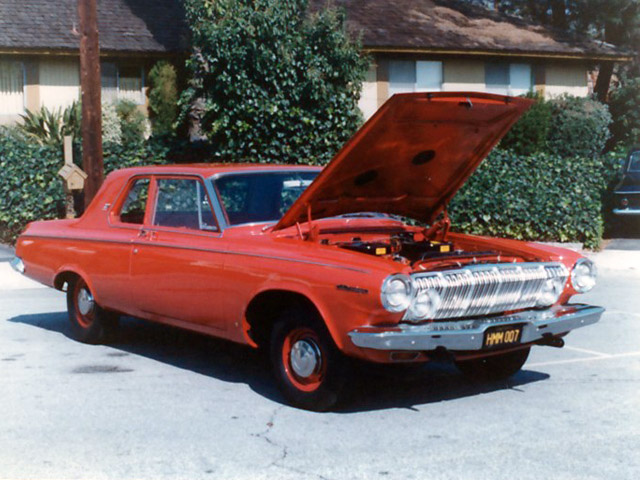
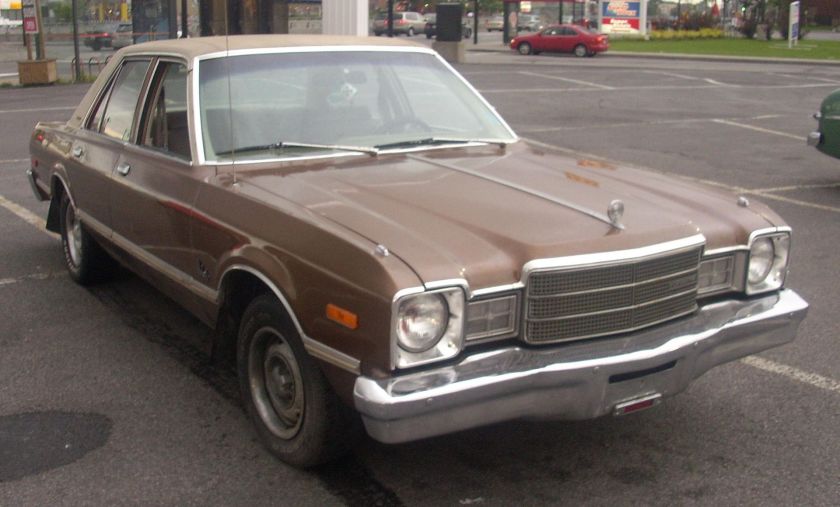
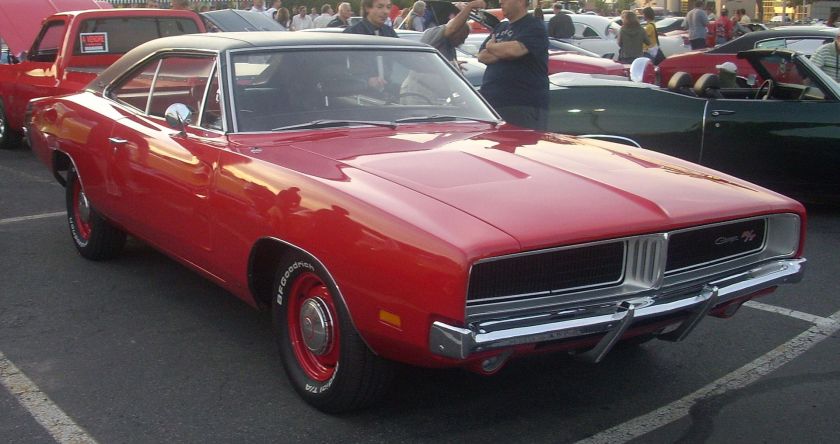
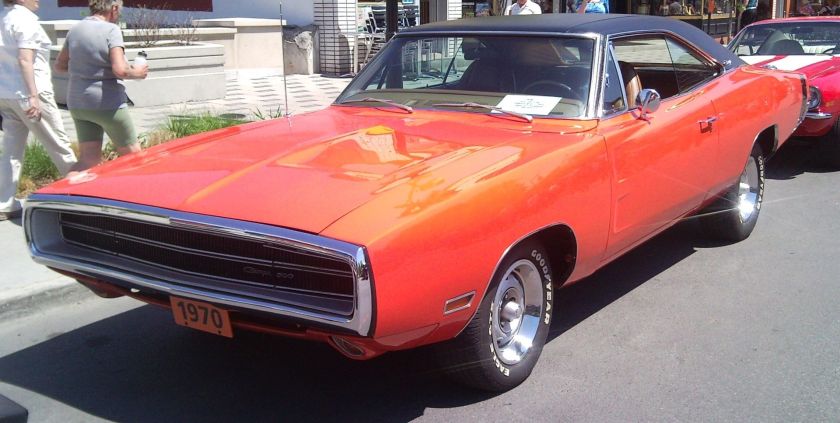
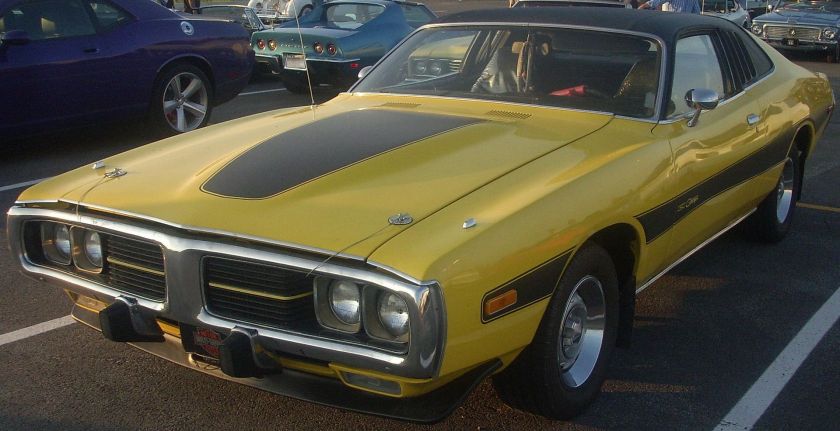
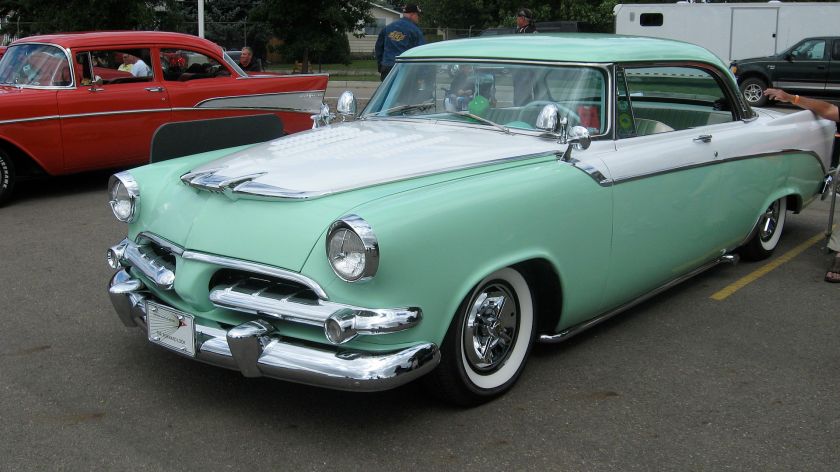
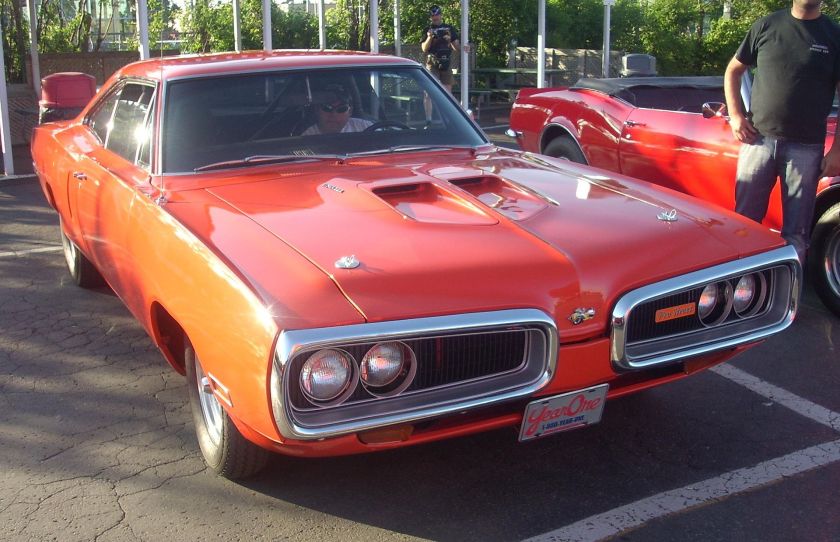
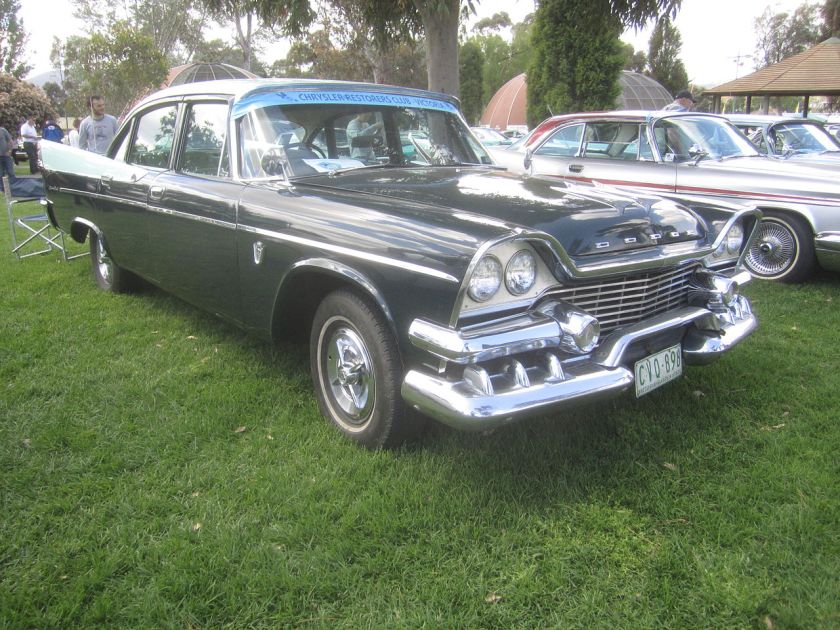
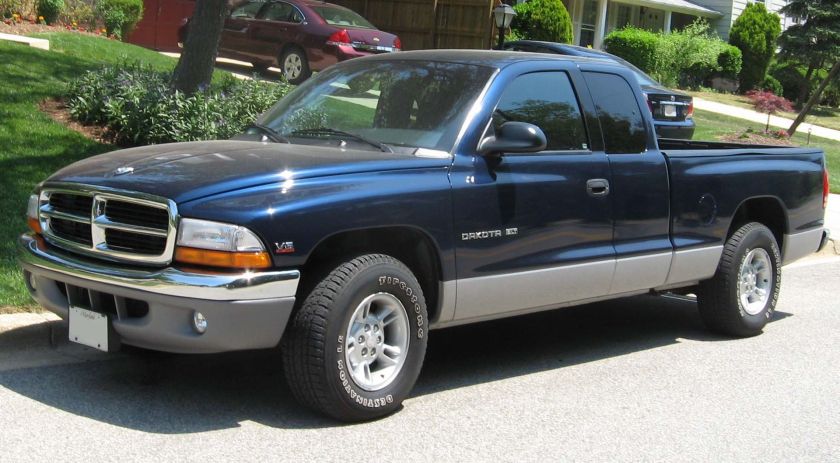
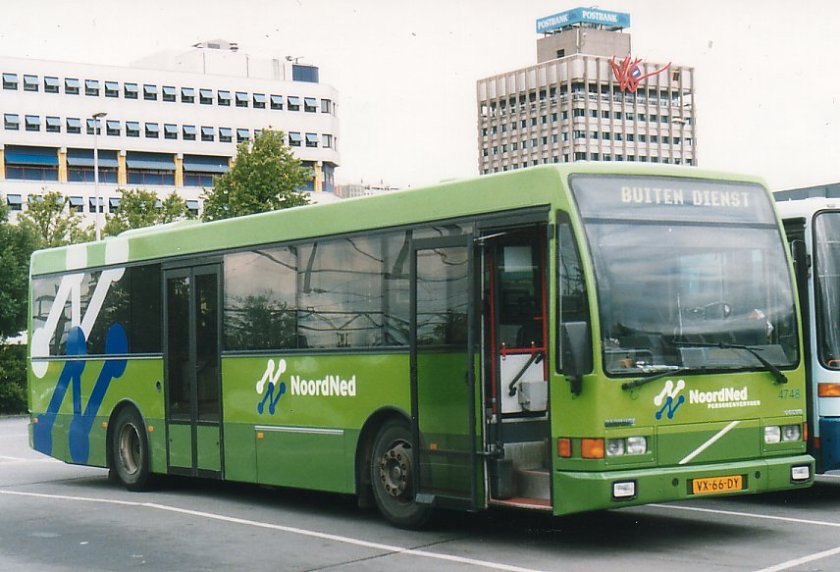
1962 Dodge Lancer 170 2-Door Sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1955–1959 1961–1962 1985–1989 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | FR layout A-body (for 1961–62) FF layout H-body (for 1985–89) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Dart (for 1963) Dodge Spirit (for 1989) |
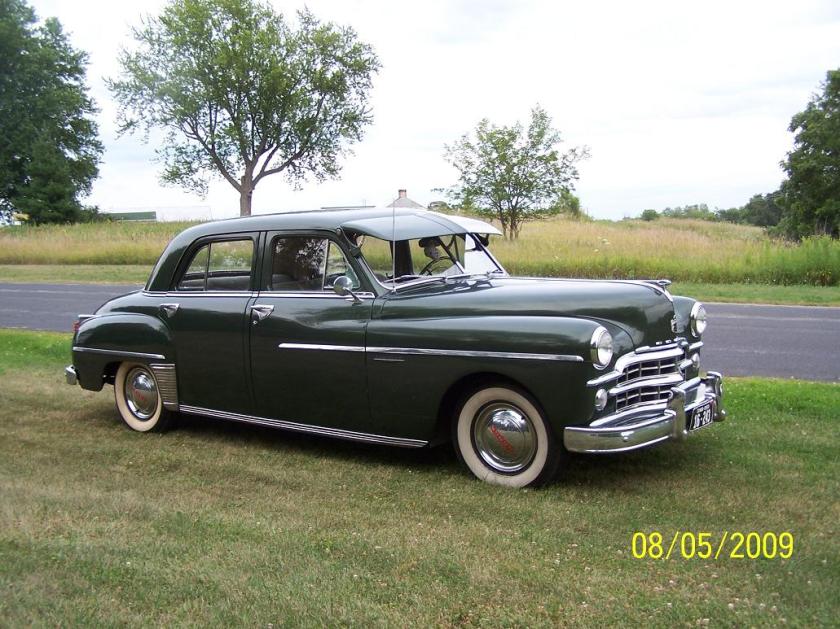
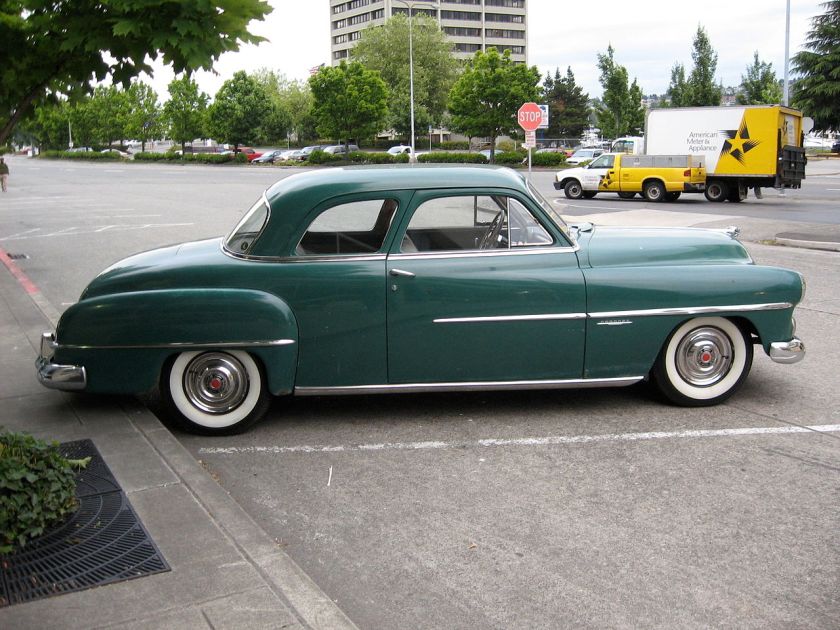
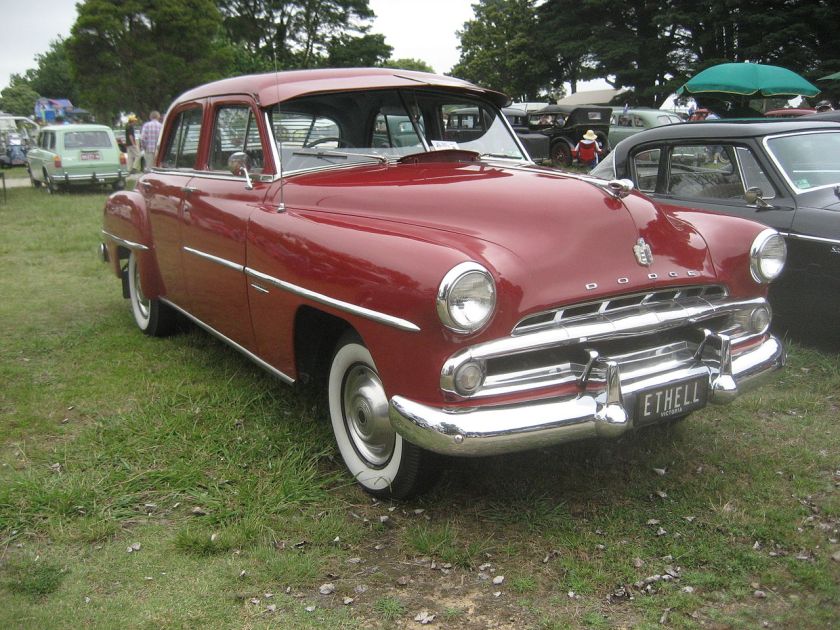
The Dodge Lancer is a passenger car from the Dodge division of Chrysler Corporation. Dodge used the Lancer name on three different vehicles over the years.
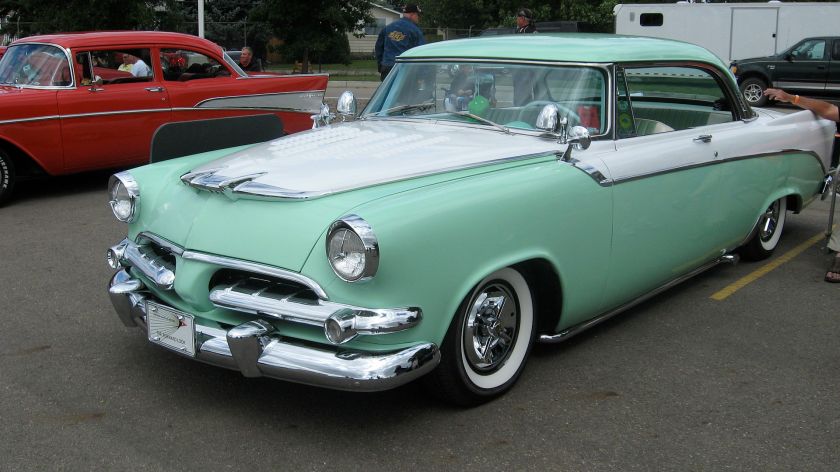
1955–1959 Coronet Lancer, Royal Lancer and Custom Royal Lancer
Dodge used the Lancer name from 1955 to 1959 to designate the two- and four-door hardtop (no B-pillar) models in the full-sized Coronet, Royal, and Custom Royal lines. The Custom Royal Lancer was a hardtop only and top-of-the-line model for Dodge in 1959. There were 6,278 two-door and 5,019 four-door hardtops made in 1959. A total of 11,397 Custom Royal Lancers were made.
The Custom Royal Lancer featured a big-block V8 engine, the 361 cu in (5.9 L) producing 305 hp (227 kW; 309 PS). A D-500 option was available, which included a 383 cu in (6.3 L) engine with a single Carter four-barrel carburetor rated at 320 hp (239 kW; 324 PS), as well as a Super D-500 version with dual four-barrel carburetors producing 340 hp (254 kW; 345 PS).
The Custom Royal Lancer also featured a padded dashboard and steering wheel, Lancer emblems on the fenders, steering wheel, hubcaps, foot-operated windshield wipers, dual radio antennas, deluxe side trim, and thick chrome eyebrows. Optional equipment included power windows and brakes, air conditioning, and swivel seats. The Lancer designation was dropped for 1960.
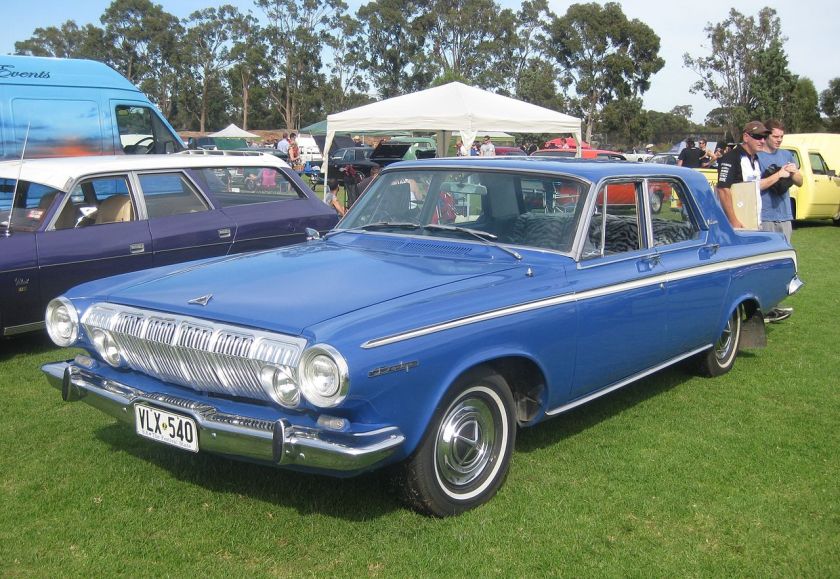
1961–1962 Lancer
| 1961–1962 | |
|---|---|
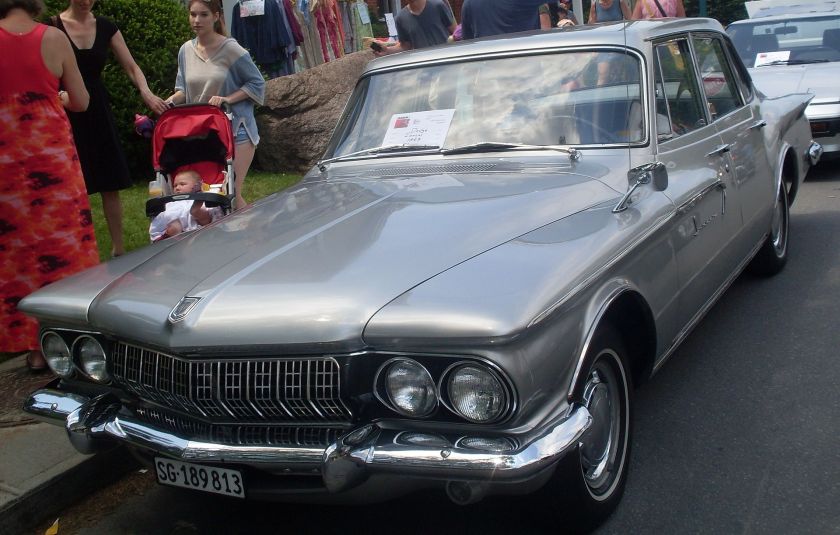

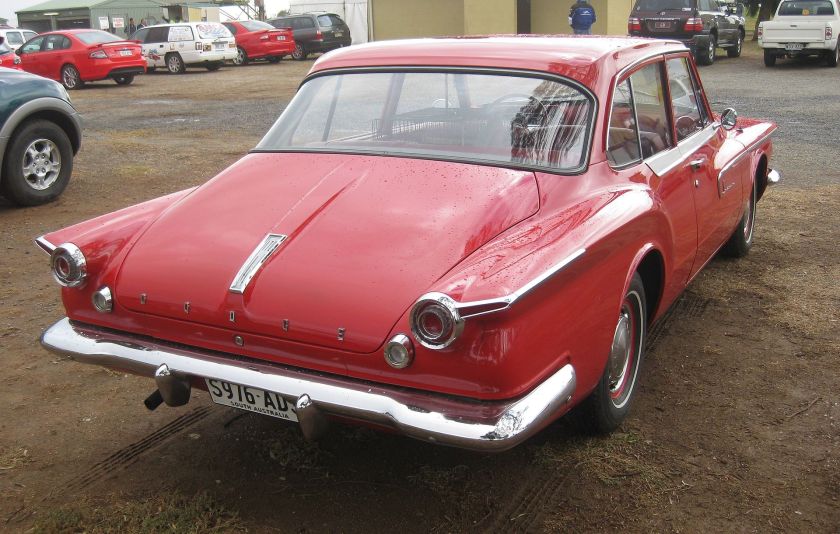
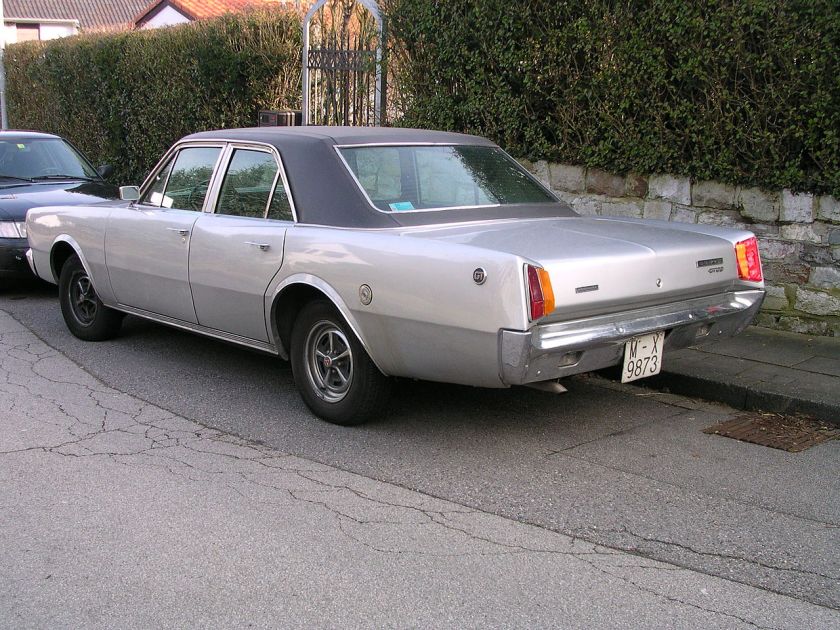
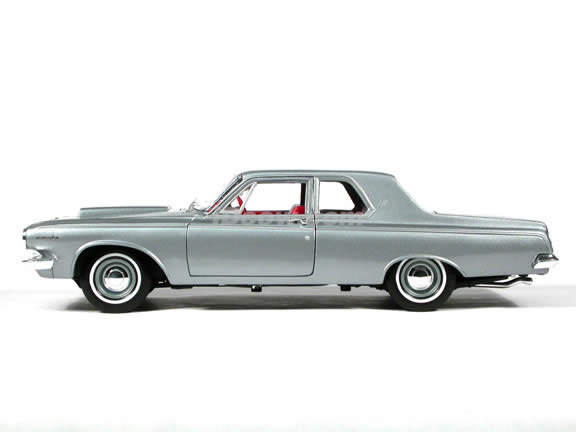
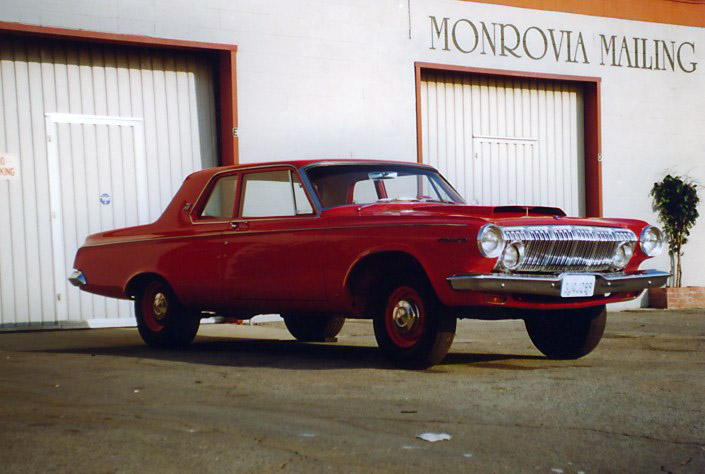
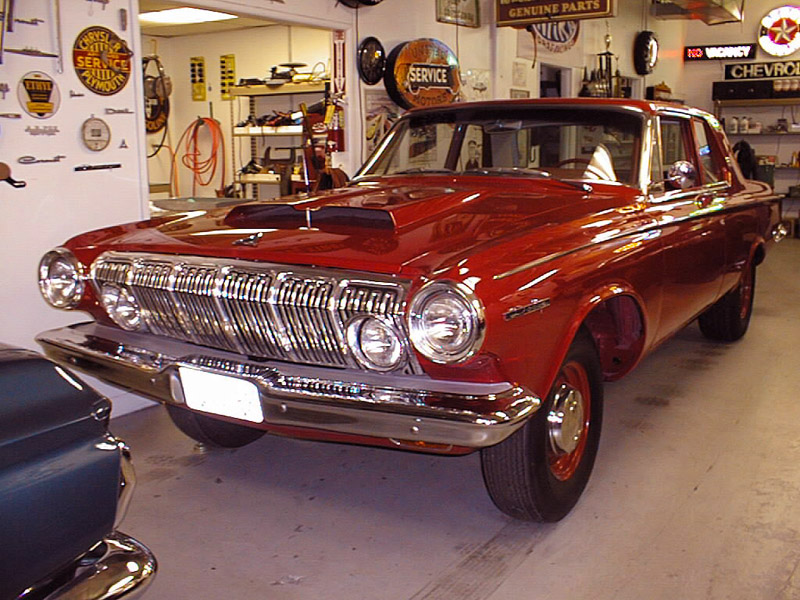
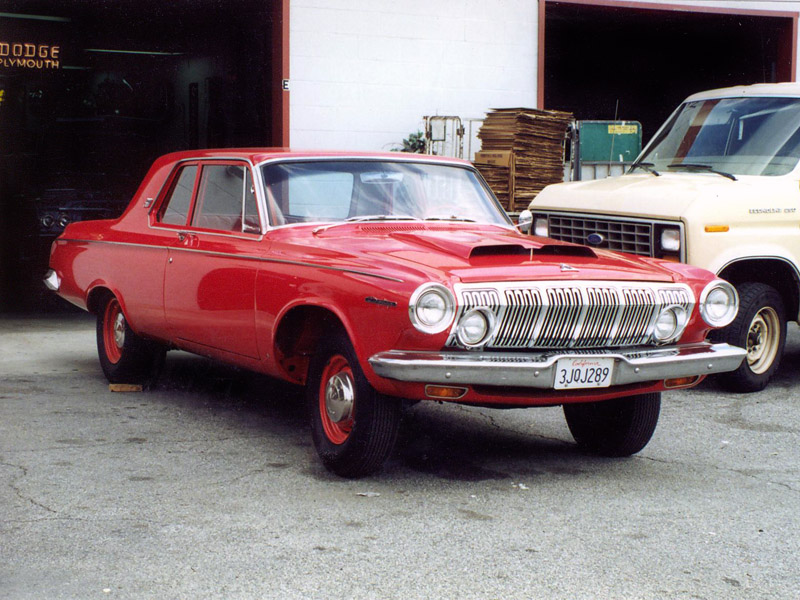
1962 Dodge Lancer 4-Door Sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1961–1962 |
| Assembly | United States: Detroit, Michigan Hamtramck, Michigan Los Angeles, California Newark, Delaware St. Louis, Missouri Mexico: Mexico City Switzerland: AMAG Automobil- und Motoren, Schinznach |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact |
| Body style | 2-door hardtop 2-door sedan 4-door sedan 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | A-body |
| Related | Plymouth Valiant Chrysler Valiant |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 170 cu in (2.8 l) Slant-6 225 cu in (3.7 l) Slant-6 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 3-speed A904 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 106.5″ |
| Length | 188.8″ |
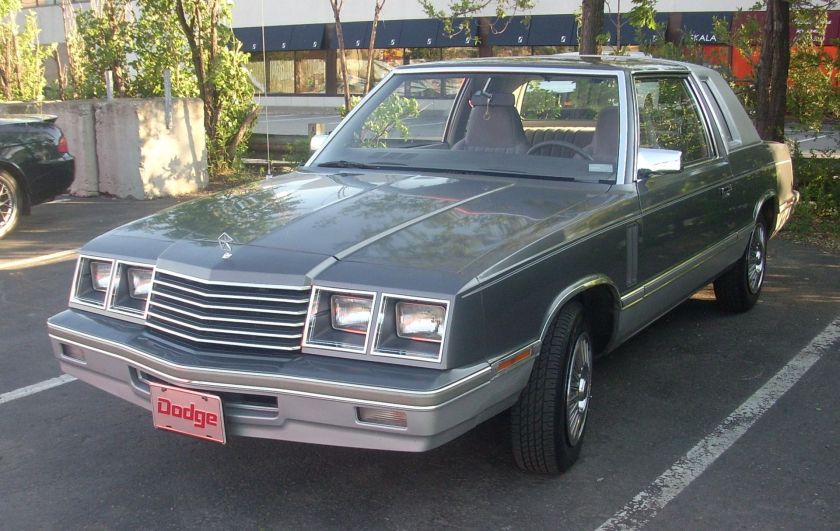
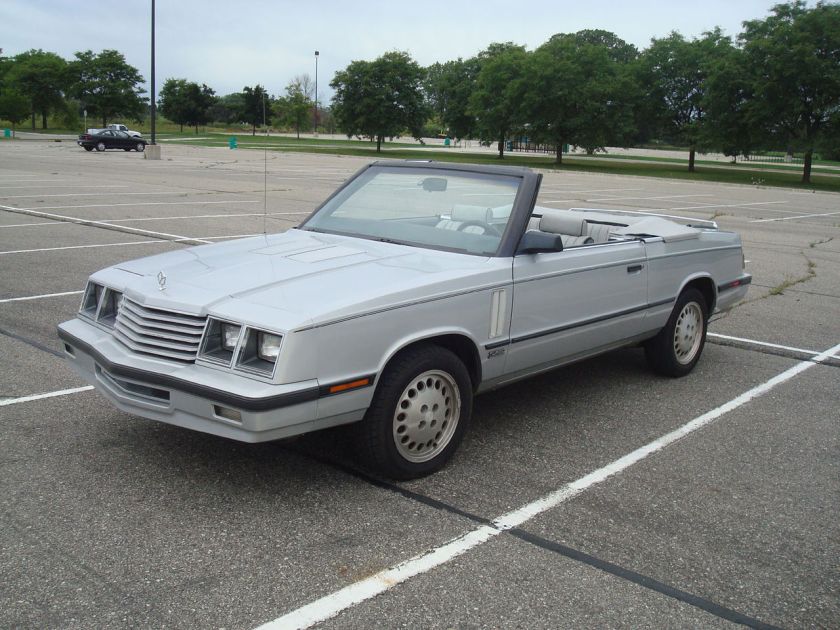
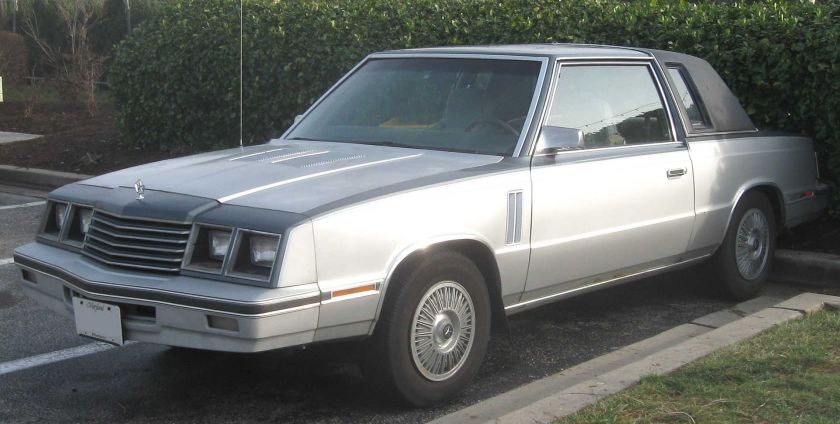
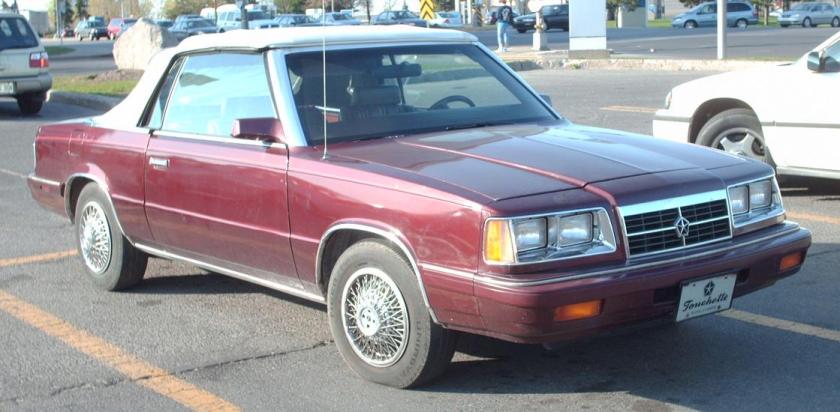
For the 1961 model year, Dodge applied the Lancer nameplate to its higher-priced, upmarket badge-engineered clone of Chrysler’s very popular Valiant compact. The model was introduced when Chrysler officially assigned the Valiant to the Plymouth division for 1961, leaving Dodge dealers without a compact to sell. All the same body variants available on the Valiant were also available on the Lancer: two- and four-door sedans, two-door coupes and four-door wagons.
Styling & trim
The Lancer wheelbase and body shell were identical to those of the Valiant, but interior and exterior trim were fancier on the Lancer. Lancers featured round taillights and a full-width grille, instead of the Valiant’s cat’s-eye taillights and central grille. For 1961, trim levels were the basic “170” and the premium “770”. In 1961, the two-door hardtop was marketed as the “Lancer 770 Sports Coupe”, essentially a performance appearance package. For 1962, the Sports Coupe was given the more concise model name of “GT” and carried premium trim; two-tone paint was available and instead of the front bench seat, there were two bucket seats. Also for the 1962 model, “Lancer GT” medallions were mounted on the doors’ interior trim panels below the vent window and on the sides of the front fenders just aft of the headlamps. “GT” emblems were placed on the hood, the deck lid and on the vinyl dash pad. The headlamp bezels and the grille’s horizontal slats were blacked-out. The GT also lacked certain ornamentation found on the 170s and 770s such as the “Lancer” door scripts, the slanted chrome hash marks on the lower quarter panel, and the hook-ended stainless steel door-to-fender spears.
Powertrains
The Lancer used the slant-6 engine. The base engine was the 170 cu in (2.8 l) unit, rated at 101 bhp (75 kW). The optional power package consisted of the larger 225 cu in (3.7 l) engine, rated at 145 bhp (108 kW). After the start of the 1961 model year, a die-cast aluminum version of the 225 engine block was made available. The aluminum 225 weighed 45 pounds (20 kg) less than the iron 170 and 80 pounds (36 kg) less than the iron 225. Any of the available engines could be equipped at the dealer with Chrysler’s Hyper Pak parts kit for a significant power upgrade: the 170 Hyper Pak’s published output was 148 bhp (110 kW), while the 225 Hyper Pak’s was 196 bhp (146 kW). The Hyper-Pak shaved more than four seconds off the 0 to 60 mph (97 km/h) time versus the standard 225, and was over a second quicker and seven miles per hour faster in the quarter mile. With the Hyper Pak, a 225 Lancer could go from 0 to 60 mph (97 km/h) in 8.6 seconds and turn in a standing quarter mile time of 16.4 seconds. 1962 cars had the engine and transmission moved for a flatter front floor.
Transmission options were a Chrysler-built A903 three-speed manual with the shifter on the floor in 1961 and on the steering column in 1962, or a pushbutton-operated A904 Torqueflite three-speed automatic.
Drag strip & sales competition
In the 1962 NHRA Winternatonals, Wayne Weihe took home the win in the C/FX (Factory Experimental) class with his Hyper-Pak-equipped Lancer, clocking a 15.67 E.T. Although the bigger Dodges were beginning to appear at drag strips around the country, the “Golden Lancer” of Dode Martin and Jim Nelson was just about the fastest compact on the strips in 1962. Stuffed into the engine compartment was a 413 cu in (6.77 liters) Chrysler RB V8 engine modified by the Chrysler engineers’ “Ramchargers” racing team. The Golden Lancer raced successfully in A/FX class and could do the quarter mile in 12.68 seconds at 113 mph.
Lancer sales did not meet expectations and sold about half as well as the Valiant. As a late part of the total redesign of Dodge’s compact car for 1963, the Lancer name was discontinued. Dodge compacts for 1963 through 1976 were named Dart, a name that had previously been assigned to a larger car produced by Dodge from 1960 to 1962.
South African market
In South Africa, a right hand drive version of the Lancer was sold from 1961 through 1963, badged as the “DeSoto Rebel” not very long after the DeSoto name was discontinued in the U.S. All Rebels were equipped with the 170 cu in (2.8 l) Slant 6 engine, and most were equipped with the three-speed manual transmission. As with the Australian RV1 and SV1 Valiants, the Rebel used the instrument cluster from the U.S. 1961 Plymouth Valiant. White reflectors were mounted to the front bumper, in compliance with South African vehicle equipment regulations. The Rebel name was re-introduced by Chrysler South Africa in 1967 as the economy-priced “Valiant Rebel”.
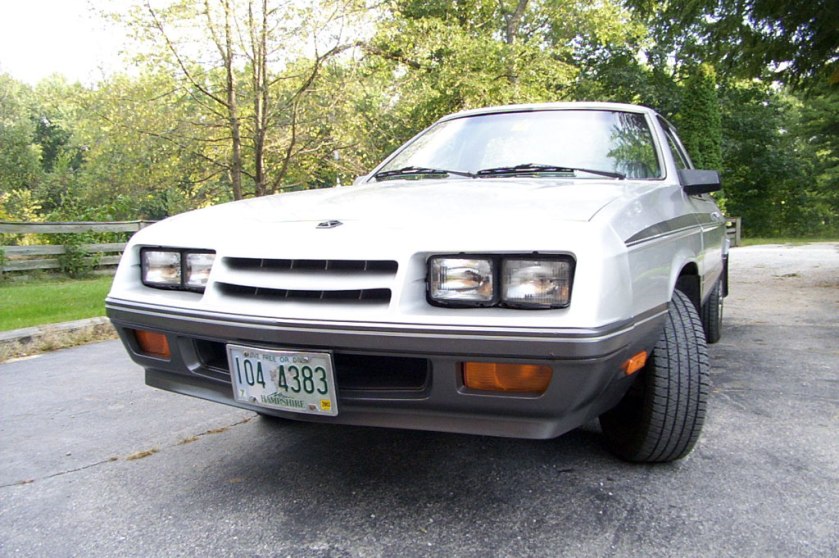
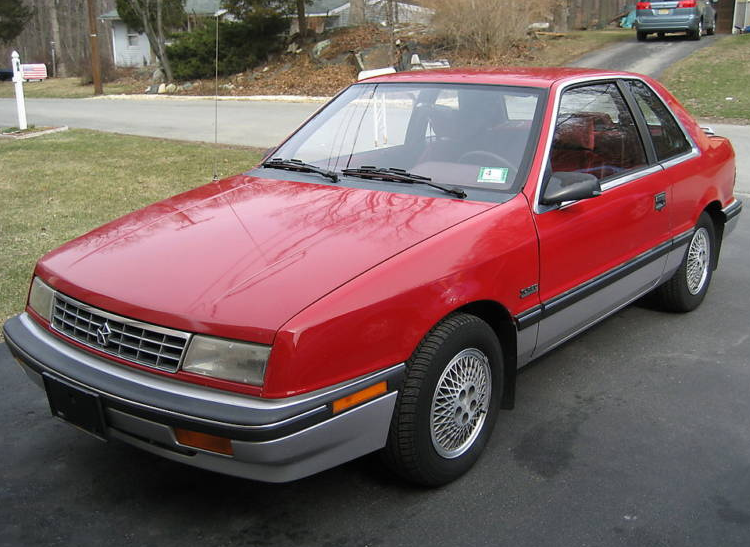
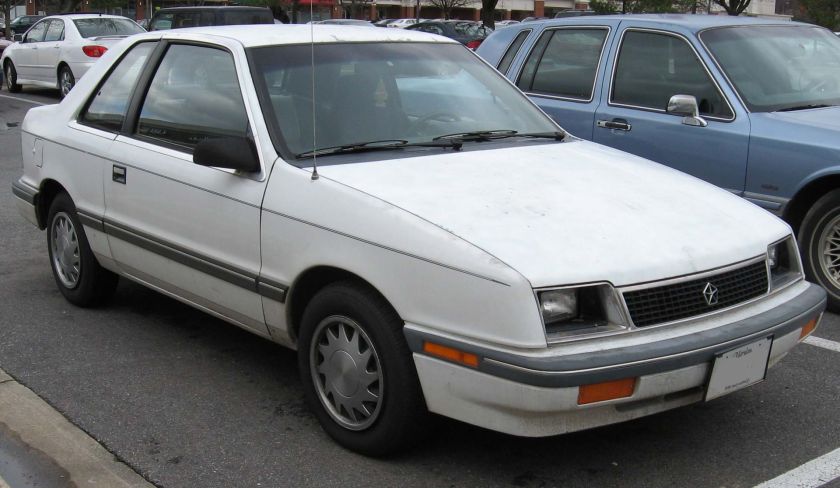
1985–1989 Lancer
| 1985–1989 | |
|---|---|
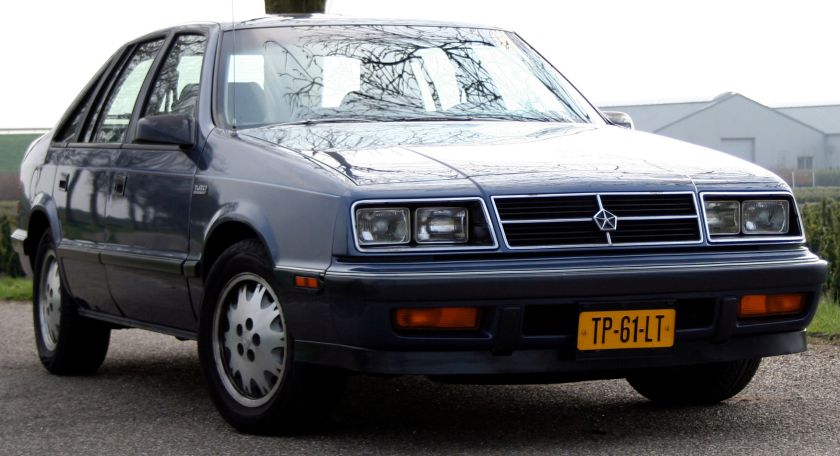

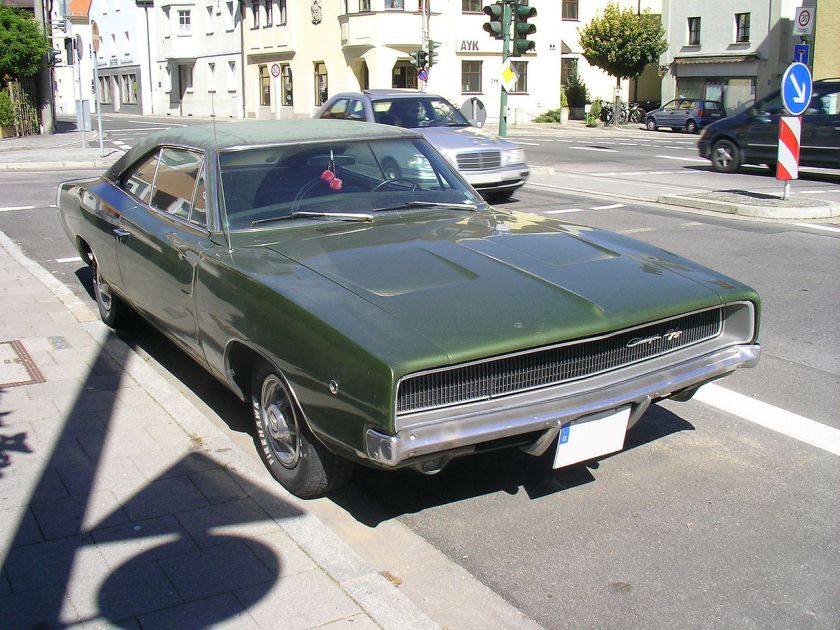
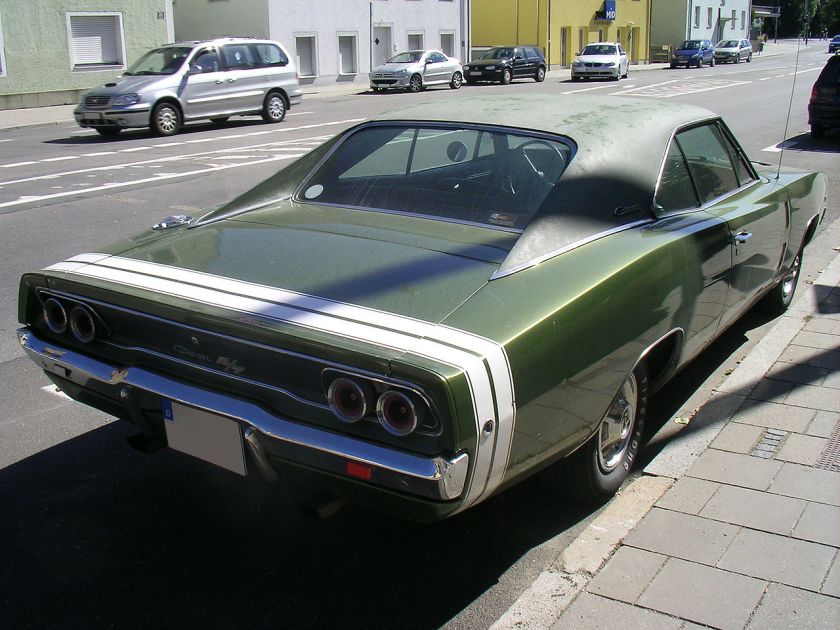
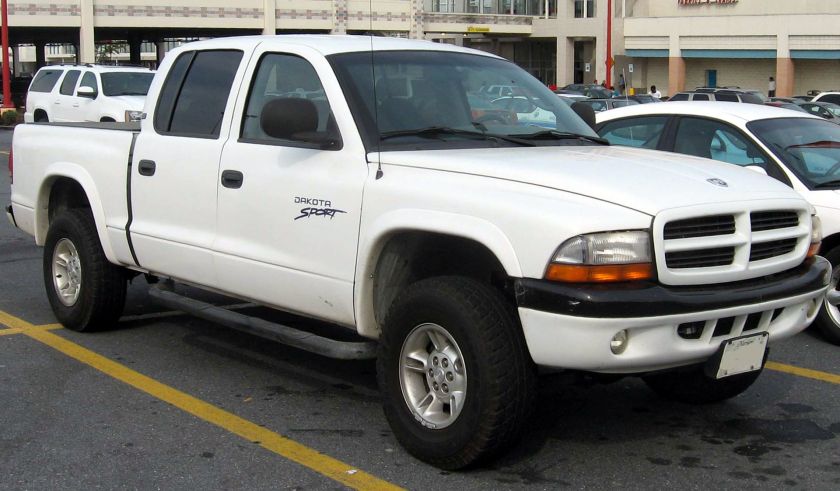
1988 Dodge Lancer ES Turbo
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1985–1989 |
| Assembly | Sterling Heights, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 5-door hatchback |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | H-body |
| Related | Chrysler LeBaron GTS Chrysler LeBaron Chrysler GTS (Europe) Shelby Lancer |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.2 l (134 cu in) K I4 2.2 l (134 cu in) Turbo I I4 2.2 l (134 cu in) Turbo II I4 2.5 l (153 cu in) K I4 |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 3-speed A413 automatic |
The Dodge Lancer was re-introduced in 1985 as a mid-sized 5-door hatchback. It was a rebadged version of the more expensive Chrysler LeBaron GTS and was based on the Chrysler H platform, a stretched version of the Chrysler K platform. The Lancer eventually slotted between the Aries and the 600. All Lancers were built in Sterling Heights, Michigan. Production ended on April 7, 1989, replaced by the Spirit.
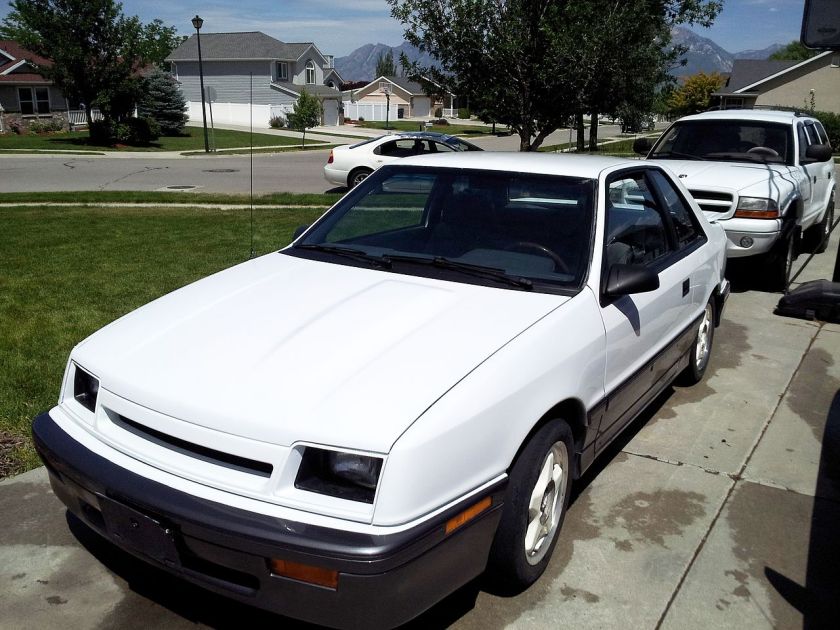
Lancer Shelby
The 1988 to 1989 “Lancer Shelby” was a factory appearance and handling package including upgraded sway bars, shorter springs, and quicker steering along with an assortment of comfort and convenience features including leather seats, power locks, windows, seats and mirrors, a tilt steering wheel and a two-position cup holder. It was inspired by the 1987 Shelby Lancer, which was built by Shelby Automobiles in Whittier, California. Chrysler took over production starting with the 1988 model year, building them in the same Sterling Heights plant as regular Lancers.
The intercooled Turbo II engine with the manual transmission provided 175 hp (130 kW). The automatic variant was equipped with the 146 hp (109 kW) Turbo I. Although it was not planned as a limited edition, only 279 Lancer Shelbys were produced in 1988 and 208 in 1989.
European market
In April 1988, Chrysler started offering some models on the European market. One of them was the “Chrysler GTS”, a rebadged version of the Dodge Lancer ES. Due to European vehicle regulations, the exterior appearance was slightly different. The rear turn signals were amber rather than red, the front sidemarkers and the centre high mount stop lamp (CHMSL) were blanked off, small round repeaters were installed into the front fenders and the sideview mirrors were of spring-hinged rather than rigid design. The engine options included the naturally aspirated 2.2 l (134 cu in) Four, and a turbocharged version of the same engine. From 1989 on, the 2.5 l (153 cu in) Four became available with or without a turbocharger. The 2.2 engine was dropped, except for the Turbo II version that was standard equipment on the Chrysler GTS Shelby, the European sibling of the Dodge Lancer Shelby. A five-speed manual gearbox was standard, with a three-speed automatic transmission as an extra cost option. The GTS Shelby came only with the manual transmission.
The Chrysler GTS had few buyers in Europe; the competition was too hard. Even the comparatively low prices could not help, and sales figures were very low. By the end of 1989, the GTS was replaced by the Saratoga.
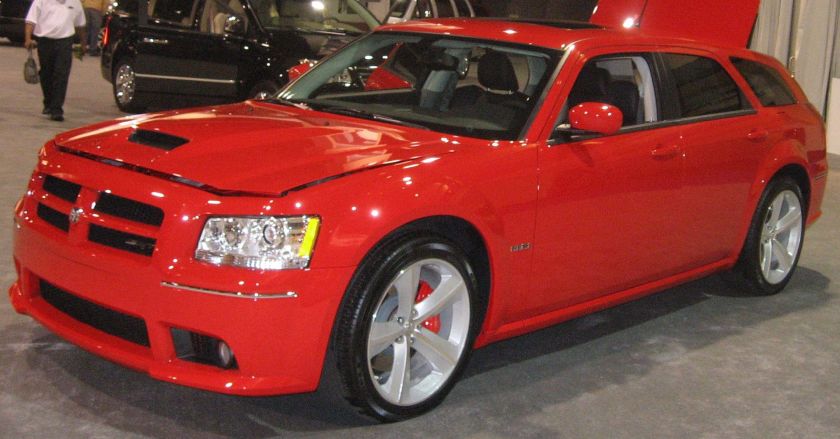
- Magnum (1978–1979, 2005–2008)
Dodge Magnum
| Dodge Magnum | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation (1978–1988) DaimlerChrysler (2005–2007) Chrysler LLC (2008) |
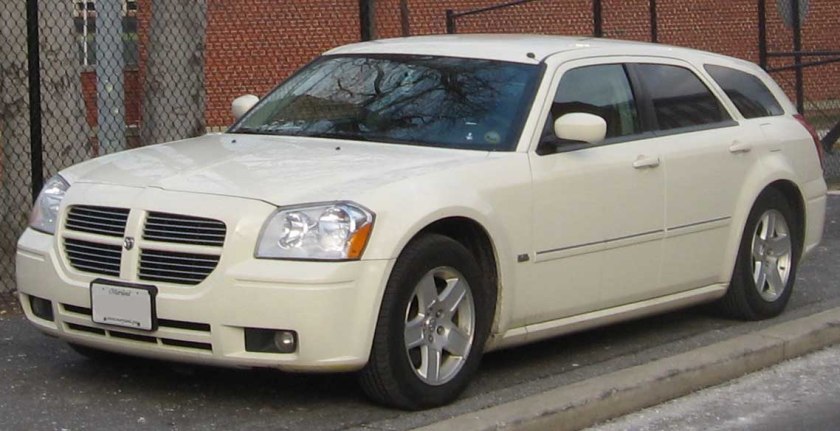
The Dodge Magnum is nameplate used by several Dodge vehicles, prominently as a large coupe marketed from 1978 to 1979 in the United States as well as a rear-wheel drive station wagon introduced in 2004 for the 2005 model year and produced until the end of the 2008 model year and assembled at Brampton Assembly Plant, near Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
In Brazil, the Magnum nameplate was a top of the line version of the local Dodge Dart from 1979 to 1981.
In Mexico, the Dodge Magnum was a sporty rear-wheel drive two-door car based on Chrysler’s M body (American Dodge Diplomat/Plymouth Gran Fury). It had a 360 CID (5.9L) V-8 engine with a single 4 barrel carburetor rated at 300 hp (224 kW). From 1983 to 1988 Dodge marketed a sporty two-door K-car with available turbocharger from 1984 on as the Magnum. Four engines were offered for the Mexican Magnum K, a SOHC I-4 2.2L (K-Trans-4), a turbocharged SOHC I-4 2.2L (1983–86) and two other 2.5L SOHC I-4s, with and without turbocharger (1987–88). The Mexican front-wheel drive Magnum was officially called “Dodge Magnum 400” between 1983 and 1984, as it was a sporty Mexican variation of the American Dodge 400 of the early eighties. For 1985, the “400” suffix was dropped. For the 1987 season, the turbocharger received an intercooler and the power from the turbo engine changed from 140 to 150 hp (112 kW).
1978–1979
| 1978–1979 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1978–1979 |
| Assembly | Windsor, Ontario, Canada |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 2-door coupe |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | B-body |
| Related | Chrysler 300 (1979) Chrysler Cordoba Dodge Charger Dodge Monaco Plymouth Fury |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) B V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed A727 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 115.0 in (2,921 mm) |
| Length | 215.7 in (5,479 mm) |
| Width | 77.2 in (1,961 mm) |
| Height | 53.1 in (1,349 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Charger |
| Successor | Dodge Mirada |
The 1978 and 1979 Dodge Magnum in the United States and Canada was an addition to the Chrysler line up that allowed Richard Petty to continue racing with a Mopar. The Magnum was sold in two forms; the “XE” and the “GT”. It was the last vehicle to use the long running Chrysler B platform. The appearance was somewhat of a rounded off Charger, and was in response to getting a car that would be eligible for NASCAR that would be more aerodynamic, something the 1975-78 Charger was not. Styling features included four rectangular headlights behind retractable clear covers, with narrow opera windows, and an optional T-bar or power sunroof. The Magnum was well-featured with power steering, brakes and seats; the suspension included Chrysler’s standard adjustable, longitudinal torsion bars, lower trailing links, and front and rear anti-sway bars. The base engine was the 318 in³ V8 with Lean Burn, while two and four-barrel carbureted 360 and 400 V8s were also available; weight was nearly 3,900 lb (1,800 kg). The 400 was dropped from the option list in 1979 as Chrysler stopped production of big-block V-8’s in production cars at the end of 1978. A performance model, the “GT” was available with the 400 V8 in 1978 and the “E58” police interceptor (360 V8-195 HP) engine in 1979 along with HD suspension, special axle, special “GT” badging and a “turned metal” dash applique. Technology was advanced for the time with an onboard spark control computer from inception, electronic ignition, and a lockup torque converter. The Magnum name was discarded quickly in favor of the Mirada, a smaller car that was also shared an all new body with the Chrysler Cordoba. The Magnum has something of a cult following today, with several clubs and enthusiasts who are dedicated to the recognition and preservation of Chrysler’s “last B-body”. In 1979, they made 3,704 Dodge Magnums with the T-Top.
NASCAR
For the 1978 NASCAR season, the 1974 Charger that Chrysler teams had continued to use was no longer eligible for competition. Chrysler worked on several car designs to smooth out the current 1975 bodied Charger into something that would be reasonably aerodynamic for the big racetracks and the Magnum design was settled on early in 1977 for use in the 1978 racing season. While not as aerodynamic as the previous 1974 Charger body, the shape of the Magnum showed promise, and the Petty Enterprise built test cars easily reached 190 mph (310 km/h) on test runs. At first it seemed that out on the tracks the cars ran well with Richard Petty almost winning his Daytona 125 (finishing 2nd), and lead 30+ laps of the Daytona 500 until a blown front tire caused him to wreck. However, the lack of factory development support of the small-block Chrysler 360 V8 as a race engine was becoming more of a problem, and in high speed racing traffic the Magnum did not handle well. Richard Petty was particularly harsh in his criticism of the car.
By the latter half of the 1978 season, Petty and Neil Bonnett (the two top Mopar teams) gave up on the cars inconsistent performance and switched to Chevrolets, leaving independent drivers Buddy Arrington (who bought a few of Petty’s Magnums, along with some parts) and Frank Warren, and C&W singer Marty Robbins to soldier on without any substantial (Chrysler did provide sheet metal and some engine parts to teams driving Magnums) factory support. From August 1978, 2-5 independent teams showed up with Magnums in NASCAR races until January 1981, when NASCAR switched to smaller bodied cars. The Magnum never enjoyed the racing heritage of its predecessors, but it was not without its own glorious moments. Petty scored 7 top five finishes in his 17 races with the car, and Neil Bonnett won three poles and scored 5 top five finishes with his. Richard Petty recognized the Magnum with a commemorative decal, depicting his famous number 43 emblazoned on a Magnum for his 1992 Fan Appreciation Tour. Though Petty never won a race in a Magnum, his son, Kyle Petty drove one of his father’s year-old Dodge Magnums in his first race (1979 Daytona ARCA 200), and won. Kyle raced in 5 NASCAR races using the left-over Magnums in 1979, but wrecked them beyond reasonable repair by the 1980 Daytona 125. As of DEC 2012, only two NASCAR Magnums still exist; one (an ex-Petty car) resides in the Talledega NASCAR museum, and the other; (Marty Robbins‘ 1978 Magnum #42) has been restored and is owned by a private party in southern California. The owner occasionally races it in the vintage NASCAR series.
Dodge Magnum (Brazil)
| Brazilian Dodge Magnum (1979–1981) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1979–1981 |
| Assembly | São Bernardo do Campo, São Paulo, Brazil |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | A-body |
| Related | Dodge Dart |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.21 L) LA V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual, 3-speed automatic |
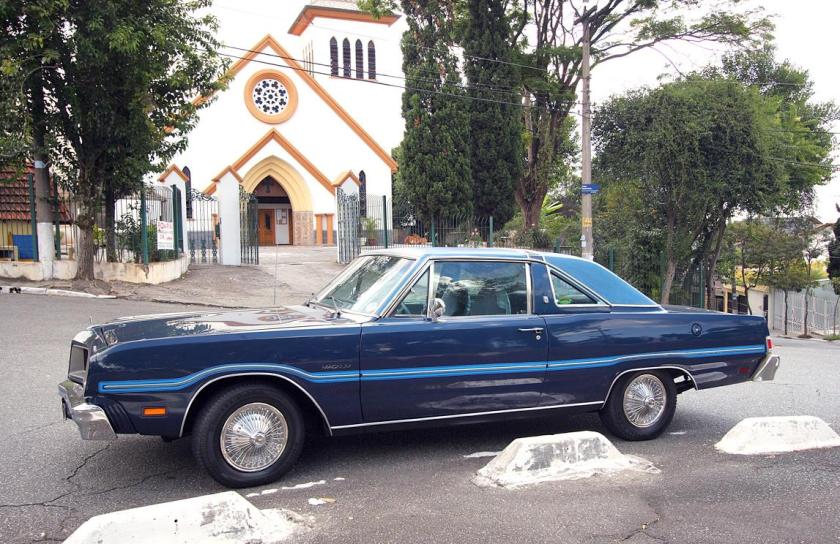
In the old Simca Factory in São Bernardo do Campo, São Paulo, Brazil, the Dodge Dart was produced from 1969 until 1981 (more than 92,000 cars were sold). They were built with minor changes from the original model, starting in 1969, and were all largely based on the 1968 Dart GT (and GTS). For its last three years of production, a two-door upper trim level version of the Dart was sold as the Magnum, featuring the 318 in³V8 engine used in all Dodge coupe and sedan models in Brazil. A unique fiberglass front fascia that included four headlights to give it a more modern look was used, while the rear end was very similar to the American Dart 1975 (the Dart model from the same year having been identical to the Swinger from USA). The Magnum (top of the line) was sold as a separate model from the Dart (bottom line), despite being technically almost identical to the Dart.
The Dodge was very well received in Brazil. Today one can find car clubs with many Dodge coupes in good condition. The coupe and sedan models in Brazil were (all variations from the Dart 1968 model): Dart [1969-1981] (as a 2-door coupe from 1970 until 1981 or as a four-door sedan from 1969 until 1981), sporting but lower priced Dart SE, better equipped Dart DeLuxo (two or four doors), Gran Coupe (more luxurious yet than the Dart DeLuxo, with two doors only), Gran Sedan (above the Dart DeLuxo model, with four doors only), Charger R/T [1971-1980] (coupe bodywork only, from 1971 to 1980 it was the top model in sport segment), LeBaron (replacing the ‘Gran Sedan’ with four-door sedan body, from 1979 to 1981) and Magnum (substitute for the ‘Gran Coupe’, Brazil’s top model in the luxurius segment from 1979 to 1981).
Dodge Magnum (Mexico)
| First generation Mexican Dodge Magnum (1981–1982) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1981–1982 |
| Assembly | Toluca, Mexico (Toluca Car Assembly) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | M-body |
| Related | Dodge Diplomat Plymouth Gran Fury Chrysler LeBaron Plymouth Caravelle Salon |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed A833 manual 3-speed A727 automatic |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Valiant Super Bee |
First generation
In 1980, the F-body cars were discontinued in Mexico, as well in the U.S, so the compact cars Dodge Dart (using the front of the volare and the rear of the aspen) and the Valiant Volare (using the front of the aspen and the rear of the volare) were dropped for this year. The sport compact, the Super Bee that share the F-Body platform was also discontinued, so Chrysler of Mexico had to replace it with a new sport car. In 1979, Chrysler de México introduced the Chrysler LeBaron based in the M-Body Platform, and two years later it introduced the Dodge Diplomat as Dodge Dart. This Mexican M-body Dart was very similar to the American Plymouth Gran Fury in appearance/trim, but had Chrysler’s Rallye road wheels instead of deluxe wheel covers. As the same case that in 1970, Chrysler de Mexico used a small platform and the name of an American sports car (the B-Body Dodge Magnum) and equipped it with the 360 LA V8 engine. The Mexican Dodge Magnum had the 360 CID (5.9L) engine with a Carter Thermoquad four barrel carburetor rated in 300 hp (224 kW), Mopar oil cooler, a 3-Speed A727 automatic transmission, with the 4-speed A833 manual transmission optional, heavy duty suspension, power brakes, stabilizer bars in the front and rear and a Dana 44 differential with positive pass and positraction. All the windows and windshield chromed metals were painted flat black, only the bumpers and the front grill were chromed, and the front fascia wore “Magnum” logo, in the side of the front fenders was put again the “Magnum” logo with a 5.9L decal. The Mexican RWD Dodge Magnum was offered only for the 1981-1982 model years.
Second generation
| Second generation Mexican Dodge Magnum 400/Magnum K (1983–1988) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1983–1988 |
| Assembly | Toluca, Mexico (Toluca Car Assembly) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe |
| Layout | FF layout |
| Platform | K-body |
| Related | Dodge 400 (USA) Plymouth Caravelle K (Canada) Dodge Aries K (USA) Plymouth Caravelle (USA) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | Chrysler SOHC K-Trans-4 engine 2.2L-2.5L I4 Chrysler Turbo SOHC K-Trans-4 engine 2.2L I4 Turbo |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual 5-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Chrysler Shadow GTS |
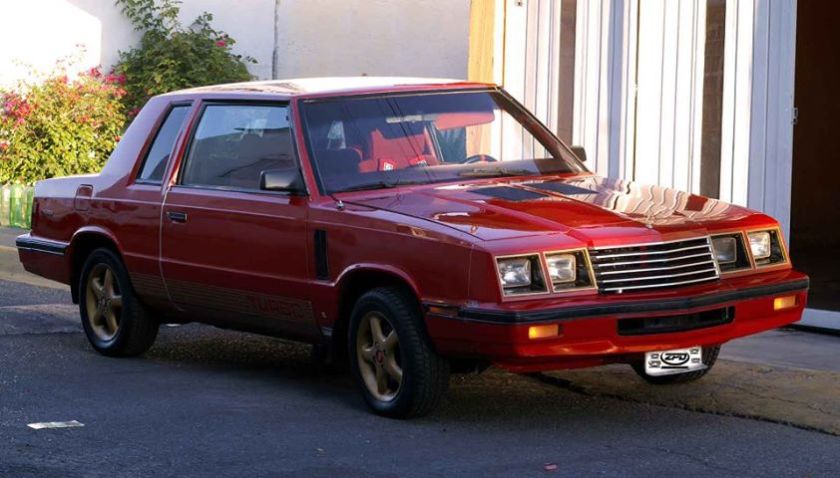
The K-car based Mexican Dodge Magnum was a sporty 2-door compact, based on the Dodge Aries coupe body (with blackout 1982-1985 Dodge 400 grille in 1983-1985 and a blackout 1986-1988 Plymouth Caravelle grille in 1986-1988) offered from 1983 to 1988 with available turbocharger (“TurboChrysler” engine) from 1984 on. Four engines were offered for the Mexican Dodge Magnum K, a SOHC I-4 2.2L (K-Trans-4, 1983–86), a turbocharged SOHC I-4 2.2L (1984–1986) and two other 2.5L SOHC I-4s, with and without turbocharger (1987–88). When it was introduced, the Mexican Dodge Magnum 400 Turbo was advertised as “Mexico’s fastest car” in the TV commercials of the time, and it surely was in 1985, when the “Fox” (1979–1984) 5.0L Mexican Ford Mustang was dropped from the catalog of Ford Mexico. The Mexican front-wheel drive Magnum was officially called “Dodge Magnum 400” between 1983 and 1984, as it was a sporty Mexican variation of the American Dodge 400 of the early eighties (without the vinyl roof of the US version and with high output 2.2L engine (available turbocharger from 1984 on), heavy-duty suspension, sporty wheels, tires, dash, steering wheel, console, shifter and seats). In 1984, the Mexican Magnum 400 Turbo was the closest thing to an American Dodge Daytona Turbo south of the border. For 1985, the “400” suffix was dropped. For the 1987 season, the turbocharger received an intercooler and the power from the turbo engine changed from 140 to 150 hp (112 kW). The K-car based Magnum was replaced by the Mexican Chrysler Shadow GTS for the 1989 model year.
2004–2008
| Dodge Magnum (2004–2008) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 2004–2008 |
| Model years | 2005–2008 |
| Assembly | Brampton, Ontario, Canada |
| Designer | Ralph Gilles Freeman Thomas |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 5-door station wagon |
| Layout | Front engine, rear-wheel drive /four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler LX platform |
| Related | Chrysler 300 Dodge Charger |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.7 L (167 cu in) EER V6 3.5 L (215 cu in) EGJ V6 5.7 L (345 cu in) EZB HEMI V8 6.1 L (370 cu in) ESF HEMI V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed 42RLE automatic 5-speed W5A580 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 120.0 in (3,048 mm) |
| Length | 197.7 in (5,022 mm) |
| Width | 74.1 in (1,882 mm) |
| Height | 2005-07: 58.4 in (1,483 mm) 2008-present: 58.3 in (1,481 mm) SRT8: 57.9 in (1,471 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Intrepid |
| Successor | Dodge Journey |
The Magnum name was revived in 2004 as a 2005 station wagon on the Chrysler LX platform. The new Magnum was a badge engineered station wagon version of the Chrysler 300 manufactured at the same plant inBrampton, Ontario, Canada.
The Magnum is the last mid-size station wagon (140 to 160 cubic feet of combined passenger and cargo volume) sold by an American automobile manufacturer in the United States, though Chrysler marketed the Chrysler 300 Touring variant in Europe and Australia.
The Magnum had four engine options; the SE features the 190 hp 2.72 L LH V6, the SXT had the 250 hp (190 kW) 3.5 L V6, and the RT had the new 340 hp 5.7 L Hemi V8. The SRT-8 has a 425 hp 6.1 L Hemi engine.
All-wheel drive became an option in 2005 on SXT and RT models. The SRT8, AWD SXT, and the RT use a Mercedes-Benz-derived 5-speed automatic transmission, while all other models use a four-speed automatic.
The Magnum was on Car and Driver‘s Ten Best list for 2005.
SRT-8
A high performance SRT-8 version debuted at the 2005 Los Angeles Auto Show. The SRT-8 was based on a concept car that was displayed at the 2003 Los Angeles Auto Show. It went on sale in 2005 as a 2006 model. Like the 300C SRT-8, it featured the new 6.1 L (370 cu in) Hemi engine, which produces 425 hp (317 kW). 20″ wheels, firmer suspension, bigger brakes (Brembo), new lower-body treatment, and a revised front and rear-fascia completes the transformation. The SRT-8 was named Best New Modern Muscle Car in the 2006 Canadian Car of the Year contest.
Motor Trend Test Results:
- 0-60 mph: 5.1 sec
- 0-100 mph: 11.7 sec
- Standing 1/4-mile: 13.1 sec @ 108 mph (174 km/h)
Europe and Australia
In Europe and Australia, the Magnum was sold as the Chrysler 300 Touring. It was essentially the same as the U.S.-market Magnum, but with the Chrysler 300C’s front end and interior, and right-hand-drive for Australia and the U.K. The 300C Touring added an available 3.0L CRD Turbo Diesel version. The 300C Touring was assembled in Austria.
2008 changes
For the 2008 model year, the Magnum received a facelift as well as an updated interior in line with that of the Dodge Charger. The front fascia sported new aggressively squared off headlights and a smaller rectangular grille more reminiscent of the Charger. The SRT-8 variant gained a new hood scoop. A new bright red paint scheme was introduced. The new changes brought the car closer to its Charger platform mate, away from the Chrysler 300.
Cancellation
On November 1, 2007, Chrysler announced that, as part of its restructuring plans, the Dodge Magnum would be one of four models discontinued after the 2008 model year. In Chrysler’s words: “The Magnum, along with the PT Cruiser convertible, the Crossfire, and the Pacifica were not earning their keep”. Production ended on March 28, 2008. The Dodge Magnum, (along with the short-wheelbase Dodge Caravan), has been replaced by the Dodge Journey.
- Matador (1960)
Dodge Matador
| Dodge Matador | |
|---|---|

1960 Dodge Matador
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Production | 1960 |
| Designer | Virgil Exner |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door hardtop 4-door sedan 4-door hardtop 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Related | Dodge Polara |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 361 cu in (5.9 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed manual 2-speed PowerFlite auto |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 122 in (3,099 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Coronet (Fourth generation) |
| Successor | Dodge Polara |
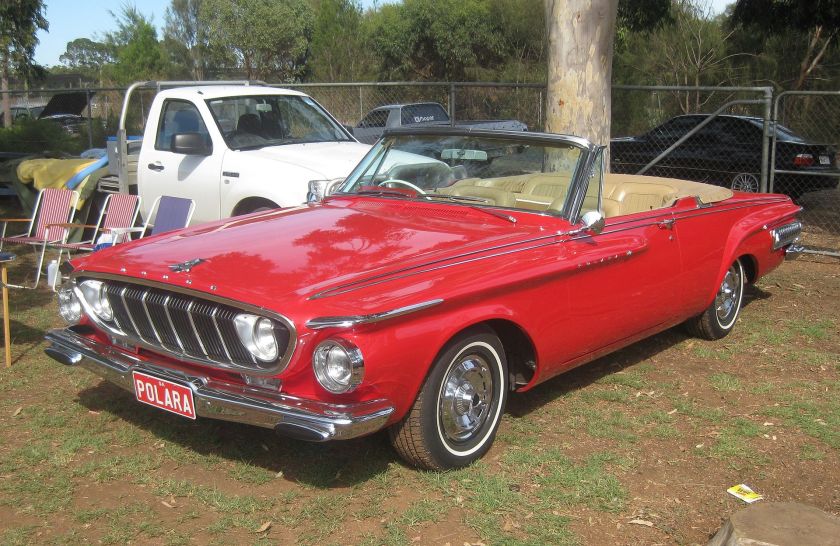
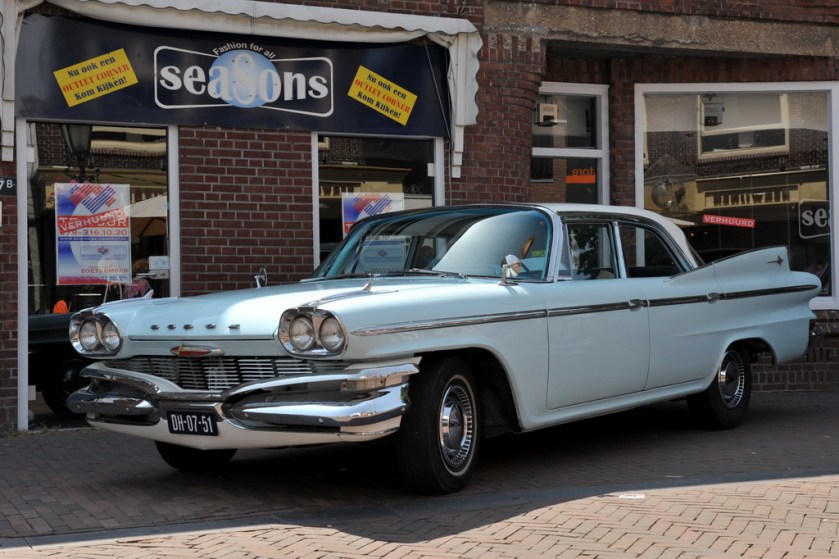
The Dodge Matador was a full-sized automobile produced for the 1960 model year by the Dodge division of the Chrysler Corporation.
Design
The Matador (“bullfighter” in Spanish) was one of two new models produced by Dodge in 1960 when the marque dropped its long-running Coronet, Custom, Custom Royal, and Lancer models. Sharing the same newly engineered unibody platform as the slightly smaller Dodge Dart, the Matador was designated Dodge’s full-size base trim vehicle, with the Dodge Polara becoming the make’s full-sized premium model. The 1960 Matador and Polara were built on 4-inch (102 mm) longer wheelbase along with the 1960 DeSoto and Chrysler models. All Matadors featured a standard “Super Red Ram” 295 hp (220 kW; 299 PS) 361 cu in (5.9 L) V8 engine. The “D-500 with Ram Induction” 383 cu in (6.3 L) with dual four-barrel carburetors was optional, along with a three-speed TorqueFlite automatic transmission.
The Matador (and the similar, better-trimmed Polara) featured styling cues that were carried over from 1959 models, themselves an evolution of Virgil Exner‘s “Forward Look” cars introduced in 1957. Now built on a new unibody chassis, the 1960 Matador continued the Dodge styling hallmarks of stacked “jet pod” taillights, however, the size of the lights was greatly exaggerated, with the lower light set into the rear bumper. The design also incorporated Dodge’s trademark (shortened) tailfins, which included small vertical taillight lenses placed on the vertical surface at the back of the fin; again. The purpose of the shortened fin was meant to exaggerate the length of the “jet pods” holding the taillights. The front end featured a small grille comprising six stacks of aluminum rectangles nested in a massive (and complex) front bumper assembly.
All 1960 Dodge station wagons used the 122 in (3,099 mm) wheelbase providing 98.5 cubic feet (2.79 m3) of cargo space with the back seats folded flat. The Matador trim was available in six- or nine-passenger (with rear-facing third row bench seat) versions featuring a roll-down rear window into the tailgate.
The Matador had less exterior chrome trim and plainer interiors than found on the Polara. The majority of cars built by Dodge and sold during the 1960 model year were in Dodge’s new “smaller” and less expensive full-sized model, the Dodge Dart, which fielded three sub-series (Seneca, Pioneer and Phoenix) of its own.
A total of 27,908 Dodge Matadors were produced for 1960. Low sales volume — and the popularity of the Dart model — led Dodge to drop the Matador nameplate for the 1961 model year.
Legacy
The name was subsequently used by American Motors Corporation from 1971 to 1978 for the mid- and full-sized AMC Matador cars. The automaker was purchased in 1987 by Chrysler Corporation.
- Mayfair (1953–1959)
Dodge Mayfair
The Dodge Mayfair was an automobile built by Chrysler Corporation of Canada Ltd. This vehicle was produced solely for the Canadian market from 1953 to 1959. Its American equivalent was the Plymouth Belvedere. It was based on the Plymouth, a vehicle that Chrysler of Canada had been offering since 1935 and Chrysler in Detroit started offering in export markets in 1936.
1956 Dodge Mayfair Convirtible
The Mayfair name first appeared as a 2-door hardtop in the 1951 Dodge Regent series, just as the Belvedere appeared in the Cranbrook series. The 1952 Mayfair adopted the same paint scheme as the 1952 Belvedere with the roof color sweeping down onto the rear trunk.
1956 Dodge Mayfair ad.
When the 1953 models were introduced, the Mayfair was again the hardtop in the Dodge Regent series. In April, 1953, though, Chrysler of Canada introduced a new, upscale series to do battle with the Chevrolet Bel Air and Pontiac Laurentian.
Thus the D43-3 Dodge Mayfair was introduced in both hardtop and sedan models. (Contrary to published articles, the D43-3 series was not a wagon). The exterior had the front fender trim extend onto the front door and backup lamps were standard. Interiors were two-tone, in either blue or green, with a matching steering wheel. With the new D43-3 Mayfair, the Regent Mayfair hardtop was dropped.
1957 Dodge Mayfair Sedan (Canada)
Under the hood, the engine was increased from 218.0 CID to 228.1 CID. And Chrysler of Canada introduced Hy-Drive on Plymouth and Dodge models. The system was a torque converter that shared its oil with the engine, along with a clutch and a 3-speed manual transmission.
1958-dodge-mayfair coupé
For 1954 the Mayfair used the interiors of the new full-line Plymouth Belvedere. The engine continued to be a 228.1 CID unit, and Hy-Drive continued as an option. For the first time since 1937, Chrysler of Canada offered a convertible in its Plymouth-based models, importing the Mayfair convertible from Detroit, being a Dodge Kingsway Custom convertible with Mayfair nameplates.
The V8 engine came to Chrysler of Canada’s low-priced models in 1955. The engines were imported from Detroit with various covers, manifolds, electrical pieces and rubber parts added in Windsor. Only the Mayfair offered the V8. And both Plymouth and Dodge offered PowerFlite, 2-speed automatic with its new dash-mounted control lever. The Hy-Drive unit was eliminated.
Things changed in 1956 when Chrysler of Canada opened a new V8 engine plant. The Mayfair was now V8 only, while the lower-priced Dodge Crusader and Dodge Regent could be had with either the six or V8. Early in the model the 270 cubic inch engine was installed while later in the year the all new 277 cubic inch version was introduced. A 4-door hardtop was added to the Mayfair line and the Powerflite automatic was controlled by new dash-mounted pushbuttons.
Totally new bodies designed by Virgil Exner debuted for 1957. They were a styling sensation with their low lines, plenty of glass and thin roof designs. Body engineering and tooling errors, though, resulted in a car that quickly gained a reputation for poor quality and rust. Chrysler Corporation’s new 3-speed Torqueflite automatic was now available on all Mayfair models, still only with the 303 CID V8 engine, and all Chrysler Corporation cars adopted Torsion-Aire torsion bar front suspension.
Sales for 1957 were down from 1956 for all Canadian built Dodge models, but 1958 was a disaster with sales falling over 40%. Grilles, taillights and trim were all that were new for 1958. The Dodge Mayfair adopted the 313 CID poly V8 engine.
The Mayfair’s last year was 1959, when it was downgraded a notch to take the place of the Regent, while the Crusader was dropped from the line up. The 1959 Mayfair still came in two and four door versions of the sedan and hardtop, plus the imported 3-seat Custom Suburban station wagon and convertible. Although the wagon models were 318 CID V8 only, the other models were now available with either the 251 CID flathead six or the 313 CID V8.
For 1960 the Canadian Dodge based on the Plymouth would be replaced by another Plymouth-based car, the Dodge Dart. The Mayfair would become a sub-model of the Dart line for 1960, and renamed the Phoenix.
The vehicle has been commonly referred to as a Plodge because of the extensive use of Plymouth components with Dodge front grilles and sold at Dodge sales outlets.
- Meadowbrook (1949–1954)
Dodge Meadowbrook
| Dodge Meadowbrook | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1949–1954 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 2-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
The Dodge Meadowbrook is a full-size car produced by Chrysler in the United States from 1949 to 1954.
1949-1954
| First Generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1949–1954 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 2-door station wagon |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 230.2 cu in (3.8 L) 1-bbl., L-head, I6103 hp (77 kW) engine(1949-1953); 2-bbl., 110hp(1954) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 123.5 in (3,137 mm) (1949), 119 in (3,023 mm) (1954) |
| Length | 203.6 in (5,171 mm) (1949), 205.5 in (5,220 mm) (1954) |
| Width | 74 in (1,880 mm) (1949), 73.5 in (1,867 mm) (1954) |
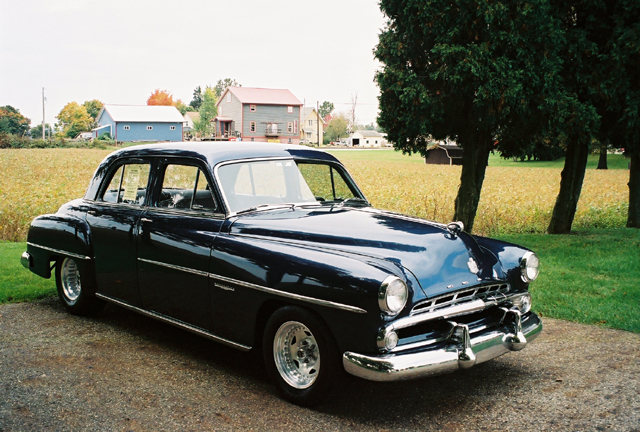
The Dodge Meadowbrook was produced by Dodge and offered as the base line trim level from 1949-1954. In its first year it made up 30% of Dodge’s sales, and came with “Safe-Guard Hydraulic Brakes” which included 2-cylinders per front brake. Dodge also advertised a new “cradled” ride, which was supposedly softer than all the others makers cars. For 1950, the six-cylinder was called the “Get-Away” engine. It had a wide, 42.7 ft (13.0 m) turning circle. In 1952, the Meadowbrook made up 32.50% of Dodge’s sales. A two door model and a station wagon were added for 1953. 1954 was the last year of the Meadowbrook, and it had a new Powerflite automatic.
- Mirada (1980–1983)
Dodge Mirada
| Dodge Mirada | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1980–1983 |
| Assembly | Windsor, Ontario, Canada |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 2-door coupé |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | J-body |
| Related | Chrysler Cordoba Imperial |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant 6 I6 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed A904 automatic 3-speed A727 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 112.7 in (2,863 mm) |
| Length | 209.5 in (5,321 mm) |
| Width | 72.7 in (1,847 mm) |
| Height | 53.3 in (1,354 mm) (1980) 53.2 in (1,351 mm) (1981–83) |
| Curb weight | 3,373 lb (1,530 kg) (1980) 3,380 lb (1,533 kg) (1981–83) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Magnum |
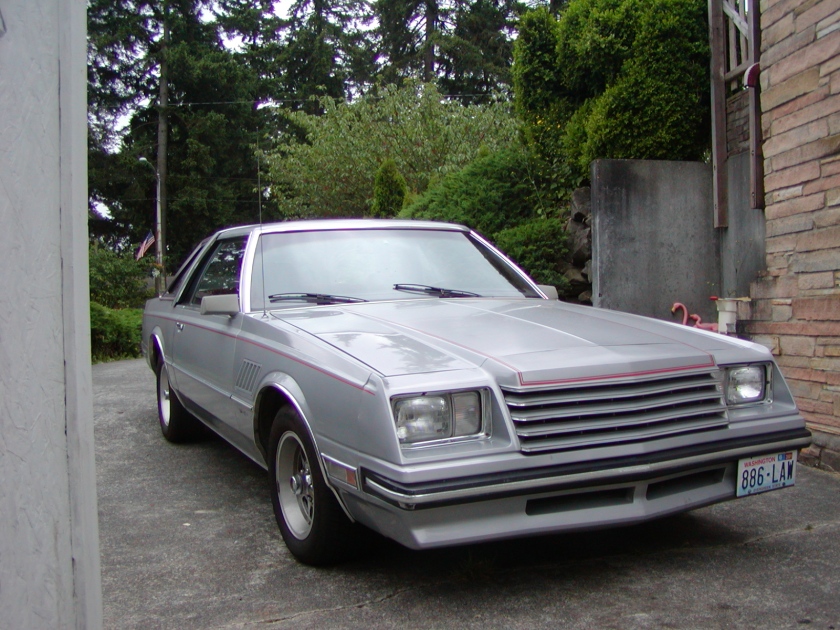
The Dodge Mirada was a mid-sized, rear-wheel drive coupe built from 1980–83, and was one of the three cars based on the Chrysler J platform, the other models being the second generation Chrysler Cordoba and the Imperial, these three vehicles being Chrysler’s response to the downsizing of its car lines. The Mirada was 800 lb (360 kg) lighter and its wheelbase 2.3″ shorter (112.7″ vs 115″) than the Magnum it replaced. Production numbers were low, with just under 53,000 units sold during its production run. The Mirada would stay relatively unchanged during its 4-year run, with the exception of paint colors and engines. Because of the low production and survival rate, Miradas today are garnering some limited interest from collectors, particularly models with the 5.9 liter V8.
Marketing
The Mirada was marketed as a personal luxury car, an extremely popular segment at the time. Advertising and marketing were limited, as the car was introduced when Chrysler was in deep financial difficulty.
NASCAR

It was hoped that the Mirada would reopen the door to Dodge success in NASCAR racing, as the nameplate had not won a race since November 1977. Lee Iacocca personally called Richard Petty, a longtime Dodge driver, in late October 1980 and asked him to build and test a race spec Mirada, saying Chrysler would supply Petty Enterprises the necessary body sheetmetal and engine parts Petty would need to build and campaign the car. Petty, who had left Dodge for General Motors in 1978, agreed, and had his team immediately set about and build a Mirada based race-car. A few other teams including Junior Johnson’s team built race-spec Mirada’s to test. Johnson’s team would have been a major coup for Dodge, as they had been running GM cars since the team’s inception and the team had just signed Darrell Waltrip away from DiGard Motorsports to drive for them (Waltrip having won 22 races in GM cars prior to this).
After their car was built, the Petty team thought the Mirada looked like a great race car, and some initial testing pleased the longtime Dodge driver. A January 17, 1981 test session at Daytona Speedway (where 15,000 or so Petty fans showed up to watch) however, showed the Mirada to be 8 mph (13 km/h) slower than the GM and Ford cars of the day.[2] This testing of the car, as well as the Junior Johnson teams testing, revealed that while it looked fairly aerodynamic, the bodystyle actually had a very high coeficient of drag that made it incapable of speeds over 185 mph. The Petty team removed the Mirada sheet metal (passing it to Buddy Arrington) and like the Johnson team elected to build Buick Regal bodied racecars, and this put an end to Chrysler’s attempt to re-establish itself in NASCAR. However, two small and independent racing teams, Arrington Racing (which was using, strangely enough, secondhand rebadge Petty Dodges) and Negre Racing, decided to make a go of the car and campaigned it during the 1981 to 1984 racing seasons. Buddy Arrington managed 17 top-ten finishes during those years, though all were on short (1 mile or less) length tracks. A few other drivers (Dave Marcis in four races, and Dick May in three) ran Mirada’s occasionally in 1981, but the cars were either plagued with mechanical issues, or finished several laps off the leaders. Up until the end of 1984, Miradas raced from time to time, but without much success, and ultimately lead to Dodge disappearing from NASCAR until 2001.
Powertrain
The 3.7 L inline slant-6 engine was available in the base Mirada, with the 5.2 L V8 offered as optional, and the 5.9 L V8 available in the Mirada CMX. All of these engines were mated to the A904 automatic transmission except the 360 (5.9L), which received the beefier A727.
| engine displacement, type, carburetor type |
max. motive power at rpm |
max. torque at rpm |
transmission |
|---|---|---|---|
| 225 cu in (3,687 cc) Slant 6 I6 1-barrel |
90 bhp (67 kW; 91 PS) (1980) 85 bhp (63 kW; 86 PS) (1981–83) @ 3,600 |
160 lb·ft (217 N·m) (1980) 165 lb·ft (224 N·m) (1981–83) @ 1,600 |
3-speed A904 automatic |
| 318 cu in (5,211 cc) LA V8 2-barrel |
120 bhp (89 kW; 122 PS) (1980) 130 bhp (97 kW; 132 PS) (1981–83) @ 3,600 |
245 lb·ft (332 N·m) (1980) 230 lb·ft (312 N·m) (1981–83) @ 1,600 |
|
| 360 cu in (5,899 cc) LA V8 4-barrel |
185 bhp (138 kW; 188 PS) @ 4,000 |
275 lb·ft (373 N·m) @ 2,000 |
3-speed A727 automatic |
Suspension
The suspension of the Mirada utilized transverse torsion bars in the front and leaf springs with a sway bar in the rear. A “Sport Handling Package” was offered, which included heavy-duty shock absorbers, torsion bar bushings, springs, as well as anti-sway bars in both the front and rear. The braking system used power assisted disc brakes in the front and drum brakes in the rear.
Trims and options
There were several different types of rooflines offered. The base models all received a basic metal roof with a chrome beauty strip extending from the bottom of the opera windows and across the roof. Those who chose to have their Mirada look a bit sportier could opt for either a power sunroof, or a glass T-top roof; and those who wanted a more luxurious look could choose either chose a vinyl Landau roof or a Cabriolet roof, which was basically a mock convertible top. The T-tops and Landau would be offered every year except for 1983, and the Cabriolet top would be offered every year. However, the power sunroof was not very popular and was only offered for 1980 and 1981.
There were a few basic wheel options. The base models came with 15” steel wheels with turbine-like hubcaps, or polished ten-spoke, 15” aluminum wheels with painted section and bright chrome center caps.
Mirada was offered in the following trims:
- Base
- S (also referred to as “SE”)
- CMX
Interior
The interior of the Mirada was offered in a variety of materials and colors. The base model dashboard was black with a faux woodgrain finish, which surrounded the gauges and center console, but the CMX came with a brushed aluminum finish replacing the woodgrain. The seat options were either vinyl bucket seats, leather bucket seats, or a 60/40 split cloth bench seat. Since the Mirada could be chosen with either a column shift or floor shift, the bench seat was only offered with the column shifter. Buyers had the choice of either an AM/FM stereo or an AM/FM/cassette stereo, an AM/FM/8-Track stereo, and a Chrysler CB radio could be chosen as well. The steering wheels offered were either an interior-matched two-spoke wheel with horn buttons in the spokes. The standard steering wheel for the CMX in 1980 and 1981 was the Mopar “Tuff Wheel”, which was similar to the sport wheel found on the vintage Mopar muscle cars such as the early 1970s Dodge Challenger. Manual windows were standard on the base model, but the power windows from the CMX could be ordered on the base models as well. A rare option was a Cabriolet mock-convertible roof, featuring a blocked-out quarter window.
- Monaco (1965–1978, 1990–1992)
Dodge Monaco
| Dodge Monaco | |
|---|---|
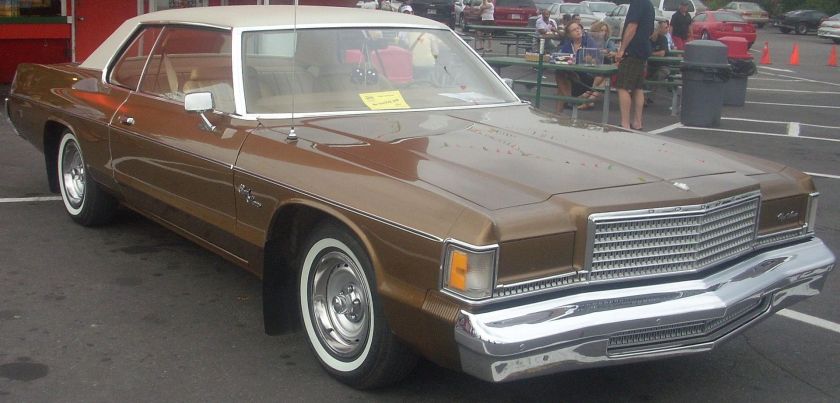

1976 Dodge Royal Monaco 2-door hardtop
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Dodge Division of Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1965–1978 1990–1992 |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Custom 880 (For 1965) Dodge Diplomat (For 1990) |
| Successor | Dodge St. Regis (for 1979) Dodge Intrepid (for 1993) |
The Dodge Monaco was a full-size automobile built and sold by the Dodge division of the Chrysler Corporation from 1965 to 1978, and 1990 to 1992.
1965–1968
| First generation | |
|---|---|
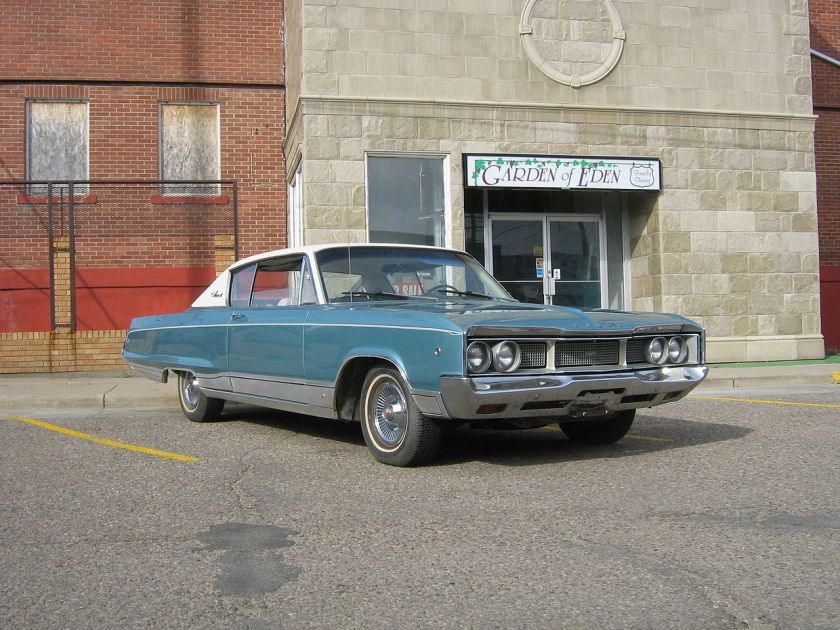

1968 Dodge Monaco 2-door hardtop
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1965–1968 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door hardtop 4-door sedan 4-door hardtop 4-door station wagon 2-door convertible (Canada) |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | C-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.69 L) Slant-6 318 cu in (5.21 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 383 cu in (6.28 L) B V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) B V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) RB V8 |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 121 in (3,100 mm) |
| Length | 213.3 in (5,420 mm) |
| Width | 80 in (2,000 mm) |
| Height | 56.4 in (1,430 mm) |
On introduction for 1965, the Dodge Monaco was intended to compete with the Pontiac Grand Prix in what came to be known as the personal luxury market, but ended up filling in for Dodge in the full-size, luxury line instead. Introduced on September 25, 1964, the 1965 Monaco was based on the Custom 880 two-door hardtop coupe body. The Monaco received special badging, different taillight and grille treatment, and a sportier interior with a full-length center console, as well as a 383 cu in (6.28 L) 315 hp (235 kW) V8 engine as standard equipment. Larger, more powerful engines were also available as options. Ford came out with its luxury LTD (the top-of-the-line model in the Galaxie 500 series) at the same time, and both the Monaco and LTD no doubt forced Chevrolet to introduce the luxurious Caprice package for its Impala Sport Sedan later in the model year, and Plymouth to issue a luxurious VIP model for its Fury series (for 1966). These models provided serious competition for mid-priced sedans like Chrysler, Oldsmobile, Buick,and Mercury.
Chrysler Canada Ltd. fielded a Dodge Monaco which was Dodge’s version of the Plymouth Sport Fury in Canada. It was available in hardtop coupe or convertible body styles. However, Canadian Monacos were equipped with Plymouth dashboards in 1965 and 1966. Unlike the American Monaco, the Canadian Monaco could be had with the 318 cu in (5.21 L) V8 or even the slant six.
Taking over for the Custom 880
For 1966, in the U.S., the Monaco replaced the Custom 880 series and the former Monaco became the Monaco 500. The basic Monaco was available in hardtop coupe, 4-door (pillarless) hardtop sedan, conventional 4-door (pillared) sedan, and 4-door station wagon bodystyles. In the U.S., the Monaco 500 was available only as a hardtop coupe. Although there was no convertible in the 1966 US Monaco range, there was in the 1966 Canadian Monaco lineup. The Canadian Dodge hung onto the “Monaco” name for the Sport Fury equivalent and Polara 880 for the Fury III competitor.
For 1967, all full-sized Dodges, the Monaco included, received a significant facelift with all-new exterior sheet metal. Chief designer Elwood Engel‘s work featured generally flat body planes with sharp-edged accent lines. The hardtop coupes got a new semi-fastback roofline with a reverse-slanted trailing edge on the rear quarter window.
In Canada, the Monaco name was applied for ’67 to all of the premium full-sized Dodge cars, replacing the Polara 880 at the top of the Dodge line. Taking the Monaco’s place as a premium full-size model was the Monaco 500, which was available only as a two-door hardtop and convertible.
Changes were minimal for 1968. The Monaco 500 was dropped at the end of the 1968 model year in the United States and at the end of the 1970 model year in Canada.
1969–1973
| Second generation | |
|---|---|

1973 Dodge Monaco 2-door Hardtop
|
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Chrysler 383 (South Africa) |
| Production | 1969–1973 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door hardtop 4-door sedan 4-door hardtop 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | C-body |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 122.0 in (3,100 mm) |
For the 1969 model year, the wheelbase of the Monaco was increased from 121 inches to 122 inches, and the length was increased to about 220 inches. Returning for ’69 was the “500” option, which in the U.S. market gave the Monaco front bucket seats and a center armrest. In Canada, the Monaco 500 was a separate series that used the side trim of the Polara 500 sold in the U.S. Canadians could also buy a Monaco convertible; U.S. Dodge full-size convertible shoppers had only the lower-end Polara and Polara 500 to choose from.
All full-sized Dodge cars including the Monaco adopted Chrysler Corporation’s new “fuselage” styling, in which the upper and lower body were melded into a uniformly curved unit. Curved side glass added to the effect, as did the deletion of the “shoulder” along the rear. The look started in the front of the car, with a nearly straight-across bumper—demanded by a Chrysler executive after a Congressional committee attacked him over the seeming inability of car bumpers to protect cars from extensive damage in low-speed collisions—and a five-segment eggcrate grille that surrounded the headlamps. When the cars failed to spark buyers’ interest, Dodge executives demanded a change. By the summer of 1969, the division released new chrome trim for the front fender caps and leading edge of the hood as an option, which gave the appearance of a then-fashionable loop bumper without the tooling expense. At the rear, Dodge’s signature delta-shaped taillamps were presented in a new form that required the top of the bumper to slope downward toward each end.
The standard-equipment engine on the 1969 Monaco was Chrysler’s 290-horsepower (220 kW) B-block 383 cu in (6.3 L) V8 engine with a two-barrel carburetor. Buyers could order the 383 with a four-barrel carburetor that increased power to 330 hp (250 kW), or they could opt for the 375-horsepower (280 kW) 440 cu in (7.2 L) Magnum RB-block engine. Wagon buyers choosing the 440 got a 350 horsepower (260 kW) version.
The 1969 Monaco offered, as a $50 option, the first modern polyellipsoidal (projector) automotive road lamp. Called Super-Lite and mounted in the driver’s side of the grille. This auxiliary headlamp was produced in a joint venture between Chrysler Corporation and Sylvania. It used an 85 watt halogen bulb and was intended as a mid-beam, to extend the reach of the low beams during turnpike travel when low beams alone were inadequate but high beams would produce excessive glare to oncoming drivers.
Available models for 1969 included a two-door hardtop coupe, four-door hardtop sedan, four-door pillared sedan, and four-door station wagons with six- or nine-passenger capacity. A new Brougham option package included a vinyl roof on sedans and hardtops and a split-bench front seat with a reclining mechanism on the passenger side (except on the two-door hardtops). Monaco wagons received woodgrained vinyl trim along their sides and across the dual-action (side- and bottom-hinged) tailgate.
Sales of the Polara and Monaco were down by nearly 20,000 cars compared with 1968, with the Monaco line accounting for 38,566 of the 127,252 full-size cars made by Dodge for the year.
1970
The 1970 models got completely new front and rear styling that included expensive-to-make loop bumpers front and rear. In the front, the new bumper enclosed a new diecast grille and the headlamps. At the rear, the double-loop bumper enclosed the taillamps. Reversing lamps were moved up into the endcaps that terminated the quarter panels, in slotted body-color housings. The designers chose to emphasize the length of the hood this year, which meant that the redesigned front end grew by three inches. However, the new rear end was four inches (102 mm) shorter.
Improvements to the suspension were promoted as the new “Torsion-Quiet” system, which used strategically-placed rubber isolators to reduce road noise and vibrations. The rear wheel track was broadened by nearly three inches as Dodge installed the rear axle previously used only on Wagons on all 1970 Monaco models.
The Brougham and 500 option packages continued, as did the availability of the Super-Lite, but the 440 Magnum V8 was dropped. The 350 horsepower (260 kW) version 440, available only in wagons for ’69, became the new top engine for all Monacos. Despite all of the changes, which cost Chrysler a rather large sum of money, Monaco (and Polara) sales tanked. Only 24,692 Monacos were built for the model year.
1971
The 1971 Monaco got less of a facelift than had been originally planned, but did get a new grille within the bumper that had been used the previous year, and other minor styling changes that were focused mainly at the rear. The Super-Lite was no longer available because of a lack of consumer interest and challenges to its legality in some states. A new single-loop rear bumper and larger taillamps were installed.
The 500 option package was deleted although a stereo cassette player/recorder with microphone was new on the option list. Bucket seats remained available despite the loss of the 500 package, and the Brougham package was also still available for $220, despite the addition of a separate Polara Brougham series.
All available engines had their compression ratio reduced so they could all run satisfactorily on regular-grade gasoline. As a result, the two-barrel 383’s power rating dropped to 275 hp (205 kW), the four-barrel 383 dropped to 300 hp (220 kW), and the 440 dropped to 335 hp (250 kW).
Monaco station wagons, which in 1969 and ’70 had worn their woodgrain trim on the lower bodysides, got completely new woodgrain up high on the sides, even around the windows. The new vinyl decals were translucent, allowing some of the paint color to show through.
Despite the power losses and mild styling change, sales slightly rose. About 900 more Monacos were built for ’71 (approximately 25,544 — an exact number isn’t known).
1972
For the 1972 model year, the full-sized Dodges finally got the all-new sheetmetal that had originally been planned for 1971.
Setting off the new look for the Monaco was a new front end with hidden headlamps set above a completely new bumper-grille assembly. The sides of the car lost their previous plump appearance in favor of a new, lean look with a new feature line that started on the front fenders and ran back through the doors, kicking up ahead of the rear wheels. Sedan and hardtop rooflines were new and more formal-looking. At the rear, there was yet another new loop bumper and full-width taillamp which, like the rest of the car, looked much more expensive and impressive. Station wagons got a new rear appearance, too, with stacked vertical taillamps.
The Monaco got a smaller standard V8 for ’72. The 360 cu in (5.9 L) A-block V8 engine, which had been introduced in ’71 as an option on Polaras, developed 175 horsepower (130 kW), now measured as net instead of gross. Replacing the 383 was a new 400 cu in (6.6 L) B-block V8. The 440 remained available, but it now produced 230 horsepower (170 kW) (net). 1972 sales nearly matched 1969 levels, with 37,013 built for the model year.
1973
For its last year in the fuselage body, the Monaco continued with its 1972 styling, except for another new rear bumper with redesigned taillamps, along with a new decklid and rear-quarter endcaps. Large black rubber guards were added to the bumpers to comply with new Federal five-mile-per-hour impact standards. Hardtop and sedan models gained about 6.5 in (16.5 cm) due mostly to the bumper guards.
Inside, new fire-retardant materials in virtually every visible part of the interior meant added safety. Under the hood, all three available engines gained reliability with the addition of Chrysler’s new electronic ignition system as standard equipment, which extended spark plug life and virtually eliminated periodic ignition system maintenance.
Despite the cars’ improvements, sales dropped again to 29,396.
1973 proved to be the Monaco’s final year as Dodge’s top-of-the-line full-size car. After 14 years, the Polara name was dropped and, for 1974, all big Dodges carried the Monaco name.
1974–1977
| Third generation | |
|---|---|

1975 Dodge Monaco 4-door sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1974–1977 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door hardtop 4-door sedan 4-door hardtop 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | C-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) V8 |
The 1974 Dodge was completely redesigned with an all-new unibody platform and all-new sheet metal. Unfortunately, within days of their introduction, the 1973 oil crisis began. Chrysler was excoriated in the media for bringing out huge new cars, and sales suffered accordingly. Many in the automotive press also criticized the car’s new design as being too derivative of what they thought resembled a 3-year-old Buick or Oldsmobile full-size car.
For 1974, the long-running Polara and Polara Custom models were discontinued. They were replaced by a basic Monaco and Monaco Custom respectively. The previous Monaco was renamed Monaco Brougham. The Brougham name had long been used on the luxury option package which was available from 1969 to 1973. The hidden headlamps of the previous models were replaced by fixed headlamps on all Monacos.
For the 1975 model year, changes to the base Monaco were minimal. However, the Monaco Custom was renamed the Royal Monaco, and the Monaco Brougham became the Royal Monaco Brougham. These newly named models featured hidden headlamps. 1975 was the last year the four-door hardtop was available. Some models, depending on equipment and the state they were sold in, received catalytic converters to comply with increasingly strict vehicle emissions control regulations. After the start of the 1975 model year, a limited-production option for Royal Monaco Brougham coupes was introduced: the Diplomat package featured a landau vinyl roof with opera windows and a wide steel roof band. It was available in only 3 colors—Cold Metallic, Silver Cloud Metallic and Maroon Metallic. Engine options were the 400 cu in (6.6 L) with a 2- or 4-barrel carburetor, or a 440 cu in (7.2 L) with a 4-barrel carburetor. The car weighed over 4000 pounds with a top speed of 127 mph.
Exterior changes to the 1976 model were minimal, though Chrysler’s new Lean Burn system was introduced to reduce exhaust emissions. The virtually unchanged 1977 models (except for bumper corner tip radius details) were the last big full-size Dodges. All full-size models were badged Royal Monaco for ’77, as the mid-size Coronet was renamed Monaco.
Popular culture
The 1974–1977 Monacos received star treatment as the Bluesmobile in the 1980 feature film The Blues Brothers, directed by John Landis. In it, a 1974 Monaco which was formerly a Mount Prospect, Illinois police cruiser is purchased by Elwood Blues (Dan Aykroyd) and used as the brothers’ transportation. Jake, just released from prison, disapproves of the vehicle, but Elwood states its technical specifications as “It’s got a cop motor, a 440-cubic-inch plant. It’s got cop tires, cop suspension, cop shocks. It’s a model made before the catalytic converter so it’ll run good on regular gas.” Monacos from 1975 to 1977 are also featured as Illinois State Trooper cars and Chicago city police cars.
The California Highway Patrol cruisers used in the first three seasons of CHiPs were of this generation Monaco.
Also in the 1980 feature film Smokey and the Bandit 2, a world-record automobile jump was captured on film during the “roundup sequence,” when stuntman Buddy Joe Hooker jumped a 1974 Dodge Monaco over 150 feet. Hooker suffered a compressed vertebra as a result of a hard landing.

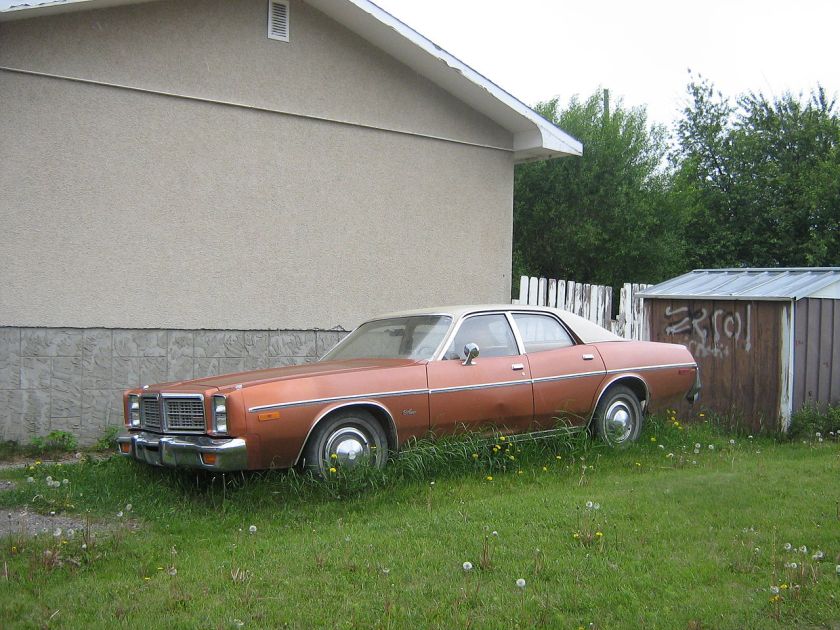
1977–1978 (B platform)
| Fourth generation | |
|---|---|

1977 Dodge Monaco 4-door sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1977–1978 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size car |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door hardtop 4-door station wagon |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | B-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.69 L) Slant 6 318 cu in (5.21 L) LA V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) B V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) RB V8 (police) |
As a lingering result of the 1973-74 energy crisis, Chrysler decided to shift the Monaco nameplate to the mid-size B platform for 1977 while the previous year’s full-size C platform Monaco carried on one more year as the Royal Monaco. The “new” 1977 mid-sized Monaco replaced the previous Coronet 4-door sedan, 4-door station wagon and Charger hardtop coupe. The Monaco Brougham replaced the previous Coronet Brougham 4-door sedan and Charger Sport hardtop coupe, while the Monaco Crestwood station wagon replaced the previous Coronet Crestwood. The Charger S.E., which at this point became the sole Charger still available, continued unchanged.
The “new” Monacos, for all of the marketing hype, were little-changed from the Coronets which had gone before. A revised front end design with stacked rectangular headlamps gave the cars a resemblance to the contemporary Chevrolet Monte Carlo when viewed head-on. With Chrysler Corporation in dire financial straits during these years, there was little that could be done to give the cars a fresh look, so changes had to be minimal and as inexpensive as possible.
The 1977 and 1978 models can be seen as the police vehicles in the 1980–1985 seasons of The Dukes of Hazzard, also the TV Police Drama Hunter (U.S. TV series) as Rick Hunter’s L56 (also known “Lincoln 56”). Large numbers of still-unsold vehicles were bought inexpensively and then suffered ignominious ends, destroyed in stunt crashes but due to the toughness of the design, were often repaired and reused repeatedly.
The Monaco nameplate disappeared at the end of the 1978 model year. Both the mid-sized Monaco and the full-sized Royal Monaco were replaced by the St. Regis for the 1979 model year. While it never came close to matching the Monaco it replaced in sales to the general public, the St. Regis did relatively well as a police car. In fact, after its first year, the vast majority of St. Regis sales were to law enforcement agencies. However, even those sales couldn’t save the car, which, along with its Chrysler and Plymouth siblings, was killed off halfway through the 1981 model year.
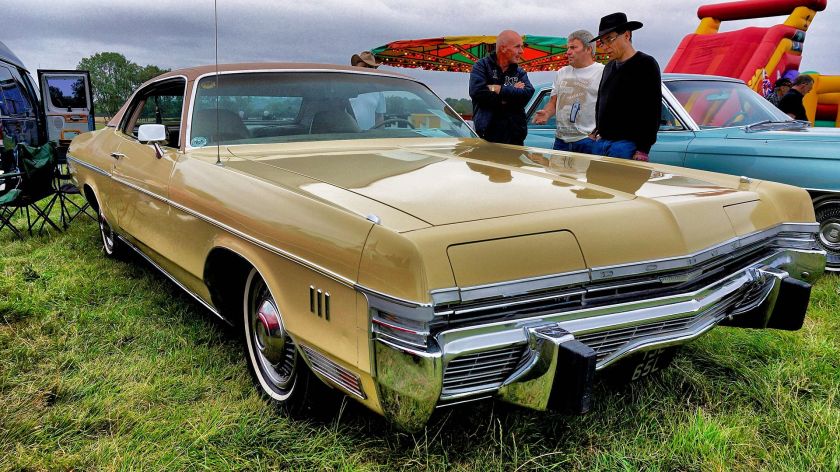
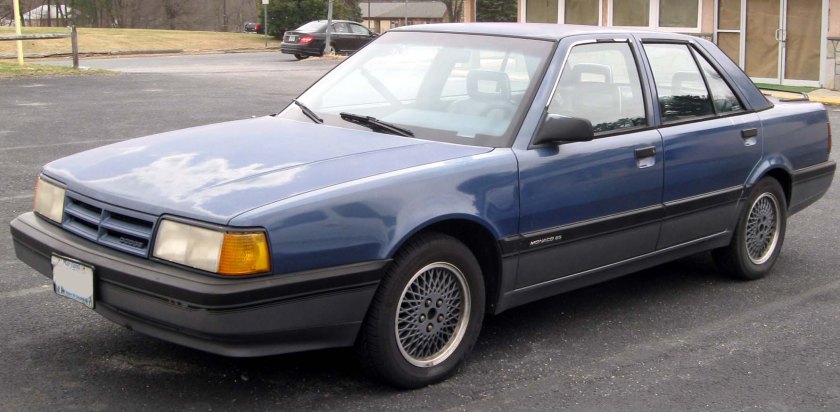
1990–1992
| Fifth generation | |
|---|---|

1990-1992 Dodge Monaco ES
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1990–1992 |
| Assembly | Brampton, Ontario, Canada |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | Longitudinal front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | B-body |
| Related | Eagle Premier/Renault Premier Eagle Medallion/Renault Medallion Renault 21 Renault 25 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 3.0 L (180 cu in) PRV V6 |
| Transmission | 4-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 106.0 in (2,690 mm) |
| Length | 192.8 in (4,900 mm) |
| Width | 70.0 in (1,780 mm) |
| Height | 54.7 in (1,390 mm) |
| In 1987, Chrysler bought the assets of American Motors, mostly for the Jeep brand. With Jeep came the new Eagle brand of cars, which were a mix of models designed and produced by Renault and Mitsubishi Motors. As part of the purchase, Chrysler agreed to purchase a set number of Renault drivetrains for use in the Eagle Premier. |
Chrysler management determined that the Premier alone could not sell in sufficient numbers to meet the requirements of the Renault contract. The solution to fulfill their obligation was to create another model using Premier parts.
With Dodge being the company’s highest-volume division (Though Dodge already had a large front-wheel-drive car in the Dynasty), the new rebadged Premier was designated a Dodge. The Monaco name was revived for the car, which differed from the Premier only in its crosshair grille, different taillights and badging. The car became Dodge’s top-of-the-line model and replaced the rear-wheel drive Diplomat, which was discontinued after the 1989 model year. Chrysler Canada did not replace the Dodge Diplomat as Chrysler was discontinuing all larger Dodge & Plymouth vehicles at the time and moving them to the Chrysler brand.
Fewer Monacos were sold than Premiers. The similarly-sized yet less technically sophisticated K-car based Dynasty, which had been introduced only two years earlier as a 1988 model, outsold the new Monaco. Fleet buyers such as rental companies and government agencies liked the fact that the Dynasty could be equipped with any of three different engines and sold for a lower price. The Monaco, on the other hand, came with only one engine and was more expensive.
The Monaco did not gain wide acceptance from a public that was wary of the reliability of previous French-designed AMC cars. The Premier and Monaco did indeed suffer from significant mechanical and electrical problems related to the mandated Renault-based components.
The Monaco, built at the Brampton, Ontario plant alongside the Premier, was never sold in Canada. At that time, the Dodge Spirit ES was Dodge’s top-line sedan in that market. The Monaco and Premier were discontinued during the 1992 model year. The French-designed platform, its state of the art manufacturing plant, and the key executive from American Motors behind the Premier/Monaco design, Francois Castaing, would lead to the successful and highly rated “cab-forward” LH Dodge Intrepid, Chrysler Concorde and Eagle Vision in late 1992 when production resumed at Brampton Assembly.
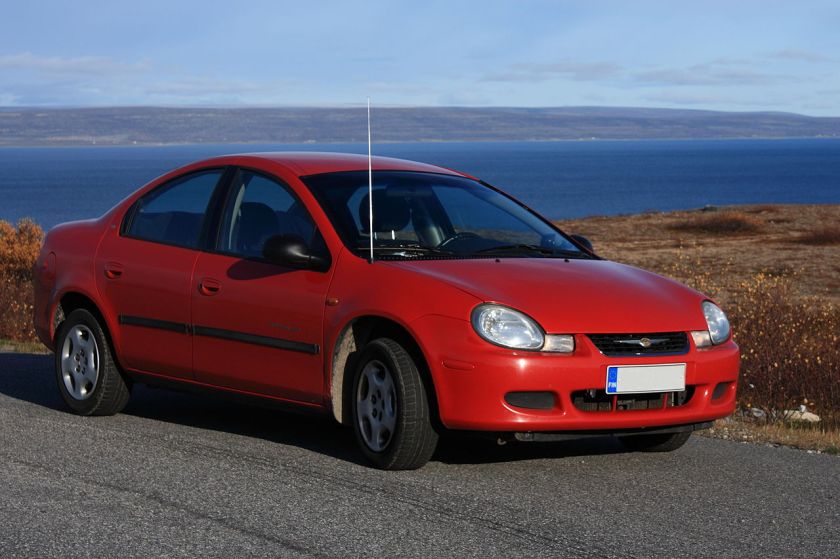
- Neon (1995–2005)
Chrysler Neon
| Chrysler Neon | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Also called | Dodge Neon Chrysler Neon (Europe) Dodge SX 2.0 (Canada) |
| Production | 1993–2005 |
| Assembly | United States: Belvidere, Illinois(Belvidere Assembly) Mexico: Toluca, Mexico State(Toluca Car Assembly) Venezuela: Valencia, Carabobo(Carabobo Assembly) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler PL platform |
| Related | Dodge SRT-4 Chrysler PT Cruiser |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | |
| Successor | Dodge Caliber |
The Plymouth/Dodge Neon, sold in United States, and elsewhere outside Europe, Mexico, Canada, as the Chrysler Neon, is a compact front wheel drive car introduced in January 1994 for the 1995 model year byChrysler Corporation‘s Dodge and Plymouth brands. It was branded as a Chrysler model in Japan, Europe, and Australia export markets (where it was the first car to be sold as a Chrysler since 1981), as well as inMexico, Canada, and Egypt. It replaced the Dodge Shadow and Plymouth Sundance models and the Dodge Colt. The two-door model also replaced the Plymouth Laser in Plymouth’s lineup. The Neon was offered in multiple versions and configurations over its production life, which ended on September 23, 2005.
First generation (1994–1999)
| First generation | |
|---|---|
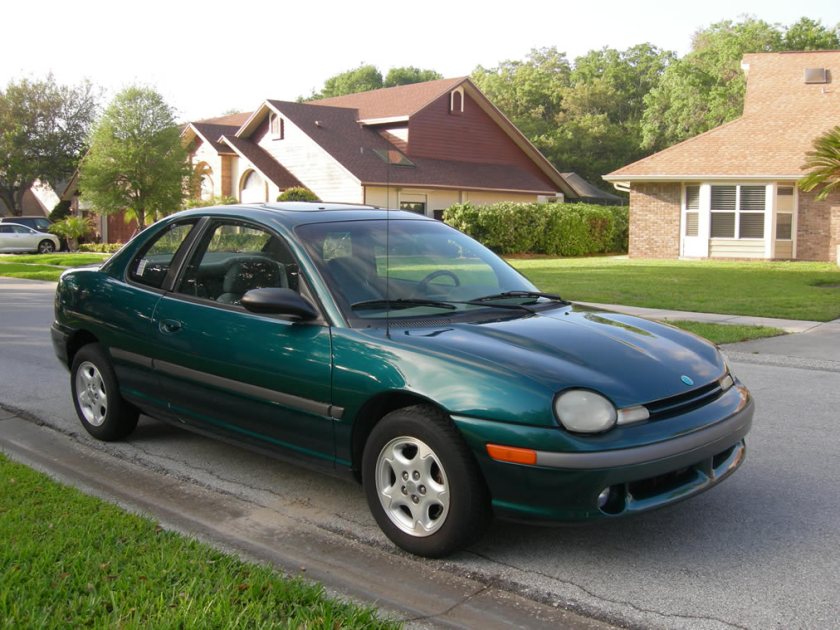 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Chrysler Neon Dodge Neon Plymouth Neon |
| Production | November 10, 1993–August 1999 |
| Designer | Thomas Gale (1991) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.8 L EBD I4 (gasoline) 2.0 L A588 I4 (gasoline) 2.0 L ECC I4 (gasoline) |
| Transmission | 5-speed NVG T-350 manual 3-speed TorqueFlite 31TH automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 104.0 in (2,640 mm) |
| Length | 171.8 in (4,360 mm) |
| Width | 67.5 in (1,710 mm) |
| Height | 54.9 in (1,390 mm) |
The first generation Neon was introduced in January 1994 and manufactured until August 1999. It was available as a four-door sedan and a two-door coupe. Available engines were SOHC and DOHC versions of Chrysler’s 2.0 L 4-cylinder engine producing 132 hp (98 kW) at 6000 rpm and 129 lb·ft (175 N·m) at 5000 rpm or 150 hp (110 kW) at 6500 rpm and 133 lb·ft (180 N·m) at 5600 rpm, respectively; transaxle options were a 3-speed Torqueflite automatic or a five-speed manual.
The car was badged and sold as both a Dodge and a Plymouth in the United States and Canada; in Mexico, Europe, Australia and other export markets it was sold as the Chrysler Neon. At the Neon’s release, then president of Chrysler Corporation Bob Lutz said, “There’s an old saying in Detroit: ‘Good, fast, or cheap. Pick any two.’ We refuse to accept that.” The Japanese press touted the Neon as the “Japanese car killer”, due to a spiralling Yen and the lower production cost of the Neon. The Neon received praise for its appearance, price, and power when compared to competing cars such as the Honda Civic DX at 102 hp (76 kW), the Civic EX at 127 hp (95 kW), the Nissan Sentra at 115 hp (86 kW), the Ford Escort ZX2 at 130 hp (97 kW), the Toyota Corolla at 115 hp (86 kW), and the Chevrolet Cavalier Base and LS models at 120 hp (89 kW), among others. Car and Driver tested the DOHC 5-speed equipped Neon R/T and reported that it could run 0-60 in 7.6 seconds and 15.9 seconds in the quarter mile. First-generation Neons were competitive in SCCA Solo autocross and showroom-stock road racing.
Equipment
Neons had unconventional option availability, including the lack of power windows in the rear doors. Certain color base-model Neons, including red and black, had bumper covers molded in color rather than painted. These covers, while textured and not as glossy as paint, absorbed scuffs and scrapes with less visible damage. The mid-level Highline models in 95 & 96 used wheel covers with a bubble design. Initially, Neons were available in many bold colors including Nitro yellow-green, Lapis Blue, Aqua, and Magenta, however paint color choices became more subdued by the 1998-1999 model years, as the majority of buyers opted for more traditional colors.
The Australian-market Chrysler Neon came in two models, the SE and the better-equipped LX. Later, the LX model was replaced by the LE with the updated model in 1999.
It was the first Chrysler small car sold in Japan, starting in 1996-1998, but only the sedan was offered, and was available at Japanese Mitsubishi dealerships as well as Yanase dealerships. Very similar to the Australian version, it was installed with right hand drive, and had amber turn signal indicators next to the tail lights to comply with Japanese regulations, and a side indicator behind the front wheel installed in the fender. Sales were curtailed by the fact that the width dimension did not comply with Japanese Government dimension regulations, so it was regarded as too expensive in comparison to Japanese products of the same class. The Neon offered in Japan was available with very limited optional equipment to justify the annual tax Japanese consumers had to pay for choosing a Neon. Sales were also affected by the Japanese economic recession due to the collapse of the Japanese asset price bubble, otherwise known as the “bubble economy”.
In the United States, the lineup started out as Base, Highline, and Sport, with different styles and options in each line, but the lineup titles changed frequently (other trim lines included Expresso, SE, ES, SXT, ACR, and R/T).
In Europe, the car was available with a 1.8 L engine. Europe received one limited edition model, the CS, which came only in Platinum paint. It was fitted with the 131 bhp (98 kW) SOHC engine, American R/T specification suspension (slightly lower, 3.5 cm (1.4 in) rear, 2.7 cm (1.1 in) front), rear spoiler, unique alloy wheels, standard leather interior, double stainless steel exhaust, 6CD changer and a shorter 5-speed manual gearbox.
Trim levels
Plymouth Neon: 1994–1999
- base – 1994-1995
- Highline – 1994–1999
- Sport – 1994–1996
- Expresso – 1995–1999
- EX – 1997–1999
- ACR – 1994–1999
- Style – 1997–1999
Dodge Neon: 1994–1999
- base – 1994-1995
- Highline – 1994–1999
- Sport – 1994–1999
- EX– 1997–1999
- ACR – 1994–1999
- R/T – 1997–1999
Chrysler Neon (Canada): 1999–2002
- LE – 1999–2002
- LE “Limited Edition” – 2000-2001 (automatic R/T version)
Chrysler Neon (Europe): 1994–1999
- LE – 1994–1999
- LX – 1994–1999
- SLX – June 1997-1999
- GLX – October 1997–1999
- CS – February 1998–1999
ACR
The ACR Neon, available with either the SOHC or DOHC engine, featured four-wheel disc brakes, Arvin non-adjustable struts for 1995–1996 models and Koni adjustable dampers for 1997–1999 models, thicker anti-sway bars, stiffer suspension bushings, fast-ratio steering, heavy-duty wheel hubs, and a five-speed manual transmission with a shorter .81 fifth gear and final drive ratio of 3.94 for quicker acceleration. 1995 through 1997 models featured adjustable camber. The computer-controlled speed limiter was removed from 1995 ACR models (limited to 130 mph (210 km/h) on later models), and ABS was also, to save weight. The ACR offers no badging to distinguish it from other Neon models; the only visible differences are a bumper with fog light holes, but no fog lights and a lack of side moldings. For 1995, the ACR was only offered to SCCA members, but in subsequent years it was available to the general public. The name “ACR” was initially the internal ordering code for the “Competition Package”, as it was termed in dealer materials; however, as knowledge of the model spread, the ACR name stuck. The backronym “American Club Racer” was coined due to its popularity with club and grassroots racers.
R/T
The R/T model (Road/Track) debuted in the 1998 model year. Offered only with a 5-speed DOHC configuration, the R/T featured many of the ACR’s mechanical upgrades including the numerically higher ratio 3.94 5-speed manual transmission, with the .81 5th gear and 130 mph speed limit. The R/T, however, was intended for the street, with more comfort and convenience features standard or available, and specialized parts like the adjustable dampers removed, although the dampers as well as the front coil springs found on R/T models were slightly stiffer, offering an advantage over standard model Neons. R/Ts featured optional stripes over the top of the car, silver “R/T” badging on the front door panels and the right side of the trunk deck lid, and a functional wing. The “Stripe Delete” option was available from the factory, but with no credit to the Neon’s price. All striped R/Ts (black, red, blue) had silver colored stripes, with the exception of the White R/Ts, which came with dark blue colored stripes. The R/T also came in 4-door form with limited numbers made.
Second generation (1999–2005)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
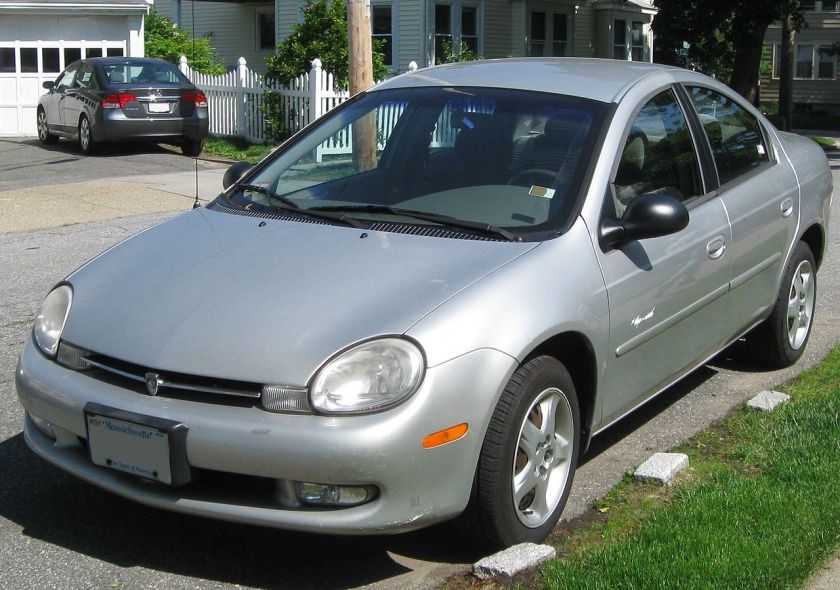 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Chrysler Neon Dodge Neon Plymouth Neon Dodge SX 2.0 |
| Production | 1999–2005 |
| Designer | Robert McMahan; Robert Boniface (1996) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Related | Dodge SRT-4 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.6 L EJD I4 (gasoline) 2.0 L A588 I4 (gasoline) |
| Transmission | 5-speed NVG T-350 manual 3-speed TorqueFlite 31THautomatic 4-speed Ultradrive 40TE automatic 4-speed Ultradrive 41TE automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 105.0 in (2,670 mm) |
| Length | 174.4 in (4,430 mm) |
| Width | 67.4 in (1,710 mm) |
| Height | 56.0 in (1,420 mm) |
Sales of the second generation model started with model year 2000 and production ended with the 2005 model year. The second generation Neon was only available as a four-door sedan. In some global sales regions, including the U.S., the sole engine was the 2.0 L SOHC engine, the power output remaining at 132 hp (98 kW). An optional Magnum engine configuration (with an active intake manifold) that produced 150 hp (110 kW) was available. Both engines had a redline of 6762 rpm.
The second generation was more refined than the first generation car. It was advertised that the second generation Neon had over 1,000 refinements from the original generation. The first generation’s frameless windows were replaced with a full-framed door. Other NVH refinements were implemented. The new interior and greater size increased weight. The DOHC engine (Chrysler code name ECC) was no longer available.
In 2000, The R/T trim returned after a one-year hiatus. The R/T consisted of a new 150 hp (110 kW) SOHC Magnum 2.0 L Engine, 16 in (41 cm) wheels, spoiler, dual chrome exhaust tips, quicker steering box and stiffer springs. The 2001 and 2002 R/Ts had a flat, ‘hammerhead’ spoiler. From 2000-2003, the R/T was sold as a Chrysler in Europe. The Neon was offered with a sport package for the 2001 model year only commemorating Dodge’s return to the NASCAR scene. It consisted of an R/T wing, R/T 16 in (41 cm) wheels, R/T springs, Goodyear NASCAR raised yellow-lettering tires, ‘Dodge Motorsports’ side decals, white instrument cluster and R/T steering box. It was an R/T visually except for the lack of dual exhaust, R/T lower mouldings, fog lamps and R/T exclusive front bumper. The Sport only came equipped with the base model’s 132 hp (98 kW) engine and was available with an automatic transmission (unlike the manual-only R/T model). 2001 was the last year for the Plymouth Neon, and the Plymouth brand as well. The last Plymouth Neon, which was also the last Plymouth ever produced (a silver four-door sedan), rolled off the assembly line on June 28, 2001.
The former Dodge and Plymouth Neon were briefly sold under the Chrysler name in Canada from 1999–2002, until being renamed as Dodge SX 2.0 for 2003. In Europe, Australia, Mexico, and Asia, the car had always been sold as a Chrysler, as Dodge and Plymouth passenger cars were not marketed outside the U.S. and Canada at the time. Besides the 2.0 L engine, it used the same Tritec 1.6 L unit found in the MINI prior to 2007. The 1.6 L unit is a variation of the 2.0 L SOHC engine designed by Chrysler and built by Tritec.
Originally, the second generation Neon featured a five-speed manual transmission using the former ACR gear ratios to improve acceleration. However, this hurt gas mileage and made the car noisier on the highway, and eventually the original gear ratios were restored. A four-speed automatic (41TE) was offered in the Neon for the 2002-05 model years, replacing the earlier 3-speed 31TH.
The Neon’s name was changed to SX 2.0 in Canada in 2002. In Australia and Canada, the Chrysler Neon was discontinued in 2002. In 2002, the front clip was changed slightly to match the R/T and ACR front clip with the exception of missing a lower lip. This was done by making the grille smaller.
The Neon was facelifted once again for 2003 with large “crosseyed” headlights and crosshair grille to make it look more like a Dodge Caravan and Dodge Stratus.
The ACR model was discontinued for 2003; the R/T model for 2004. The Chrysler Neon continued to be sold in Europe until 2004.
In Brazil, the Neon was marketed as a luxury mid-size sedan; for Mexico it was a competitor to the Ford Escort, and sold as a Chrysler with either the 1.6 or 2.0 L engine and European-style taillights (with separate amber indicator lights), except for the R/T model, which was a Dodge, with U.S.-style taillights.
For the Dutch market, the Neon proved more successful than for the rest of the Continent. Trim levels were 2.0 LX and 2.0 SE. However, some grey import versions came in from Mexico.
This generation continued to be offered in Japan from 1999-2001, but as with the previous generation, the width dimension did not comply with Japanese Government dimension regulations which affected sales. The Japanese version was installed with leather interior, and was marketed as a small luxury car to Japanese consumers. In 2002, the Neon was replaced by the Chrysler PT Cruiser in Japan.
Trim levels
Dodge Neon: 2000–2005
- Highline – 2000–2001
- ES – 2000–2002
- SE – 2001–2005
- R/T – 2001–2004
- Motorsports Edition – 2001
- ACR – 2002
- base – 2002
- S – 2002
- SST – 2002
- SXT – 2002–2005
- SRT-4 – 2003–2005
Plymouth Neon: 2000–2001
- Highline – 2000–2001
- LX – 2000–2001
Chrysler Neon: 2000–2004 (Europe)
- R/T – 2000–2003
- LX – 2000–2004
- SE – 2000–2003
Chrysler Neon: 2000–2004 (Canada)
- LE – 2001 Limited Edition
- SE – 2000–2004
- Nitro (2006–2012)
Dodge Nitro
| Dodge Nitro | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Group LLC |
| Production | August 2006–December 16, 2011 |
| Model years | 2007–2012 |
| Assembly | Toledo, Ohio, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact SUV |
| Body style | 4-door SUV |
| Layout | Front engine, rear-wheel drive /four-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler KA platform |
| Related | Jeep Liberty |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 3.7 L (226 cu in) PowerTech V6 4.0 L (241 cu in) SOHC V6 2.8 L VM Motori I4 Diesel (Europe only) |
| Transmission | 6-speed NSG-370 manual (2006–2008) 4-speed 42RLE automatic 5-speed A580/5G-Tronic Mercedes automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 108.8 in (2,764 mm) |
| Length | 178.9 in (4,544 mm) |
| Width | 73.1 in (1,857 mm) |
| Height | 69.9 in (1,775 mm) |
| Curb weight | 4,162 lb (1,888 kg) |
The Dodge Nitro is a compact SUV from the Dodge division of Chrysler produced from the 2007 to the 2012 model year. The Nitro shared its platform with the second generation Jeep Liberty. It was assembled at theToledo North Assembly Plant in Toledo, Ohio. The Jeep facility is part of an automobile complex which includes the Toledo South Assembly Plant, home to the Jeep Wrangler since the 1940s.
Background
The Nitro made its debut in February 2005 at the Chicago Auto Show, as a concept car featuring an aluminum themed interior design. Aluminum-trimmed vents behind the front fenders, and other aluminum trim around the door handles and rear hatch, were routinely displayed as the center stack and shifter also included a finish in satin silver.
The Nitro became Dodge’s first compact SUV model since the Raider was discontinued in 1990. It also became the first modern Dodge branded automobile to be sold in Europe since its introduction in early 2007. In the U.S., the Nitro went into production in August 2006 and went on sale in September of the same year as a 2007 model. All Nitros were available with rear-wheel drive, and part-time four-wheel drive was available as an option. The Nitro was Dodge’s entry-level SUV until the 2009 model year, when the larger, car-based Dodge Journey crossover SUV priced below it, arrived in showrooms. Compared to its shared platform with the Jeep Liberty, the Nitro is longer, lower, and wider. The extra length is split between the rear seat and the cargo area.
The Nitro originally came equipped with an SUV class-leading 5,000-pound (2,300 kg) towing capacity. Safety features such as electronic roll mitigation, traction control, and side curtain airbags, as well as a functional sliding cargo floor called Load ‘N Go were also offered as standard equipment. Similar to a system offered on the Saab 9-5 station wagon, the floor can be extended through the rear hatch by 18 in (457 mm) to ease loading. Another attribute of the SUV, is its aggressive hot rod styling; complete with a bulged muscular appearance and pronounced fenders.
Model years
For its initial debut in 2007, two-wheel drive and four-wheel drive drivetrains were offered, along with a choice of a 3.7 L or 4.0 L V6 engines. The model designations were the SXT, SLT, and R/T. There were three types of upholstery made available; basic cloth, stain-repellant cloth, and perforated leather. Standard safety features included; front and rear side airbags, side curtain airbags, an electronic stability program with traction control and brake assist, electronic roll mitigation and a tire-pressure monitor. The four-cylinder version was sold exclusively in Europe.
During 2008, the Nitro came in both a 4×2 and a 4×4 versions with each offering two trims: SXT and SLT. Both trims came with a standard 210-hp 3.7 L V6 engine. The SXT trim included a standard six-speed manual transmission with an optional four-speed automatic. The SLT trim came with a standard four-speed automatic, but the optional R/T package increased the level of equipment with a 260-hp 4.0 L V6 engine mated to a five-speed automatic transmission. The Nitro’s SXT trim included standard power mirrors, windows and door locks with remote keyless entry, satellite radio, air conditioning, and seating for five. The SXT and R/T added alloy wheels, power driver’s seat, stain repellent cloth, the Load ‘N Go retractable cargo floor, cruise control, and an overhead console with a trip computer, compass, and exterior temperature display. Standard safety features included; front airbags, side curtain airbags, traction and stability control with roll-over mitigation, brake assist, and a tire-pressure monitor.
In 2009, the Nitro was offered in both a 4×2 and a 4×4 versions with two trims levels: SE and SLT. Both came with a standard 210-hp 3.7 L V6 engine mated to a four-speed automatic transmission. The SXT with its six-speed manual transmission had been replaced by the SE trim that featured the automatic transmission. The SLT trim offered the optional R/T package which was made available with a 260-hp 4.0 L V6 engine mated to a five-speed automatic transmission. The Nitro’s SE trim standards included power mirrors, windows and door locks with remote keyless entry, satellite radio, air conditioning, and seating for five. The SXT and R/T added alloy wheels, power driver’s seat, stain repellent cloth, the Load ‘N Go retractable cargo floor, cruise control and an overhead console with a trip computer, compass, and exterior temperature display. Standard safety features included; front airbags, side curtain airbags, traction and stability control with roll-over mitigation, brake assist, and a tire-pressure monitor.
For the 2010 model year, three new model designations became available: Heat, Detonator, and Shock trim levels in either 4×2 or 4×4 versions. The Heat trim was equipped with a 210-hp 3.7 L V6 engine mated to a four-speed automatic transmission. The Detonator and Shock trims included a 260-hp 4.0 L V6 engine mated to a five-speed automatic transmission. The Heat trim level had power mirrors, windows and door locks with remote keyless entry, satellite radio, and air conditioning. The Detonator added a rear-park assist, remote start system, power driver’s seat, cruise control, an overhead console with a trip computer, compass, and exterior temperature display. The Shock trim added heated front seats, leather trim interior, and a power sunroof. Among standard safety features were: front airbags, side curtain airbags, active head restraints, traction and stability control with roll-over mitigation, brake assist, and a tire-pressure monitor. The Load ‘N Go sliding trunk floor feature was discontinued.
The 2011 model year continued the previous models in 4×2 or 4×4 versions with the same engines and transmissions. New for 2011 was the Heat 4.0 lifestyle package. The Heat 4.0 came standard with a five-speed automatic transmission, Uconnect Phone, and an upgraded eight-speaker sound system. Also, select models came with upgraded interiors with new cloth and leather with premium colored stitching. Detonator and Shock were branded with Dodge Brand’s signature racing stripes. Additionally, all models became available with nine exterior colors, including Bright White Clear Coat, Blackberry Pearl Coat, Toxic Orange Pearl Coat, and Redline Two Coat Pearl.
Chrysler built 2012 model year Dodge Nitros for the fleet market only. The final Nitro came off the assembly line on December 16, 2011.
Australia
In Australia, versions could be had only as the 3.7 L V6 in SXT trim with automatic transmission. No manual option was offered, but diesels were on sale until 2010 MY.
Controversy
In early 2007, a TV advertisement in the U.S. for the Nitro with the tag line: “charged with adrenaline”, showed a dog getting electrocuted after touching the SUV’s front wheel. The ad gained a substantial amount of negative attention and was quickly pulled.
- Omni 024 (1979–1982)
Dodge Omni 024
| Dodge Omni 024 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Dodge 024 Plymouth Horizon TC3 Plymouth TC3 |
| Production | 1979–1982 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Subcompact |
| Body style | 3-door hatchback |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | L-body |
| Related | Dodge Omni Dodge Rampage Plymouth Horizon |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 1.7 L Volkswagen I4 2.2 L K I4 |
| Transmission | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 97 in (2,453 mm) |
| Length | 174 in (4,419 mm) |
| Width | 67 in (1,694 mm) |
| Height | 51 in (1,290 mm) |
| Curb weight | 2,551 lb (1,157 kg) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Charger / Plymouth Turismo |
The Dodge Omni 024 was a modified version of the popular Dodge Omni made from 1979 to 1982. Analogous to the VW Scirocco, this car was a lower, sportier version of the Chrysler/Simca Horizon, using the four-door hatchback’s floor pan and chassis as a basis. The cars were designed in-house at the prompting of Lee Iacocca.
It used the same chassis and engine options as the Omni but had a fastback and a new front fascia. The base engine was a 1.7 L Volkswagen inline four producing 70 hp (52 kW), with a 2.2 L, 84 hp (63 kW) Chrysler inline four as an option beginning in 1981. For the first year, the wheels were painted in the exterior color, and had a folding back seat. The car’s looks promised more performance than the engine could deliver, and the car was not as practical as the Omni. Both the Omni and Horizon prefixes were dropped for 1981, making them the “024” and “TC3”, respectively.
The 024 did not sell well and was renamed as the Dodge Charger for the 1983 model year, a name which had been gradually introduced as part of a special “Charger 2.2” package beginning in 1981. The 024 had a twin called the Plymouth Horizon TC3. (The name “TC3” may have referred to the car being a Touring Coupe with 3 doors.) It, too, was renamed in the 1983 model year: to the Plymouth Turismo. The “Turismo” label had already been used on a sport package beginning in 1980.
In its last year, many parts from the 024 and TC3 were recycled into the Dodge Rampage and Plymouth Scamp coupe utilities. This included the chassis, engine and front fascia.
In 1980 the Plymouth Horizon TC3 also became available with the Turismo sport package. For the Dodge Omni 024 this was called the DeTomaso package, with De Tomaso designed trim and wheels but the standard drivetrain. 1,333 De Tomaso 024’s were built in 1980, followed by 619 more in 1981. The 1981 De Tomasos were only available with the new 2.2 litre engine.
Also in 1980, in cooperation with Chrysler partner Mitsubishi, the Chrysler Omni 024 was briefly sold in Japan. It was available for two years at Mitsubishi dealerships and it complied with Japanese Government dimension regulations. Unfortunately it didn’t sell well, with only 1491 finding Japanese buyers.
- Omni (GLH) (1978–1990)
- Phoenix (1960–1973)
Dodge Phoenix
| Dodge Phoenix | |
|---|---|
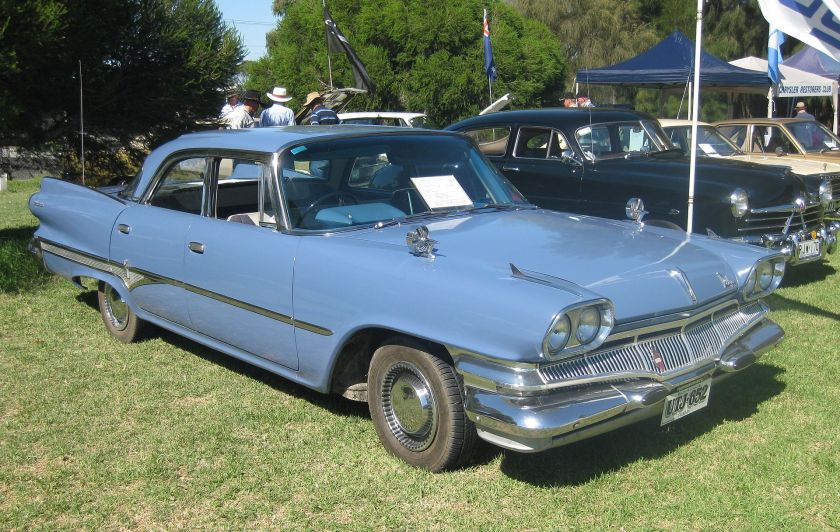

1960 Dodge PD4 Phoenix
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Australia |
| Production | 1960 to 1972 |
| Assembly | Mile End, Australia Tonsley Park, Australia Port Melbourne, Australia |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 4-door hardtop |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Related | Dodge Dart Dodge 440 Plymouth Fury |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 383 cu in (6.3 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 3spd automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | (1968) 119.0 in (3023 mm) |
| Length | (1968) 213.1 in (5413 mm) |
| Width | (1968) 77.7 in (1974 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Custom Royal |
| Successor | Chrysler by Chrysler |
The Dodge Phoenix is an automobile which was produced by Chrysler Australia from 1960 to 1972.
The Phoenix was introduced in May 1960 as an Australian assembled version of the American Dodge Dart, positioned above the locally developed Chrysler Royal as Chrysler Australia’s luxury model. It borrowed its name from the top Dart, the Dodge Dart Phoenix, but unlike its American namesake it was offered only as a four-door sedan and only with a 318 cubic inch V8 engine.
The Phoenix was subsequently restyled in line with the 1961 and 1962 Dodge Dart. For 1963 the new TD2 series Phoenix was derived from the US Dodge 440, and for 1965 and beyond the Phoenix was based on the Canadian Plymouth Fury III. Like the 1965 Fury, the 1965 Phoenix featured vertically stacked headlamps. A four-door hardtop body style joined the sedan in 1967. The hardtop was fitted with a 383 cubic inch V8 engine whilst the sedan continued with the smaller 318 cubic inch V8. The two body styles continued to be offered until the Australian Phoenix was discontinued.
Although the 1965 and later Phoenixes were basically Plymouth Furys, they did feature the North American style full size Dodge Polara instrument panel (adapted for right hand drive). They also continued to use the old-fashioned “clapper” windshield wipers (while North American models used modern parallel-action wipers).
After the Phoenix was discontinued, the Australian developed Chrysler by Chrysler inherited the role of the top level luxury model in Chrysler Australia’s model range.
Model history
PD4
The first Australian Dodge Phoenix, coded the PD4, was released in May 1960. A Canadian Dodge with a Plymouth dashboard, it was imported in CKD packs and assembled at Chrysler Australia‘s Mile End facility. The PD4 Phoenix was offered only as a 4 door sedan, in two trim levels, the De Luxe and the Luxury Liner. The PD4 had a 118 inch wheelbase and was powered by a 318 cubic inch OHV V8 engine. The Phoenix name was derived from the Dodge Dart Phoenix.
RD4
The RD4 Phoenix of 1961 used the cabin section the RD4 with new front and rear bodywork. Dimensions remained unchanged, as did the mechanical specifications.
SD2
The SD2 of 1962 featured a shorter 116 inch wheelbase and a completely new body which was both shorter and narrower than its predecessor.
TD2
The TD2 of 1963 was the first Phoenix to be based on the Dodge 440 model. The 4 door sedan body style and the 318 cubic inch engine were retained.
VD2
The VD2 Phoenix was introduced in 1964. The wheelbase was now 119 inches and the overall length increased by four inches to 212.
AP2D
The AP2D Phoenix was introduced in 1965. This model was a rebadged Canadian Plymouth Fury III, a strategy that Chrysler Australia would continue through to the end of 1972. The 1965 model featured vertically stacked four-headlight frontal styling. The 318 cubic inch engine were retained.
DP6
The 1966 Phoenix was coded DP6. Changes included a new grille, revised rear panels, new taillights and a new bootlid.
DC
The 1967 Phoenix was coded as the DC series. It was the first Phoenix to be available with a choice of bodystyles, a 4 door hardtop now offered in addition to the 4 door sedan. The sedan retained the 313 cid V8 engine and while the hardtop was fitted with a 383 cid V8. In the later part of 1967 Chrysler Australia shifted Phoenix assembly from Tonsley Park to its Port Melbourne facility.
DD
The 1968 Phoenix was coded DD. The main changes for 1968 were new rear sheet metal and new taillights.
DE
The DE Phoenix was introduced in 1969. The new model featured horizontal dual headlights, and a 120 inch wheelbase. Overall length was now 214.5 inches. It was marketed as the 400 Limited Edition series with each car carrying a numbered dashboard badge. 371 examples of the DE were built at Chrysler Australia’s Port Melbourne facility in 1969 and a further 385 in 1970.
DF
The DF Phoenix was introduced in 1970. 298 were built at Port Melbourne in 1970 and 110 in 1971.
DG
The DG Phoenix was introduced in 1971. 298 were built at Port Melbourne in 1971.
DH
The DH Phoenix was introduced in 1972. 73 were built at Port Melbourne in that year. A decision to close the outdated Port Melbourne facility led to the discontinuation of the Phoenix.
Gallery
- Polara (1960–1973)
Dodge Polara
| Dodge Polara | |
|---|---|

1972 Dodge Polara 4-Door Sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1960–1973 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Layout | FR layout |
The Dodge Polara was an automobile introduced in the United States for the 1960 model year as Dodge‘s top-of-the-line full-size car; after the introduction of the Dodge Custom 880 in 1962, the Polara nameplate designated a step below the full sized best trimmed Dodge model; the Polara that year had been downsized to what as in effect intermediate status. In its various forms, the Polara name was used by Dodge until 1973, when its position in Dodge’s line-up was replaced by the Dodge Monaco. The name Polara is a reference to the Polaris star, in a marketing attempt to appeal to the excitement surrounding the Space Raceduring the early 1960s. The Polara was a competitor to the Ford Galaxie 500 and the Chevrolet Impala.
1960 marked the first year that all Chrysler models, save the Imperial, used unibody construction.
1960–1961
| First generation | |
|---|---|
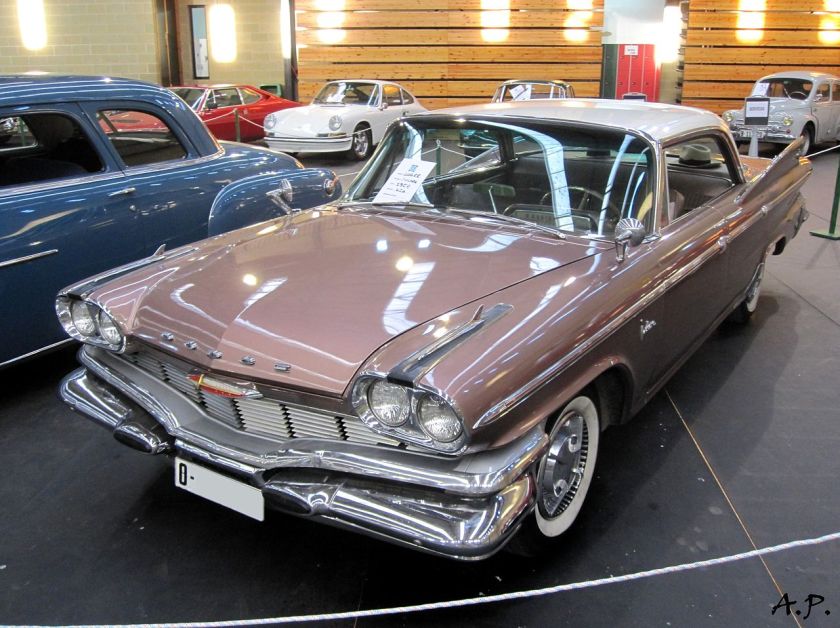

1960 Dodge Polara 4-Door Hardtop
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1960–1961 |
| Assembly | Detroit, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupe 2-door convertible 4-door station wagon |
| Related | Dodge Dart Dodge Matador |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 3,099 mm (122.0 in) |
| Length | 217.0 in (5,512 mm) |
The 1960 Polara and other full-sized Dodges featured styling cues carried over from 1959 models, itself an evolution of Virgil Exner‘s “Forward Look” cars introduced in 1957. The top-of-the line Polara and Dodge Matador continued to ride on the 122-inch (3,099 mm) wheelbase of their predecessors, while a new line-up of still full-sized Dodge Darts rode on a shorter 118-inch (2,997 mm) wheelbase. The Polara was available as a 2-door convertible, 2-door hardtop coupe, 4-door hardtop sedan, 4-door hardtop station wagon, and conventional (pillared) 4-door sedan.
Like these cars, both 1960 full-sized Dodges continued with the make’s styling hallmarks of stacked “jet pod” tail lights, however, the size of the lights was greatly increased compared to the previous year’s lamps, with the lower lights set into the rear bumper. The design also incorporated Dodge’s trademark shortened tail fins, which, on the Polara, included small vertical tail light lenses placed on the vertical surface at the back of the fin; again, the purpose of the shortened fin was meant to exaggerate the length of the “jet pods” holding the tail lights. The fins on Darts were shorter both in length and height because unlike the full sized Dodge’s, the Polara and Matador, the Darts were based on the Plymouth and used much Plymouth sheet metal forms and the Plymouth rear door. The Plymouth rear door did not have any part of the fin whereas on the full sized Dodges the fin actually started on the rear door (on the 4-doors) and continued back from there. This allowed the fin to start sooner, on the door, and end sooner, relative to the tip of the round tail light and still appear as long or longer than on the Dart. The net effect was that the fins on the Dart look stunted whereas on the Polara and Matador the fins appear in proper proportion to the rest of the car. Up front, the car featured a small grille consisting of eight stacks of anodized aluminum rectangles nested in a massive (and complex) chrome front bumper assembly. As the top model in the line-up, the Polara featured better interior fabrics and trim treatments. Polaras also received more trim on the outside of the car, most notably a chrome stone guard aft of the rear wheel housings, a full-length chrome spear, and a wide chrome base to the chrome spear atop the headlight housings.
For 1961, Dodge dropped the Matador, leaving the Polara as the sole “senior” Dodge model. Darts on the shorter wheelbase continued. For 1961, Exner’s styling department reversed the car’s fins, making them taller as they flowed toward the rear window. As the fins sloped towards the rear of the car, they cut slightly towards the center (to allow the single tail light housing on each side) of the rear of the vehicle, wrapping downward and then back along the side fender to form a C-shaped line accentuated in chrome. The overall effect made the rear of the car seem to “pucker” from the angles the design created. Up front, the massive bumper treatments that had been a Dodge hallmark since 1957 were replaced with a simple bar design, above which was a massive concave grille shared with the Dodge Dart.
The 1961 styling overhaul of the Dodge line-up was different from anything else on the US market at that time (save the 1961 Plymouth, which was equally unique in its styling) and consumers voted on the 1961 restyle with their car-shopping dollars. Sales of fullsize Dodges plunged to their lowest levels since the firms founding in 1914, with only 14,032 units produced in the United States. For the second straight year, the make was carried by the Dart which saw sales of 142,000 units for the year. Total Dodge sales for 1961 were down 53% compared to 1960, dropping the make from sixth in the American market to ninth place.
1962–1964
| Second generation | |
|---|---|

1964 Dodge Polara 500 Convertible
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1962–1964 |
| Assembly | Detroit, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupe 2-door convertible 4-door station wagon 4-door Hardtop |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 1962: 2,946 mm (116.0 in) 1963-64: 3,023 mm (119.0 in) |
All Dodge models were given a smaller, lighter, sculpted body with a 116-inch (2,946 mm) wheelbase for 1962. This move came after Chrysler’s president overheard and misunderstood Chevrolet chief Ed Cole to have said Chevrolet’s largest cars would be downsized for 1962. Chrysler designers were forced to take the planned 1962 Dodge full-size line and shorten the design to fit a more compact wheelbase in a last-minute effort to compete with what was supposed to be a smaller new Chevrolet. However, Chevrolet in fact offered a range of truly full-size cars for 1962, and Dodge and Plymouth alike were stuck with smaller cars the public and motoring press found stylistically awkward. The new Dodge models were sized closer to Ford‘s new intermediate Fairlane than to Ford’s or GM’s full-size models.
Quickly realizing the critical mistake they had made, Dodge hurriedly put together a new full-size car using the front end from the 1961 Dodge Polara and the body from the 1962 Chrysler. This new full-size model was known as the Custom 880, and became Dodge’s top-of-the-line model when it was introduced on January 21, 1962. In 1963 a lower specification version was offered, known simply the Dodge 880. A/C was $455.
Among the “sized in the middle of the big and little” 1962 Dodges was a bucket-seated sporty 2-door hardtop called the Polara 500. It was also available as a convertible, and a 4-door hardtop was added in December. Positioned beneath the Polara 500 in descending order were the Dart 440 and the Dart 330. These models were marketed in Canada as the Dodge 440 and Dodge 330, and a Canada-only basic-specDodge 220 model was offered as well.
This model proved somewhat popular, but Dodge failed to capitalize on its success and never developed it to its full potential. The Dodges were available with optional V8 engines of up to 413 cu in (6.8 L). These mid-sized Dodges (and similar models from Plymouth) competed successfully as stock cars in NASCAR races, where their smaller size and lighter weight gave them an advantage over the larger competitive cars from Ford and General Motors.
The basic body of the 1962 model continued until 1964, revised and lengthened by the new Chrysler Vice President of styling Elwood Engel. The Polara range eventually grew to include a 4-door sedan. The Polara 500 was available only as a convertible or hardtop coupé.
For the 1963 model year, the wheelbase was increased to 119 inches (3,023 mm) and the car received new sheet metal. The Dart name was reassigned to Dodge’s line of compact cars that had previously been known as the Dodge Lancer. Positioned below the Polara were the plain 440 and 330. The 1964 models received a revised front end and new tail lamps to distinguish them from the 1963 cars. Rear end treatment took its inspiration from the Chevrolet Impala, the Polara models now featuring six small, square-shaped taillights (three on each side) surrounded by an attractive bright trim panel. Lesser big Dodges featured only four taillights (two on each side) and lacked the bright trim panel. A sensational new “C” pillar for the hardtop coupes, combined with the more attractive front and rear end styling, made the ’64s look totally new (and longer/ lower/wider as well), resulting in a significant increase of sales over 1963.
The Polara 500 continued as Dodge’s sporty full sized model, competing with the Ford Galaxie 500/XL and Chevrolet’s Impala Super Sport, featuring an engine-turned anodized aluminum trim strip along the car’s flanks, bucket seats and deluxe vinyl upholstery.
1965–1968
| Third generation | |
|---|---|
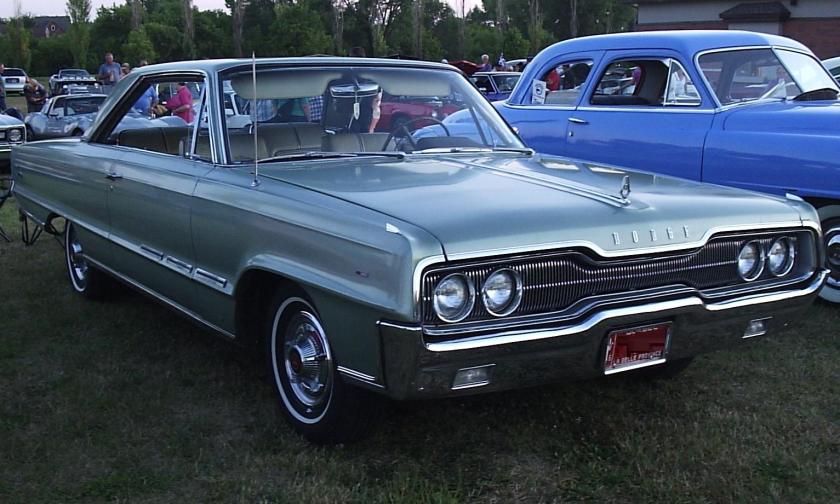

1966 Dodge Polara 2-door hardtop
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1965–1968 |
| Assembly | Detroit, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupe 2-door convertible 4-door station wagon |
| Platform | C-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 440 cu in (7.2 L) V8 (1966-68) 426 cu in (7.0 L) V8 (1965) 413 cu in (6.8 L) V8 (1965) 383 cu in (6.3 L) V8 (1965-1968) 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 (1965-1968) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 121.0 in (3,073 mm) 1965-66; 122.0 in (3,099 mm) 1967-on |
| Width | 80.0 in (2,032 mm) |
| Height | 62.0 in (1,575 mm) |
For 1965, Chrysler moved the Polara back to a Chrysler “C” fullsize platform that was shared with Chrysler and Plymouth models. Once again offered in a full range of bodies (sedans, hardtops, station wagons, etc.), the Polara, in effect, replaced the 880 and remained a step below the Custom 880, and the new Monaco hardtop coupe was now Dodge’s top model. The previous mid-sized Dodges that were sold under the names Polara 500, Polara, 440, and 330 continued in production under the name Dodge Coronet, their wheelbase shrinking to 117 inches (2,972 mm). These Polaras were criticized for low fuel economy, with some configurations going only 12 miles on a gallon of gasoline. In the 1966 model year, the Monaco would replace the Custom 880 as the mid-level model while a new Monaco 500 would replace the previous 1965 Monaco. 1967 models received a facelift and the hardtop coupe adopted a semi-fastback roof style with a reverse-slant rear quarter window. 1967 models also saw a new U.S. Government-required safety package that included an energy-absorbing steering column and safety steering wheel, blunt dashboard controls, more interior padding, and a dual-circuit brake master cylinder. 1968s got outboard front shoulder belts and side marker lights in addition to the ’67 safety equipment.
One constant of the 1965 to 1968 models was taut, square-edged styling, which was updated each year. From 1965 to 1970, the Polara would be the only full-sized Dodge available in the U.S. as a convertible.
1969–1973
| Fourth generation | |
|---|---|

1973 Dodge Polara 2-door Hardtop
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1969–1973 |
| Assembly | Detroit, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupe 2-door convertible 4-door station wagon |
| Platform | C-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 383 cu in (6.3 L) V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) V8 225 cu in (3.7 L) I6 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 3-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 122.0 in (3,099 mm) |
| Length | 1969-1970: 220.8 in (5,608 mm) 1971-73: 220.0 in (5,588 mm) |
| Width | 1969-1970: 79.3 in (2,014 mm) 1971-73: 79.0 in (2,007 mm) |
| Height | 1969-1970: 56.8 in (1,443 mm) 1971-73: 63.4 in (1,610 mm) |
Where the previous four years’ Dodges had been very straight-lined and lean (thanks to the talents of Elwood Engel), the new 1969 Polara wore a broad-shouldered and far more streamlined look. Called the “Fuselage Look”, this style would persist through five model years, with subtle variations. The resulting look made these Polaras and Monacos appear much larger than the 1968 and earlier models. 1969 models got front outboard head restraints as required by Federal law.
For 1969, the Polara 500 was reintroduced as a mid-level series between the standard Polara and top-of-the-line Monaco. The Polara 500 was available as either a convertible or hardtop coupe. Available powerplants included 318, 383, and 440 cubic-inch V8 engines, along with a 225 cubic-inch slant-6 I6 engine. The 1969 Dodge Polara models offered the Super-Lite option, which placed a quartz auxiliary “turnpike beam”headlamp in the driver side grille.
In 1970, the Polara would receive new front and rear styling that included a bumper that wrapped around the grill and headlights. The Polara 500 was replaced by the Polara Custom in hardtop coupe, 4-door hardtop sedan, and conventional 4-door sedan body styles. There was also a stripped-down Polara Special available as either a 4-door sedan or station wagon. 1970 was the last year that the Polara would be available in a convertible body style (with a scant 842 produced, making it extremely rare today), and Dodge would never again offer a full-sized convertible. Also exceptionally rare for 1970 was the “medallion” rear bumper. This bumper featured in all of the sales literature was discontinued after late August or early September 1969 production and replaced with a plain bumper lacking the center Fratzog medallion. Despite the fanfare, Dodge dropped the “Super-Lite” option at the end of the 1970 model year because of lack of consumer interest and various challenges to its legality in certain states. 1970s also received a new locking steering column which locked the steering wheel and column shift lever when the key was removed.
The Polara Special disappeared for 1971, but a new sub-series was the Polara Brougham positioned above the Polara Custom, but still a step below the Monaco, the Polara Brougham was available only as a hardtop coupe or 4-door hardtop sedan.
The 1972 model year would see a fairly significant facelift with new sheet metal and the disappearance of the Polara Brougham model. 1973 models received new front-end styling (which resembled the big 1970 Chevrolet), in which they lost the previous wrap-around front bumper.
Sales of the Polara were falling by this time, however. Having been eclipsed by the Monaco, Dodge decided to drop the Polara after 1973. The energy crisis in the fall of 1973, spurred on by the Arab/OPEC oil embargo, resulted in a serious drop in sales of all full-size American automobiles, which were seen as gas-guzzling monsters. The Polara shared the same fate as the other big cars from Detroit. The redesigned 1974 Monaco would only serve for four model years before being replaced by the unsuccessful Dodge St. Regis.
In Argentina
Variants of the North American Dodge Dart — using the same 111 in (2,819.4 mm) wheelbase but different sheet metal) were produced in Argentina from 1968 to 1980 by Chrysler-Fevre Argentina S.A.. Sedan models were called Coronado, but the Polara name was applied to coupé models, in conjunction with R/T and GTX designations for special sport coupés. Available engines were the 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6, a 318 cu in (5.2 L) Chrysler V8, and a diesel. The 318 was rarely ordered in Argentina, as local market preferences leaned more towards 4- or 6-cylinder engines. Three- and four-speed manual and 3-speed automatic transmissions were offered. The general impression of these cars, designed exclusively for the Argentine market, are that they look like the 1968 Plymouth Satellite for the sedan and the Dodge Charger–Plymouth Road Runner for the coupé, but they are smaller (although larger than the Dodge Dart). However, the interior, especially the dashboard, are similar to those of the early 70s Dodge Dart–Plymouth Valiant. These coupes were not available in large numbers, but are collected by enthusiasts. They are hard to sell, since gas consumption is high, compared to the 4- and 6-cylinder cars the Argentine consumer is used to. Several restyling jobs of the whole line with new front and rear ends were carried out within its lifetime.
An automobile magazine, Corsa, road-tested a Polara GTX coupé with a V8 rated at 212 hp (158 kW) at 4400 rpm, 308 lb·ft (418 N·m) at 2600 rpm and 8.5:1 compression ratio and obtained 189 km/h (117 mph) of top speed and 10.2 seconds from 0–100 km/h (0–62 mph).
There was also a version of this model built from 1971 to 1978 as a CKD imported from Argentina known as the Dodge 3700 in Spain. A 3700 GT is seen in the first Batman movie directed by Tim Burton.
Dodge Polara GTX→ Technical Data (in Spanish)
In Brazil
In Brazil, the Dodge Polara was revived – in name only – in 1977, on a version of the British Chrysler Avenger (which in the early 1970s had been sold in North America as the Plymouth Cricket). They were sold until 1981.
There was also a version of this model in sedan and station wagon built in the 1970s in Argentina of the same car known as the Dodge 1500 until Volkswagen took over Chrysler Fevre Argentina SAIC, and the tooling for the car, in 1980. From then until 1988 the car was sold in Argentina as the Volkswagen 1500 (not to be confused with the Volkswagen Type 3, also sold as the Volkswagen 1500 in most markets including Brazil).
- Power Wagon (1945–1980)
Dodge Power Wagon
| Dodge Power Wagon | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Production | 1945–1980 |
| Model years | 1946–1980 |
| Assembly | Warren, Michigan, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size pickup truck |
| Layout | Front engine, four-wheel drive |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 126 in (3,200 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Ram |
The Dodge Power Wagon is a four wheel drive light truck produced in various model series from 1945 through the present. The original version was based on Dodge’s 3/4 ton WC series of World War II military trucks. The civilian Power Wagon continued the Dodge lineage of four wheel drive trucks from the 1930s, proving basic four wheel drive design concepts and representing a significant predecessor to the many four wheel drive trucks in modern use today. UPdated variants continued in production until 1980.
The Power Wagon nameplate was reintroduced under the Ram Trucks brand in 2005, and became an official model in 2013.
History
Derived from the Dodge 3/4 ton WC series World War II military trucks, the Power Wagon was introduced in 1946 as the first civilian 4×4. Meant to compete with military-based Ford/Marmon-Herrington and GMC trucks, it had an enclosed all-weather civilian cab and a purpose-designed 8-foot cargo box. It had a 126 inch (3,200 mm) wheelbase chassis and featured the 230 cubic-inch flathead inline-six engine, a two-speed transfer case, a 4-speed manual transmission with a power take off (PTO) which would send power front or rear for operating auxiliary equipment, and 9.00/16-8 ply tires on 16×6.50 inch 5-stud wheels. In 1961 the 230 was replaced with the 251 cubic-inch flat head six.[1]
The nominal one-ton rated Power Wagon’s gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) was 8,700 pounds. Its maximum payload was 3,000 pounds. A big-block 383 V8 engines became an option starting in 1967. From 1961 to 1971 the body was called the “Sweptline,” then transitioned to a more modern body image from 1972 through 1980 with varied grilles and paint schemes. In 1975 the 4-wheel drive became full-time with a 2-speed transfer case; this was changed back to part-time 4-wheel drive in 1980 due to the energy crisis. A huge boost in sales followed the 1974 release of the extended “Club Cab,” popular with families and camper towing. The 4-door Crew Cab was far less common and is quite desirable to collectors for restoration. Utility and function was unmatched by few competing models, as the towing, payload, and snow plowing capacity of the Power Wagon equipped with “Dana 60” 8-lug axles was very popular with municipal and regional road crews.
The Power Wagon was sold through the 1980 model year. A number of engineering and styling improvements were made over the years as the truck grew in size and weight, but the basic package remained generally constant throughout its life and underwent one last major body change in 1972. If you are interested in test driving a power wagon please call PowerWagonMotorSports LLC at (800)-382-5633
Variants
W100 and W200
The first light-duty Power Wagons came out in 1957 with the introduction of the W100 and W200 pickups (beginning in 1957 1⁄2-ton 2WDs were D100s and 4WDs were W100s). These trucks featured conventional cabs and front sheet metal and the cargo boxes used on the 2WD models. Their 4WD mechanical components—axles, transfer cases and transmissions—were sourced from outside manufacturers. Chrysler Corporation owned the New Process Gear Company (competitors generally used Spicer (Dana) transfer cases and Borg-Warner or in-house transmissions).
W300
A one-ton W300 light-duty/civilian type Power Wagon was released in 1958. For the next ten years the Power Wagon lineup consisted of the “military-type” W300M, and the W100, W200, and W300 “civilian-type” Power Wagons. Standard models included pickups and chassis cabs only. 1957 Through 1966, W100 Power Wagon Town Panels and Town Wagons were also standard models. In 1961 a W200 Crew Cab pickup was added to the line. Dana 70 axles were used in the front and rear of these trucks.
W500
The two-ton W500 Power Wagon (only a chassis cab was built) was introduced in 1956 as the C3-HW, and lasted through the 1971 model year. This was replaced in 1972 with the W600 (also cab and chassis only), which was produced until 1977, when all Dodge medium-duty models were discontinued. To compensate for the loss of the medium-duty W600 a new W400 chassis cab was introduced in 1977.
Willock Chassis Swivel
From about 1952 through 1958 an option known as the Willock Chassis Swivel was available. With this option the frame was split into two pieces at the point where the bed of the truck met the rear of the cab. A longitudinal swivel system allowed these two pieces to rotate with respect to each other, with the result that almost without regard to the terrain all four wheels would always be on the ground. Somewhere between 50 and 100 examples were built. While Willock is no longer in business the chassis swivel is still manufactured by third-party vendors and can be incorporated into existing vehicles.
Replacement by Dodge Ram
The Power Wagon nameplate was discontinued in 1981 with the introduction of the Dodge Ram, with the four-wheel-drive models being sold under the “Power Ram” nameplate through 1993. 1989 to 1993 models saw the addition of an optional 6-cylinder CumminsTurbo-diesel engine.
First generation gallery
|
2005–present
For 2005, Dodge resurrected the Power Wagon name on a version of the Dodge Ram 2500. It was a special off-road version of the Ram 2500 with a 5.7L Hemi V8 as the only engine option. Interior configurations remain similar to standard production Ram. As of 2010, the Power Wagon is only available as a Crew Cab Short Bed model. Special features of the Power Wagon include:
- Electronically controlled locking differentials (front and rear)
- Electronically disconnecting front sway bar
- Integrated 12,000 lb electric Warn winch
- 17 inch diameter Alcoa forged wheels
- Large 33 inch diameter BF Goodrich All Terrain T/A 285/70R17 tires
- Bilstein Monotube Gas Charged Shocks
- Extensive skidplating: front stabilizer bar, transfer case, fuel tank, special skid plate crossmembers welded to the frame with open bars bolted to them across the midsection.
- 1.4″ factory lift in front, 1.0″ in rear (0.4″ front and rear due to larger tires). Softer rate springs.
- Strengthened torque converter
- 4.56:1 axle ratios (4.10 as of the 2014 model)
- Revised clutch fan
- Strengthened steering gear
- Low range 4×4 throttle mapping changed.
Upgraded suspension and larger tires naturally give the truck a taller ride height. Clearance lights and tow hooks are standard equipment. Fender flares are standard equipment as well. The fender flares assist with tire coverage due to the Power Wagon’s wider tires.
Powertrain
Transmission
A six speed manual transmissions was standard, with an automatic transmission optional. As of 2010 the manual transmission is no longer an option. 2012 models have the 66RFE 6 speed automatic transmission, instead of the 545RFE 5 speed automatic in the previous models.
Transfer case
The transfer case was a New Venture 271 and had a 2.72:1 low range gear ratio. A transfer case skid plate was and is standard equipment. A manual shift-on-the-fly transfer case is the only available, the electronic shift on-the-fly has never been an option. As of the 2012 model year, the transfer case has changed to a Borg-Warner 44-47 manual shift-on-the fly. Low range is now 2.64:1.
Axles
The axles are manufactured by American Axle & Manufacturing, Inc. The front is an AAM 9.25 and the rear is a hybrid AAM 10.5 with the larger axle shafts from the AAM 11.5. Despite the fact the axles have locking differentials, the rear axle is also a helical-type limited slip differential when unlocked. The axles are only available with a 4.56:1 gear ratio. Non Power Wagon 2500 Ram trucks only have 3.42:1, 3.73:1, or 4.10:1 gear ratios. 2010 models (along with other Ram trucks) received larger universal joints.
2012 Weight ratings:
- GVWR – 8510 lbs
- GCWR – 17,000 lbs
- GAWR (front) – 4500 lbs
- GAWR (rear) – 6200 lbs
- Max payload – 1880 lbs
- Max towing – 10,250 lbs
- Curb weight – 6800 lbs
2013 updates
The New Venture Gear transfer case is replaced by a Borg-Warner unit. Interior updated ala 1500 Rams.
2014 updates
The RAM Power Wagon will have a 6.4 Hemi V8 as the standard engine; the 5.7 Hemi V8 goes away. The 6.4 has 410 horsepower and is also available in standard Rams. The transmission and transfer case remain unchanged (Borg Warner 44-47). The axle gears change from 4.56:1 gear ratios to 4:10 gear ratios. The rear axle is now a 11.5 AAM axle (with selectable locker). The rear suspension now has a 5-link coil spring arrangement instead of leaf springs. The front suspension has been changed to a radius arm arrangement (3-link) instead of the 5-link used since 2005.
|
See also
- Dodge WC series
- Dodge W-series/Power Ram
- Dodge Town Panel and Town Wagon, available as Power Wagon carryalls
- List of Dodge automobiles
- Commercial Utility Cargo Vehicle
- Ram 50 (1979–1996)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mitsubishi_Triton
1983 Dodge Ram 50
Dodge Ram 50 (US)
- Ram SRT 10 (2004-2006)
Dodge Ram SRT-10
| Dodge Ram SRT-10 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler |
| Production | 2004–2006 |
| Assembly | Saltillo, Coahuila, Mexico (Saltillo Truck Assembly) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Sport pickup truck |
| Body style | Pickup truck |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | Chrysler DR/DH/D1 platform |
| Related | Dodge Ram |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 8.3 L (505 cid) V10 |
| Transmission | 6-speed manual 4-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | Regular: 120.5 in (3,061 mm) Quad: 140.5 in (3,569 mm) |
| Length | Regular: 203.1 in (5,159 mm) Quad: 227.7 in (5,784 mm) |
| Width | 79.9 in (2,029 mm) |
| Height | Regular: 74.4 in (1,890 mm) Quad: 74.7 in (1,897 mm) |
The Dodge Ram SRT-10 is a sport pickup truck that was produced by American automaker Dodge in limited numbers. It was introduced at the January 2002 North American International Auto Show, but was not put into production until 2004. Unlike previous Ram trucks, the SRT-10 was built solely for the purpose of speed.
Development
The Dodge Ram SRT was created by DaimlerChrysler’s PVO (Performance Vehicle Operations) division, using Dodge Viper and Plymouth Prowler engineers. Extensive wind tunnel testing was used in styling the exterior of the Ram SRT-10. This is the second time that Dodge has put a Viper engine into a Ram pickup. At the 1996 Chicago Auto Show, Dodge introduced a concept Dodge Ram with a Viper Generation 2 engine, but it was not put into production. The Dodge Ram VTS was painted Banzai Blue with dual white skunk stripes, housed a 8.0 L (488 cid) V10, a six-speed Borg-Warner manual gearbox, and 17-inch (430 mm) Viper GTS wheels wrapped in BF Goodrich 275/60-HR17 Comp T/A HR4 tires.
Overview
The SRT-10 featured an 8.3 litres (Chrysler 8.3 L Viper V10) V10. This engine produced 500 bhp (373 kW; 507 PS) at 5,600 rpm and 525 lb·ft (712 N·m) of torque at 4,200 rpm. The regular cab, with a total curb weight of 5,130 lb (2,330 kg), reached a top speed of 154 mph (248 km/h), and could accelerate from 0 to 60 mph (97 km/h) in 4.9 seconds, whereas the Quad Cab, weighing 5,618 lb (2,548 kg), achieved 0-60 mph in 5.6 seconds and reached a top speed of 147 mph (237 km/h). The regular cab could complete the 1⁄4 mi (400 m) in 13.6 seconds at 106 mph (171 km/h), the Quad Cab in 13.7 seconds at 100 mph (160 km/h). The engine produced one horsepower for every 10.3 lbs of vehicle weight in the regular cab. The regular cab generated .86 g of grip on a 300 ft (91 m) skidpad, while the Quad Cab generated .83 g. The regular cab was rated by the EPA at 9 MPG city/15 highway, while the Quad Cab was rated at 9 city/12 MPG highway.
Drivetrain
The V10 Viper engine delivered 90 percent of its torque from 1500 to 5600 rpm. The cast aluminum cylinder block had cast-iron liners and cross-bolted main caps. The bore and stroke had been increased over previous Viper models. Compression ratio, firing order, rod length, block height and block length were unchanged from the second-generation Viper engine. The regular cab featured a Tremec T-56 transmission, while the Quad Cab utilized a 48RE four-speed automatic transmission modified from the Ram Heavy Duty transmission. Both regular cab and Quad Cab used a Dana 60 rear axle.
48RE
| Gear | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Final Drive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio | 2.45:1 | 1.45:1 | 1:1.00 | 0.69:1 | 4.56:1 |
Suspension
PVO engineers modified the Ram Heavy Duty’s rack and pinion steering and independent front suspension for use in the Ram SRT-10. A fully hydroformed Dodge Ram frame was used in conjunction with a custom-tuned suspension, lowering the Ram SRT-10’s ride height one inch in the front and 2.5 inches in the rear. Bilstein shock absorbers, performance-tuned springs and unique aerodynamic aids were used to enhance the Ram SRT-10’s higher-speed performance. An additional 5th shock was used on the rear axle to prevent wheel hop during wheel-spin.
Exterior
The Ram SRT-10 had a unique hood that featured a wide power bulge and honeycomb grill hood scoop. The hood scoop allowed cool air to enter as well as forcing hot air to exit from the engine bay, thus helping the engine to run cooler. “Viper Powered” badges were added to the sides of the power bulge, to indicate the SRT-10 engine under the hood. Large chrome Srt-10 logos were mounted to the driver and passenger side doors and rear tailgate right side on the Quad cab and Single Cab 2005 models replaced in 2006 by smaller chrome and red srt10 logo badges . All models were outfitted with large molded kickerpanels painted to match body color. Another exterior feature was a tonneau cover with an attached spoiler that was supposed to come standard on the 2005 Quad Cab version and all 2006 models, but due to manufacturing problems was not installed on nearly half of the Ram SRT-10s intended. To help remedy this situation, Dodge added a $1000 credit and a regular spoiler to the Ram SRT-10s that did not receive the tonneau cover. In addition to style, the spoiler also helped with air flow and provided a reduction in lift and drag. The Ram SRT-10 had a bed size of 6 ft 3 in (1.91 m), giving the regular cab an overall length of 17 ft 7 in (5.36 m), and 19 ft 2 in (5.84 m) overall length for the Quad Cab. The Ram SRT-10 also had a lower ride height than regular Ram trucks.
Interior
The Truck audio had 3 options of the Dodge Ram SRT-10 by 2006 and consisted of 8 Infinity brand speakers with a DVD based large color lcd map navigation system and a mid tier CD turn by turn graphics cd based system with small color lcd finally a standard led Radio with cd player; all built and designed by Alpine audio and 10 inch sub woofer mounted under the rear passenger seat with silver bezel and 575 watts of total system output, Bluetooth by uconnect for hands free communication through your car stereo as a factory option also full digital Satellite radio. The doors on both the Standard cab and Quad can had silver large accents along the middle above the arm rest. It also came with a leather trimmed steering wheel and with heavily bolstered racing-derived suede-trimmed charcoal leather seats. The center stack was adorned with silver trim, and a silver trim strip with the SRT-10 logo resided under the passenger-side air bag cover. Taking a cue from the Dodge Viper, the Ram SRT-10 came with a red start button on the dash. The manual transmission regular cab featured a Hurst shift lever, which sprouted from a silver metal shift bezel and was fitted with a Viper shift knob. Aluminum performance-inspired pedals replaced the stock setup. The gauge cluster featured satin silver-faced gauges and Viper font and graphics. The speedometer and tachometer were re-calibrated to match the Ram SRT-10’s increased performance.
Colors
Excluding the special editions, the 2004-2005 Ram SRT-10 came in three colors: Brilliant Black Crystal Pearl Coat, Bright Silver Metallic Clear Coat, and Flame Red Clear Coat. The redesigned 2006 Ram SRT-10 came in Mineral Gray Metallic, Inferno Red, and Brilliant Black Crystal Clear Coat.
Wheels and brakes
The stock 22-inch (560 mm) wheels were fitted with Pirelli Scorpion P305/40R-22 performance tires and modeled after the 10-spoke wheels available on the Viper. The brakes for the 2004 model (front and rear) and 2005-06 (rear) were modified from the Ram Heavy Duty truck for use in the Ram SRT-10. The standard ABS-equipped brakes were fitted with 15-inch (380 mm) rotors in front and 14-inch (360 mm) rotors out back. 2004 models used red-painted two-piston sliding brake calipers front and rear; these were replaced with larger four-piston monoblock calipers up front in 2005-06, designed by TRW and unique to the SRT-10. Two NASCAR-inspired brake cooling ducts integrated into the front fascia provide cooling for the Ram SRT-10’s brakes.
Quad cab
Following the success of the Ram SRT-10 regular cab, Dodge decided to introduce a Quad Cab version starting in the 2005 model year. The new Quad Cab was aimed at the performance truck enthusiast who wanted a performance pickup, but not at the expense of room for passengers and towing capacity. The Dodge Ram SRT-10 Quad Cab was fitted with a 4.56 final-drive gear ratio to improve low-end acceleration and was rated at 7,500-pound (3,400 kg) towing capacity. A body-color aluminum tonneau cover with an aerodynamic spoiler came standard on the Quad Cab. The Quad Cab was only offered with a 4-speed automatic transmission, a 48RE borrowed from the Ram Heavy Duty with Cummins turbo diesel. The 48RE was rated to handle up to 700 ft lbs of torque.
Special editions
Dodge released several limited editions of the Ram SRT-10 alongside the standard regular cab and Quad Cab versions.
- VCA (Viper Club of America) Edition – 52 produced, released at the 2004 Daytona Motor Speedway Race in February. Where people were able to enter a raffle, And only the winners of the raffle were able to purchase the vehicle, but, of course the winners were able to sell them again to a third-party. Its paint scheme was white rally stripes on Electric Blue. Engine was also signed by Wolfgang Bernhard, Chrysler Group’s former Chief Operating Officer. Available as a 2004 model.
- Yellow Fever – 500 produced, painted in Solar Yellow exterior paint and black “fanged” stripe on top of hood, came with two-tone interior which featured a yellow center stack bezel, yellow door spears, yellow stitching on steering wheel, seats and Regular Cab manual transmission shifter and yellow embroidering on the SRT-10 floor mats. Also came with special Yellow Fever Edition badges and a serialized Yellow Fever dash plaque. Available as a 2005 model.
- Commemorative Edition – 200 produced, featured Bright White exterior paint with Electric Blue stripes. Interior enhancements included blue stitching on the seats, shift boot, shift knob and steering wheel. Floor mats were embroidered in matching stitching with the SRT-10 logo. In addition, the Commemorative Edition included standard polished wheels, brushed aluminum scuff plates, and a hard tonneau cover. Available as a 2005 model.
- Night Runner – 400 produced, painted in Brilliant Black exterior paint, came with Dark Nickel Pearl finish 22-inch (560 mm) wheels, black chrome grill inserts, unique Night Runner badges, a black center stack and center console bezel overlay, and a serialized Night Runner dash plaque. Available as a 2006 model.
End of production
The first SRT-10 was produced November 11, 2004. Ram SRT-10 production ended after the 2006 model year Total production for the 2004 Dodge Ram SRT-10 was 3,057. For 2005, the total production was 4,097 and the 2006 total production was 2,373. Over the 3-year lifespan of this truck, just 9,527 Dodge Ram SRT-10s were manufactured.
| 2004 Color Breakdown | Regular Cab |
|---|---|
| Flame Red | 1040 |
| Black | 1269 |
| Bright Silver Metallic | 698 |
| VCA Edition | 50 |
| Total | 3057 |
| 2005 Color Breakdown | Regular Cab | Quad Cab | Year Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 471 | 1136 | 1607 |
| Flame Red | 453 | 777 | 1230 |
| Bright Silver Metallic | 280 | 280 | 560 |
| White (CE) | 200 | 0 | 200 |
| Yellow Fever | 200 | 300 | 500 |
| Total | 1604 | 2493 | 4097 |
| 2006 Color Breakdown | Regular Cab | Quad Cab | Year Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brilliant Black Crystal | 220 | 465 | 685 |
| Inferno Red | 221 | 417 | 638 |
| Mineral Gray | 131 | 310 | 441 |
| Black Clear Coat | 87 | 93 | 180 |
| Night Runner | 200 | 200 | 400 |
| Flame Red | 7 | 8 | 15 |
| Bright Silver Metallic | 6 | 8 | 14 |
| Total | 872 | 1501 | 2373 |
World record
In February 2004, a Dodge Ram SRT-10, driven by NASCAR driver Brendan Gaughan set both the Guinness World Record and Sports Car Club of America‘s record for the world’s fastest production truck with an average speed of 154.587 mph (248.784 km/h). As of August 2014 it is still the Worlds fastest full size factory pickup truck. Note: There were a total of three Dodge Ram SRT10 trucks used to break the world speed record. Vin # 3D3HA16H44G257254 reached a top speed of 157.327 mph but was disqualified because of what was considered an illegal exhaust system. 154.587 is the official speed that is used.
- Ram Van (1971–2003)
Dodge Ram Van
| Dodge Ram Van | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Assembly | Windsor, Ontario, Canada |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Van |
| Body style | 3-door van 4-door van 3-door wagon 4-door wagon |
| Platform | Chrysler B platform |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge A100 |
| Successor | Dodge Sprinter |
The Dodge B-Series was a full-size van marketed under the Dodge brand by the Chrysler Corporation (1971–1998) and later DaimlerChrysler (1998–2003). Starting in 1981, the B-Series was sold as the Dodge Ram Van; the passenger variant was known as the Dodge Ram Wagon and Plymouth Voyager.
DaimlerChrysler discontinued production of the Ram Van and Ram Wagon after more than 30 years of production following the 2003 model year, replacing them with the Dodge Sprinter. All Ram Vans and Wagons were built at the Pillette Road Truck Assembly plant in Windsor, Ontario, Canada, which has since been demolished.
History
Built on the B platform (later AB), the full-size vans entered production for the 1971 model year. Due to a one-welded-piece “Uniframe” design, the Dodge platform was lighter and stronger and featured a lower cargo floor than the competition, at the expense of NVH. The resulting lower center of gravity improved handling versus the competing products. The B-series van was popular for cab-over motorhome conversion until Chrysler Corporation’s egress from that market during their financial difficulties in the late 1970s.
All generations of the B-series van feature similar construction, with only small variation from era to era. The most pronounced changes were to the front fenders, hood, grille, and bumpers, which tended to follow their full-size truck counterparts in each era. Much of this was a result of the need to meet Federal “crashworthiness” standards. Additionally, the first generation’s side door was mounted back several inches, using a fixed panel between the passenger’s side front door and the side door, allowing for more access to the side door without interfering with the front passenger’s seat. This panel was eliminated in 1978 which was a transitional year for the B-series van. Similar construction for the entire 32 years of production made the Dodge Van very popular with upbuilders, service companies, and other fleets due to the compatibility of installable options from year to year without necessitating a redesign.
Dodge first pioneered the extended-rear 15-passenger van favored by school and church groups and dominated this market until overtaken by Ford in the 1990s. It offered a sliding side door as well as a unique side-swinging tail door with a full-width window.
It was also popular in class-C RV and ambulance conversions.
The minivan, pioneered by Chrysler, eventually took over the passenger wagon market. With the Sprinter, Chrysler left behind American-style full-sized vans in favor of more fuel efficient European-style models.
The B-series van was available with nearly every engine used in a rear-wheel-drive Chrysler product during its production. Six-cylinder engines included the 225 in3 Slant Six I6 (1971–1987), the 3.9 L LA V6 (1988–1991), and the 3.9 L Magnum V6 (1992–2003). Small-block V8 engines included the LA-series 318 in3 (1971–1991), 360 in3 (1972–1992), the Magnum 5.2 L (1992–2003), and the Magnum 5.9 L (1993–2003). Big-block V8 engines were the 400 in3 and 440 in3 (1976–1978). Certain model years came with an optional 5.2-liter engine utilizing Compressed Natural Gas, with a range of up to 300 miles (480 km) on a full tank, and CNG-powered Ram Vans were classified as an Super Ultra Low Emission Vehicle in 1999.
Dodge was the last of the four major full-size van makers to market a short-wheelbase van and passenger wagon. The rest of the Big Three took their shortest full-size vans off the market early in the 1990s.
DaimlerChrysler discontinued production of the Ram Van and Ram Wagon after the 2003 model year, replacing them with the M-B-based Dodge Sprinter.
Original B-Series
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1971–1978 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size van |
| Body style | 2-door or 8–15 passenger van |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) Slant-6 360 cu in (5.9 L) LA V8 318 cu in (5.2 L) LA V8 400 cu in (6.8 L) B V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) RB V8 |
For the first eight model years, the different configurations of B vans were given names. Sportsman passenger vans had side windows and passenger seating not present in the otherwise identical Tradesman models. The same range of gasoline-powered slant-6 and V8 engines was offered in these vans as was offered in the Dodge D Series pickup truck.
Dodge pioneered the American 15 passenger van genre with the introduction of the Maxiwagon along with the other front engine B series vans that were new for 1971. Ford didn’t produce a 15 passenger van until 1978, and GM did not introduce theirs until 1990. Little changed on Dodge vans produced between 1971 and 1977, with only a grille change from metal to plastic for the 1974 model year. 1978 was a transition year for B series vans, consisting of the nose from 1977 and earlier vans (with a one-year only Dodge symbol in the grille) but with a completely new dashboard and rear end cap. On the standard length vans, the rear end cap just contained new larger tail lamps, but the extended length Maxivan and Maxiwagon had a completely redesigned rear extension which was longer and had large windows that wrapped around the corners for better visibility. This was unique to the B vans, and this same extension was used until the B vans were discontinued in 2003. On the 1971-77 models, the rear side doors were set back about two feet towards the rear wheelwells, with a filler panel between them and the front doors. Passenger models had a small window between the front and rear doors. In 1978, the filler panel was removed and the doors were moved forward to be next to the front passenger door, similar to the Ford and Chevrolet vans.
In the late 1970s, Chrysler marketed the B van in their lineup of “Adult Toys”, along with the D-Series-based Dodge Warlock, Dodge Lil’ Red Express Truck, and Dodge Macho Power Wagon, plus the Dodge Macho Ramcharger.
Street Van
Dodge vans, particularly Tradesman vans from the 1971–1977 model years, were very popular as the basis for many custom vans during the custom van craze that occurred during the mid to late ’70s and early ’80s. Dodge capitalized on this craze, creating a factory customization package called the “Street Van” package. This was advertised alongside the Lil’ Red Express and Warlock trucks as “Adult Toys”. The Street Van package consisted of a “Street Van” logo on the passenger and driver’s side door in lieu of the Tradesman logos, chrome trim on the grille and windshield, simulated wood grain inlays in the steering wheel horn cover and passenger side glare shield, five slot chrome wheels or white spoked “off-road” type wheels, chrome front and rear bumpers, chrome trim on the gauges, smaller chrome side view mirrors, patterns and plans to create custom interiors, and membership in the “Dodge Van Clan”. This package was available from the 1976 model year until it was discontinued in the early ’80s. This was not an overly popular option from the factory, and Street Vans are somewhat rare. The chrome metal Street Van emblems found on later Street Vans (emblems through mid-1978 were stickers) in good shape are quite valuable to collectors or restorers.
Kary-Van
The name “Kary Van” comes from the cube shape of the cargo section of the van. Dodge used the van body for the front end of its 1973–1978 cube-vans usually with dual rear axles and heavy-duty 1-Ton suspensions. Many examples of these cube-vans can still be found on the streets today as they were typically owned by companies that kept them in service for some time. Thanks to regular maintenance, some still see service.
Rebadged variants
During the last two years of its existence Fargo offered a rebadged variant of the Tradesman and Sportsman in Canada for 1971 and 1972 only. Plymouth also received a rebadged variant of the Sportsman, called the minivan for the 1974 model year. While never as popular as the Dodge version, Plymouth marketed the Voyager in this format through 1983, after which the nameplate was transferred to the new minivan that was introduced for 1984 as a rebadged Dodge Caravan.
Second generation
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1979–1993 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Plymouth Voyager (1979–1983) |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 3.7L (225cid) I6 110 HP (79–88) 3.9L (239cid) V6 (88–03) 5.2L (318cid) V8 (79–03) 5.9L (360cid) V8 155 HP (79–03) 6.6L (400cid) V8 190 HP (71–78) 7.2L (440cid) V8 195 HP (71–78)Horsepower figures for 1978 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 4-speed automatic 3-speed manual (column shift) 4-speed (floor shift) manual5-speed manual (floor shift) |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 150 SWB: 109.6 in (2,784 mm) LWB: 127.6 in (3,241 mm) |
| Length | 1988–1990 150 SWB: 178.9 in (4,544 mm) 1988–1990 150 LWB, 250 & 350 SWB: 196.9 in (5,001 mm) 1998–1990 250 & 350 LWB: 222.9 in (5,662 mm) 1991–93 B150 (Wagon Only): 187.2 in (4,755 mm) 1991–93 B250 & B350 SWB (Wagon Only): 205.2 in (5,212 mm) 1991–93 B250 & B350 LWB (Wagon Only): 231.2 in (5,872 mm) |
| Width | 1988–1990: 79.2 in (2,012 mm) 1991–93 Wagon: 79.0 in (2,007 mm) 1991–93 Van: 79.8 in (2,027 mm) |
| Height | 1988–1990 150: 78.3 in (1,989 mm) 1988–1990 250: 79.9 in (2,029 mm) 1988–1990 350: 80.5 in (2,045 mm) 1991–93 B150 Wagon: 78.1 in (1,984 mm) 1991–93 B250 Wagon: 78.6 in (1,996 mm) 1991–93 B350 Wagon: 80.5 in (2,045 mm) 1991–93 B150 Maxi Wagon: 80.7 in (2,050 mm) 1991–93 Van (Extended): 80.1 in (2,035 mm) |
In 1979 the van received a redesigned front end, including a new grille with wraparound turn signals. Lower end models had single round headlights, while Royal Sportsman and other high-end vans received four rectangular headlights. The van would keep this body style and the 1978 dash intact with only grille changes all the way through the 1993 model year. The Sportsman, Tradesman, and Adventurer names were phased out after 1980, replaced with the Ram Van moniker, which included the Ram Wagon for passenger models. As with the D-series trucks, B100 and B150 models were 1/2-ton rated, B250 models were 3/4-ton, and B350s were one-ton. The body shell and most fixtures would be one of the longest running of any US vehicle, remaining nearly identical from the vans’ introduction in 1971 through their discontinuance in 2003, while Ford and GM would go through two or three generation platform redesigns.
In 1986 the Ram Van was given a new grille to resemble those of the 1986 Ram trucks. In 1994 the entire front end was redesigned with flush headlamps to resemble the all new Dodge Ram pickups, and new taillights wrapped around the sides of the van. The 1978-style dash was kept.
Third generation
| Third generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1994–2003 |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | Magnum 3.9L 175 hp (130 kW) V6 Magnum 5.2L 230 hp (170 kW) V8 Magnum 5.2L 220 HP V8 (CNG)Magnum 5.9L 250 hp (190 kW) V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic4-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 1998–2003 1500 SWB: 109.4 in (2,779 mm) 1994–97 1500 SWB: 109.6 in (2,784 mm) 2500 & 3500: 127.6 in (3,241 mm) |
| Length | 1500: 187.2 in (4,755 mm) 2500: 205.2 in (5,212 mm) 3500: 231.2 in (5,872 mm) |
| Width | 79.8 in (2,027 mm) 1994–96 Van: 79.0 in (2,007 mm) |
| Height | 79.5 in (2,019 mm) 3500 & 2500: 79.9 in (2,029 mm) |
In 1994 the entire front end was redesigned with flush headlamps to resemble the all new Dodge Ram pickups, and new taillights wrapped around the sides of the van. The 1978-style dash was kept. In 1998, the van went through the most thorough update since its introduction in 1971. The engine was moved forward in the chassis to improve crash protection, and the front end sheetmetal was redone with a longer nose to accommodate this change. Moving the powertrain forward also resulted in a smaller dog house (engine access cover) which increased front interior room and allowed better access when moving between the front seats. The 1978-style dashboard and door panels were finally replaced with a modern design using components from contemporary Chrysler products. The side view mirrors were now break-away units mounted to the sail portion of the front window openings. This change resulted in the elimination of the front door vent windows. The van remained mostly unchanged until it was discontinued after the 2003 model year.
Revival of the Ram Van
In 2012 a Dodge Caravan-based cargo van, previously sold as the Dodge Caravan C/V, was renamed the Ram C/V Tradesman. In 2013, a new full-sized van based on the Fiat Ducato was introduced and sold under the name Ram ProMaster, which is the modern descendant of the original Dodge B-Series full-size van. The Ram ProMaster City, a Fiat Doblo-based replacement for the Ram C/V Tradesman will be introduced in 2014. The Promaster City is said to be a modern descendant of the Dodge A100 compact van.
- Ramcharger (1974–2001)
Dodge Ramcharger
| Dodge Ramcharger | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1974–2001 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size SUV |
| Body style | 2-door SUV |
| Platform | Front engine, rear-wheel drive /four-wheel drive |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Durango (2004) |
The Dodge Ramcharger was a large sport utility vehicle built by Dodge from 1974 to 1993 (and from at least 1986 until 2001 in Mexico) based on the shortened wheelbase of the Dodge D Series/Ram pickup truck chassis. A Plymouth version, named the Trailduster was offered from 1974 to 1981, the brand’s only SUV, though one can argue that with similar classifications of early Plymouth station wagons, and the Plymouth Voyager minivan.
First and second generations
| First generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Also called | Plymouth Trailduster (1974–1981) |
| Production | 1974–1980 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | Chrysler AD platform |
| Related | Dodge D Series Dodge Ram |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 cu in (3.7 L) I6 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 400 cu in (6.6 L) V8 440 cu in (7.2 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed manual 3-speed TorqueFlite automatic |
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1981–1993 (1988–1996 In Mexico) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Platform | Chrysler AD platform |
| Related | Dodge Ram |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed automatic 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 106.0 in (2,692 mm) |
| Length | 1988–1990: 184.6 in (4,689 mm) 1991–93: 188.0 in (4,775 mm) |
| Width | 79.5 in (2,019 mm) |
| Height | 1988–1990 2WD: 69.7 in (1,770 mm) 1988–1990 4WD: 73.1 in (1,857 mm) 1991–93 4WD: 74.1 in (1,882 mm) 1991–93 2WD: 70.6 in (1,793 mm) |
The Ramcharger was primarily produced as a full-time four wheel drive vehicle, although a two-wheel drive version was available starting in 1975. During development, it was known as the “Rhino”.[1] 1974 through 1980 models have a removable hard top, although dealer-installed soft tops were available. The first year model differs from the others in that its door pillars are attached to the removable roof.
Like many vehicles, the Ramcharger was used in rallying, although its use was very limited. It did have some success, as demonstrated by achieving first place at Sno*Drift in 1975. In 1978 and 1979 the 360 CID’s horsepower was bumped up to 195 horsepower (145 kW). 1978 was the last year for the 440 CID, which by then only put out 215 horsepower (160 kW).
The Ramcharger and Trailduster followed the D-series pickup’s 1981 redesign into the Ram and is considered the second generation. These models had a non-removable welded steel top instead of the removable top. The Trailduster was only available for one year with the Ram design and steel non-removable top, as it was dropped after 1981.
Mechanicals
The vehicle was usually powered by a Chrysler LA engine, the most common being the 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8. Optional was the 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 and even big-block B series 400 cu in (6.6 L) V8 and RB 440 cu in (7.2 L) V8 were offered in the early years. Initially a normally aspirated carburetor, in 1988 the 318 gained throttle-body fuel injection with the 360 following in 1989. Power output for the TBI 318 was 230 horsepower (170 kW) and 280 lb·ft (380 N·m) of torque. The TBI 360 had 240 hp (180 kW) and 283 to 295 lb·ft (400 N·m). In 1992 the multiport fuel injected Magnum 318 was the standard engine while the LA 360 with TBI was still offered. In 1993 the Magnum 360 replaced the LA engine version.
Many manual transmissions were offered throughout the years, starting with the A-230 three-speed and ending with the A-535 five-speed in 1992. The NP435 “granny gear” 4 speed was the most common in 4WD models, as well as the close ratio version, the NP445. In 1988 the clutch was converted from a mechanical linkage to a hydraulic system. Automatic transmission models had the Chrysler Loadflite TF-727A or B until, in 1991, it was replaced with the A-500/A-518 four-speed.
A full-time four-wheel drive NP-203 transfer case was standard until 1980, when it was replaced with the part-time NP-208. This was supplanted by the NP-241 in 1988.
Axles were Dana 44 front and 9¼” rear. Full time 4WD models (1973–1979) were equipped with the full time version of the Dana 44 that had no provision for locking hubs and had a front wheel bearing design with a somewhat dubious reputation. In 1980 when the part time 4WD system was introduced, the front Dana 44 was equipped with a more conventional front wheel bearing design and automatic locking hubs. Late in the 1984 model year the Dana 44 was switched to a CAD (Center Axle Disconnect) version. The CAD Dana 44 was vacuum actuated by a switch on the transfer case and powered by engine vacuum. The CAD Dana 44 was carried on until the end of Ramcharger production in 1993. Users often ran into problems with the CAD system. The vacuum switch on the transfer case would occasionally fail and either leave the CAD engaged or not engage the CAD at all. Limited slip differentials were available for the 9¼” rear axle. The full-time 4WD versions used a 5 on 4½” wheel bolt circle and the part time models used a 5 on 5½” bolt circle.
Third generation
| Third generation | |
|---|---|
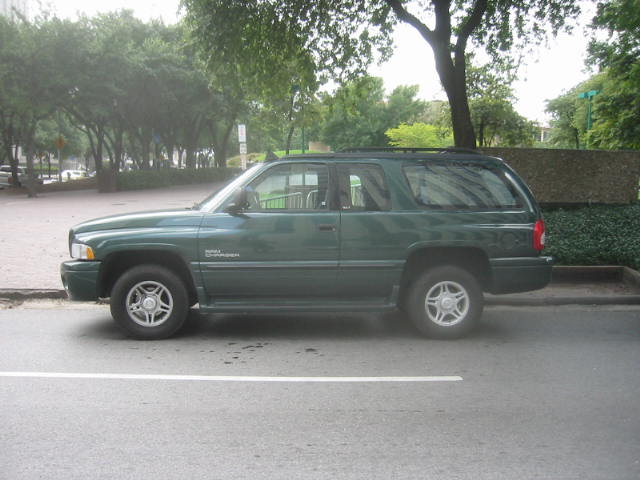 |
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 1999–2001 |
| Assembly | Saltillo, Coahuila, Mexico |
| Body and chassis | |
| Related | Dodge Ram |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 360 cu in (5.9 L) V8 318 cu in (5.2 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 4-speed automatic 4-speed manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 113.7 in (2,888 mm) |
| Length | 198 in (5,029 mm) |
| Curb weight | 5,300 lb (2,404.0 kg) |
In 1999, a new Ramcharger was produced in Mexico based on the second generation Ram pickup and using parts from the Dodge Ram pickups and other Chrysler vehicles. Sold only in Mexico, where the previous generation Ramcharger had been quite successful, it was not offered in the U.S. Because of this and other issues, this generation never enjoyed the sales of the previous generations of Ramchargers. Powered by the 5.9 and 5.2 Liter (360 CID and 318 CID) Magnum V8 and offered only in 2WD versions, it was discontinued around 2002. One of the most interesting features of this generation was a small folding seat in the cargo area, facing sideways, not a full-sized seat, making it uncomfortable for long trips. The rear hatch door was borrowed from 1996–2000 model Dodge Caravan. The Mexican-market Ramcharger was probably not marketed in the U.S.because the SUV market was favoring 4 or 5-door SUVs as opposed to 2-doors. Also, DaimlerChrysler already had two successful mid-sized SUVs (Jeep Grand Cherokee and Dodge Durango). Two-door SUV sales had been declining, to which GM ended production of its 2-door Tahoe and Yukon, and Ford replaced the long-running 2-door only Ford Bronco around the same time with the 4-door only Ford Expedition.
- Rampage (1982–1984)
Dodge Rampage
| Dodge Rampage | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Plymouth Scamp |
| Production | 1982–1984 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Coupe Utility |
| Body style | two-door truck |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | L-body |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.2 L K I4 |
The Dodge Rampage was a subcompact, unibody[1] coupe utility based on Chrysler‘s L platform and manufactured from 1982–1984. First released as a 1982 model, the Rampage was later joined by its rebadgedvariant, the Plymouth Scamp.
The Rampage borrows the car’s unibody construction and the front fascia from the sporty 024/Charger variant.
It was available with a Chrysler built and designed 2.2 L carbureted straight-4 engine with 96 hp (72 kW) and a curb weight of around 2,400 lb (1,100 kg). In the first year, it had leisurely performance due to the four-speed manual transmission along with a three-speed automatic transmission.
Performance was improved with the introduction of a five-speed manual transmission in 1983. The truck had a load capacity of 1,145 lb (519 kg), for a true “half ton” rating. This compared favorably to General Motors‘ Chevrolet El Camino‘s rating of 1250 lbs. The Volkswagen Rabbit Sportruck and Subaru BRAT were the Rampage’s only real competition in the United States market.
The Dodge Rampage was based on the popular Dodge Omni and Plymouth Horizon. Their fuel economy (21 MPG city/29 MPG highway, according to the EPA) and price were good for the time.[citation needed] The Rampage’s front-wheel drive configuration was a source of either love or hate depending on one’s preferences. A front-wheel drive layout is not usually used for trucks in North America; however, it gave the Rampage great road-holding and traction when unladen without the “fish-tailing” that comes with most rear-wheel-drive pickups. In short, the Rampage drove less like a truck and more like a compact car. A re-badged version,the Plymouth Scamp, was only sold in 1983. The Rampage lasted three years before being dropped from production after the 1984 model year. There are many myths about the existence of a “Shelby Rampage”, but the there is no official record of the existence of such a vehicle.
While a radical and unique design, the Dodge Rampage (17,636 sold in 1982, 8,033 in 1983, 11,732 in 1984, its final season) didn’t take off in the market as had been expected. Its Plymouth Scamp clone would only last for one year—1983. Sales totals for the Scamp were 2184 “base” models and 1,380 in GT trim, almost all of which were taken from its Dodge twin. The market for “car-trucks” was fast drying up in the mid-1980s as one after another was dropped from automakers’ North American product lines. Even the El Camino was not immune and it was also withdrawn from production before the decade was through.
- Royal (1954–1959)
1955 Dodge
| 1956 Dodge | |
|---|---|

1956 Dodge Custom Royal Lancer
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Dodge Coronet Dodge Suburban Dodge Royal Dodge Sierra Dodge Royal Lancer Dodge Custom Royal Dodge Custom Royal Lancer |
| Production | 1955–1956 |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 2-door coupe 4-door sedan 2-door hardtop coupe 2-door wagon 4-door wagon 2-door convertible |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 230 in³ (3.8 L) Getaway I6 270 in³ (4.4 L) Red Ram V8 325 cu in (5.3 L) V8 350 cu in (5.7 L) V8 361 cu in (5.9 L) V8 |
| Transmission | 2-speed automatic 3-speed manual 3-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 120 in (3048 mm) |
| Length | 212.1 in (5387 mm) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | 1957 Dodge |
The 1955 Dodge lineup, consisting of the entry-level Coronet, Royal, and ornate Custom Royal, was a major departure for the company. Driven almost out of business in 1953 and 1954, the Chrysler Corporation was revived with a $250 million loan from Prudential and new models designed by the legendary Virgil Exner. The Dodge lineup was positioned as the mainstream line in Chrysler’s hierarchy, between Plymouth and DeSoto.
Overview[edit]
The 1955 Dodge was all-new with a longer 120 in (3048 mm) wheelbase and 212.1 in (5387 mm) overall length than the 1954 cars. They shared their basic mechanicals with the De Soto, but featured special styling. These cars lasted through the 1955 and 1956 model years before being replaced by the all-new 1957 design.
Coronet
The Coronet (and Suburban station wagon) was the base model. This was the only line to feature the 230 in³ (3.8 L) Getaway I6 as well as the 270 in³ (4.4 L) Red Ram V8. Coronets were available in all body styles except the convertible. Sedans feature “Coronet” badges on the fenders, while the station wagons are called “Suburban”. Although the hardtop coupe was officially named “Lancer”, it wore only “Coronet” badges.Turn signals were standard on the Royal and Custom Royal models but optional on the base Coronet.
Royal
The Royal (and Sierra wagon) were the next step up. Featuring only the V8 engine, the Royal also lacked the 2-door sedan and wagon models available in the Coronet line. Early hardtop coupes lack the “Lancer” script, although they were officially Lancers, but later models wore “Royal Lancer” badges.
Custom Royal
The flagship model was the Custom Royal. All hardtop coupe and Custom Royal-only convertible models were called “Custom Royal Lancer”, and the “Custom Royal” sedan gained the Lancer badge soon after its introduction as well. The Custom line featured unique chrome tailfins (although early model year cars went without this trim), special tail light surrounds, and an upscale interior. Backup lights were standard on the Custom line but optional on all others. The Custom Royal also featured the hemi 270CID Super Red Ram engine.
La Femme
- See also Dodge La Femme
The La Femme was a special package oriented towards women, who made up an increasing share of Dodge buyers. It came in Heather Rose and Sapphire White colors and included a cape, boots, umbrella, and shoulder bag that matched the floral tapestry-like fabrics. Changes to the car include built-in compartments in the seatbacks to hold these accessories.
D-500
The 1956 D-500 was a high-performance model derived from the standard 1956 Dodge but differing in many ways. It included a heavy duty suspension and other chassis upgrades from the New Yorker and Imperial lines, upgraded brakes, and a high-performance 315 in³ (5.2 L) Hemi-head V8. A four-barrel Carter carburetor pushed output to 260 hp (194 kW) and 330 lb·ft (447 N·m). The 3-speed manual transmission was standard, with the PowerFlite 2-speed automatic as an option. A rare NASCAR-specific option was the D-500-1(Dash-1), which upped power to 285 hp (213 kW). The D-500 originally used only the Coronet 2-door sedan and Royal Lancer hardtop and convertible bodies.
1957
For the 1957 model year, Chrysler embarked on a second total linewide redesign. Virgil Exner’s “Forward Design” brought about cars that were bigger and more sleek than anything before, and instantly put a company that had traditionally regarded styling as unimportant on the forefront of automotive design. Unfortunately, two total redesigns in as many years resulted in severe build quality and rust problems, so that many 1957 Chryslers, Dodges, and Plymouths were off the road within three years of their purchase.
1958
While many of the quality issues were resolved for the 1958 model year, which brought about some minor styling tweaks, a recession struck that was particularly damaging to sales of mid-range cars. Dodge production had exceeded 337,000 cars for 1957 but the 1958 total fell by over half to less than 140,000, although some of this loss was due to negative publicity from the cars’ poor quality control.
1959
1959 Dodges were facelifted to gain a heavy, drooping look with hooded headlamps. Swivel-out seats became an option. Production for the model year totaled 156,395 cars, a modest increase over 1958. The highlight of the lineup was the performance-oriented D-500 package.
- Shadow (1987–1994)
Dodge Shadow
| Dodge Shadow | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called |
|
| Production | 1986–1994 |
| Model years | 1987-1994 |
| Assembly |
|
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Compact |
| Body style |
|
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler P platform |
| Related | Shelby CSX |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine |
|
| Transmission | |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase |
|
| Length |
|
| Width | 67.3 in (1,709 mm) |
| Height |
|
| Curb weight |
|
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | |
| Successor | Dodge / Plymouth Neon |
The Dodge Shadow and Plymouth Sundance are compact 3-door and 5-door hatchbacks that were introduced for the 1987 model year. For 1991, a 2-door convertible variant was added to the Shadow lineup; but not the Sundance lineup. The 3-door hatchback model replaced the Dodge Charger (L-body) model, while the 5-door hatchback model replaced the Dodge Omni model; of their respective marque. With the 1987 acquisition of American Motors by Chrysler from Renault, the Shadow/Sundance also replaced the American Motors-built Renault Alliance sedan and convertible marking the official withdraw of Renault from the United States and Canadian markets.
The first vehicle rolled out of Sterling Heights Assembly on August 25, 1986. In late 1988, production of the Mexican market version called the Chrysler Shadow began at Toluca Car Assembly. The Shadow/Sundance was also sold in Europe from 1988 to 1991 as the Chrysler ES. Production ended on March 9, 1994, with the Shadow/Sundance being replaced by the Chrysler Neon.
Design
The Shadow/Sundance employed a variant of the K-car platform, the P-body, which was based on a combination of the Dodge Daytona‘s suspension (alongside some of its interior styling cues) with a shortened version of the Dodge Lancer‘s body. While they appeared to have a trunk, it was actually a hatchback. Chrysler considered this a special feature and advertising literature referred to it as “hidden hatchback versatility”. The relatively large storage capacity of these vehicles was a major selling point for the company. The Peugeot 309 which had been developed to replace the European Chrysler Horizon used a similar layout.
Safety
A motorized passenger’s side seat belt was added to US-market Shadows/Sundances in 1994, to comply with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208’s requirement for passive restraints. These motorized seat belts do not comply with Canada’s safety standards; Canadian-market Shadows/Sundances continued to use a manual passenger seatbelt, and 1994 Sundances/Shadows cannot legally be imported across the US-Canada border in either direction.
At the time, the Shadow/Sundance was the lowest-priced car on the market with a standard driver’s side airbag, which had been made standard on all US-market domestic Chrysler Corporation cars in 1990. Giving them a remarkable crash test rating for a car its size at the time.
| Year | Frontal Driver | Frontal Passenger |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | ||
| 1992 | ||
| 1993 |
Engines
The Shadow/Sundance was offered with variety of four cylinder engines, all either of 2.2 or 2.5 L, some were turbocharged. Naturally aspirated versions were fuel injected, except those sold in Mexico. The engines were tuned for torque rather than horsepower, resulting in horsepower and torque numbers that appear to be reversed from competitors such as the Honda Civic. A Mitsubishi-built 3.0 L V6 engine was added later, replacing the turbocharged engines. All engines were available with a five-speed manual transmission, while a 3 speed automatic was optional on the four cylinder equipped cars and a 4-speed automatic transmission was optional on the V6 powered cars.
| Years | Engine | Power | Torque | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1987-1994 | 2.2 L K I4 | 93 hp (69 kW) | 122 pound-feet (165 N·m) | |
| 1987-1988 | 2.2 L Turbo I I4 | 146 hp (109 kW) | 170 pound-feet (230 N·m) | |
| 1988-1994 | 2.5 L K I4 | 100 hp (75 kW) | 135 pound-feet (183 N·m) | |
| 1989-1992 | 2.5 L Turbo I I4 | 150 hp (110 kW) | 190 pound-feet (260 N·m) | Shadow |
| 1989-1991 | Sundance | |||
| 1990 | 2.2 L Turbo IV I4 | 175 hp (130 kW) | 205 pound-feet (278 N·m) | Shadow |
| 1992-1994 | 3.0 L 6G72 V6 | 142 hp (106 kW) | 171 pound-feet (232 N·m) |
Year to year changes
- 1989, the Shadow/Sundance received a facelift, with the sealed-beam headlamps discarded in favor of more aerodynamic composite units. All-new grilles and tail lights were among the changes as well.
- 1990, the manual transmission was modified to make shifting into reverse easier by moving from the “left of first” position to the ” below fifth gear” position.
- 1991, a convertible version of the Shadow debuted, the same year the coupe and sedan models’ “base” submodel was split into the entry-level “America” or S (S was used on Canadian market versions) version and mid-level Highline submodels.
- 1992, a Mitsubishi-built 3.0 L V6 was added to the lineup, replacing the turbocharged engines.
- 1993, a low pressure Bendix-4 ABS was available.
Options
Features varied with years, but some features included: power windows, power adjustable mirrors, power door locks, power adjustable driver seat, cruise control, tilt steering wheel, variable intermittent delay windshield wipers, overhead console with map lights and compass/temperature display, upgraded “highline” instrument cluster with tachometer, “light package” that added lighting in the trunk, glove box, under-hood mounted light and rear door dome light switches (4 door models), remote trunk release, rear window defroster, Fog lights, mag wheels, Four wheel disc brakes, Infinity sound system, a cassette player, a sunroof, anti-lock brake systems and on turbocharger equipped cars, there was also a vacuum/boost gauge and a message center that monitored four vehicle functions, door ajar, washer fluid level, etc..
Trim levels
Hatchback:
- Base 1987-1990, 1993-1994
- America/S 1991-1992
- Highline 1991-1992
- ES 1987-1994 (Shadow)
- RS 1988-1991 (Sundance)
- Duster 1992-1994 (Sundance)
Convertible:
- ES 1991-1993
- Highline 1991-1993
Plymouth Sundance
For the Sundance’s first year, it was available in a single base model. For 1988, a higher-end RS model was available. The RS model, which stood for Rally Sport, came with standard features that included two-tone paint, fog lights, and a leather-wrapped steering wheel. It was also available with a turbocharged 2.2L I4 engine, and other amenities like an Infinity sound system, tinted window glass, and dual power mirrors. For 1991, the base split into two distinct models: entry-level America and mid-level Highline, in addition to the high-end RS. The stripped-down America, had previously been offered for the Plymouth Horizon‘s final year in 1990.
For 1992, the RS model was dropped, in favor of the revival of the Duster name for a performance version of the Sundance. The Duster featured a 3.0 L V6, special alloy wheels, “Duster” graphics, a body-colored grille & trim, as well as other equipment. Although the Sundance was criticized by some as being a poor choice to bear the “Duster” name, the car offered very good performance and decent handling at a low cost (only about $2,000 more than a base Sundance), which was said to be part of the reason why Chrysler used the “Duster” name, as those were the qualities the original car offered.
For the 1993 model year the America model was replaced by a better-equipped base model, the Highline would also be dropped for 1993.
European market
Between April 1988 and mid-1991, Chrysler offered the Dodge Shadow in numerous European markets. Called Chrysler ES, it was based on the Dodge Shadow ES and was virtually the same car, just without any “Shadow”-badges. Offered only as a 3-door hatchback, the standard engine was the fuel injected 2.2 L, with an optional turbocharger. For 1989, the 2.2 L was replaced by the more modern 2.5 L unit. Engines were linked to a standard five-speed manual transmission, with a three-speed automatic available as an extra-cost option. As European sales figures turned out to be very poor, sales of the Chrysler ES ended in mid-1991, leaving the segment without any direct successor until the introduction of the Chrysler Neon in 1995.
Shelby CSX
Carroll Shelby Enterprises modified Shadows into several performance-oriented vehicles such as the Shelby CSX, which was equipped with a turbocharged 2.2 L engine producing 174 hp (130 kW). Because of the car’s light weight and good engine in an era of government emissions choked engines, it was capable of acceleration equal or greater than that of many contemporary muscle and sports cars of the time. A version without the intercooler, rated at 150 hp (112 kW), was sold to Thrifty as the CSX-T.
Dodge Spirit
| Dodge Spirit | |
|---|---|

1991 Dodge Spirit R/T
|
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Also called | Plymouth Acclaim Chrysler Spirit Chrysler Saratoga |
| Production | 1989–1995 |
| Model years | 1989–1995 |
| Assembly | Newark Assembly, Delaware, U.S. Toluca Car Assembly, Toluca,Mexico |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | AA-body |
| Related | Chrysler LeBaron Chrysler Saratoga Plymouth Acclaim |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.2 L Turbo III I4 2.5 L K I4 2.5 L Turbo I4 3.0 L Mitsubishi 6G72 V6 |
| Transmission | 5-speed A523 manual 5-speed A568 manual 3-speed A413 automatic 3-speed A670 automatic 4-speed A604 automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 1989–1990: 103.3 in (2,624 mm) 1991–95: 103.5 in (2,629 mm) |
| Length | 181.2 in (4,602 mm) |
| Width | 1991–95: 68.1 in (1,730 mm) 1989–1990: 67.3 in (1,709 mm) |
| Height | 53.5 in (1,359 mm) |
| Curb weight | 2,901 lb (1,316 kg) |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge 600 Dodge Aries Dodge Lancer |
| Successor | Dodge Stratus |
The Dodge Spirit is a mid-size 5- or 6-passenger sedan that was introduced in January 1989 as a replacement for the similarly sized Dodge 600. The Spirit was Dodge’s version of the Chrysler AA platform, a stretched variation of the Chrysler K platform. It was assembled at Newark Assembly in Newark, Delaware as well as Toluca Car Assembly in Toluca, Mexico, and shared its basic design with the 1990 to 1994 Chrysler LeBaron sedan, the 1989 to 1995 Plymouth Acclaim, and the export-only 1989 to 1995 Chrysler Saratoga.
The Spirit has also been described as a replacement for the smaller Aries and the hatchback Lancer, though the Shadow launched in 1987 is closer than the Spirit in most dimensions to the Aries and Lancer. A total of 60,000 Dodge Spirits were sold in its first year, enough that Aries production was stopped mid-season. Spirit production ended on December 9, 1994, along with the Plymouth Acclaim and it was marketed through 1995. The “cab-forward” Stratus was introduced as a replacement.
Design
The Spirit could seat six passengers with an optional front split-bench seat. It had a large trunk, a solid-beam rear axle, and a MacPherson strut front suspension. The Spirit differed from the other A-bodies primarily in the grille and rear lamp styling, and in the availability of a sportier, higher-performing R/T version.
The Spirit is dimensionally comparable to its contemporaneous Ford Tempo, and was also compared with the Ford Taurus, Honda Accord, and Toyota Camry by Consumer Reports. The Spirit sold well; with higher consumer acceptance than the Stratus that replaced it.
Changes through the years
- 1991 – Antilock four-wheel disk brake system was added as a new option.
- 1992 – A 3-speed automatic transmission became available with the V6 engine.
- 1993 – A facelift included a body-color grille with the Dodge crossbars theme and new full-width taillamps that despite their amber lower sections, did not include amber rear turn signals. Only two trim levels went on sale: Highline and ES. The Chrysler corporate pentastar emblem was replaced with the brand’s new RAM emblem. Stainless steel exhaust system and tinted glass became standard on all Spirits.
- 1994 – A motorized passenger’s side seat belt was added to U.S.-market Spirits to comply with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208‘s requirement for passive restraints. These motorized belts do not comply with Canada‘s safety standards; Canadian-market Spirits continued to use a manual passenger seatbelt, and 1994–1995 Spirits therefore cannot legally be permanently imported across the US/Canada border in either direction.
- 1995 – The 2.5 L engine received a slightly revised cylinder head, and both the 4-speed A604 automatic transmission and anti-lock brakes were dropped from the option list. Otherwise, the Spirit remained mostly unchanged, much as it had throughout its six-year run.
Trims
- 1989–95: Base
- 1989–91: LE
- 1989–93: ES
- 1991–92: R/T
The Spirit ES and R/T featured Eurocast (also called Snowflake) alloy wheels through 1991. For 1992, the Turbo Blade wheel was introduced. Some of the alloy wheels were color-keyed to the vehicle body:
- White body with white painted wheels (ES, R/T)
- Black, silver, or dark red body with clear-coated wheels (ES only)
- Bright Red body with bright red painted wheel inserts (R/T only, 1991)
Starting in 1993, the Spirit was offered with a Gold package similar to that offered on the 1993-94 Plymouth Acclaim and Dodge Caravan/Plymouth Voyager minivans. This included goldtone-trimmed alloy wheels and gold pinstripes. The Gold package was available with both 4- and 6-cylinder models, with certain body colors.
Engines
The base engine for Spirit and Spirit LE models was a 2.5 L (150 cu in) TBI 4-cylinder engine producing 100 hp (75 kW; 101 PS). Optional on all models except the Spirit ES was a 141 hp (105 kW; 143 PS), 3.0 L (180 cu in) L V6 made by Mitsubishi. Also available in 1989 through 1992—and standard equipment on the Spirit ES—was a 150 hp (112 kW; 152 PS) turbocharged version of the 2.5 L engine. In 1993, 1994, and 1995, a flexible-fuel Spirit was offered, powered by a 107 hp (80 kW; 108 PS) multipoint fuel injected version of the 2.5 L engine specially modified to run on fuel containing up to 85% methanol. The R/T version came with a powerful 2.2 L (135 cu in)DOHC turbo III with cylinder head engineered and made by Lotus. This engine was rated at 224 hp (167 kW; 227 PS) and 217 lb·ft (294 N·m).
Transmissions
Several five-speed manual transmissions were available with the naturally aspirated and turbocharged 4-cylinder engines, but relatively few Spirits were equipped with manual transmissions. All the Spirit R/Ts came with the A-568 heavy-duty 5-speed manual transmission. From 1989 to 1991, all V6 Spirits came with the electronic four-speed A604 overdrive automatic, which became optional equipment in 1992 and remained optional until 1995. The three-speed Torqueflite automatic was the most popular installation on 4-cylinder Spirits, and was also standard equipment with the V6 engine from 1992 through 1995. A 5-speed manual was offered with the V6 engine in the smaller Shadow, but this combination was not available in the Spirit.
R/T

In 1991, Chrysler introduced the Spirit R/T, featuring a version of the 2.2 L engine with a 16-valve DOHC head designed by Lotus, who won a design competition against Maserati and Hans Hermann. Fed by a Garrettintercooled turbocharger, the Turbo III engine produced 224 hp (167 kW; 227 PS) and 217 lb·ft (294 N·m). The R/T also featured unique interior and exterior trims. The only transmission was a heavy-duty A568 5-speed manual transmission built by Chrysler’s New Process Gear division, with a gearset supplied by Getrag. Heavy-duty vented four wheel disc brakes were standard equipment, with optional anti-lock brakes. Color-keyed 15-inch alloy wheels were standard, with P205/60R15 tires.
At the time, the R/T was advertised as “the fastest sedan made in America”, and one of the quickest performance sedans under $40,000, with Chrysler placing its performance above the BMW M5. It could reach 60 mph (97 km/h) in 5.8 seconds, according to Car and Driver, making it one of the quickest front wheel drive cars ever offered in the American market. It was chosen as Motor Trend magazine’s “Domestic Sport Sedan of the Year”, beating the Ford Taurus SHO for 1991 and 1992.
All R/Ts were built in Mexico. A total of 1,208 were sold in the U.S. in 1991 — 774 in red and 434 in white. An additional 191 were sold in the U.S. in 1992 — 92 red, 68 white, and 31 silver. The only discernible changes for 1992 were a lower first gear ratio for reduced turbo lag, woodgrain dashboard trim as used on the Chrysler LeBaron sedan, blacked out upper and lower grille inserts, clear rather than amber lenses for the front parking and turn signal lights, and a speedometer calibrated to 150 mph (240 km/h) rather than 120 mph (190 km/h).
Mexican and South American markets


Spirits were marketed in Mexico. They were badged as Chryslers rather than Dodges, since the Dodge brand at the time was used only on trucks. The Spirit was introduced in the Mexican market for 1990, one year after its début in the U.S. and Canada. The 1990-1991 Mexican versions were equipped with the U.S. market Plymouth Acclaim tail lights. The initial 1990-model Spirits used a version of the 2.5 L engine operating on leaded gasoline, equipped with a carburetor, a tubular exhaust header, and electronic control of ignition timing. This induction and ignition system used technology and components very similar to those employed in Chrysler’s U.S.-market Lean Burn emission control systems of the late-1970s.
For the 1991 model year, Mexico enacted new-vehicle emission regulations similar to those in the U.S. and Canada. The carbureted leaded-fuel engine was too dirty to comply with the new regulations, so a fully integrated engine management system with fuel injection was added to the Spirit. This was not the TBI system used in the U.S., Canada, and Europe. Rather, the Mexican-market Spirits came with a more advanced MPFI setup. The MPFI 2.5 improved performance and driveability, as well as achieved cleaner emissions than its TBI counterpart, but was not used in the U.S., Canadian, or rest-of-world export markets except on turbocharged and FFV models. The Chrysler Spirit with MPFI 2.5 L engine was sold in Mexico from 1991 through 1995, and was exported to Argentina and Brazil from 1993 through 1995. It was employed by the Argentine police in Buenos Aires.
Chrysler de Mexico also sold two versions of the Spirit R/T. The base R/T, sold from 1991 through 1995, used a Mexico-only 168 hp (125 kW; 170 PS) intercooled Turbo II version of the 8-valve SOHC 2.5 L engine and the 3-speed A413 automatic transmission. These R/Ts were used by Mexican police departments.
The top-line R/T. called “R/T DOHC”, available from 1992 through 1993, came with the same 2.2 L 16-valve DOHC engine that was used in the American-market in the 1991 to 1992 R/T with a 5-speed manual transmission. More options and higher equipment levels were available in Mexico, including leather upholstery, sunroof, and 16-inch alloy wheels, none of which was offered on the R/T in America. In addition, Mexican-market R/Ts could be ordered in a variety of different colors, not just the red, white, and silver offered in the U.S. All Mexican-market Spirit R/Ts were badged as Chryslers. A variant of the R/T family, the Chrysler Phantom R/T, was a special-order Mexico-only premium version of the LeBaron coupe equipped with the 2.2 L 16-valve DOHC engine and the Getrag 5-speed manual transmission.
- Sprinter (2004–2009)
Dodge-Sprinter
- SRT-4 (2003–2005)
Dodge Neon SRT-4
| Dodge Neon SRT-4 | |
|---|---|
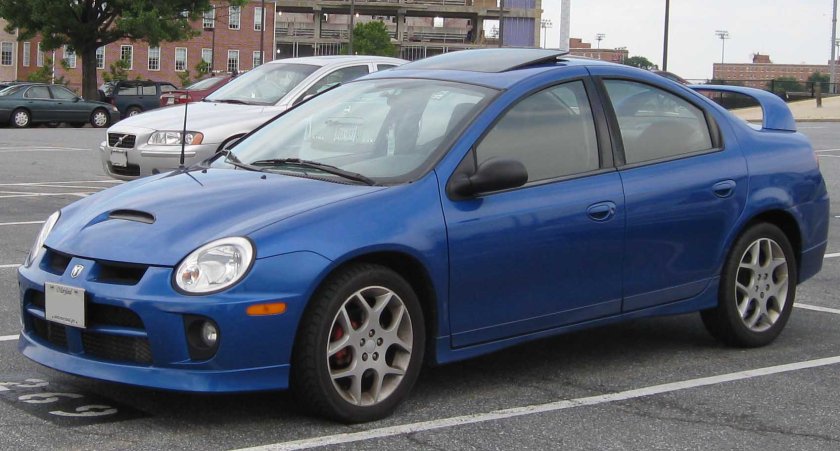 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Dodge |
| Production | 2003–2005 |
| Assembly | Belvidere, Illinois, United States |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Sport Compact |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Platform | Chrysler PL platform |
| Related | Dodge Neon |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.4 L turbocharged DOHC I4 |
| Transmission | 5-speed NVG T-850 manual |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 105.0 in (2,670 mm) |
| Length | 174.4 in (4,430 mm) |
| Width | 67.4 in (1,710 mm) |
| Height | 56.0 in (1,420 mm) |
| Curb weight | 2,900 lb (1,300 kg) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Dodge Caliber SRT-4 |
The Dodge Neon SRT-4 is a sport compact car manufactured by Dodge from 2003 to 2005. A turbocharged variant of the Neon, the car was developed by DaimlerChrysler‘s in house PVO (Performance Vehicle Operations) tuner group. PVO was officially renamed SRT (Street and Racing Technology) in 2004. The “4” in the SRT-4’s name denotes the number of cylinders of the engine. ACR (American Club Racing) and Commemorative Edition models were later introduced as well.
History
In 1998, Tom Gale, (then Executive Vice President of Chrysler Product Development and Design), attended the 1998 Specialty Equipment Market Association (SEMA) Show in Las Vegas. Gale noted a list of performance features he saw on the sport compact cars at the show, and wanted to integrate those features into Chrysler’s compact production car, the Dodge Neon. Gale was the design chief of the original Dodge Viper concept vehicle, and recognized an opportunity to build a sport compact that would appeal to the younger auto generation who grew up on tuner cars, who may prefer a new car with the same performance appeal right off the showroom floor.
A group of young Dodge and Chrysler talent was assembled to put together a vehicle to meet Gale’s request, with all of the team members sharing first-hand knowledge and familiarity of the existing Dodge Neon. They created a concept car, the 2000 Neon SRT, in just 4 months, with a 2.0 L 16-valve four-cylinder topped with a 45-cubic-inch Eaton supercharger, which produced 208 hp (155 kW) and 180 lb·ft (240 N·m) of torque at the flywheel on 11 psi (0.76 bar) of boost. (Sport Compact Car magazine tested the car in the Feb. 2001 issue and dynoed 179 hp (133 kW) and 149 lb·ft (202 N·m) torque at the wheels.)
The group put more than 1000 miles on the test track with the vehicle in under two weeks. In November of 1999, the car was shown at the SEMA show with a glowing response. The vehicle was then shown at the Los Angeles Auto Show in January 2000, center stage on a turntable. The team continued to work on the car, to try to bring it to the level of production vehicle, creating a second car using more production-oriented parts in an effort to lower the costs necessary to justify production. They even parked the second car in Gale’s parking spot in order to get it noticed. Regardless, in fall of 2000, the executive committee rejected the production car proposal. The team put together a list of reasons why the car was not approved, and worked through the list item by item to find solutions to every issue presented. After three more versions of the car, the company’s Specialty Vehicle Engineering (SVE) team took over the project. The executive committee once again considered the vehicle in the spring of 2001, and this time gave the go ahead for the project.
During that time, SVE became known as Performance Vehicle Operations (PVO). The PVO group was responsible for developing the concept car into a production car. A turbocharged 2.4 liter inline-4 gasoline engine (A853 engine) was used. This engine was nearly identical to the 2003 Chrysler PT Cruiser (A855 engine), except the SRT-4 did not have the unique intake manifold required to fit the engine into the PT Cruiser engine bay. The car was then given a New Venture Gear T-850 five-speed manual transmission (based on the unit from the European turbodiesel minivans), equal-length half shafts, and a high capacity Sachs performance clutch. The suspension had stiffer springs, SRT-tuned Tokico struts (with travel reduced to provide clearance for the larger wheels), and larger front and rear sway bars were added. A unique steering gear, PT Cruiser steering knuckles, and an updated K member were also incorporated. Front brakes used 11.0 in (280 mm) vented disc brakes with extra thick rotors to prevent warping, and 10.6 in (270 mm) non-vented disc brakes in the rear, with single piston calipers (57mm front, 36mm rear).
17 x 6 inch cast aluminum wheels were used, with an offset of 43mm, along with 205/50/17 Michelin Pilot Sport performance tires. The wheels were designed with a unique spoke pattern to allow for improved airflow to the brakes, and were similar to that of the TSW VX1 wheels used on the original 2000 Neon SRT. Unique side skirts, rear fascia, and a large rear wing (spoiler) were used to upgrade the exterior look of the vehicle. The cooling ducts (front nostrils) were added to the pre-production car in late 2002 on the front fascia to help reduce temperatures in the engine bay of the vehicle.
On the interior, the standard agate-colored front seats were modeled after the Dodge Viper SRT-10 seats, and featured enhanced lumbar and lateral side bolsters to stabilize occupants during performance driving. In 2004, base Neon side air-bag seats were added as an option. A faux carbon fiber steering wheel and shift boot were used, along with a satin silver “cue ball” type shift knob and silver aluminum floor pedals. Unique gauge designs in the SRT-4 (which were exclusive to the SRT lineup) featured special silver faces with satin silver ring accents, and the SRT-4 logo on the facing. The same satin metal trim was also featured on the instrument panel center stack, climate control knobs and on the door handles. A silver (white in early 2003 models) Auto-Meter brand turbo boost/vacuum gauge was set to the right of the instrument cluster. Like all other Neon models, the SRT-4 had power front windows, and manual rear windows, a costs saving feature. Overall, the vehicle’s entire powertrain (engine and transmission), suspension, braking system, exhaust, wheels, and tires were upgraded from that of the base model Neon, along with the interior upgrades. The production model was produced in Belvidere, Illinois, with 84% US content.
PVO would later become Street & Racing Technology (SRT), Chrysler’s high-performance automotive group, and in 2003, the Dodge Neon SRT-4 went on sale to the public. At the time, the car was the second fastest stock production vehicle in the Chrysler/Dodge lineup, second only to the Viper. The 2004 model was updated with more power and torque, and included a torque-sensing Quaife limited-slip differential, larger fuel injectors, new engine management software, BF Goodrich g-Force T/A KDW-2 three season ultra-high-performance tires, and paint/trim changes. Dodge removed the “Neon” designation from the vehicle in 2004, marketing the car simply as the “SRT-4”. In 2005, an American Club Racer (ACR) package and limited edition numbered Commemorative version of the SRT-4 were also offered.
Initially, Dodge expected to sell a conservative number of only 2,500 units per year. However, during the three year production run (2003 through 2005), more than 25,000 Neon SRT-4s were produced. With the demise of the PL platform after model year 2005, the SRT-4 ceased production. In 2008 Dodge introduced the Caliber SRT-4 as a replacement.
Performance
Dodge SRT-4 engine
| Power: | SAE 215 hp (160 kW) (2003 model) SAE 230 hp (170 kW) (2004–2005 models) In 2004, the SRT-4 received a power increase, with larger fuel injectors and a recalibrated engine computer.Manufacturer’s specification when the SRT-4 was released was 230 hp (170 kW). However, several independent tests have produced results indicating 230-238 whp and 250-262 lb-ft. This would indicate that the SRT-4 produces more power than the manufacturer claims. The flywheel power is estimated to be around 265-270 hp(194-198 kW) and around 285-300 lb-ft (386-406 N·m) |
|---|---|
| Torque: | 245 lb·ft (332 N·m) @ 3200-4200 rpm (2003 model) 250 lb·ft (339 N·m) @ 2400-4400 rpm (2004–2005 models) |
| 0-60 mph (97 km/h) time: | 5.6s (2003) 5.3s (2004, 2005) (Car and Driver) |
| Rev Limiter/Redline: | 6240 |
| 1⁄4 mile (400 m) time: | 14.1s (2003) 13.9s (2004, 2005) |
| 1⁄4 mile speed: | 102 mph (164 km/h) (2003) 103 mph (166 km/h) (2004, 2005) |
| Top speed: | Car and Driver magazine achieved a maximum speed of 153 mph (246 km/h). |
Engine details
The SRT-4 used the same basic engine block as the naturally aspired 2003+ 2.4L, and was different from the years previous used in the naturally aspirated Chrysler 2.4L mid-size cars such as the PT Cruiser and four-door Stratus. The SRT4 engine had many improvements, including: stronger crank case webbing, a thicker deck with 11 mm head bolts (vs 10 mm), an oil drain back for the turbo, a cast aluminum structural oil pan, a higher capacity oil pump, a crankshaft of higher hardness steel, improved machining of bearing journals, oil squirters (to cool underside of pistons), eutectic aluminum alloy pistons made specially by Mahle, and forged connecting rods with cracked caps and 9 mm bolts. The cylinder head was also different for turbo engines, from naturally aspirated. The turbo version (PT Cruiser GT Turbo and SRT-4) included: larger diameter valves and seats, exhaust valves made of Inconel, improved cooling and larger oil drain back passages, different camshafts. The PT Cruiser Turbo engine package differs from the SRT-4 because the intake manifold, turbocharger plumbing and intercooler are different. The SRT-4 intercooler was a front-mounted cast aluminum 8-row unit produced by Valeo, unique in its efficiency and computer designed end tanks for air flow.
The turbocharger was a reverse rotation Mitsubishi TD04LR-15Gk with a 6 cm2 (0.93 sq in) turbine inlet. Tight packaging forced some creative thinking on the turbocharger. The TD04 compressor has a compressor bypass valve built right into the compressor housing. The exhaust manifold and turbine housing were cast in one piece by Mitsubishi from high-nickel Ni-Resist steel. The one-piece design improved flow, reduced size and reduced thermal mass for quicker cat light-off. The turbine discharge was also part of the manifold/turbine housing casting, and it looped back around and hit the manifold again on its way to the catalytic converter. Where they met, there was a wastegate valve; keeping the wastegate valve away from the turbine housing improved flow where it mattered most. Maximum boost in stock form was around 14 psi (97 kPa). Piston velocities and valve-train components force a rev limit of 6240 rpm although MOPAR upped the ante with their Stage 2 and 3 kits which have a rev limit of 6500 rpm.
The exhaust system for the vehicle consists of 2.25-inch (57.15 mm) steel tubing, which is run first through the catalytic converter, then through two resonators. The exhaust then splits into two separate sections of piping, exiting through two 3.75 in (95 mm) stainless steel tips at the rear of the vehicle. The exhaust system is unique in that there is no muffler, instead relying on the turbocharger and resonators to reduce the exhaust volume. The end result is a very distinctive and audible exhaust note, specific only to the SRT-4.
| Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Block height: | 9.375 in (238.1 mm) | |
| Displacement: | 2,429 cc (148.2 cu in) | |
| Stroke: | 3.976 in (101.0 mm) | |
| Bore: | 3.445 in (87.5 mm) | |
| Rod length: | 5.944 in (151.0 mm) | |
| Main journal diameter: | 2.36 in (60 mm) | |
| Deck clearance: | 0.200 in (5.1 mm) | |
| Combustion chamber volume: | 50.0 cc (3.05 cu in) | |
| Head gasket thickness: | 0.040 in (1.0 mm) | |
| Compression ratio: | 8.1:1 | |
ACR model
This factory competition version included:
- Wider 16×7-inch (410×180 mm) BBS RX racing wheels with 40 mm (1.6 in) offset
- Wider 225/45/16 BFG KDW2 tires
- Lowered ride height (Front: 10 mm (0.39 in) from spring seat lowering, additional 22 mm (0.87 in) through smaller diameter tire; Rear: 23.5 mm (0.93 in) from spring seat lowering, additional 22 mm (0.87 in) through smaller diameter tire)
- 5 position adjustable performance Tokico Illumina dampers. Proportional compression and rebound damping adjustment is accomplished via multiple oil bleed orifices within the damper.
- Thicker rear stabilizer bar (19 mm)
- Stiffer bushings in the rear tension struts
- ACR embroidered, Viper-styled, racing seats with pass-throughs for a racing harness
- ACR decals on the bottoms of the front doors
- Full diameter P205/60R15 spare tire
- Vehicle Speed Sensor gear changed from 20 tooth to 21 tooth to correct speedometer for different stock tire heights.
- There were a total of 1,175 SRT-4 ACR’s produced for the public: 225 Flame Red (PR4), 211 Orange Blast (PVK), 306 Stone White (PW1), 433 Black (PX8).
2005 Commemorative Edition
In 2005, Dodge released an SRT-4 Commemorative Edition. This model (along with the Commemorative Edition versions of the Viper SRT-10 and Ram SRT-10) was created to celebrate the SRT vehicles.
This limited, numbered version included:
- “Electric Blue” painted “Viper” stripes over the “Stone White” colored body.
- Blue stitching on the floor mats, shift boots, seats, and steering wheel.
- Stainless steel “SRT-4” door sill plates.
- A total of 200 Commemorative Edition SRT-4’s were built.
- A “XXX/200” numbered plaque, inset just ahead of the cup holders.
- A Commemorative Edition booklet (same booklet included with the Commemorative Vipers and Ram SRT-10’s).
- No performance extras were added on the Commemorative Edition.
2003 SRT-4 Extreme LightWeight
In 2003, Dodge engineers built a special SRT-4 Extreme LightWeight for the 2003 SEMA show. It was designed to showcase the factory upgrade parts available for the SRT-4 from Mopar. The vehicle featured lightweight, carbon fiber body pieces (produced in-house), a polycarbonite rear window, and the front window glass removed for weight reduction. The interior was stripped completely, with only the stock dash remaining. A single Recaro racing seat, a harness, and a roll cage were installed for safety. The car featured the first stage 3R Mopar engine performance kit and stage 3R coilovers. Overall, the weight of the vehicle was reduced by 405 lbs, to 2,500 lb (1,100 kg) wet, and was dyno’d at 360 hp (270 kW) and 383 lb•ft (519 N•m) (at the wheels) by SportCompactCar magazine. On drag slicks, it ran an 11.83-second pass at 123 mph (198 km/h) in 70 °F (21 °C) weather. This one-off SRT-4 was used for media events and testing of the Mopar development parts, and was destroyed as an asset reduction move in 2009.
Awards
- Car and Driver magazine’s 2005 John Lingenfelter Memorial Trophy
- Was one of “Eight Great Rides” as decided by Sport Compact Car magazine (SCC) in 2003, 2004, and 2005 – all three years the SRT-4 was produced.
- Named the 2003 Car of the Year by SCC.
- Won numerous comparisons in several U.S. automotive magazines from 2003 to 2005, including:
- 1st place -, Car and Driver magazine, November 2005. The SRT-4 competed against 14 other performance vehicles, finishing 1st in the front-wheel-drive division.
- 1st place -, Serial Thrillers comparison test, Car and Driver magazine, May 2004.
- 1st place -, Automobile magazine, March 2004.
- 1st place -, Sport Sedans Comparison, Edmunds, August 2003
- 1st place -, Sport Compact Car Shootout, January 2003.
Racing
In 2003, Cory O’Brien and Erich Heuschele drove an SRT-4 to a 1st in class and 8th overall finish in the Tire Rack Cannonball One Lap of America.
In SCCA ProRally racing, the SRT-4 (and more recently the ACR version) has dominated the Group 5 (2WD) class since 2003. In just its first year competing, the Dodge ended the stranglehold that the FWD DSMs and Volkswagens had on the class. With three competing the following year, the SRT-4 won every 2004 series race and end-of-season award. The SRT-4 has won every Group 5 and 2-Wheel-Drive class championship in US ProRally and Sno Drift since 2003, and its unprecedented dominance in 2004 helped Dodge earn its first US ProRally Manufacturers Championship in 28 years.
In 2005, Jeff Lepper drove the SRT-4 to its first ever national road racing win in the NASA US Touring Car Championship at California Speedway in Fontana.
In 2005, Dale Seeley, Kolin Aspergren, and Jamin Cummings drove an SRT-4 to a 1st in class and 8th overall finish in the Tire Rack Cannonball One Lap of America.
In 2006, the Dodge SRT-4 officially became the world’s fastest production 4-cylinder car, averaging 221 mph (356 km/h) at the Bonneville Salt Flats in Utah in a car driven by Jorgen Moller. The vehicle was tuned by Dave Harris and Phil Hurst for Racedeck Racing.
Multiple SRT-4s were raced in the SCCA SPEED World Challenge – Touring Car Series, and in 2006 – their second year of competition – had become one of the more successful platforms in the series. Robb Holland, of 3R Racing, became the first Pro driver to put the SRT-4 on the podium with his 3rd place finish at Road America in August 2006. This was Dodge’s first podium and first manufacturer’s points in World Challenge Touring Car competition. Holland would finish the season with 3 top 10 finishes and two top 5 qualifying efforts in the SRT-4.
In 2007, Doug Wind, Devin Clancy, and Ken Brewer drove an SRT-4 to a 1st in class and 5th overall finish in the Tire Rack Cannonball One Lap of America.
In 2007, Curt Simmons won the U.S. Touring Car Championship in an SRT-4 and Dodge won the season manufacturers points championship by 29 points over Honda behind the strength of several SRT-4’s.
In 2007, Stan Wilson won the Speed World Challenge Touring Car Rookie Driver of the Year and the Sunoco Hard Charger of the Year awards driving the Sorted Performance Dodge SRT-4. This was Dodge’s first title in Speed World Challenge Touring Car.
In 2008, Curt Simmons attempts to defend his USTCC series championship, winning most recently June 29, 2008 at Infineon Raceway in Sonoma, CA.
- St. Regis (1979–1981)
Dodge St. Regis
| Dodge St. Regis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation |
| Production | 1979–1981 |
| Assembly | Detroit, Michigan, USA (Lynch Road Plant) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Full-size |
| Body style | 4-door sedan |
| Layout | FR layout |
| Platform | R-body |
| Related | Chrysler Newport Chrysler New Yorker Plymouth Gran Fury |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 225 in³ Slant 6 I6 318 in³ LA V8 360 in³ LA V8 |
| Transmission | 3-speed A727 automatic 3-speed A904 automatic |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Monaco |
The Dodge St. Regis is a full-size Dodge automobile built by Chrysler from 1979 to 1981.
Design
The St. Regis was based on Chrysler’s rear wheel drive R-body platform, itself based on a modified version of the circa 1971 B-body design that provided the foundation for such cars as the Dodge Charger and the Chrysler Cordoba. Available engines included the 225 in³ (3.7 L) straight-6, the 318 in³ (5.2 L), and the 360 in³ (5.9 L) V8s.
“St. Regis” was originally an uplevel trim package on the 1956 Chrysler New Yorker hardtop coupe, and again on the 1974–78 Chrysler New Yorker Brougham coupe.
Offered only as a four-door sedan, the St. Regis was differentiated from its sister models, the Plymouth Gran Fury, Chrysler Newport, and Chrysler New Yorker by retractable, transparent plastic headlight covers (introduced a year earlier on the 1978 Dodge Magnum).
Market timing
The new cars (like their 1974–78 predecessors) arrived at precisely the wrong time. A second gasoline crisis hit the U.S. in 1979, and despite the fact that the St. Regis was somewhat smaller than its predecessor, the Dodge Monaco, it was not much more fuel efficient. Also, under the sheet metal, the St. Regis was mainly the same old B-body that dated back to 1962, and could not compete with the completely new GM B-bodies and Ford’s Panther platform vehicles. At the same time, higher interest rates and Chrysler’s ongoing corporate and financial problems, all combined to keep sales low. The St. Regis, and the other R-body models, were dropped midway through the 1981 model year, leaving the Dodge Diplomat, (a mid-size car), to soldier on as the marque’s sole “full-sized” model, until the introduction of the Dodge Monaco in 1990.
Fleet use
After 1979, the bulk of St. Regis sales were for fleet use. The St. Regis, along with the Plymouth Gran Fury and even the Chrysler Newport, did sell very well as a police car during the early 1980s, although it is generally accepted that the cars were not as powerful or as fast as previous Chrysler Corporation police cars. Despite this, the 1979 St Regis, when equipped with the 360 cu in (E58 option) and 49-state police specification package, is considered one of the all-around, best performing and handling, police cars of the century. Most perceptions that the St. Regis was slower comes from police officers moving out of 440-powered cruisers. Using the same final drive ratio, the Michigan State Police tests found the 1979 St. Regis to be a superior performer to the 400 powered 1978 Monaco, in all areas except gas consumption, though performance definitely dropped as drive ratio and engine sizes went down.
| Performance comparison | 78 Fury | 78 Monaco | 79 St. Regis | 80 St. Regis | 81 St. Regis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engine (cid) | 440 | 400 | 360 | 360 | 318 |
| HP, SAE | 255 bhp | 190 bhp | 195 bhp | 185 bhp | 165 bhp |
| Axle ratio | 2.71:1 | 3.21:1 | 3.21:1 | 2.94:1 | 2.94:1 |
| Weight (lbs) | 4,413 | 4,369 | 4,530 | 4,100 | 4,086 |
| Wheelbase (in) | 117.4 | 117.4 | 118.5 | 118.5 | 118.5 |
| Road course lap time | 91.1 | 93.6 | 91.65 | 91.8 | 93.93 |
| 0–60 mph | NA | NA | 10.1 | 11.3 | 12.76 |
| 0–100 mph | 24.8 | 34.4 | 30.2 | 36.7 | 45.72 |
| Top Speed, mph | 133 | 117 | 122.9 | 122.7 | 114.7 |
| Braking, ft/sec2 | 23.3 | 22.6 | 21.4 | 23.5 | 23.67 |
| 1/4 mi. time | NA | NA | NA | 18.4 | 19.63 |
| 1/4 mi speed | NA | NA | NA | 77.5 | 74.50 |
| Fuel, EPA city | 10 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 15.5 |
Controversy
There was a controversy in 1980 with the police version of the St. Regis. The California Highway Patrol (CHP) used the St. Regis in 1979 with the 190 hp 360 cu in four-barrel V8 and it was deemed acceptable for patrol use. In 1980 all that was available in California was a 155 hp 318 cu in 4 bbl V8 with the California emissions package, mandated by the California Air Resources Board.
Officers began to complain about the underpowered engine and its inability to pace and intercept speeders. Many officers claimed that the car’s top speed was below 100 MPH with a lightbar and 65 MPH on a steep mountain grade. This issue was so severe that limited modifications were permitted to the vehicle, such as replacing the muffler with a straight pipe, removing the emission control flap, and advancing the timing. In addition, the cars were put on beats to reach the CHP’s 70,000-mile sell-off quota as quickly as possible; some were even sold outright simply to get rid of these cars, before the mileage limit was reached. Because of this problem, the CHP adopted the ‘Ford Mustang Severe Service Package’ in 1982 as a pursuit vehicle.
Television and collectors
The St. Regis also served as a workhorse on police-based television series in the 1980s, most prominently on Sledge Hammer! and T.J. Hooker.
Although the St. Regis does not hold much collector value today, fans of Chrysler products sometimes search junkyards for the cars’ disc brakes as an upgrade for earlier cars such as the Dodge Dart and Plymouth Barracuda. With the small number built, and the high percentage that were destroyed in film and TV work in the 1980s, very few St. Regis survive today.
- Stealth (1991–1996)
1991 Dodge Stealth Indy 500 Official Car
1991 Dodge Stealth RT
- Stratus (1995–2006)
Dodge Stratus
| Dodge Stratus | |
|---|---|
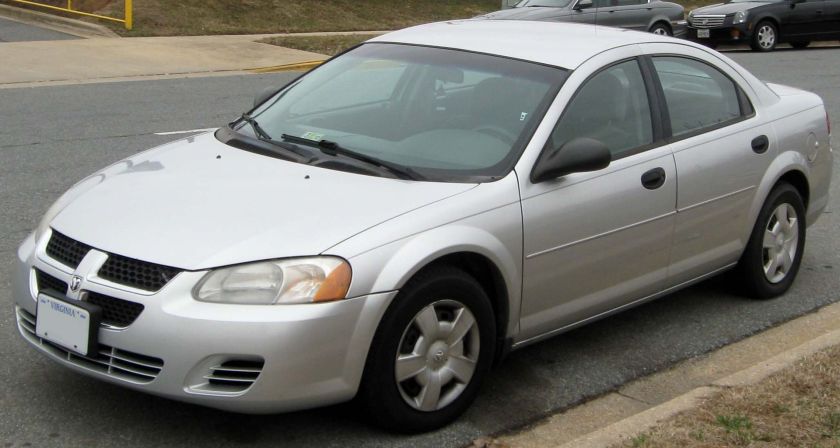 |
|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Chrysler Corporation DaimlerChrysler Mitsubishi Motors (coupes only) |
| Also called | Chrysler Stratus (Europe) |
| Production | 1995–2006 (sedan) 2001–2005 (coupe) 1995–1999 (Canada) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Mid-size |
| Layout | Transverse front-engine, front-wheel drive |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Dodge Spirit & Dodge Dynasty(sedan) Dodge Avenger (coupé) |
| Successor | Dodge Avenger (sedan) |
The Dodge Stratus is a mid-size car that was introduced in 1995, and was based on the 4-door sedan Chrysler JA platform. The Stratus, Plymouth Breeze, and Chrysler Cirrus were all on Car and Driver magazine’sTen Best list for 1996 and 1997. It received critical acclaim at launch, but ratings fell over time. An updated version of the Stratus was introduced for 2001, with the Cirrus being renamed as the Chrysler Sebring, and acoupé model was also added to the range. However, production ended at the Sterling Heights Assembly Plant in early 2006 which had built 1,308,123 Stratus and Sebrings since 2000.[1] The Dodge Avenger replaced the Stratus nameplate in early 2007 for the 2008 model year.
After the discontinuation of the Stratus sedan in 2006, the assembly line and tooling were sold to the Russian concern, GAZ, which manufactured 9,000 examples of a very slightly modified Stratus from 2008 through 2010 called the Volga Siber.
First generation (1995–2000)
The Dodge Stratus was the middle entry of the Chrysler JA platform (with the Cirrus being the higher-end model and the Breeze being the lower-end model). The three cars differed only in the front fascia, rear bumper, taillights, and wheels. The interiors also had little variation between the three models; being almost identical, save for the name on the steering wheel, and a few available options. The Stratus directly replaced the high-volumeSpirit (United States only)
Second generation (2000–2006)
| Second generation | |
|---|---|
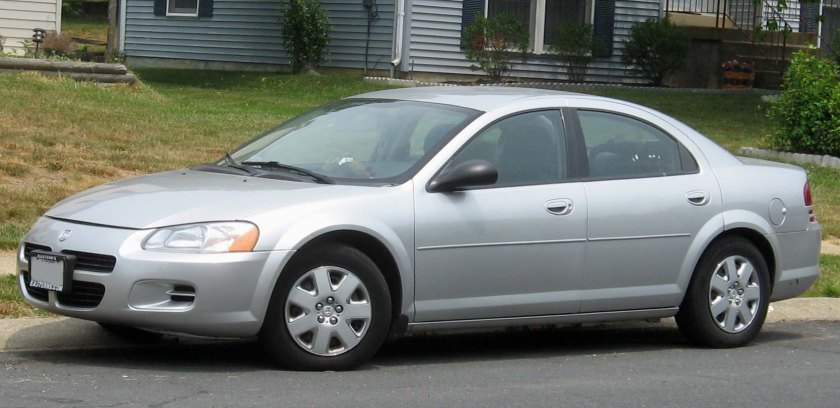

2001-2003 Dodge Stratus sedan
|
|
| Overview | |
| Production | 2000–2006 (Sedan) 2000–2005 (Coupé) |
| Assembly | United States: Sterling Heights, Michigan (Sterling Heights Assembly) (sedan) United States: Normal, Illinois(Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America) (Coupé) |
| Body and chassis | |
| Body style | 4-door sedan 2-door coupé |
| Platform | Sedan:Chrysler JR platform Coupé:Chrysler ST-22 platform |
| Related | Sedan: Chrysler Sebring sedan Volga Siber Coupé: Chrysler Sebring coupé Mitsubishi Eclipse |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 2.4 L EDZ I4 (gasoline) 2.4 L 4G64 I4 (gasoline) 2.4 L EDV/EDT I4 (t/c gasoline) 2.7 L EER V6 (gasoline) 3.0 L 6G72 V6 (gasoline) |
| Transmission | 5-speed manual 4-speed F4A42/F4A51 automatic 4-speed Ultradrive 41TE automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | Sedan: 108.0 in (2,743 mm) Coupé: 103.7 in (2,634 mm) |
| Length | Sedan: 191.2 in (4,856 mm) Coupé: 190.9 in (4,849 mm) |
| Width | 2003–06 Sedan: 70.6 in (1,793 mm) 2001–02 Sedan: 71.9 in (1,826 mm) Coupé: 70.3 in (1,786 mm) |
| Height | Sedan: 54.9 in (1,394 mm) 2003–06 R/T Sedan: 54.4 in (1,382 mm) 2003–05 Coupé: 53.9 in (1,369 mm) 2001–02 Coupé: 53.7 in (1,364 mm) |
In 2000, the Stratus became the last of the surviving Cloud Cars, with the Cirrus renamed as the Sebring, and the Breeze discontinued (along with the Plymouth brand). This generation of the Dodge Stratus was not sold in Canada, although 1999 was the last year for Dodge Stratus sales in Canada. 2002 models dropped the “DODGE” badges from the doors.
The Stratus and Sebring sedans for the second generation used a revised version of the Chrysler JA platform named JR. The coupe models with the same names were entirely different cars; they were actually based on the Mitsubishi Eclipse.
During this time, sales declined as its ratings from consumer and auto magazines fell below average among mid-size cars, while the sedan market had shifted and pushed the larger Intrepid and later Charger to record sales. 2004 brought styling revisions, which did not reverse this trend. The Stratus was discontinued in May 2006[1] (the Sebring name was continued).
In Mexico, the Stratus R/T came in a turbocharged version. The Stratus R/T’s turbocharged 2.4 L engine went through some improvements in 2001, when power was increased to 215 hp (160 kW). This improved engine would later be used in the U.S. in the Dodge SRT-4 and PT Cruiser GT. Stratus R/T engines built from March 2004 and later generated 225 hp (168 kW) at 5200 rpm and 235 lb·ft (319 N·m) of torque at 4200 rpm. Stratus R/T models with the turbocharged engine could be recognized by a rear badge saying “Turbo”.
Engines
Stratus coupe
For 2001, Dodge introduced the Stratus coupe, replacing the discontinued Avenger. This model along with the Chrysler Sebring coupe were built at the former Diamond Star Motors plant by Mitsubishi, using the ST-22 platform. Like its Chrysler counterpart the coupe models shared very little other than the name and a few exterior styling cues with sedan and convertible models. The Stratus coupe was restyled for the 2003 model year. The coupe was discontinued after 2005, one year before the sedan. The next midsize Dodge, the Avenger, did not include a coupe version.
Engines
- Town Panel and Town Wagon (1954–1966)
Dodge Town Panel and Town Wagon
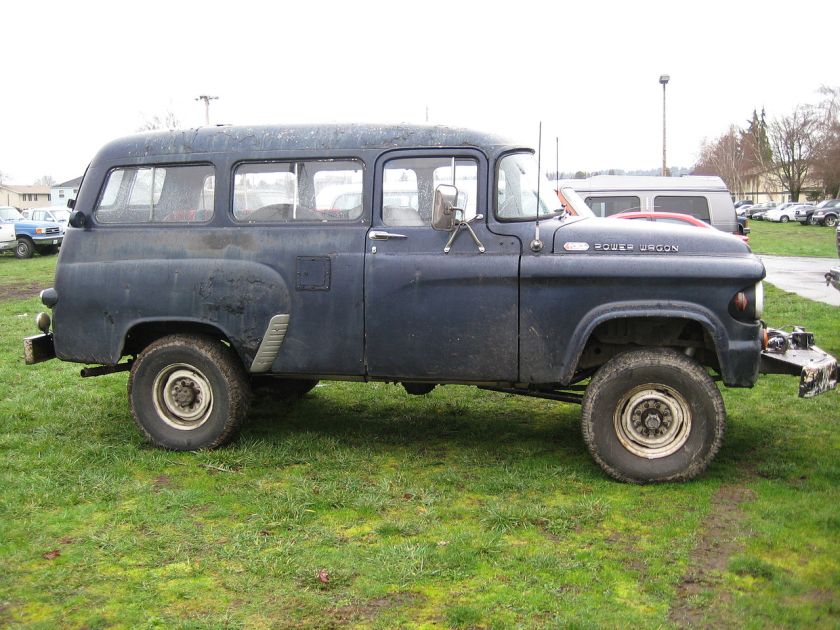

The Dodge Town Panel and Dodge Town Wagon are respectively a Panel truck and a Carryall, manufactured between 1954 and 1966 by Chrysler‘s Dodge division. The model resembles what would be called an SUVnowadays. A competitor with the Chevrolet Suburban, it was initially available in 2 wheel drive only, but the 4 wheel drive model was ultimately more popular. The Dodge “Town Wagon” model was a “twin” passenger version of the Town Panel. The Town Panel had no windows or seats behind the driver and was more of a commercial-use vehicle. Dodge had previously built panel trucks prior to the Town Panel, but the name didn’t exist for these trucks until the Town Wagon was built along with them.
The Town Wagon in four wheel drive configuration was called the Power Wagon Town Wagon, and had a “Power Wagon” badge linking it to the Dodge Power Wagon. The Town Panel and Town Wagon trucks were based upon the design of the Dodge C Series Pickup trucks with round fenders and wraparound windshields. Even after the Dodge D Series pickup trucks with square fenders and flat windshields were released, the Town Wagons retained the 1958 sheet metal design of the C Series pickups and heavy-duty trucks.
That’s it.
There will be a part IV with only pictures, and further there is a special chapter about Dodge buses, DeSoto, Commer, Askam and Karrier Buses.