Pininfarina
| Società per Azioni | |
| Traded as | BIT: PINF |
| Industry | Automotive |
| Founded | Torino, Italy (May 23, 1930) |
| Founder | Battista Farina |
| Headquarters | Cambiano, Italy |
|
Key people
|
|
| Services | Automotive design |
| €32.9 million (2012) | |
|
Number of employees
|
821 (2012) |
| Parent | Mahindra Group (76.06%) |
| Website | www.pininfarina.com |
Pininfarina S.p.A. (short for Carozzeria Pininfarina) is an Italian car design firm and coachbuilder in Cambiano, Italy. It was founded by Battista ”Pinin” Farina in 1930.On December 14, 2015, Mahindra Group, acquired Pininfarina S.p.A. in a deal worth about 168 million euros ($185 million).
Pininfarina is employed by a wide variety of automobile manufactures to design vehicles. These firms have included long-established customers such as Ferrari, Alfa Romeo, Peugeot, FIAT, GM, Lancia, and Maserati, to emerging companies in the Asian market with Chinese manufactures like AviChina, Chery, Changfeng, Brilliance, and JAC and Korean manufacturers Daewoo and Hyundai.
Since the 1980s Pininfarina has also designed high-speed trains, buses, trams, rolling stocks, automated light rail cars, people movers, yachts, airplanes, and private jets. With the 1986 creation of Pininfarina Extra they have consulted on industrial design, interior design, architecture, and graphic design.
Pininfarina was run by Battista’s son Sergio Pininfarina until 2001, then his grandson Andrea Pininfarina until his death in 2008. After Andrea’s death his younger brother Paolo Pininfarina was appointed as CEO.
At its height in 2006 the Pininfarina Group employed 2,768 with subsidiary company offices throughout Europe, as well as in Morocco and the United States. As of 2012 with the end of series automotive production, employment has shrunk to 821. Pininfarina is registered and publicly traded on the Borsa Italiana (Milan Stock Exchange).
On December 14, 2015, Mahindra Group, announced a deal to acquire Pininfarina S.p.A. in a deal worth about 168 million euros ($185 million).
History
The days as a specialist coachbuilder
When automobile designer and builder Battista ”Pinin” Farina broke away from his brother’s coach building firm, Stabilimenti Farina, in 1928 he founded “Carrozzeria Pinin Farina” with financial help from his wife’s family and Vincenzo Lancia. That first year the firm employed eighteen and built 50 automobile bodies.
On May 22, 1930 papers were filed to become a corporation, Società anonima Carrozzeria Pinin Farina headquartered in Turin, Italy, at 107 Corso Trapani. During the 1930s, the company built bodies for Lancia, Alfa Romeo, Isotta-Fraschini, Hispano Suiza, Fiat, Cadillac, and Rolls-Royce. With its close relationship with Lancia, the pioneer of the monocoque in automobile design, Pininfarina became the first coachbuilder to build bodies for the new technique also known as unibody construction. This development happened in the mid-1930s when others saw the frameless construction as the end of the independent coachbilder.
In 1939, World War II ended automobile production, but the company had 400 employees building 150 bodies a month. The war effort against the Allies brought work making ambulances and searchlight carriages. The Pininfarina factory was destroyed by Allied bombers ending the firm’s operations.
After World War II
 Nash-Healey roadster
Nash-Healey roadster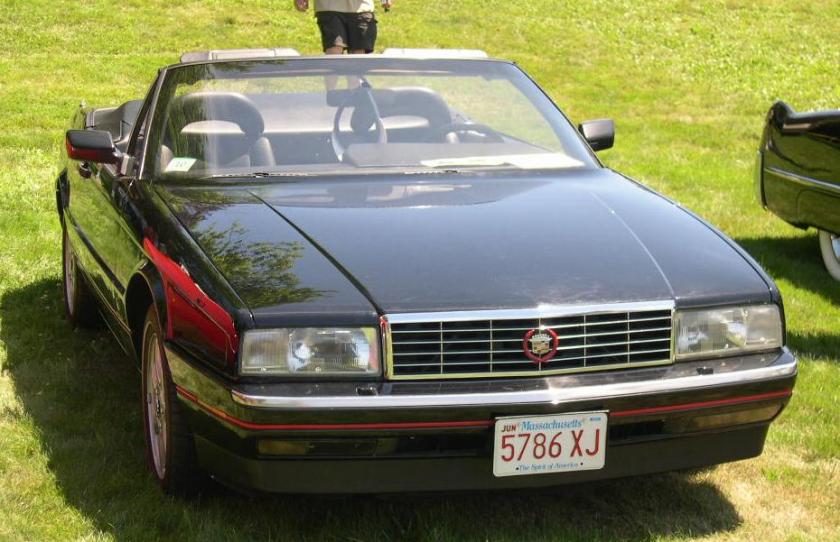 1987 Cadillac Allanté
1987 Cadillac AllantéAfter the war, Italy was banned from the 1946 Paris Motor Show. The Paris show was attended by 809,000 visitors (twice the pre-war figure), lines of people stretched from the main gate all the way to the Seine. Pinin Farina and his son Sergio, determined to defy the ban, drove two of their cars – an Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 S and a Lancia Aprilia cabriolet – from Turin to Paris, and found a place at the entrance to the exhibition to display the two new creations. The managers of the Grand Palais said of the display, “the devil Pininfarina”, but to the press and the public it was the successful “Turin coachbuilder’s anti-salon”.
At the end of 1945 the Cisitalia 202 Coupé was designed. An elegantly proportioned design with a low hood, it is the car that usually is given credit for establishing Pininfarina’s reputation. The Pininfarina design was honored in the Museum of Modern Art’s landmark presentation “Eight Automobiles” in 1951. A total of 170 Coupés where produced by Pininfarina.
The publicity of the Museum of Modern Art exhibit brought Pininfarina to the attention of Nash-Kelvinator managers. The subsequent cooperation with Nash Motors resulted in high-volume production of Pininfarina designs and provided a major entry into the United States market. In 1952, Mr. Farina visited the U.S. for the unveiling of his design for the Nash Ambassador and Statesman lines, which, although they did carry some details of Pininfarina’s design, were largely designed by Nash’s then-new in-house styling staff when the original Farina-designed model proved unsuited to American tastes, exhibiting a popular 1950s appearance called “ponton“. The Nash-Healey sports car body was, however, completely designed and assembled in limited numbers from 1952 to 1954 at Pininfarina’s Turin facilities. Nash heavily advertised its link to the famous Italian designer, much as Studebaker promoted its longtime association with Raymond Loewy. As a result of Nash’s $5 million advertising campaign, Pininfarina became well known in the U.S.
Pininfarina also built the bodies for the limited-series Cadillac Eldorado Brougham for General Motors in 1959 and 1960, assembled them and sent them back to the U.S. There were 99 Broughams built in 1959 and 101 in 1960. A similar arrangement was repeated in the late 1980s when Pininfarina designed (and partially assembled) the Cadillac Allanté at the San Giusto Canavese factory. The car bodies were assembled and painted in Italy before being flown from the Turin International Airport to Detroit for final vehicle assembly.
The Ferrari partnership
It started in 1951 with a meeting at a restaurant in Tortona, a small town halfway between Turin and Modena. This neutral territory was chosen because neither Pininfarina nor Enzo Ferrari wanted to meet at the other’s headquarters. Pinin’s son, Sergio Pininfarina recalled, “It is not difficult to imagine how I felt that afternoon when my father, without taking his eyes off the road for one moment told me his decision as we drove back to Turin: “From now on you’ll be looking after Ferrari, from A to Z. Design, engineering, technology, construction—the lot!”—I was over the moon with happiness.” “
Since that meeting the only road-going production Ferraris not designed by Pininfarina are the 1973 Dino 308 GT4 and 2013’s LaFerrari. Their relationship was so close that Pininfarina became a partner of Ferrari in “Scuderia Ferrari SpA SEFAC”, the organization that ran Ferrari’s race team from 1961–1989, Pinin was a vice president of Ferrari, and Sergio later sat on Ferrari’s board of directors.
The move to large-scale manufacturing
In 1954 to 1955 Pininfarina purchased land in Grugliasco, outside of Turin, for a new factory. “The factory in no way would look like the one of Corso Trapani. It would be a car no longer on my measurements but on those of my children, built looking like them; I had this in mind and wanted it,” said Pininfarina.
Around the same time, Alfa Romeo accepted Pininfarina’s design over Bertone for the new Giulietta Spider. The Alfa was the first vehicle that Pininfarina produced in large numbers, in fact Alfa Romeo chose Pininfarina to produce the Spider in large part because they felt confident that they could produce 20 cars a day for a run of 1,000 bodies. The Spider was a huge success for Alfa Romeo and Pininfarina, Max Hoffman the importer for the United States said he could sell as many as they could make. In 1956, the first year of production, they produced 1025 units which then expanded to over 4,000 in 1959 the first full year of the new Grugliasco factory.
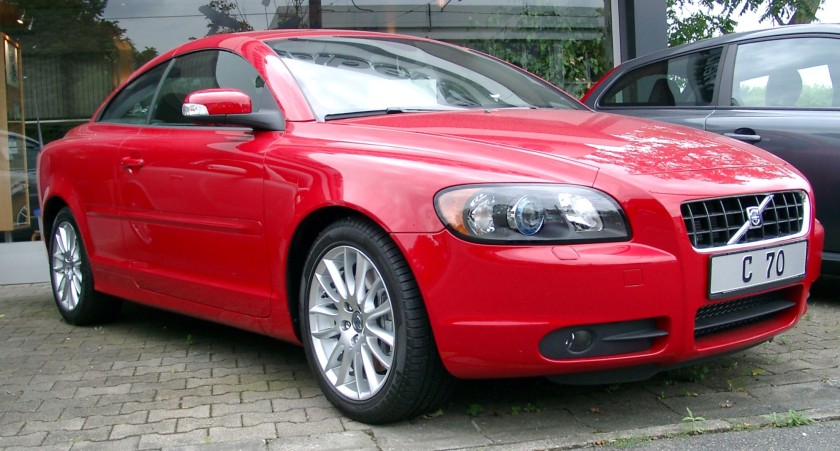 2006 Volvo C70
2006 Volvo C70The second generation of leadership
Starting with the planning for the new plant in Grugliasco in 1956, Pinin started to groom his replacements–Sergio his son and Renzo Carli his son-in-law. To his heirs apparent, Pinin said of the Corso Trapani facility “This old plant has reached the limits of its growth. It has no room for expansion and is far from being up to date. If I were alone I’d leave it as it is. But I want you to decide which way to go–to stay as we are or to enlarge. Either way is fine with me. It’s your decision to make and I don’t want to know what it is. I’m finished and it’s your time to take over. The future is absolutely up to you.” In 1958, upon leaving for a world tour Pinin added “In my family we inherit our legacies from live people–not from the dead.”
1961 at the age of 68, “Pinin” Farina formally turns his firm over to his son Sergio and his son-in-law, Renzo Carli, it was the same year that the President of Italy formally authorized the change of Farina’s last name to Pininfarina.
Pininfarina was run by Battista’s grandson Andrea Pininfarina from 2001 until his death in 2008. Andrea’s younger brother Paolo Pininfarina was then appointed as successor.
Modernizing for a new world
Starting in the mid-1960s, Pininfarina started to make investments in the science of automotive design, a strategy to differentiate itself from the other Italian coachbuilders.
In 1966, Pininfarina opened Studi e Ricerche, or the Studies and Research Centre in Grugliasco. The research centre occupied 8000 sq. metres (2 acres) and employed 180 technicians capable of producing 25 prototypes a year.
The Calculation and Design Centre was set up in 1967, the first step in a process of technological evolution which, during the 1970s, would take Pininfarina into the lead in automated bodywork design.
Then in 1972 construction of a full-sized wind tunnel was completed. The project was started in 1966. When it opened, it not only was the first wind tunnel with the ability to test full-sized cars in Italy, but also one of the first in the world with this ability. To put this foresight in perspective, GM’s full-sized wind tunnel didn’t open until 1980.
New infrastructure and expansion
The 1980s started a period of expansion for Pininfarina.
In 1982 the company opened “Pininfarina Studi e Ricerche” in Cambiano. It was separate from the factory and wind tunnel in Grugliasco, to keep design and research activities independent from manufacturing. On October 14, 2002, Pininfarina inaugurated a new engineering center. The new facility, which was built at the Cambiano campus, to give greater visibility and independence to the engineering operations.
In 1983 Pininfarina reached an agreement with General Motors to design and build the Cadillac Allanté. The Allanté project led to the building of the San Giorgio factory in 1985.
In 1996, Mitsubishi entered into talks for Pininfarina build their new compact SUV, the Pajero, in Italy. While Mitsubishi recognized Pininfarina’s expertise in design and engineering, the reason for choosing them was that manufacturing costs were half of those in Germany. After entering into an agreement in 1996, Pininfarina purchased an industrial site at Bairo Canavese near Turin, Italy. in April 1997, Bairo Canavese was dedicated to the production of the new Mitsubishi Pajero Pinin.
Pininfarina Sverige AB in Uddevalla, Sweden, was established in 2003 as a joint venture (JV) between Volvo Cars and Pininfarina to produce a new Volvo convertible that will be sold in Europe and the United States. The JV is owned 60% by Pininfarina and 40% by Volvo. The C70 model designed by Volvo’s John Kinsey—was launched on 13 April 2006, sharing the Volvo P1 platform used in the S40.
New economic realities
In April 2008, after three years of serious losses totaling 115 million euros at the end of 2007, Pininfarina made the first of several moves to raise capital and restructure its enormous debt:
April 29, 2008
Pininfarina’s announced Piero Ferrari, Alberto Bombassei, chairman of Brembo, and the Marsiaj family, founders of the Sabelt seatbelt company, will join with Vincent Bollore, a French financier, and Ratan Tata, head of India’s Tata conglomerate, who already announced their plans to invest, reports Reuters. The five will together invest €100 million.
Funding will come through the sale of stock to other investors. The Pininfarina family is willing to reduce its share from its current 55% to 30%, which is still enough to secure a controlling interest.
December 31, 2008
On December 31, 2008, Pininfarina announced a debt restructuring that would require the family to sell its stake in the company. The agreement was made after Pininfarina’s value dropped 67 per cent during 2008, and it then had a market capitalization of about €36 million. It had total debts of €598 million at the end of November. Of that amount, €555 million was the subject of the debt restructuring agreement that was agreed on with a consortium of banks.
March 24, 2009
Pincar, Pininfarina’s family holding company, announced it has hired Leonardo and Co to find a buyer for its 50.6% stake in Pininfarina per the debt restructuring agreement reached in December.
January 4, 2011
Pininfarina released a statement saying that it is still gathering “possible offers from potential buyers,” adding it would release more information when it was appropriate.
Company sources added, the family will not sell its entire 50.7% stake but that Pincar would no longer be a majority shareholder.
February 14, 2012
Italy’s Pininfarina family is set to lose control of the car design company as lengthy debt restructuring talks head toward the finish line, people familiar with the situation said on Tuesday. A 16.9 million euros loss in the first nine months of 2011 occurred after closing its manufacturing operations to re-invent itself as a smaller niche design player.
An agreement with creditor banks including Intesa Sanpaolo, UniCredit, Mediobanca and Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena to restructure net debt of 76 million euros is on track and will be reached in the coming months, said three sources close to the situation. “The debt situation is stable and the talks are not contentious, so there is no hurry,” said one of the sources, speaking on condition anonymity. “The agreement will fix the capital structure for the foreseeable future.”
When finalised, the debt accord will give control of the family’s 77 percent stake to its creditor banks, ending the Pininfarina family’s ownership.
The deal will close a chapter that began in 2008 when the banks swapped 180 million euros in debt in exchange for a promise of proceeds from a future sale of part of the Pininfarina’s family stake.
But no takers materialised. Potential buyers were not willing to acquire a design company when they can easily contract its services, said one of the people familiar with the situation.
February 15, 2012
In a statement released on 15 February, the Cambiano-based company, which owes over €100 million to a number of Italian banks, said its debt repayment date has been extended to 2018, from 2015.
The agreement, which will be signed in the next few weeks, will also see the company take advantage of interest rates “significantly lower than [current] market rates”. With the new debt restructuring deal with its creditors Pininfarina will remain under the control of the Pininfarina family.
May 16, 2012
Automotive News reports Pininfarina projects it will turn a profit for 2012, thanks in part to debt restructuring. The Italian design studio hasn’t seen a profit in eight years, but signed a deal in April to restructure $182.6 million in debt. The move effectively stretched the studio’s repayment deadline from 2015 to 2018. At the same time, Pininfarina announced it will likely see an operating loss this year, but a one-time gain of $57.6 million will result in the net profit. Last year, the company lost $8.3 million in the first quarter, though that figure has dropped to just under $4 million during Q1 2012.
Pininfarina also saw its net revenue increase by $2.9 million.
March 26, 2013
Pininfarina in the black for first time since 2004 Italian design house Pininfarina predicted last May that it would face an operating loss for 2012 but still come out with a net profit. Both predictions have come true – the company is reporting an operating loss of 8.2 million euros and a net profit of 32.9 million euros ($42.5 million US).
According to Reuters, the good news came because of a debt restructuring arranged last year that gives the company three more years to repay its $182.6 million in debt, and a one-time gain of roughly 45 million euros ($57.6 million US). It is the company’s first profit since 2004.
Acquisition by Mahindra group (2015–present)
Mahindra Group, owner of Indian automobile company Mahindra & Mahindra agreed to buy Italian car designer Pininfarina SpA in a deal worth about 168 million euros ($185 million). Mahindra group, together with affiliate Tech Mahindra, have 76 percent stake from holding company Pincar for 25.3 million euros. The Indian company will offer the same price for the remaining stock. In addition to buying stock, Mahindra will invest 20 million euros in Pininfarina and provide a guarantee to creditors of 114.5 million euros.
Corporate Governance (2016)
- President:Paolo Pininfarina
- CEO – General Manager: Silvio Pietro Angori
- Board of Directors: Manoj Bhat, C.P.Gurnani, Romina Guglielmetti, Jay Itzkowitz, Licia Mattioli, Sara Miglioli, Antony Sheriff.
- Statutory Auditors: Nicola Treves (president), Margherita Spaini, Giovanni Rayneri.
The end of car production operations
On December 10, 2011 Pininfarina announced it would end all automotive production. In truth production ended in November 2010 with the conclusion of the contract to produce the Alfa Romeo Brera and Spider at the San Giorgio plant.
Grugliasco factory
Opened in 1958 with nearly 1,000 employees, by 1960 output exceeded 11,000 car bodies. In 2009 Pininfarina sold the factory to Finpiemonte, the public finance of the Piedmont Region, at the price of 14.4 million euro. Finpiemonte, as part of the deal, leases the plant to Gian Mario Rossignol at a rent of €650,000 per year for six years renewable.
The Grugliasco sale did not include an adjacent structure that houses the wind tunnel.
San Giorgio plant
Opened in 1986 to build Cadillac Allante bodies for General Motors, the same year Pininfarina was first listed on the Stock Exchange in Milan. Automotive production ended at San Giorgio with the conclusion of the Ford production in July 2010, and Alfa Romeo production in November 2010.
Following the end of contract manufacturing activities San Giorgio Canavese is being used for production of spare parts for cars manufactured in the past.
Pininfarina opened its third manufacturing plant in 1997. Currently Pininfarina leases the plant and 57 employees to the Cecomp Group. This agreement to produce 4,000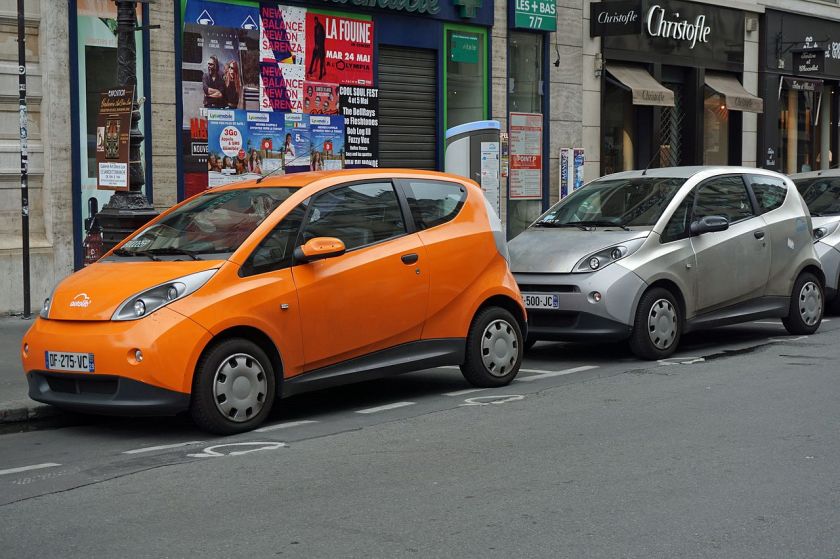 electric Bolloré Bluecars runs April 1, 2011 to December 31, 2013. On September 13, 2013 a new lease agreement was announced, this new agreement will run from January 1, 2014 until the end of 2016.
electric Bolloré Bluecars runs April 1, 2011 to December 31, 2013. On September 13, 2013 a new lease agreement was announced, this new agreement will run from January 1, 2014 until the end of 2016.
Uddevalla, Sweden Pininfarina Sverige AB
A joint venture between Pininfarina S.p.A. and Volvo Car Corporation began in 2003. Volvo and Pininfarina S.p.A. have agreed upon the termination of the joint venture agreement regarding Pininfarina Sverige AB and its operations in Uddevalla, Sweden. As of December 31, 2011 the termination this agreement would result in a 30 million euros fee paid to Pininfarina.
On June 25, 2013 the last Volvo C70 was produced and the Uddevalla assembly plant was closed.
Designers
Although Pininfarina rarely gave credit to individuals, that policy seems to have changed in recent years and many of the designers of the past have become known. As of 2011 Pininfarina employs 101 people in their styling department. That is down from 185 in 2005.
- Franco Scaglione 1951, designer for two months before he left for what is now known as Gruppo Bertone
- Franco Martinengo 1952–72, Director of the Centro Stile
- Adriano Rabbone
- Francesco Salomone
- Aldo Brovarone 1954–74, Designer; 1974–88, Managing Director Studi e Ricerche
- Tom Tjaarda 1961–65, Designer
- Filippo Sapino 1967–69
- Paolo Martin 1968–72, Chief of the Styling Department
- Diego Ottina 1970—
- Lorenzo Ramaciotti 1973-2005 deputy director of Pininfarina Studi e Ricerche, Director General and Chief Designer, CEO of Pininfarina SpA Research and Development
- Ian Cameron 1975–81
- Enrico Fumia 1976–91; 1982: Manager at Pininfarina R&D – Models and Prototypes Development; 1988: Manager at Pininfarina R&D – Design and Development; 1989: Deputy General Manager at Pininfarina R&D
- Guido Campoli
- Emanuele Nicosia 1977–85
- Elvio d’Aprile 1982–95
- Piero Camardella 1984–93
- Marco Tencone
- Leonardo Fioravanti 1988–91, Managing Director and CEO of Pininfarina Studi e Ricerche
- Maurizio Corbi 1989-
- Davide Arcangeli
- Jeremy Malick 2000–02, Designer; 2009—-, Senior Designer
- Dimitri Vicedomini 2001–12, Senior Car Designer
- Jason Castriota 2001–08
- Ken Okuyama 2004–06, Creative Director
- Luca Borgogno 2005— , Lead Designer
- Nazzareno Epifani 2006— , Lead Designer
- Lowie Vermeersch 2007–10, Design Director
- Brano Mauks 2007— , Senior Designer
- Carlo Palazzani 2010— , Lead Designer
- Felix Kilbertus 2011— , Lead Designer
- Fabio Filippini 2011— , Vice President Design and Chief Creative Officer
Vehicles
Pininfarina designs, manufactures, assembles, and tests prototypes and production vehicles under contract for other automakers.
Past production
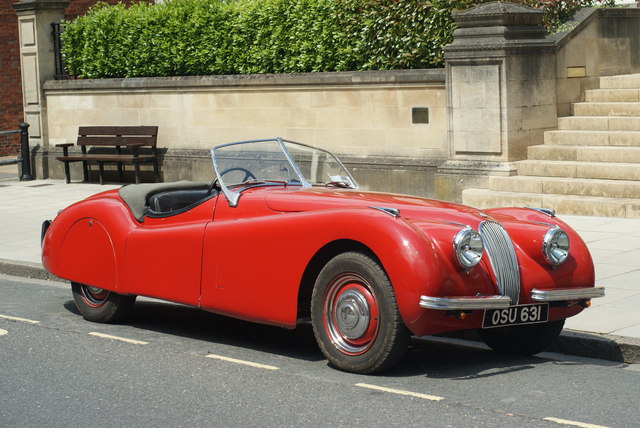
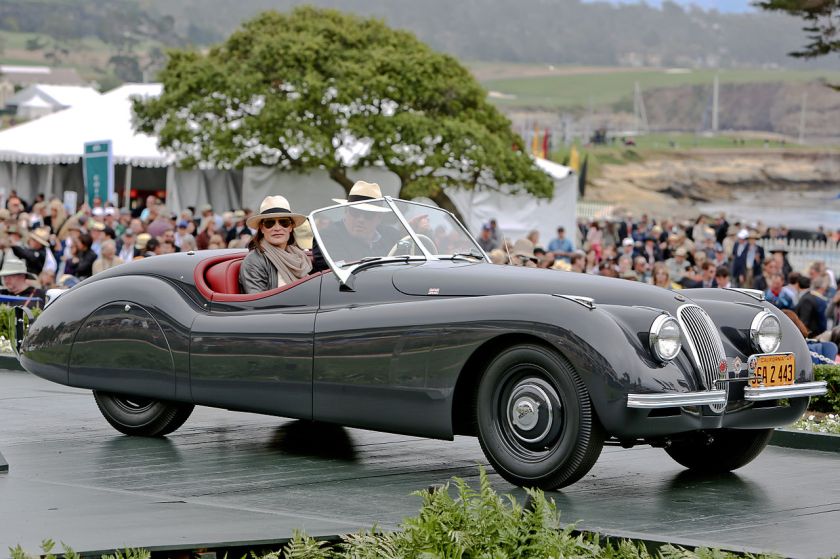
As of December 10, 2011 Pininfarina announced it would end all mass automotive production with the sale of its 40% stake in the Uddevalla, Sweden plant to Volvo in 2013. In the past Pininfarina has produced both cars and car-bodies under contract from other automakers. This production includes Pininfarina-designed cars and vehicles designed by others.
A sortable list of complete cars or car bodies manufactured in one of the five Pininfarina factories:
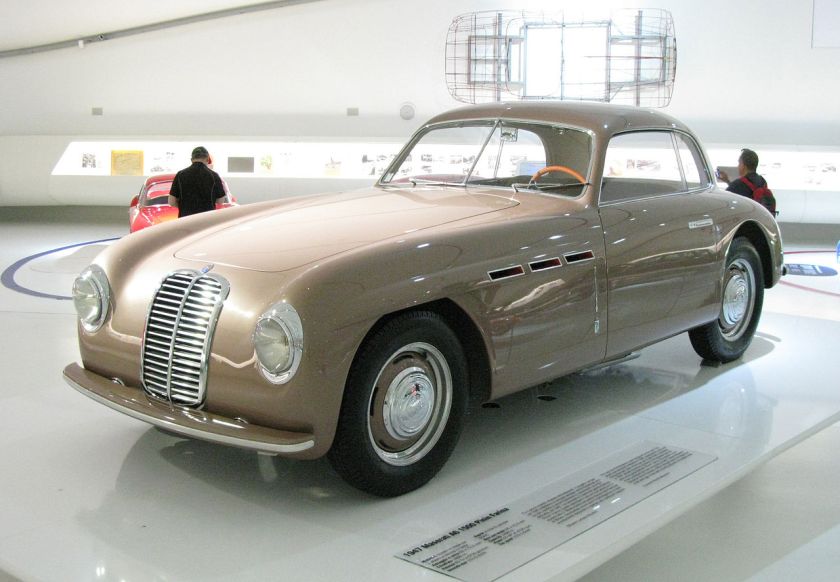
 1947 Maserati A6 1500 PininFarina
1947 Maserati A6 1500 PininFarina 1953 Maserati A6G 2000 bodied by Zagato PininFarina
1953 Maserati A6G 2000 bodied by Zagato PininFarina 1951 Cistialia 202 SC Pininfarina Coupé
1951 Cistialia 202 SC Pininfarina Coupé Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 SS Pinin Farina Cabriolet
Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 SS Pinin Farina Cabriolet Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 SS Coupé, coachbuilding by Pininfarina
Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 SS Coupé, coachbuilding by Pininfarina 1949 Maserati A6 1500 Coupé Pininfarina
1949 Maserati A6 1500 Coupé Pininfarina 1950-52 Lancia Aurelia B50 cabriolet by Pinin Farina
1950-52 Lancia Aurelia B50 cabriolet by Pinin Farina 1950-58 Lancia Aurelia B20 GT, 6th Series. Lancia Flaminia Coupe Pininfarina
1950-58 Lancia Aurelia B20 GT, 6th Series. Lancia Flaminia Coupe Pininfarina 1952 Alfa Romeo 1900 C Cabriolet PF
1952 Alfa Romeo 1900 C Cabriolet PF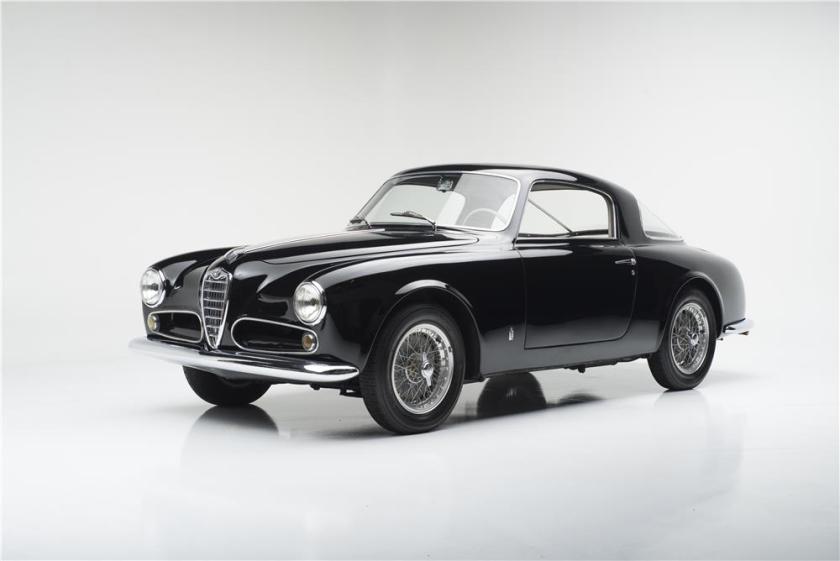 1952 ALFA ROMEO 1900 C SPRINT PININFARINA COUPE
1952 ALFA ROMEO 1900 C SPRINT PININFARINA COUPE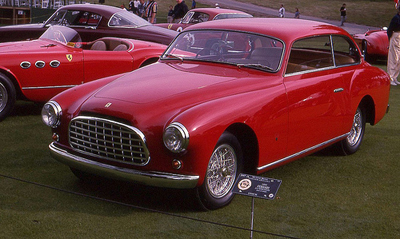 1952 Alfa Romeo 1900C PF 2+2 Cabriolet
1952 Alfa Romeo 1900C PF 2+2 Cabriolet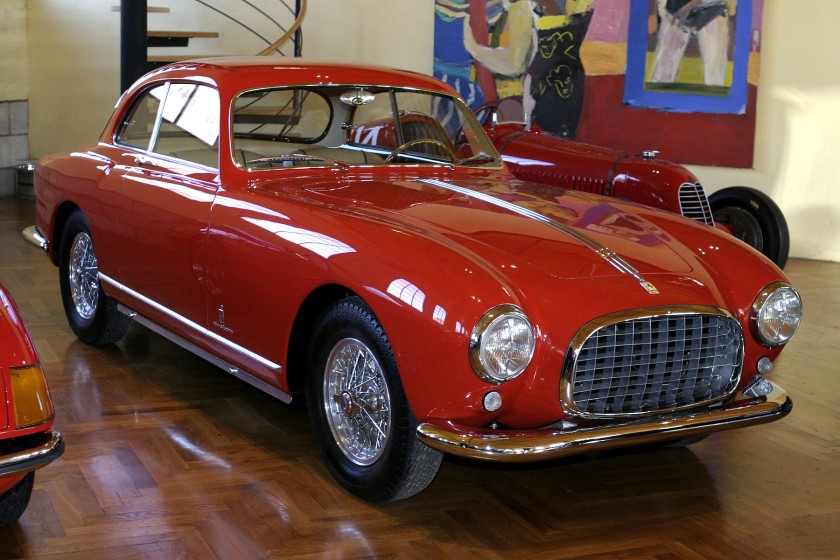 1952 Ferrari 212 Inter Pininfarina coupé
1952 Ferrari 212 Inter Pininfarina coupé
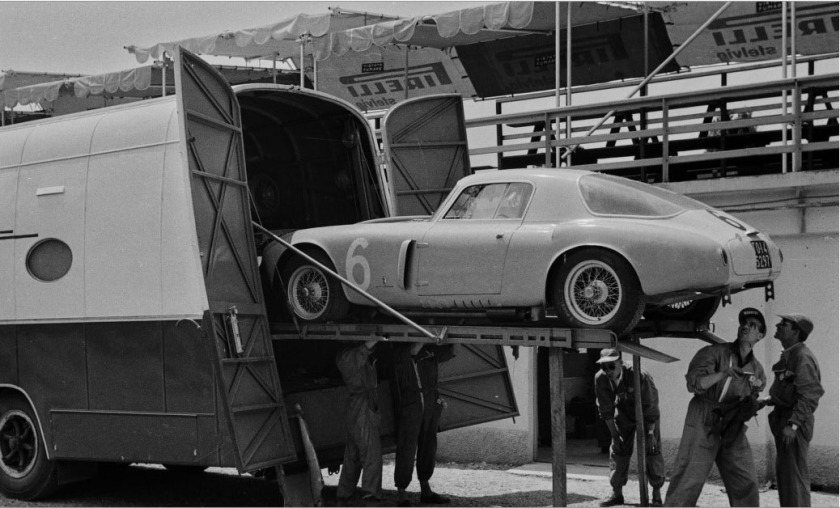


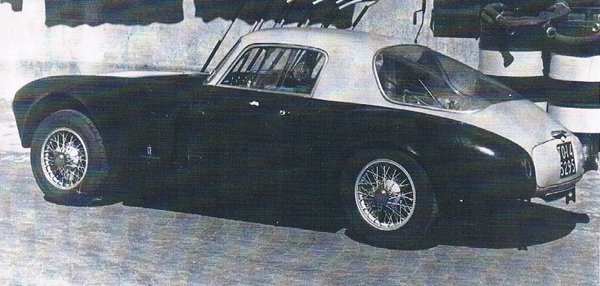
 1952 Lancia D20 Pininfarina + last one at le mans 1953
1952 Lancia D20 Pininfarina + last one at le mans 1953 1953 Nash Healey Pininfarina Roadstar
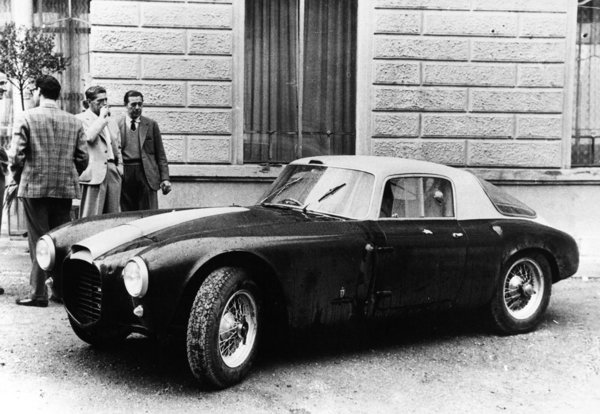
1953 Nash Healey Pininfarina Roadstar 1954 Ferrari 375 MM and Ingrid Bergman and her husband Robert Rossellini to her right.Carrozzeria Pinin Farina
1954 Ferrari 375 MM and Ingrid Bergman and her husband Robert Rossellini to her right.Carrozzeria Pinin Farina
 1953 Lancia D23 Spider Pininfarina
1953 Lancia D23 Spider Pininfarina
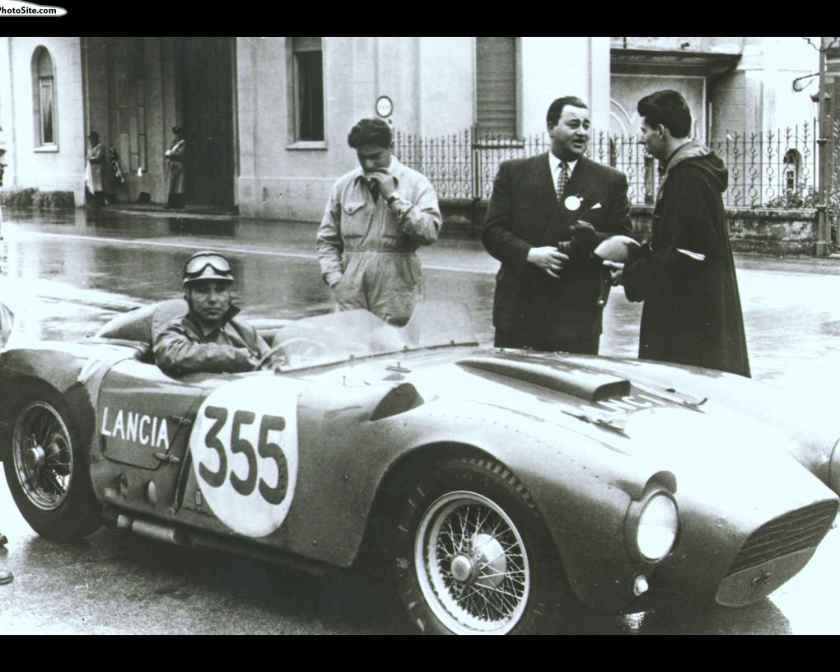
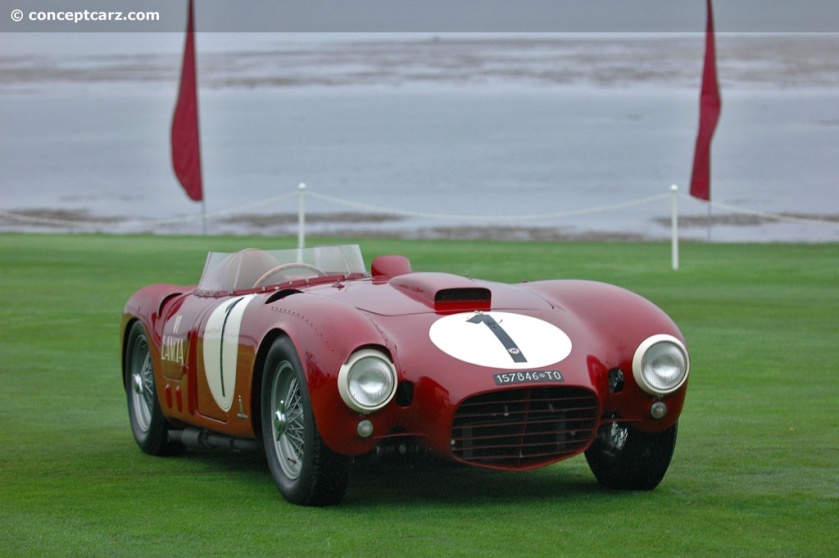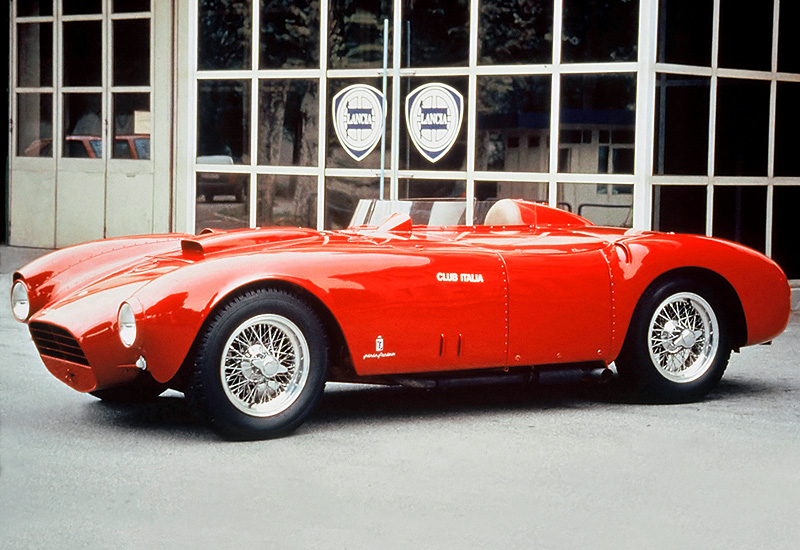

 1953-54 Lancia D24 Spyder Sport PininFarina
1953-54 Lancia D24 Spyder Sport PininFarina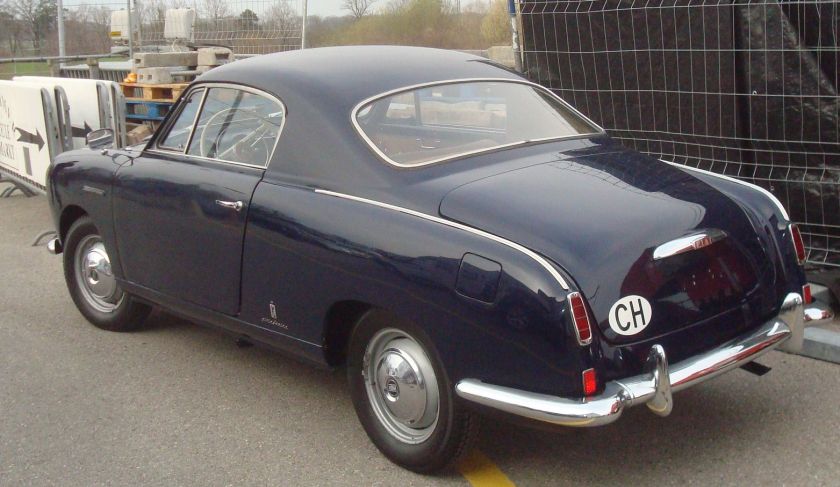 1954 fiat-1100-tv-coupe-pininfarina-1954-(italie)
1954 fiat-1100-tv-coupe-pininfarina-1954-(italie)
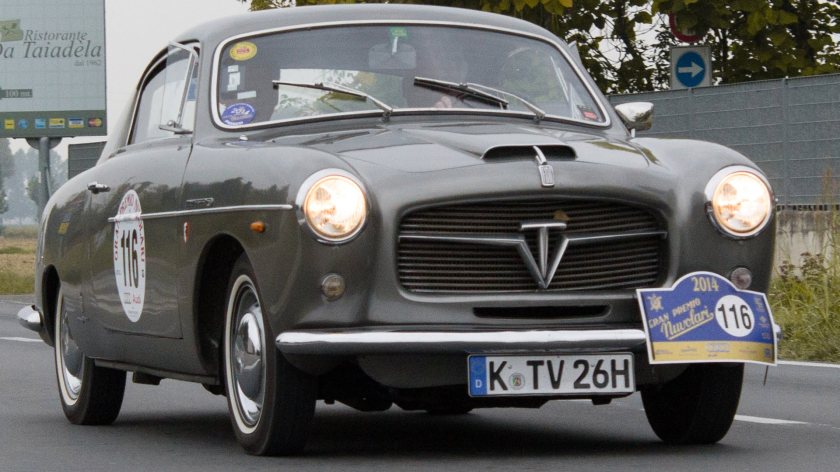 1954 FIAT 1100 TV PininFarina
1954 FIAT 1100 TV PininFarina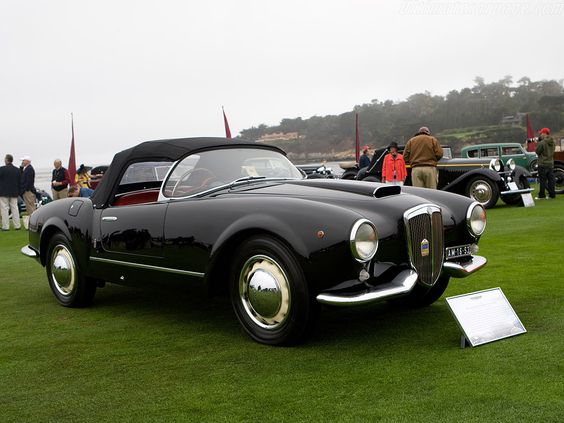
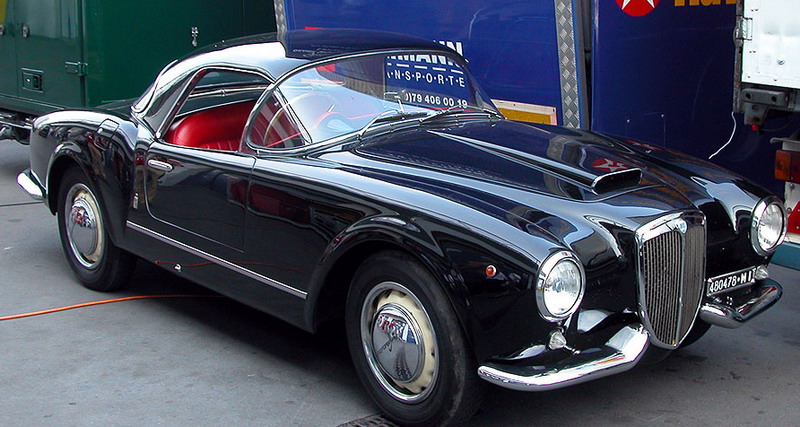
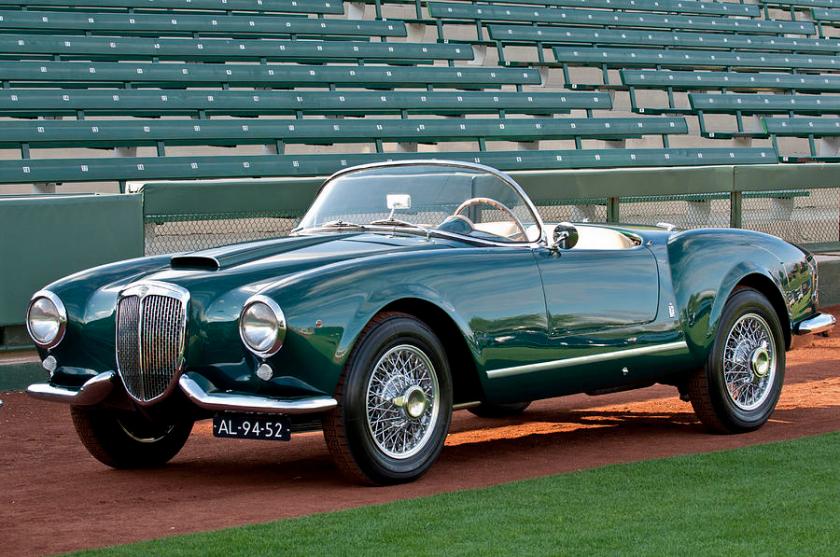
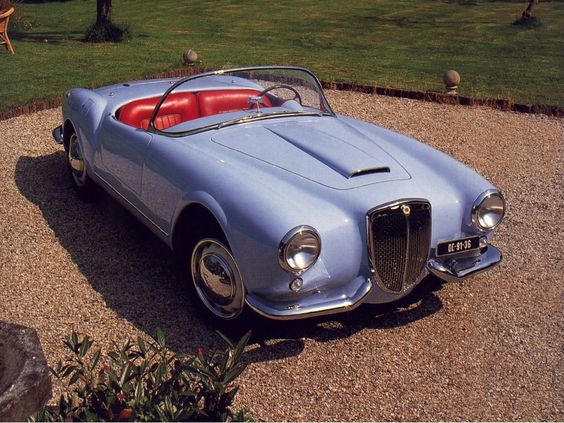




 Lancia Aurelia B24 (+B25 remakes) Spider America PininFarina
Lancia Aurelia B24 (+B25 remakes) Spider America PininFarina
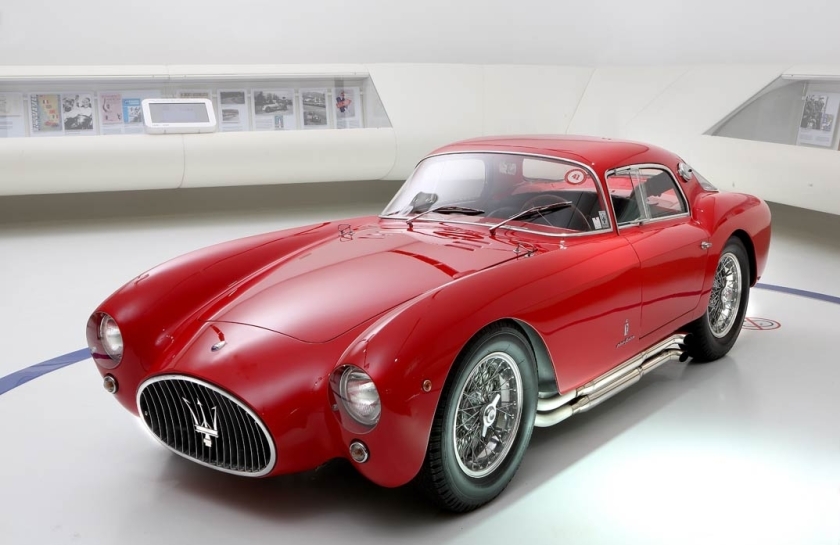
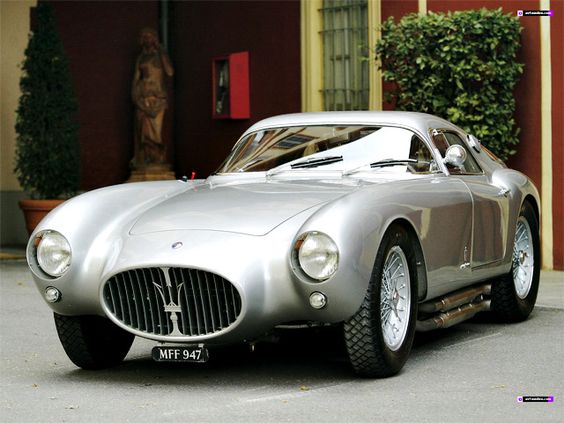
 Maserati A6 GCS/53 Berlinetta PininFarina
Maserati A6 GCS/53 Berlinetta PininFarina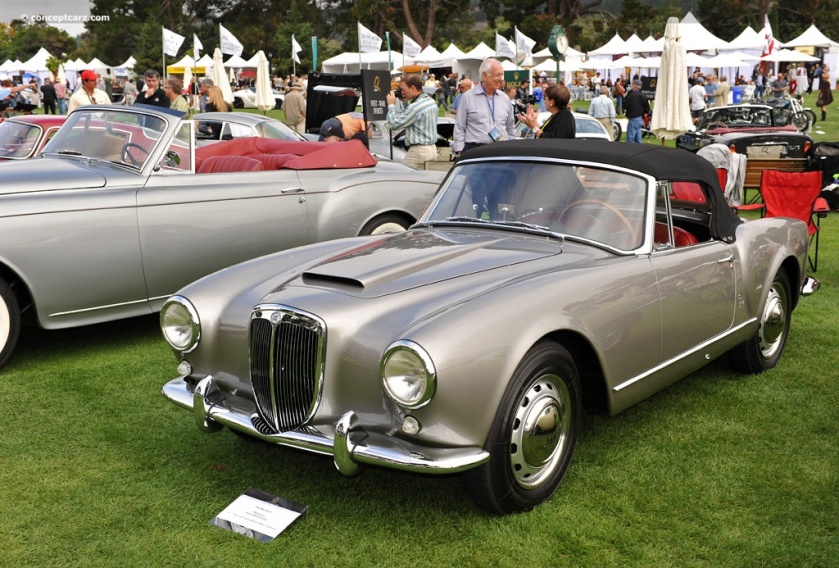 1956 Lancia Aurelia B24S Spider boasts a race-developed V6 engine, outstanding handling and beautiful Pininfarina styling
1956 Lancia Aurelia B24S Spider boasts a race-developed V6 engine, outstanding handling and beautiful Pininfarina styling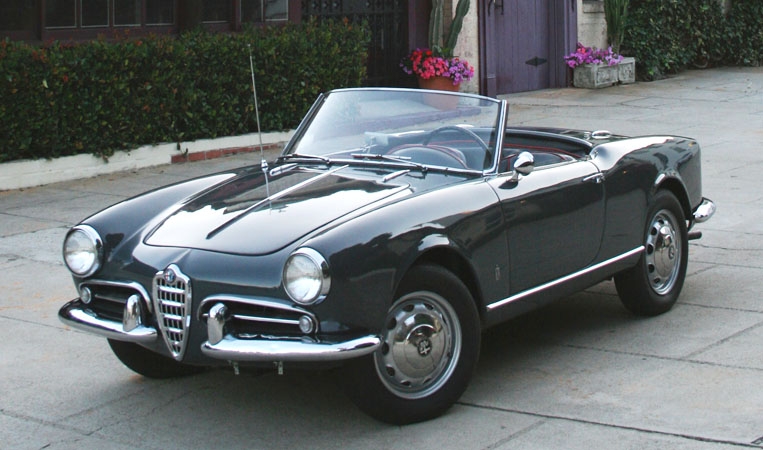 1956 Alfa Giulietta Spider Pininfarina Grey Main
1956 Alfa Giulietta Spider Pininfarina Grey Main 1958 LANCIA APPIA SERIES2+2 PININFARINA COUPE
1958 LANCIA APPIA SERIES2+2 PININFARINA COUPE 1959 Ferrari 250 GT Coupé Pininfarina
1959 Ferrari 250 GT Coupé Pininfarina 1962 Alfa Giulietta Spider Pininfarina
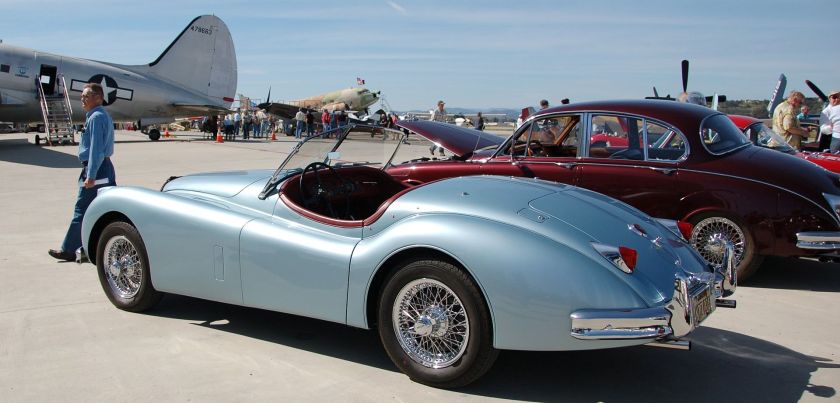
1962 Alfa Giulietta Spider Pininfarina 1959 Cadillac Eldorado Brougham by Pininfarina
1959 Cadillac Eldorado Brougham by Pininfarina 1959 Lancia Flaminia Coupé Pinin Farina
1959 Lancia Flaminia Coupé Pinin Farina 1961 Ferrari 250 GTE 2+2 Pininfarina
1961 Ferrari 250 GTE 2+2 Pininfarina 1966 Peugeot 404 Pininfarina Coupé
1966 Peugeot 404 Pininfarina Coupé 1967 Peugeot 404 Coupe Cabriolet Pininfarina
1967 Peugeot 404 Coupe Cabriolet Pininfarina 1962 MHV Lancia Flavia Pininfarina Coupé-01
1962 MHV Lancia Flavia Pininfarina Coupé-01 1965 Lancia Flavia-Pininfarina Mk1
1965 Lancia Flavia-Pininfarina Mk1 1968 Lancia Flavia Pininfarina Convertibile
1968 Lancia Flavia Pininfarina Convertibile 1971 Lancia 2000 HF Pinifarina Coupe
1971 Lancia 2000 HF Pinifarina Coupe 1963 Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Series 105 Pininfarina
1963 Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Series 105 Pininfarina 1963 Alfa-Giulia-Spider-DV-10 1600 Pininfarina
1963 Alfa-Giulia-Spider-DV-10 1600 Pininfarina 1963-68 Ferrari 330 gtc pininfarina
1963-68 Ferrari 330 gtc pininfarina 1967 Ferrari 330 GT 2+2 Pininfarina
1967 Ferrari 330 GT 2+2 Pininfarina 1964 MHV Ferrari 330GT America Pininfarina 01
1964 MHV Ferrari 330GT America Pininfarina 01 1968 Interior of Ferrari 330 GT 2+2 Pininfarina (serie II)
1968 Interior of Ferrari 330 GT 2+2 Pininfarina (serie II) 1966 Ferrari 330 GTS Pininfarina
1966 Ferrari 330 GTS Pininfarina 1967 Ferrari 330 GTC Pininfarina during the Saxony Classic Rallye 2010
1967 Ferrari 330 GTC Pininfarina during the Saxony Classic Rallye 2010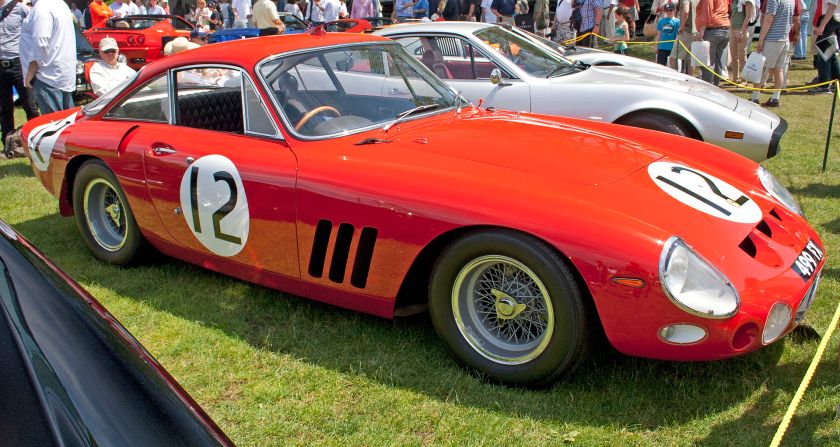 1962 Ferrari 330 LM Berlinetta Pininfarina
1962 Ferrari 330 LM Berlinetta Pininfarina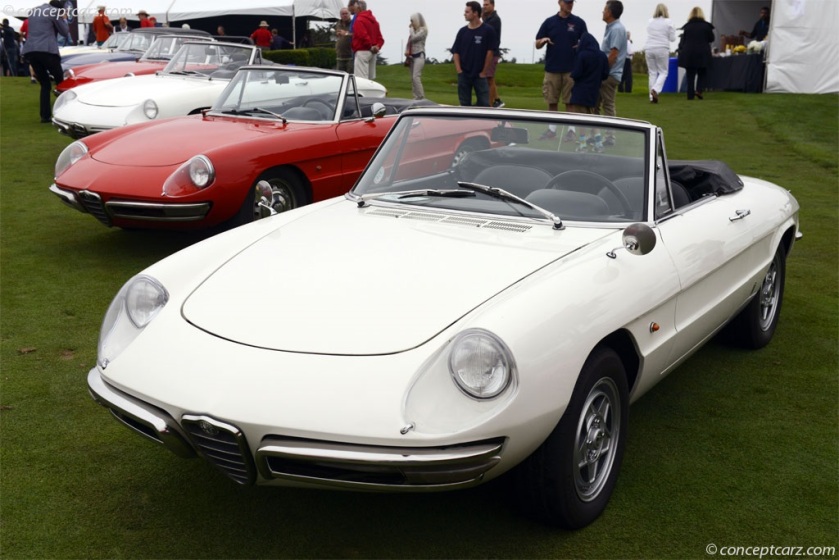 1967 Alfa Romeo 1600cc Duetto-white Pininfarina-DV-16-CI
1967 Alfa Romeo 1600cc Duetto-white Pininfarina-DV-16-CI 1968-72 Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Tubolare Zagato (TZ) Coupe by Pininfarina
1968-72 Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Tubolare Zagato (TZ) Coupe by Pininfarina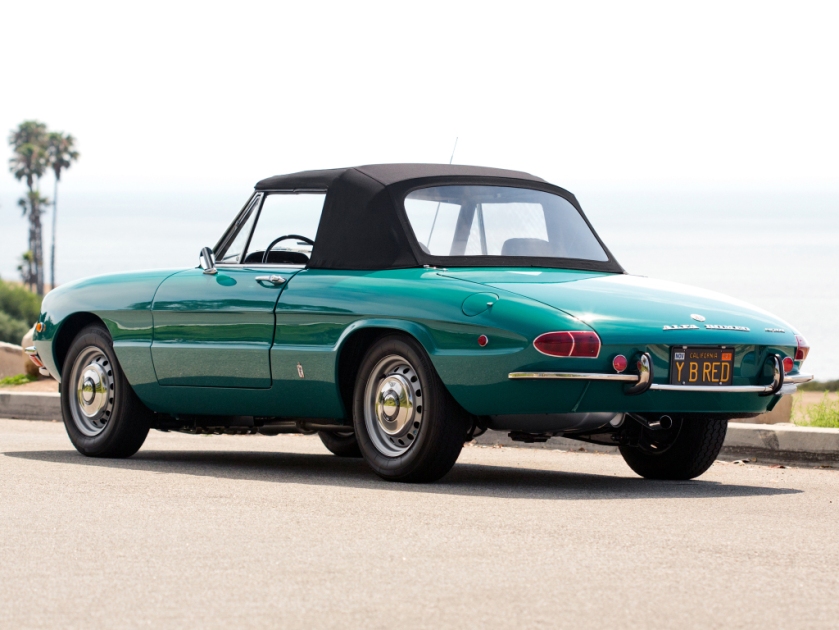 1968-70 Alfa Romeo 1750 Spider Veloce North America (105) designed by Pininfarina
1968-70 Alfa Romeo 1750 Spider Veloce North America (105) designed by Pininfarina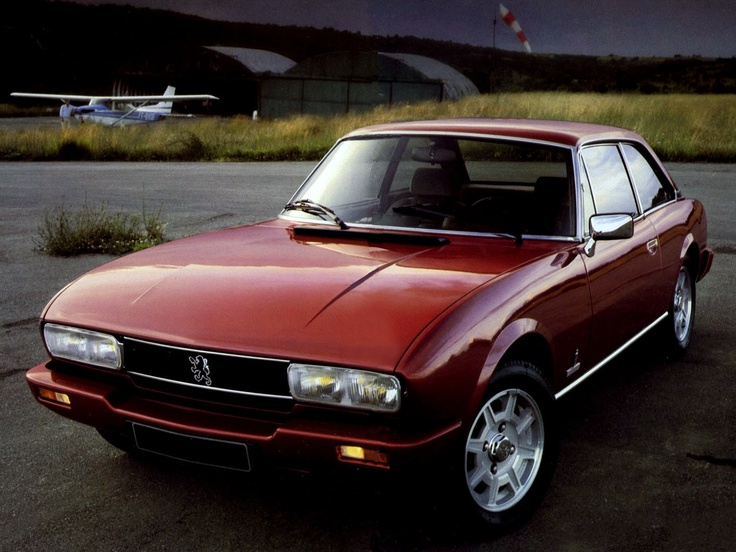 Peugeot 504 Coupé designed by Pininfarina
Peugeot 504 Coupé designed by Pininfarina Peugeot 504 Cabriolet designed by Pininfarina
Peugeot 504 Cabriolet designed by Pininfarina 1972 Ferrari 365 GTC 4 Pininfarina
1972 Ferrari 365 GTC 4 Pininfarina 1971-75 Lancia 2000 Pininfarina Berlina 1973 1991cc
1971-75 Lancia 2000 Pininfarina Berlina 1973 1991cc Ferrari 400 GT4 2+2 desined by Pininfarina
Ferrari 400 GT4 2+2 desined by Pininfarina Lancia Monte-Carlo Pininfarina
Lancia Monte-Carlo Pininfarina Peugeot-Talbot Samba Cabrio Design Pininfarina (Clássico)
Peugeot-Talbot Samba Cabrio Design Pininfarina (Clássico)
Fiat Campagniola ? 1986 Ferrari-Testarossa-Spider-by-Pininfarina
1986 Ferrari-Testarossa-Spider-by-Pininfarina 1984-86 Alfa Romeo 33 1.5 4×4 Giardinetta (905) designed by Pininfarina
1984-86 Alfa Romeo 33 1.5 4×4 Giardinetta (905) designed by Pininfarina ferrari-412 pininfarina
ferrari-412 pininfarina
 peugeot 205-cabriolet-pininfarina
peugeot 205-cabriolet-pininfarina 1990 Cadillac Allante 25 Pininfarina
1990 Cadillac Allante 25 Pininfarina 1987-93 CADILLAC Allante Cabriolet Pininfarina
1987-93 CADILLAC Allante Cabriolet Pininfarina Ferrari 456 GT Pininfarina
Ferrari 456 GT Pininfarina Pininfarina Ferrari 456GT Venice Convertible Brunei 16
Pininfarina Ferrari 456GT Venice Convertible Brunei 16 1993-00 Pininfarina designed Fiat Coupé 20v Turbo Model
1993-00 Pininfarina designed Fiat Coupé 20v Turbo Model 1993-02 peugeot 306 pininfarina designed cabriolet
1993-02 peugeot 306 pininfarina designed cabriolet Bentley Azure Mark I Convertible disigned by Pininfarina
Bentley Azure Mark I Convertible disigned by Pininfarina lancia kappa-sw-designed by pininfarina
lancia kappa-sw-designed by pininfarina Peugeot 406 Coupé designed by pininfarina
Peugeot 406 Coupé designed by pininfarina 2002 Mitsubishi Pajero Pinin ZR 5-door wagon
2002 Mitsubishi Pajero Pinin ZR 5-door wagon Alfa Romeo GTV & Spider 916 series designed by pininfarina
Alfa Romeo GTV & Spider 916 series designed by pininfarina HONDA ARGENTO VIVO BY PININFARINA
HONDA ARGENTO VIVO BY PININFARINA ford streetka designed by pininfarina
ford streetka designed by pininfarina pininfarina designed ford streetka
pininfarina designed ford streetka 2012 Pininfarina designed Alfa Romeo Brera Milan Design Week Superstudio in 2012
2012 Pininfarina designed Alfa Romeo Brera Milan Design Week Superstudio in 2012 2006 Alfa Spider VI Pininfarina
2006 Alfa Spider VI Pininfarina 2006 Alfa Romeo Spider VI Pininfarina with extracted roof
2006 Alfa Romeo Spider VI Pininfarina with extracted roof 2015 ford-focus-cabrio-render-pininfarina
2015 ford-focus-cabrio-render-pininfarina 2015 ford-focus-cabrio-render-pininfarina a
2015 ford-focus-cabrio-render-pininfarina a 2011 Volvo C70 II Pininfarina
2011 Volvo C70 II Pininfarina 2008 mitsubishi colt czc pininfarina
2008 mitsubishi colt czc pininfarina 2006-09 Pininfarina Mitsubishi Colt CZC
2006-09 Pininfarina Mitsubishi Colt CZC Lancia Beta Montecarlo pininfarina
Lancia Beta Montecarlo pininfarina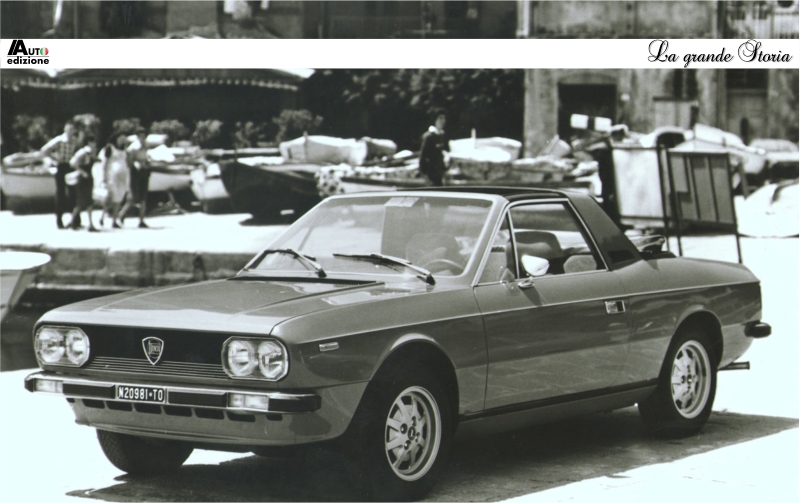 Lancia Beta Montecarlo cabrio pininfarina
Lancia Beta Montecarlo cabrio pininfarina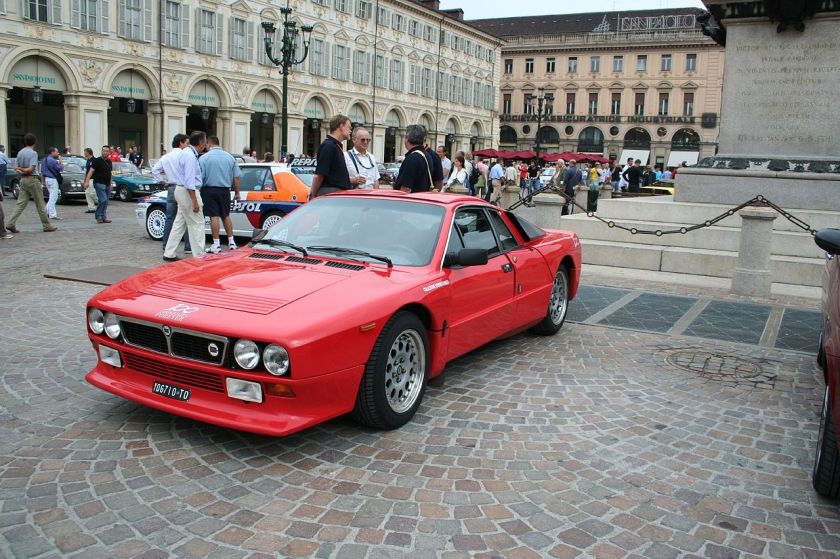 Pininfarina designed Lancia 037 en version stradale
Pininfarina designed Lancia 037 en version stradale 1975 Fiat 130 Coupe Pininfarina
1975 Fiat 130 Coupe Pininfarina Fiat Dino 2.0-pininfarina-coupe
Fiat Dino 2.0-pininfarina-coupe lancia gamma-coupe pininfarina
lancia gamma-coupe pininfarina 1934 Alfa Romeo 6C 2300 Pescara Touring Cabriolet
1934 Alfa Romeo 6C 2300 Pescara Touring Cabriolet
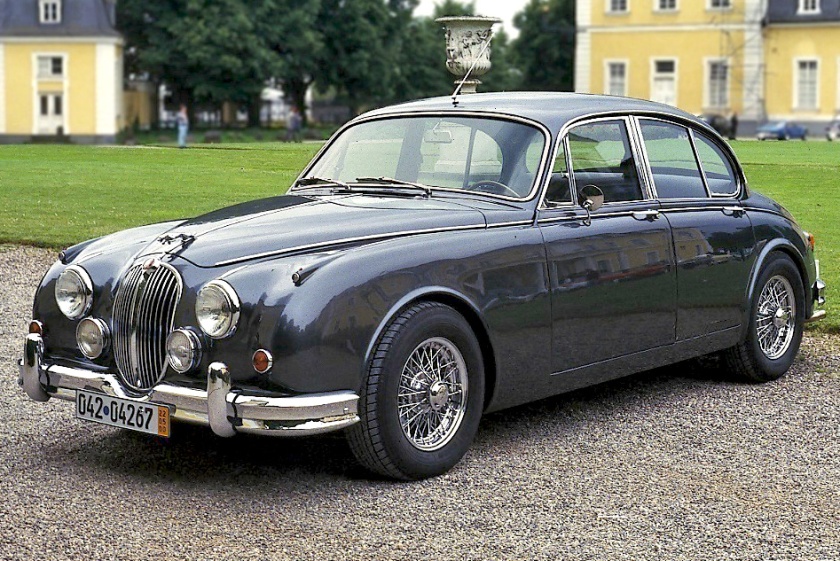
| Years | Model | Factory | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1946–1949 | Maserati A6 1500 Turismo | 107 Corso Trapani | 58 |
| 1947–1952 | Cisitalia 202 | 107 Corso Trapani | 170 |
| 1947–1951 | Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 Super Cabriolet | 107 Corso Trapani | 64 |
| 1948–1951 | Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 Super Sport Cabriolet | 107 Corso Trapani | 25-30 |
| 1948 | Maserati A6 1500 Spider | 107 Corso Trapani | 2 |
| 1950–1952 | Lancia Aurelia B50 Cabriolet | 107 Corso Trapani | 265 |
| 1950–1958 | Lancia Aurelia B20 Coupé | 107 Corso Trapani | 2,640 |
| 1952 | Alfa Romeo 1900 C Cabriolet | 107 Corso Trapani | 88 |
| 1952–1953 | Alfa Romeo 1900 C Coupé | 107 Corso Trapani | 100 |
| 1952–1953 | Ferrari 212 Inter cabriolet | 107 Corso Trapani | 2 |
| 1952–1953 | Ferrari 212 Inter coupé | 107 Corso Trapani | 11 |
| 1952–1953 | Lancia D20 coupé | 107 Corso Trapani | 7 |
| 1952–1954 | Nash-Healey | 107 Corso Trapani | 402 |
| 1953 | Ferrari 375 MM Spider | 107 Corso Trapani | 15 |
| 1953 | Lancia D23 Spyder | 107 Corso Trapani | 4 (re-bodied D20s) |
| 1953-1954 | Lancia D24 Spyder | 107 Corso Trapani | 6 |
| 1954–1957 | Fiat 1100 TV Coupé | 107 Corso Trapani | 126 |
| 1954–1955 | Lancia Aurelia B24 Spider America | 107 Corso Trapani | 240 |
| 1954 | Lancia D25 Spyder | 107 Corso Trapani | 4 (re-bodied D24s) |
| 1954 | Maserati A6 GCS/53 Berlinetta | 107 Corso Trapani | 4 |
| 1956 | Lancia Aurelia B24 Spider | 107 Corso Trapani | 521 |
| 1956–1958 | Alfa Romeo Giulietta Spider | 107 Corso Trapani | 5,493 |
| 1957–1959 | Lancia Appia Pininfarina Coupe 2 +2 Series II | – | 302 |
| 1958–1960 | Ferrari 250 GT Coupe Pininfarina | Grugliasco | 335 |
| 1959–1962 | Alfa Romeo Giulietta Spider | Grugliasco | 11,503 |
| 1959–1960 | Cadillac Eldorado Brougham | Grugliasco | 200 |
| 1959–1967 | Lancia Flaminia Coupé | Grugliasco | 5,236 |
| 1960–1963 | Ferrari 250 GTE 2+2 | Grugliasco | 955 including prototypes |
| 1961–1968 | Peugeot 404 Coupé and Cabriolet | Grugliasco | 17,223 ( 10,389 Cabriolets, 6,834 Coupés) |
| 1962–1971 | Lancia Flavia Coupé | Grugliasco | 26,084 |
| 1962–1965 | Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Spider | Grugliasco | 10,336 |
| 1963 | Ferrari 330 America | Grugliasco | 50 |
| 1964-1967 | Ferrari 330 GT 2+2 | Grugliasco | 1080 |
| 1966–1968 | Alfa Romeo Giulia Spider Duetto 1600 Spider | Grugliasco | 6,322 |
| 1966-1968 | Ferrari 330 GTC | Grugliasco | 604 |
| 1966-1968 | Ferrari 330 GTS | Grugliasco | 100 |
| 1966–1985 | Fiat 124 Sport Spider | Grugliasco | 198,120 |
| 1967 | Ferrari 330 GTC Coupe Speciale | Grugliasco | 3 |
| 1968–1972 | Alfa Romeo Giulia Spider 1300 and 1600 Junior | Grugliasco | 4,913 |
| 1968–1972 | Alfa Romeo 1750 Spider Veloce | Grugliasco | 8,920 |
| 1969–1983 | Peugeot 504 Coupé | Grugliasco | 22,975 |
| 1969–1983 | Peugeot 504 Cabriolet | Grugliasco | 8,191 |
| 1971–1972 | Ferrari 365 GTC/4 | Grugliasco | 505 |
| 1971–1975 | Lancia 2000 Coupé Berlina | Grugliasco | – |
| 1976–1985 | Ferrari 400 | Grugliasco | 1,808 |
| 1981–1984 | Lancia Beta Coupé HPE | Grugliasco | 18.917 |
| 1981–1985 | Peugeot Talbot Samba Cabriolet | Grugliasco | 13,062 |
| 1981–1986 | Fiat Campagnola | Grugliasco | 15,198 |
| 1984–1993 | Ferrari Testarossa | Grugliasco / San Giorgio | – |
| 1984–1986 | Alfa Romeo 33 Giardinetta | Grugliasco | 12,238 |
| 1985–1989 | Ferrari 412 & 412 GT | Grugliasco | 576 |
| 1984–1993 | Peugeot 205 Cabriolet | Grugliasco | 72,125 |
| 1986–1993 | Cadillac Allanté | San Giorgio Canavese | 21,430 |
| 1992–1996 | Ferrari 456 GT | – | 3289 |
| 1993–2000 | Fiat Coupé | – | 72,762 |
| 1993–2002 | Peugeot 306 Cabriolet | San Giorgio Canavese | – |
| 1996–1999 | Bentley Azure Mark I Convertible | – | 895 |
| 1996–2000 | Lancia Kappa SW | – | 9,208 |
| 1996–2004 | Peugeot 406 Coupé | San Giorgio Canavese | 107,633 |
| 1999–2005 | Mitsubishi Pajero Pinin | Bairo Canavese and Grugliasco | 68,555 |
| 2000–2004 | Alfa Romeo GTV & Spider 916 series | San Giorgio Canavese | 15,788 |
| 2002 | Honda Pininfarina Argento Vivo | – | 4–5 |
| 2002–2005 | Ford Streetka | Bairo Canavese | 37,076 |
| 2005–2010 | Alfa Romeo Brera | San Giorgio Canavese | 21,786 |
| 2006–2010 | Alfa Romeo Spider | San Giorgio Canavese | 12,488 |
| 2006–2010 | Ford Focus Coupé Cabriolet | Bairo Canavese | 36,374 |
| 2006–2013 | Volvo C70 II | Uddevalla, Sweden | – |
| 2006–2008 | Mitsubishi Colt CZC | Bairo Canavese | 16,695 |
| 1974–1981 | Lancia Beta Montecarlo Cabrio | Grugliasco | 4,375 |
| 1975–1981 | Lancia Beta Montecarlo Coupé | Grugliasco | 3,203 |
| 1981 | Lancia 037 | Grugliasco | 220 |
| 1971–1976 | Fiat 130 Coupé | Grugliasco | 4,491 |
| 1966–1972 | Fiat Dino Spider | Grugliasco | 1,583 |
| 1976–1984 | Lancia Gamma Coupé | Grugliasco | 6,790 |
Notable car designs
 1961 Fiat 2300 Pininfarina
1961 Fiat 2300 Pininfarina 1982 Rolls-Royce Camargue
1982 Rolls-Royce Camargue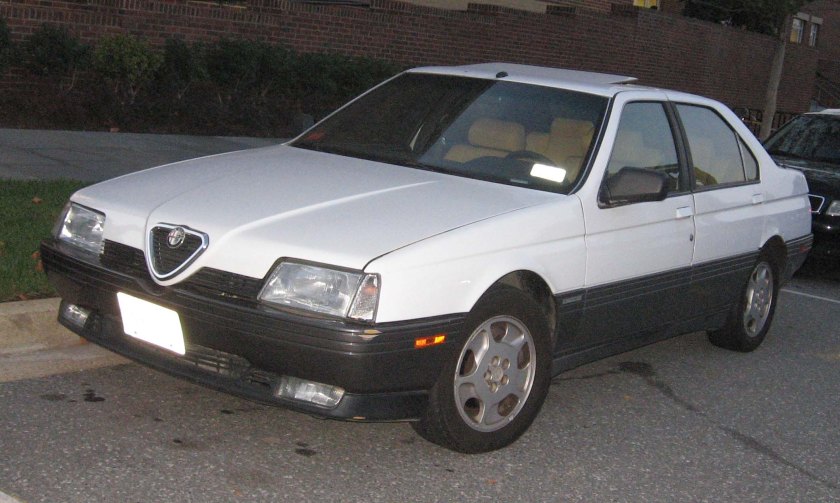 1987 Alfa Romeo 164
1987 Alfa Romeo 164Pre World War II
Before the war Pininfarina built car bodies mostly for individual customers, many of the bodies were “one offs” and not mass-produced.
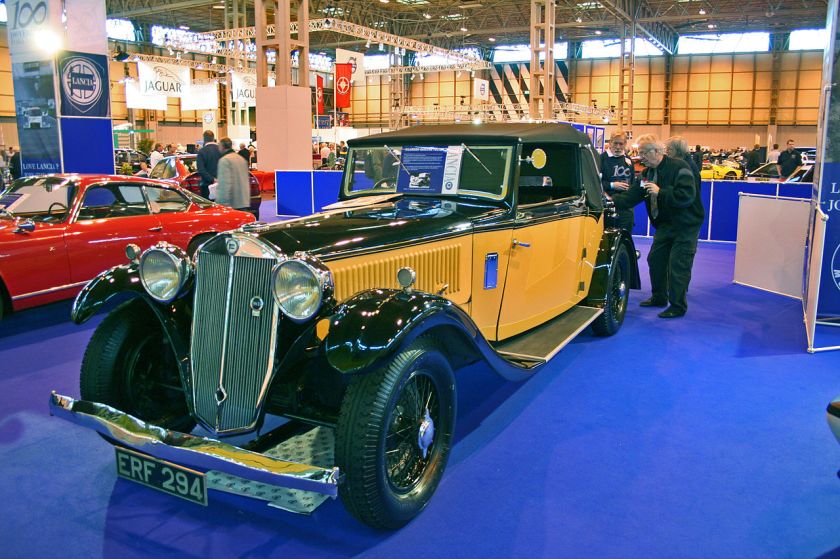 1931 Lancia Dilambda – the first official Pinin Farina special, presented at the Concours d’Elegance at Villa d’Este
1931 Lancia Dilambda – the first official Pinin Farina special, presented at the Concours d’Elegance at Villa d’Este 1931 Hispano Suiza H6C Coupé Chauffeur
1931 Hispano Suiza H6C Coupé Chauffeur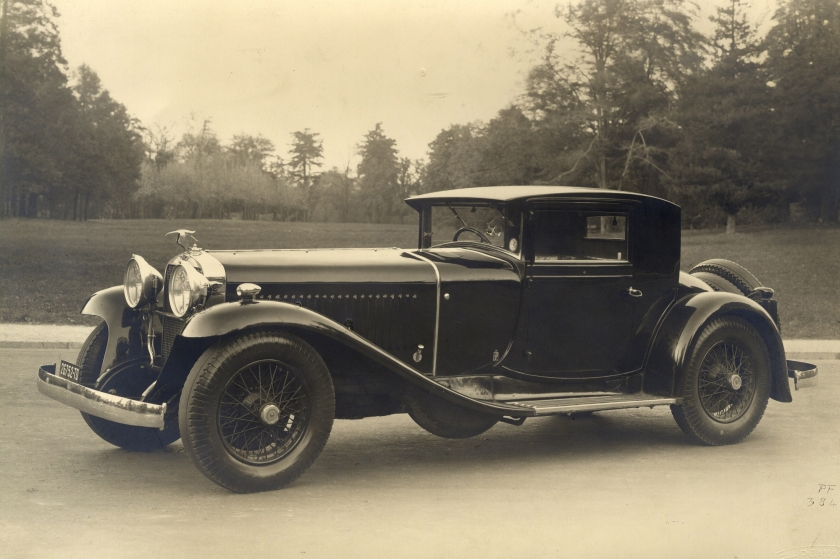 1931 Hispano Suiza Pinin Farina Coupé 1931 Hispano Suiza Coupé
1931 Hispano Suiza Pinin Farina Coupé 1931 Hispano Suiza Coupé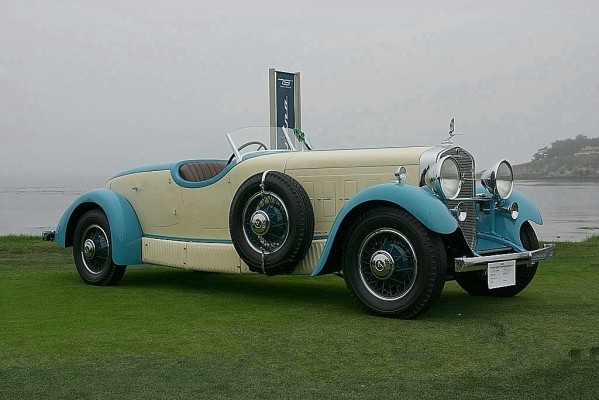  1931 Cadillac V16 Roadster – for the Maharajah of Orccha
1931 Cadillac V16 Roadster – for the Maharajah of Orccha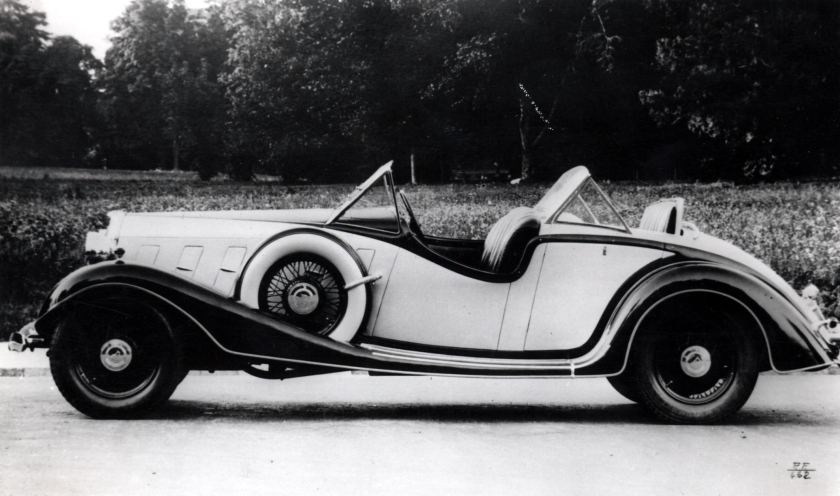 1932 Fiat 518 Ardita designed by Pininfarina 1932 Fiat 518 Ardita
1932 Fiat 518 Ardita designed by Pininfarina 1932 Fiat 518 Ardita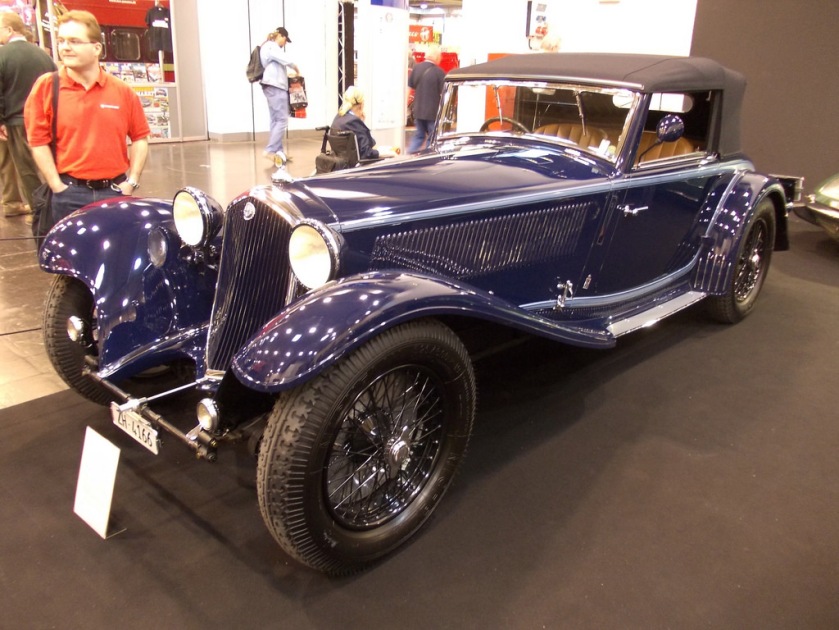 1933 Alfa Romeo 8C 2300 Cabriolet (Pininfarina)1933 Alfa Romeo 8C 2300
1933 Alfa Romeo 8C 2300 Cabriolet (Pininfarina)1933 Alfa Romeo 8C 2300 1934 Alfa-Romeo-6C-2500-S-Stabilimenti-Farina-Cabriolet-14751 1934 Alfa Rome 6C 2300 B Cabriolet
1934 Alfa-Romeo-6C-2500-S-Stabilimenti-Farina-Cabriolet-14751 1934 Alfa Rome 6C 2300 B Cabriolet 1936 Lancia Astura Cabriolet tipo Bocca – a series of six cars made for the Bocca brothers, Lancia dealers in Biella, Italy – designed by Pininfarina
1936 Lancia Astura Cabriolet tipo Bocca – a series of six cars made for the Bocca brothers, Lancia dealers in Biella, Italy – designed by Pininfarina 1935 alfa romeo 6C 2300 pescara coupe aerodinamico pininfarina 1935 Alfa Romeo 6C Pescara Coupé aerodinamico
1935 alfa romeo 6C 2300 pescara coupe aerodinamico pininfarina 1935 Alfa Romeo 6C Pescara Coupé aerodinamico 1936-39 Lancia Aprilia was manufactured by Lancia, one of the first designed using wind tunnel in collaboration with Battista Farina 1936 Lancia Aprilia
1936-39 Lancia Aprilia was manufactured by Lancia, one of the first designed using wind tunnel in collaboration with Battista Farina 1936 Lancia Aprilia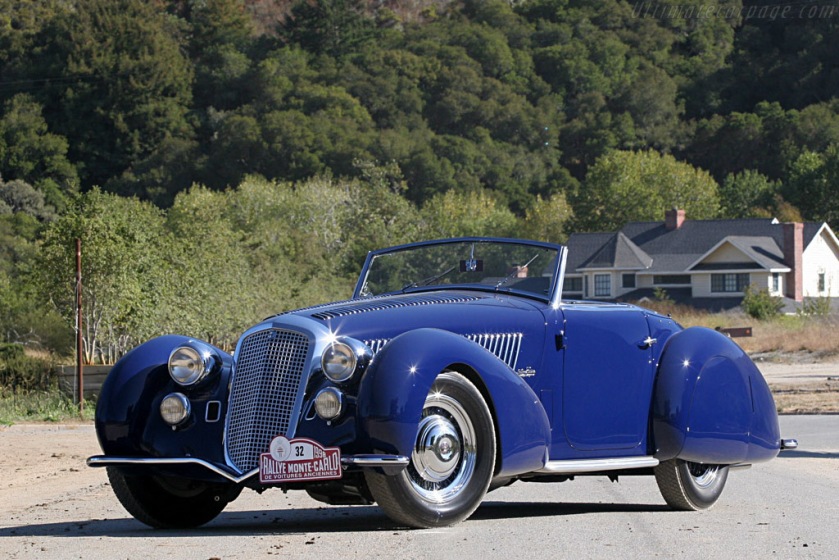 1936 Alfa-Romeo-8C-2900B-Stabilimenti-Farina-Cabriolet-25684 1936 Alfa Romeo 8C 2900
1936 Alfa-Romeo-8C-2900B-Stabilimenti-Farina-Cabriolet-25684 1936 Alfa Romeo 8C 2900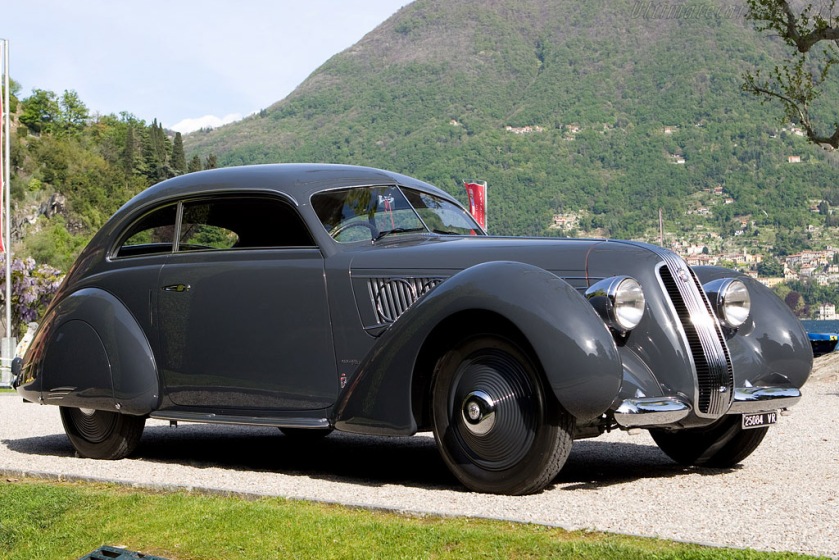 1937 Alfa-Romeo-6C-2300-B-Pescara-Pinin-Farina-Berlinetta 1937 Alfa Romeo 6C 2300-B Pescara Berlinetta
1937 Alfa-Romeo-6C-2300-B-Pescara-Pinin-Farina-Berlinetta 1937 Alfa Romeo 6C 2300-B Pescara Berlinetta 1937 Lancia Aprilia Aerodinamica Pininfarina
1937 Lancia Aprilia Aerodinamica Pininfarina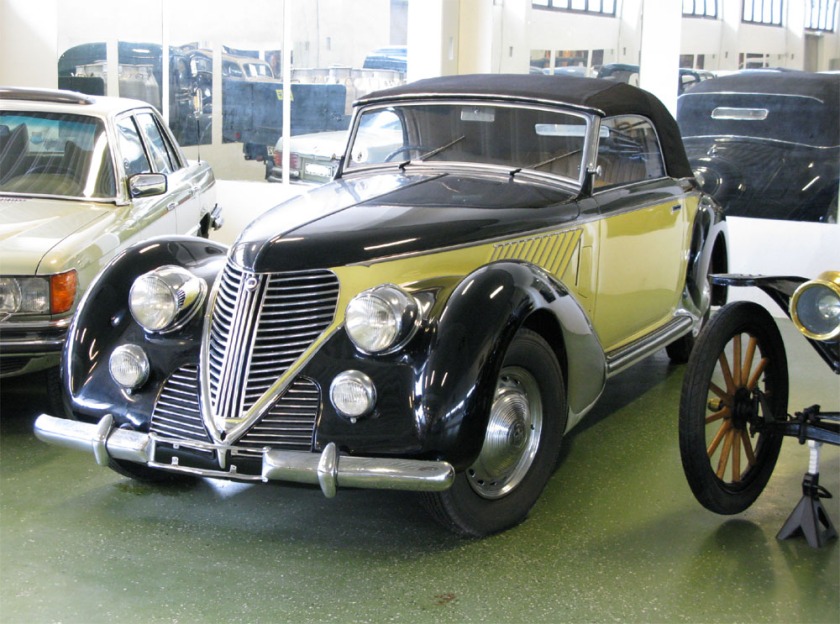
1938 Lancia Astura PF Convertible Front Laganland Bilmuseum, Sweden 1938 Lancia Astura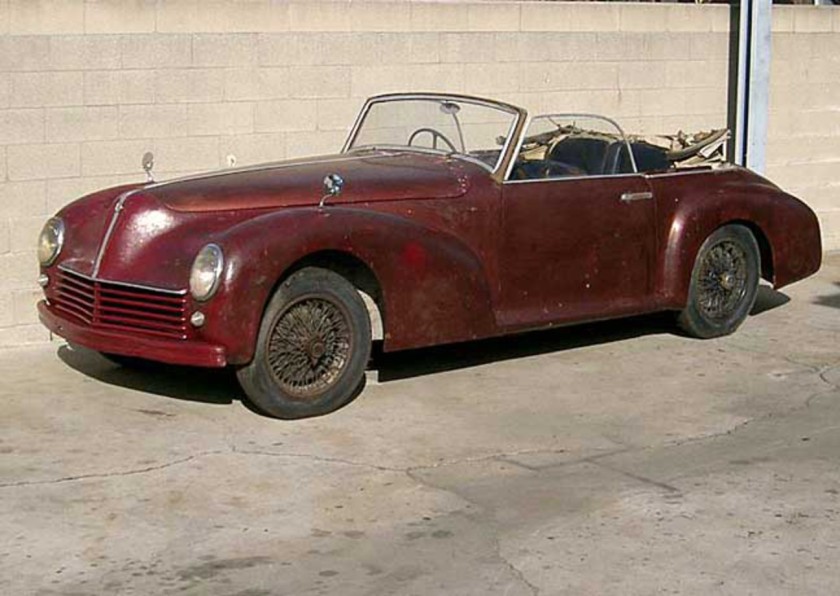 1943 Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 Super Sport Pinin Farina Cabriolet
1943 Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 Super Sport Pinin Farina Cabriolet
Concept cars, Prototypes and Individual commissions
In addition to production vehicles, Pininfarina creates prototype, show, and custom cars for auto manufacturers, as well as private clients. Most prototypes—such as the Ferrari Mythos—have served solely as concept cars, although several have become production models, including the Ferrari 612 Scaglietti and Ferrari F50.
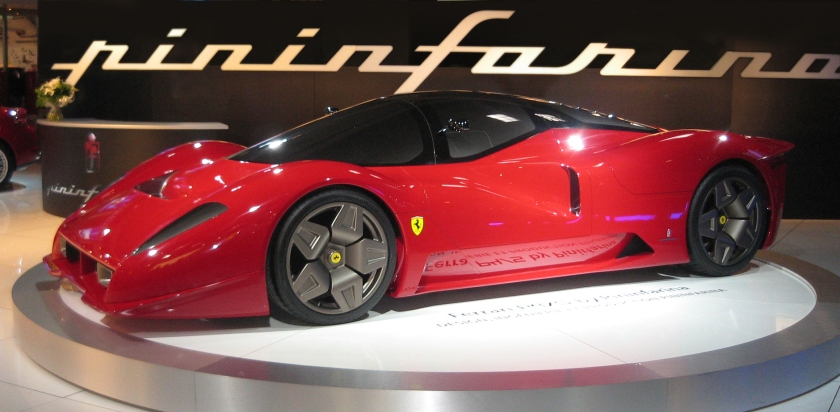
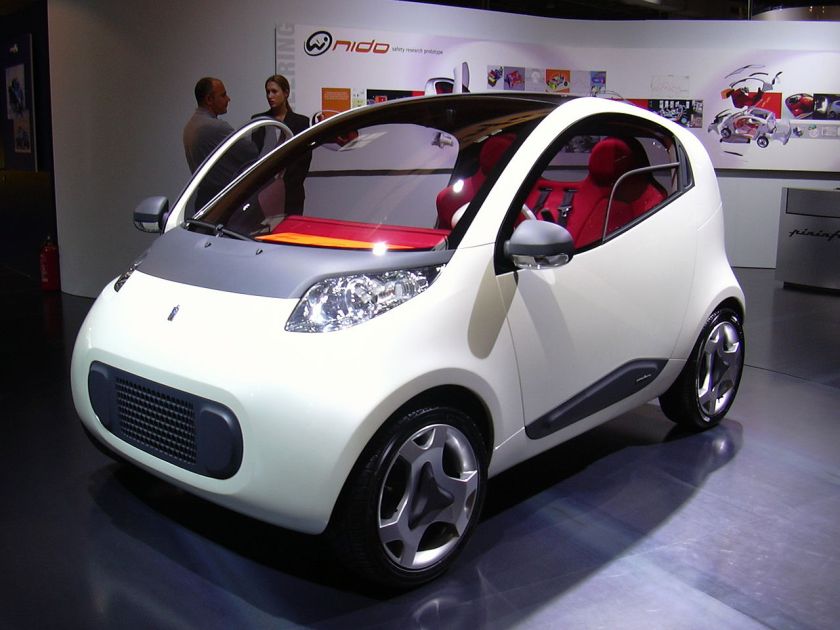
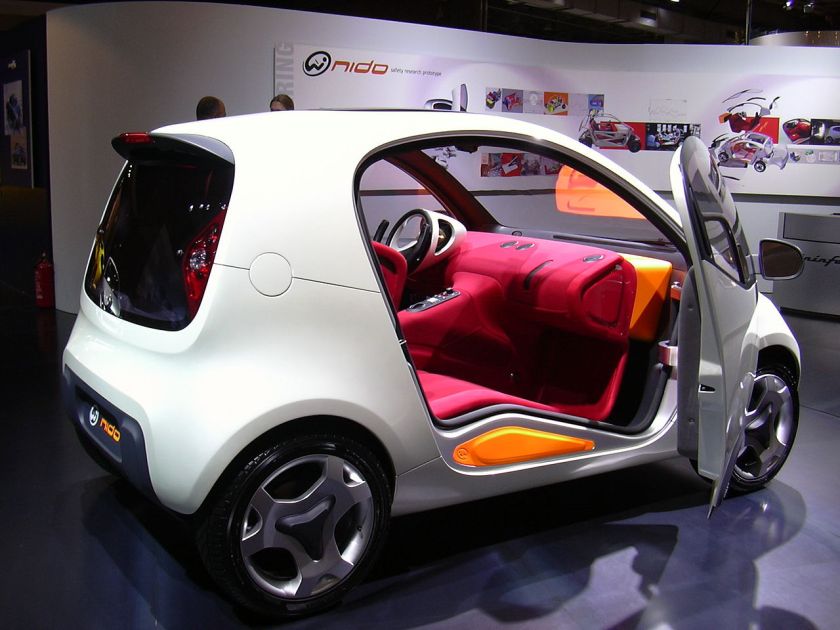
A recent privately commissioned custom example was the Ferrari P4/5 of 2006, a one-car rebody (changing the exterior design) of the Enzo Ferrari according to the client’s specifications. Its design began in September 2005 with sketches by Jason Castriota moving through computer aided sculpture and stringent wind tunnel testing. More than 200 components were designed especially for the car though the engine, drivetrain and many other components are simply modified from the original Enzo Ferrari. The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is unchanged from the Enzo it was derived from. The P4/5 was publicly revealed on August 18, 2006 at the Pebble Beach Concours d’Elegance and shown again at the Paris Motor Show in late September. Another recent prototype is the Pininfarina Nido, a two-seater sub-compact that could possibly make airbags obsolete.
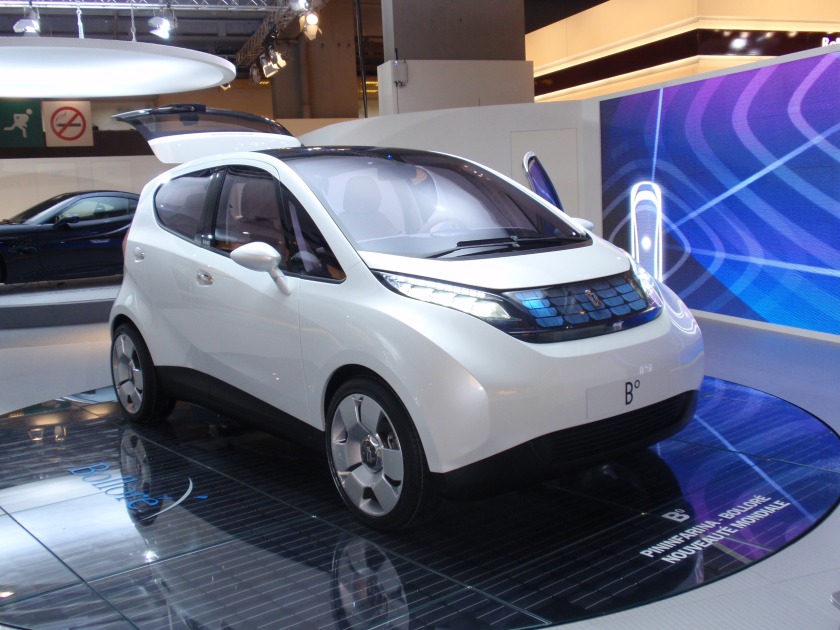
The Pininfarina B0 solar-electric concept, designed with Bolloré was shown at the 2008 Paris Motor Show featuring a range between charges of more than 150 miles (241 km) with an electronically limited 88-mile-per-hour (142 km/h) top speed, and an estimated acceleration to 37 miles per hour (60 km/h) in 6.3 seconds. The car has solar panels on the roof and on the nose, while its battery pack is said to last up to 125,000 miles (201,168 km).
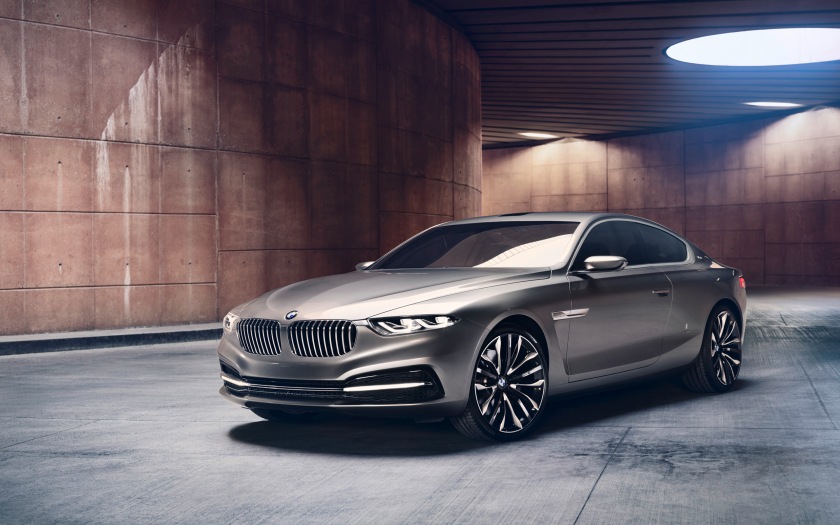
On May 15, 2013 Pininfarina announced the BMW Pininfarina Gran Lusso Coupé to be revealed on May 24 at the Concorso d’Eleganza Villa d’Este. Pininfarina announced this one-off concept car as the first collaboration between BMW and Pininfarina, but in 1949 BMW commissioned Pininfarina design and build a prototype of the BMW 501—it was rejected for being too modern.
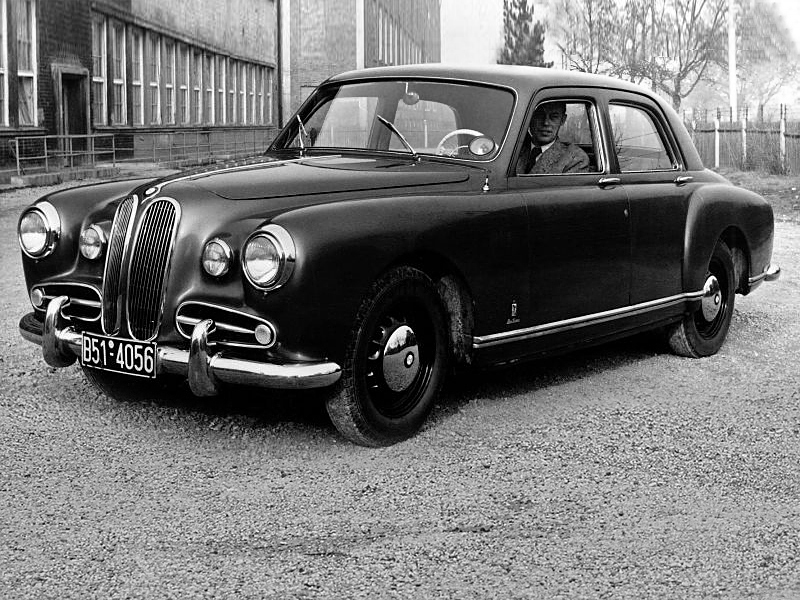
 1949 bmw-501-prototype-1949-designed-by-pininfarina 1949 BMW 501
1949 bmw-501-prototype-1949-designed-by-pininfarina 1949 BMW 501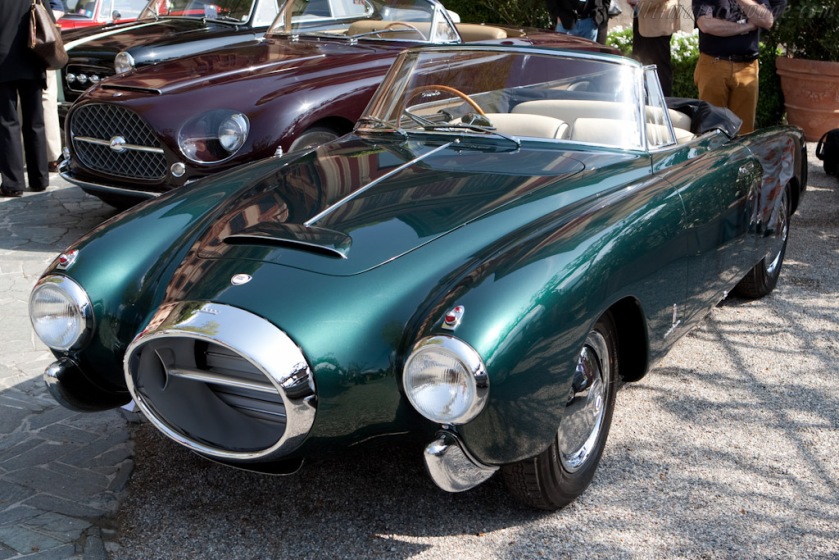 1952 Lancia-Aurelia-B52-PininFarina200-Cabriolet 1952 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 spider –version 1
1952 Lancia-Aurelia-B52-PininFarina200-Cabriolet 1952 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 spider –version 1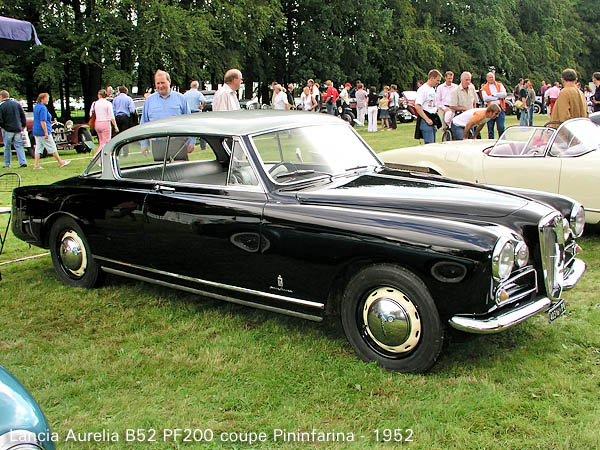 1952 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 coupé –version 1
1952 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 coupé –version 1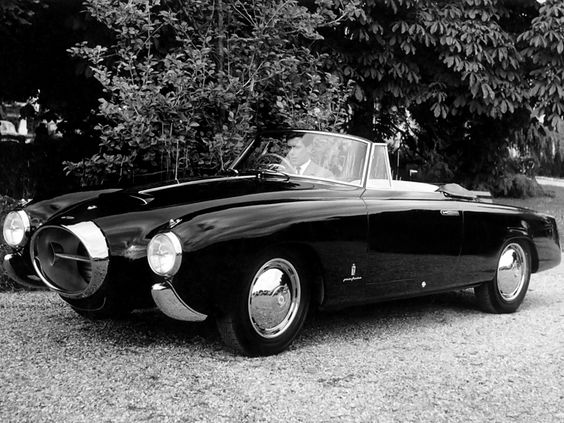 1953 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 spider –version 2 and 3
1953 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 spider –version 2 and 3

 1954 Cadillac Series 62 PF -built for Norman Granz
1954 Cadillac Series 62 PF -built for Norman Granz 1954 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 coupé –version 2
1954 Lancia Aurelia B52 PF 200 coupé –version 2 1955 Ferrari 375MM Speciale DV PalmBeach Pininfarina design
1955 Ferrari 375MM Speciale DV PalmBeach Pininfarina design 1955 Ferrari 375-America Speciale Designed by Pininfarina 1955 Ferrari 375 America Coupé Speciale
1955 Ferrari 375-America Speciale Designed by Pininfarina 1955 Ferrari 375 America Coupé Speciale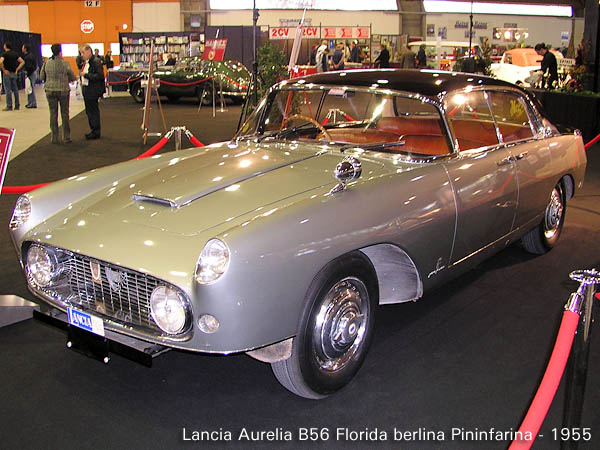
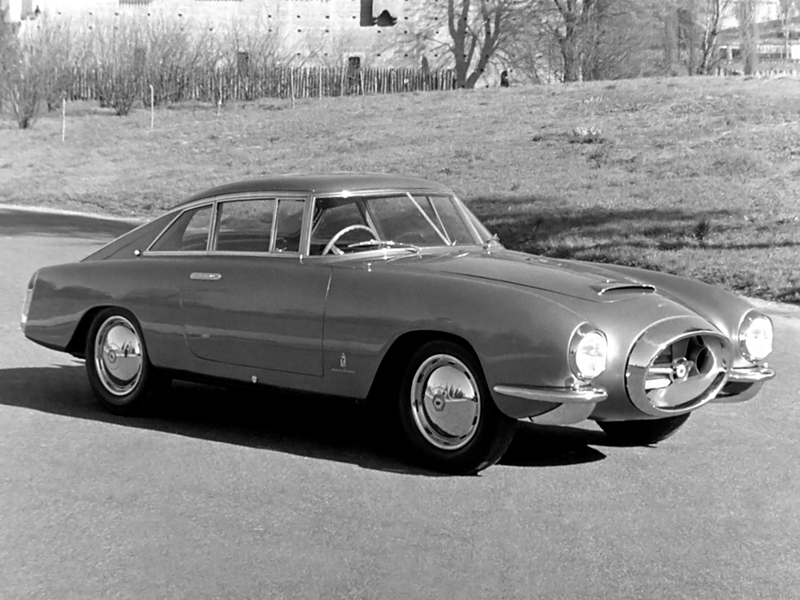 1955 lancia aurelia b55 pf200 coupe pininfarina 1955 Lancia Aurelia B55 PF 200 coupé –version 3
1955 lancia aurelia b55 pf200 coupe pininfarina 1955 Lancia Aurelia B55 PF 200 coupé –version 3 1955 Nash Pininfarina Special 1955 Nash Special
1955 Nash Pininfarina Special 1955 Nash Special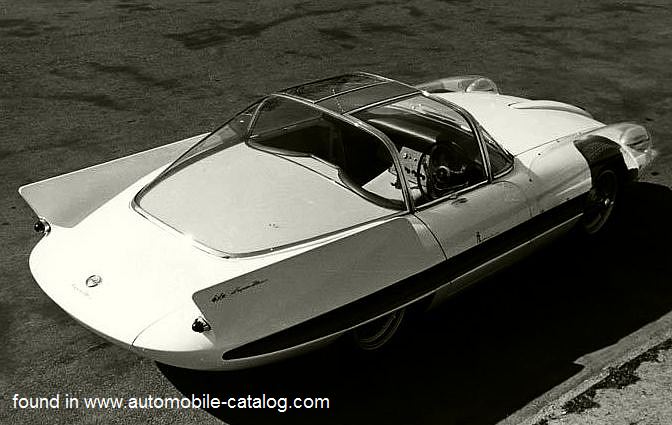 1956 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow Coupe I
1956 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow Coupe I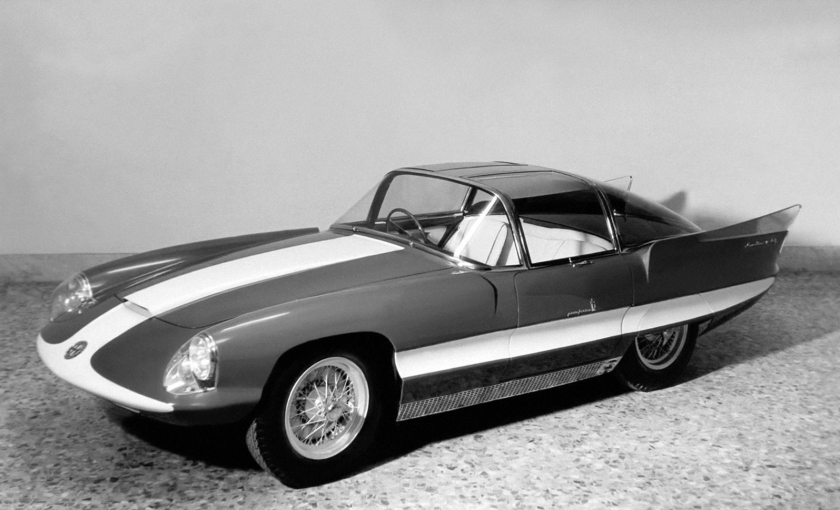 1956 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow II Coupe Pininfarina
1956 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow II Coupe Pininfarina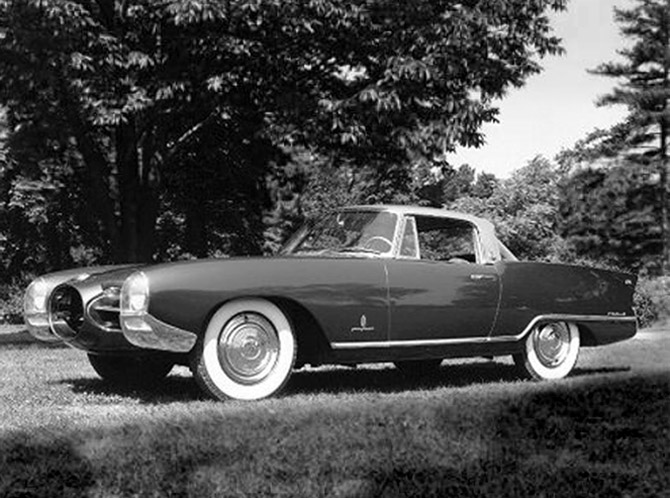 1956 PininFarina Nash Rambler Palm Beach Coupe Special D-12575 1956 Rambler Palm Beach
1956 PininFarina Nash Rambler Palm Beach Coupe Special D-12575 1956 Rambler Palm Beach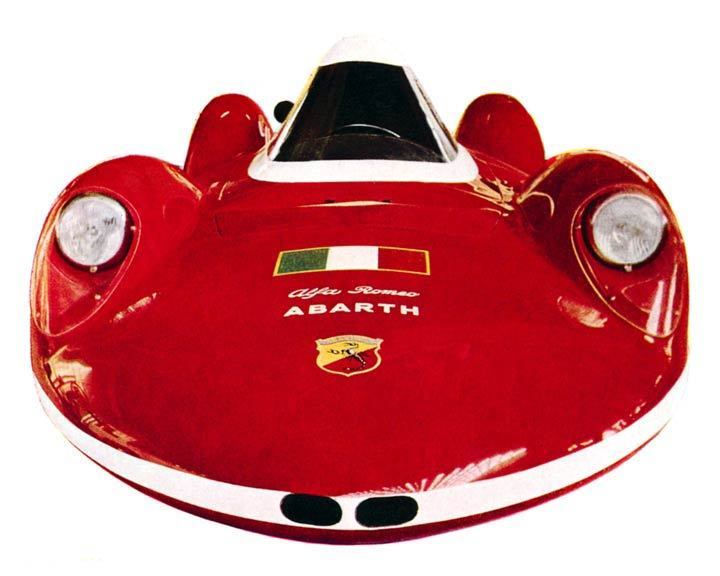 1957 Fiat Abarth 750 Pininfarina Record Car Photo 1957 Abarth 750 Bialbero Record
1957 Fiat Abarth 750 Pininfarina Record Car Photo 1957 Abarth 750 Bialbero Record
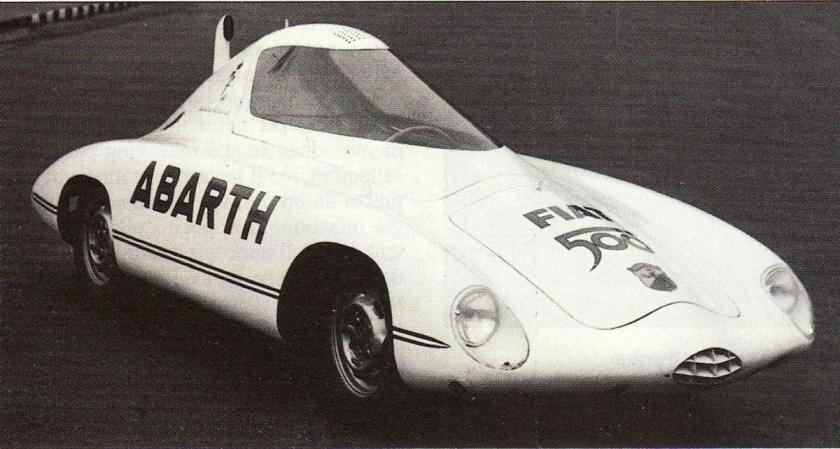
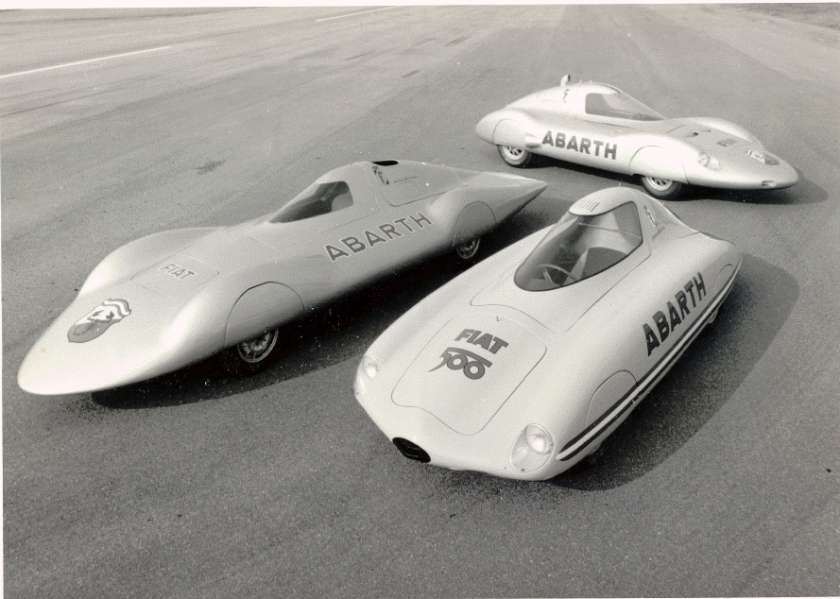

 1957 Abarth 500 750 1000 Coupe
1957 Abarth 500 750 1000 Coupe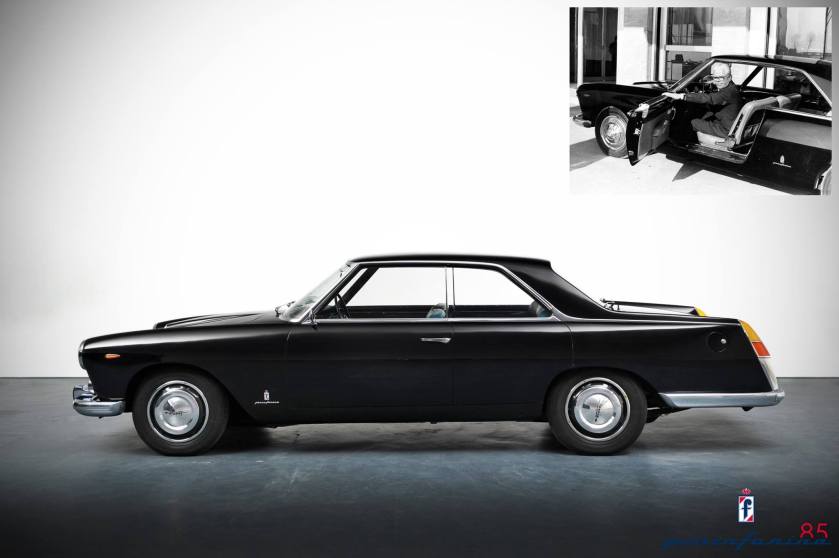 1957 Lancia Florida
1957 Lancia Florida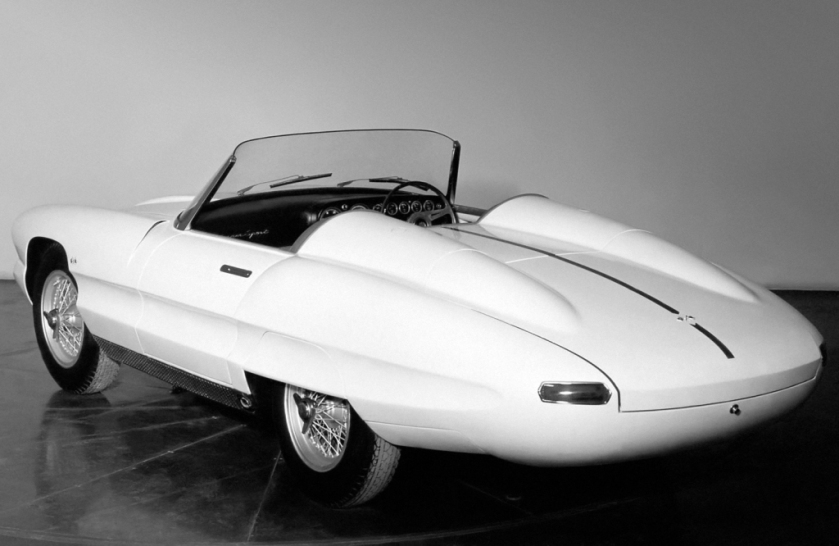 1959 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Spyder Super Sport
1959 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Spyder Super Sport
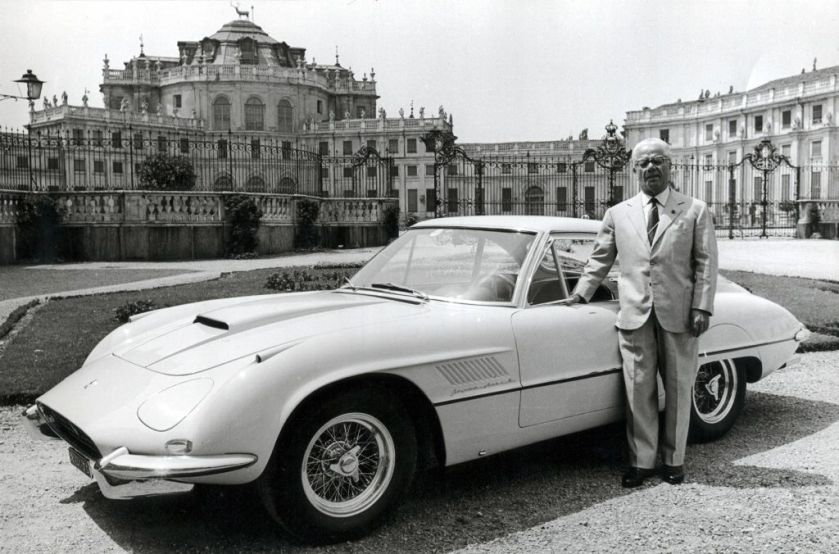 1960 Ferrari Superamerica Superfast 2
1960 Ferrari Superamerica Superfast 2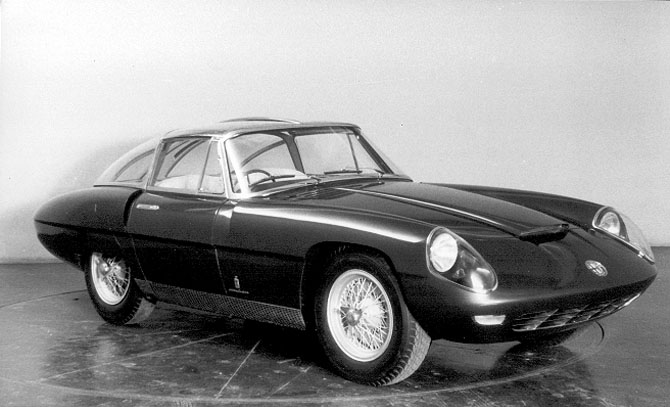 1960 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow IV Coupe Pininfarina
1960 Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow IV Coupe Pininfarina
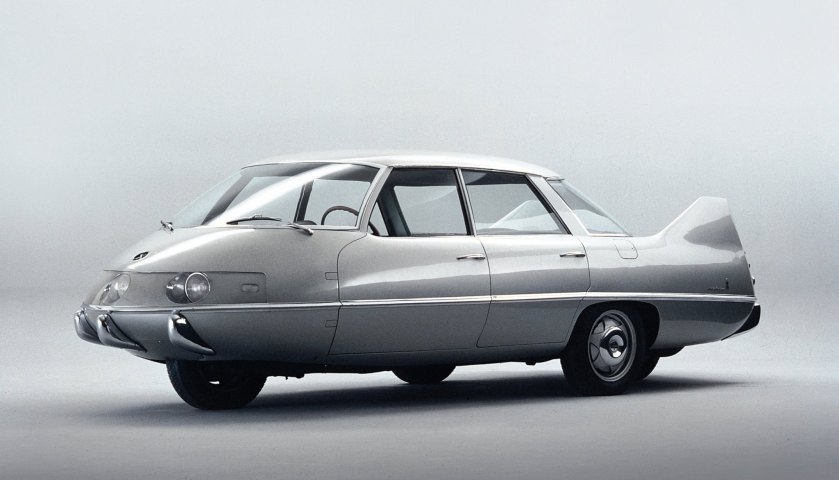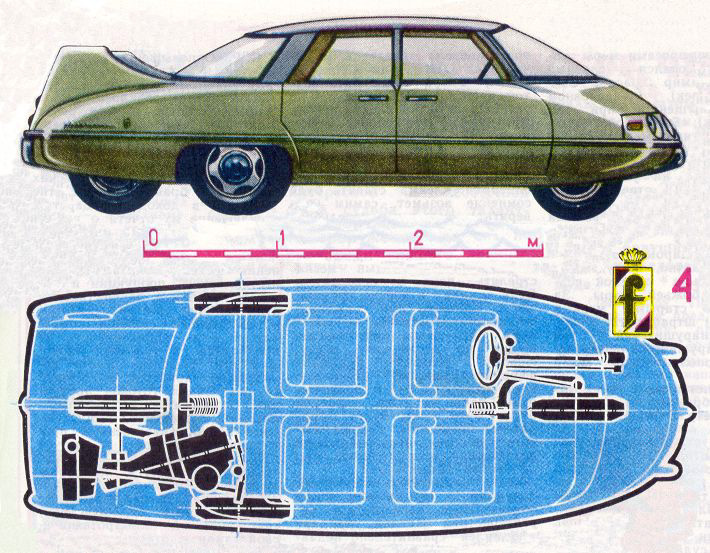
 1960 Pininfarina X
1960 Pininfarina X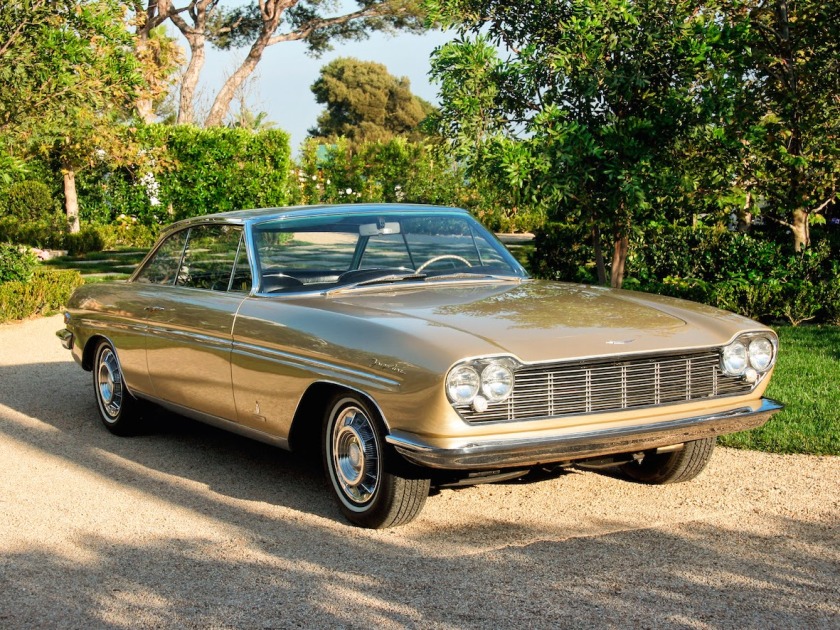 1961 Pininfarina Cadillac Brougham ‘Jacqueline’ Coupe 1961 Cadillac “Jacqueline” Brougham Coupé (named after Jacqueline Kennedy)
1961 Pininfarina Cadillac Brougham ‘Jacqueline’ Coupe 1961 Cadillac “Jacqueline” Brougham Coupé (named after Jacqueline Kennedy)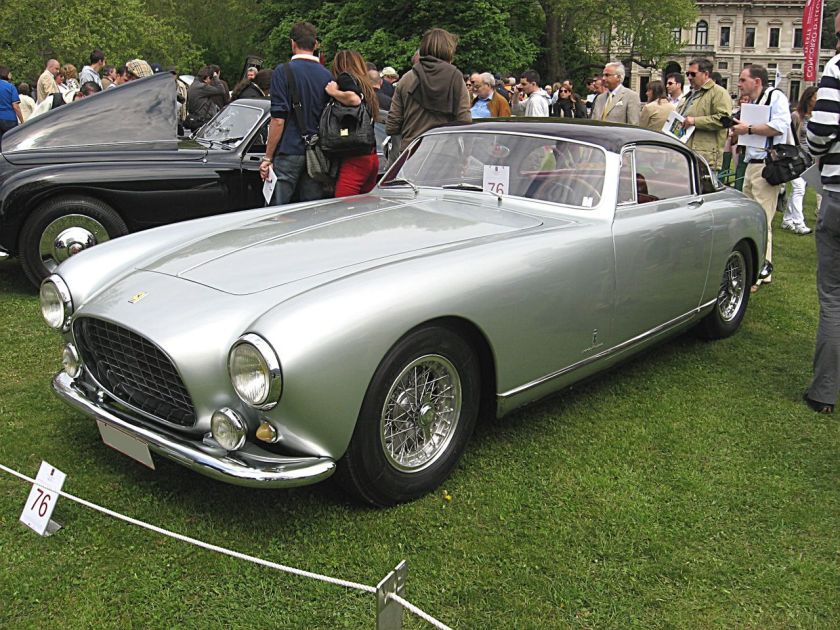 1961 Ferrari 250 GT Pininfarina Coupe Speciale
1961 Ferrari 250 GT Pininfarina Coupe Speciale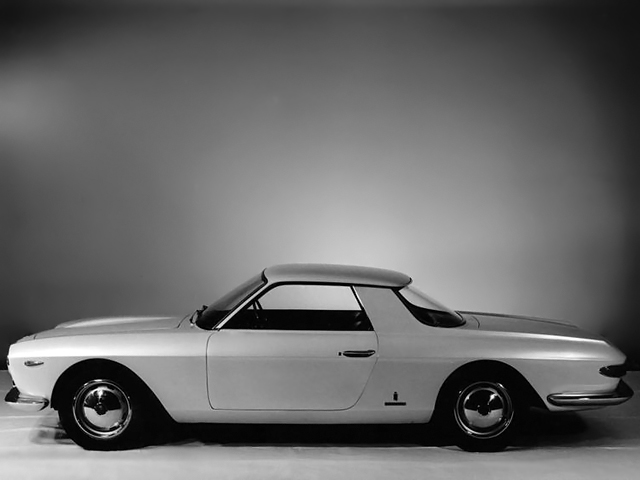 1962 Speciale designed by Pininfarina · Fiat 2300 Coupe 1962 Fiat 2300 Coupe Speciale
1962 Speciale designed by Pininfarina · Fiat 2300 Coupe 1962 Fiat 2300 Coupe Speciale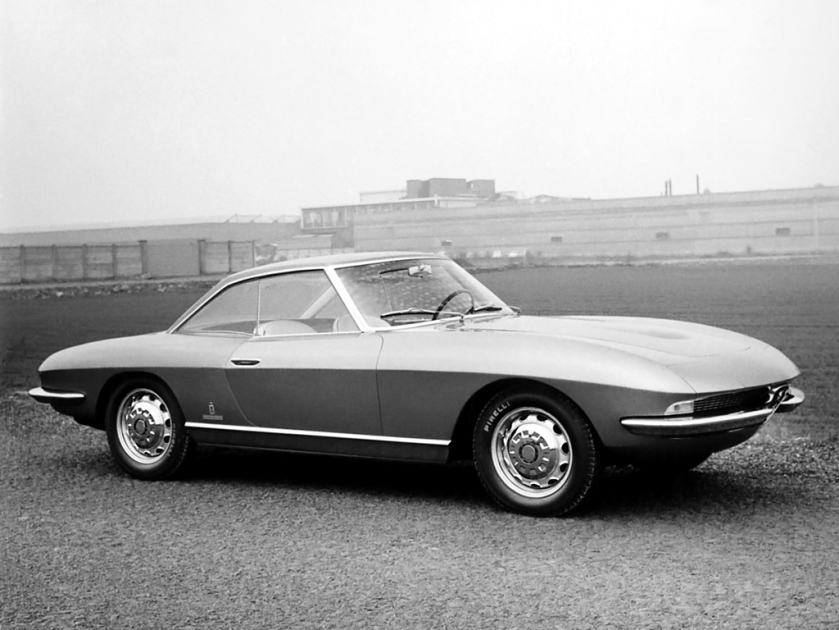 1963 Alfa Romeo 2600 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1963 Alfa Romeo 2600 Coupe Speciale
1963 Alfa Romeo 2600 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1963 Alfa Romeo 2600 Coupe Speciale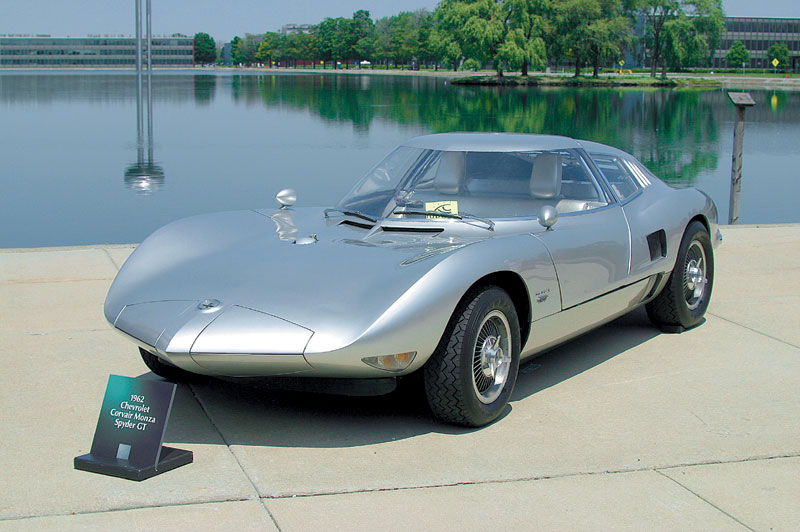 1963 Chevrolet Corvair Super Spyder Coupé Monza GT.1 designed by Pininfarina 1963 Chevrolet Corvair Super Spyder Coupé (2 built)
1963 Chevrolet Corvair Super Spyder Coupé Monza GT.1 designed by Pininfarina 1963 Chevrolet Corvair Super Spyder Coupé (2 built)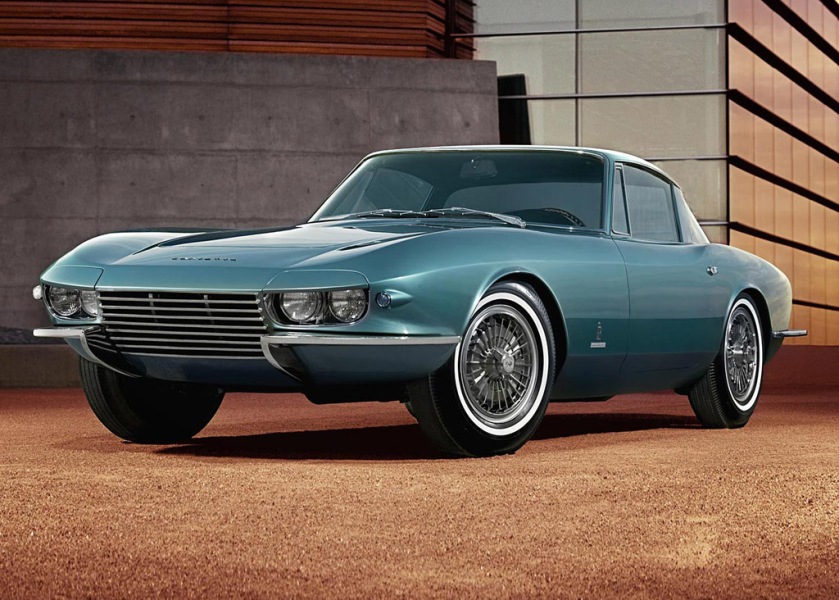 1963 Pininfarina Chevrolet Corvette Rondine Coupé
1963 Pininfarina Chevrolet Corvette Rondine Coupé 1963 Fiat 2300 Cabriolet Speciale Pininfarina 1963 Fiat 2300 Cabriolet Speciale
1963 Fiat 2300 Cabriolet Speciale Pininfarina 1963 Fiat 2300 Cabriolet Speciale 1963 Pininfarina Fiat 2300 S Speciale Lausanne Coupe 1963 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale Lausanne
1963 Pininfarina Fiat 2300 S Speciale Lausanne Coupe 1963 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale Lausanne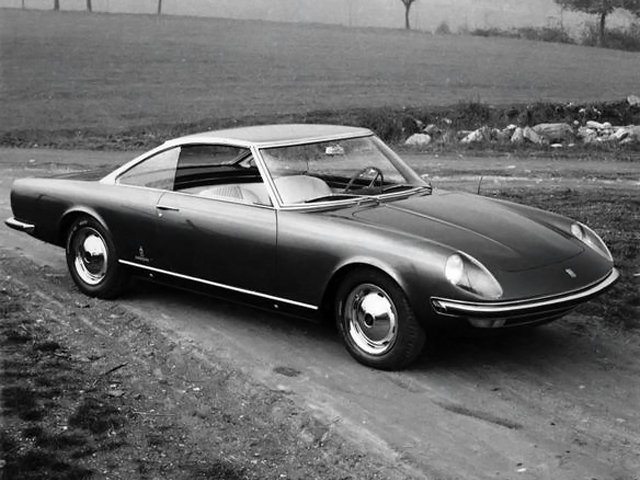 1964 Pininfarina Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale 1964 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale
1964 Pininfarina Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale 1964 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale 1963 Pininfarina PF Sigma 1963 Pininfarina PF Sigma
1963 Pininfarina PF Sigma 1963 Pininfarina PF Sigma 1963 Mercedes-Benz 230 SL Coupe (Pininfarina) 1963 Mercedes-Benz 230SL concept car (“Pininfarina Coupé”)
1963 Mercedes-Benz 230 SL Coupe (Pininfarina) 1963 Mercedes-Benz 230SL concept car (“Pininfarina Coupé”) 1964 Abarth 1000 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina)
1964 Abarth 1000 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1964 Abarth 1000 Spider (Pininfarina) 1964 Abarth 1000 Spyder
1964 Abarth 1000 Spider (Pininfarina) 1964 Abarth 1000 Spyder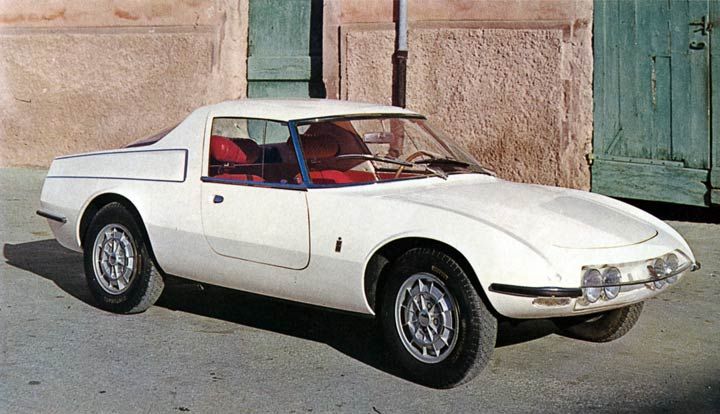 1965 Pininfarina Abarth 1000 Coupe Speciale 1965 Abarth 1000 Coupe Speciale
1965 Pininfarina Abarth 1000 Coupe Speciale 1965 Abarth 1000 Coupe Speciale 1965 Pininfarina Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Sport Tubolare 1965 Alfa Romeo Giulia Sport Tubolare
1965 Pininfarina Alfa Romeo Giulia 1600 Sport Tubolare 1965 Alfa Romeo Giulia Sport Tubolare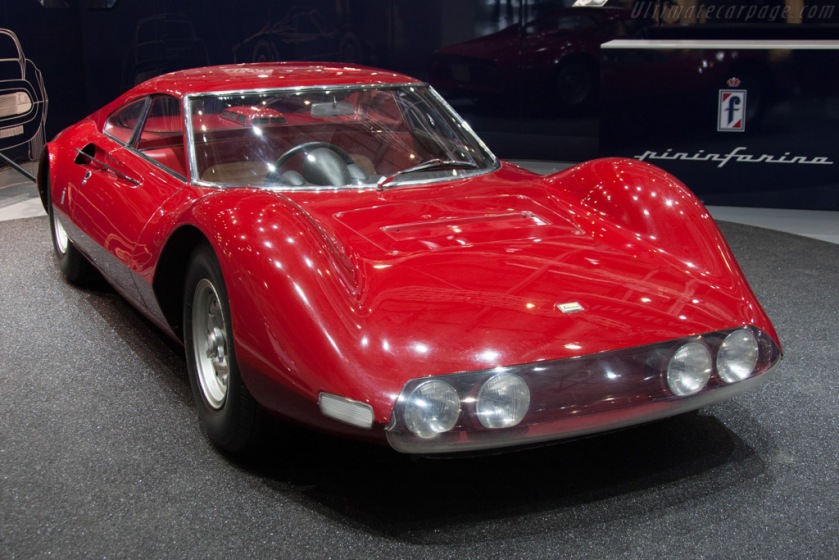 1965 Ferrari-206-P-Dino-Pininfarina-Berlinetta-Speciale 1965 Ferrari Dino 206 Berlinetta Speciale
1965 Ferrari-206-P-Dino-Pininfarina-Berlinetta-Speciale 1965 Ferrari Dino 206 Berlinetta Speciale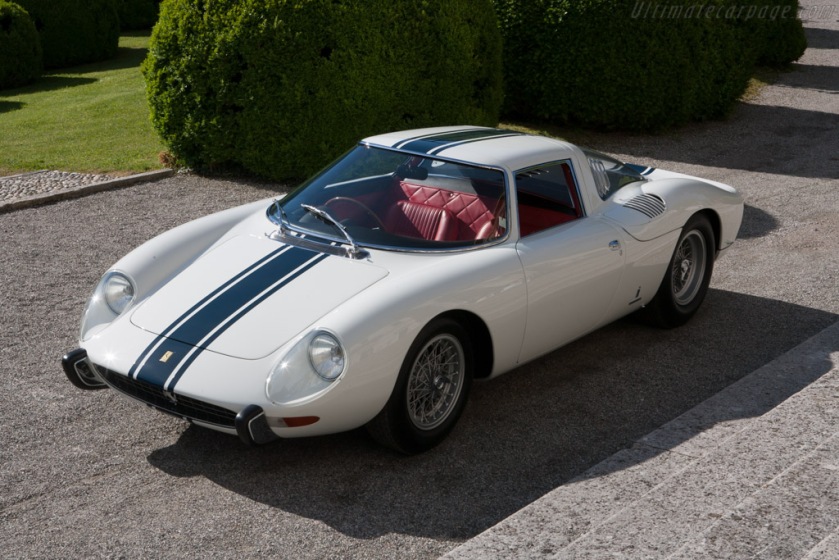 1965 Ferrari-250-LM-Pininfarina-Stradale-Speciale 1965 Ferrari 250 LM Pininfarina Stradale Speciale
1965 Ferrari-250-LM-Pininfarina-Stradale-Speciale 1965 Ferrari 250 LM Pininfarina Stradale Speciale 1965 Ferrari 365P Berlinetta Speciale 3-posti (2 built) Pininfarina 1965 Ferrari 365P Berlinetta Speciale 3-posti (2 built)
1965 Ferrari 365P Berlinetta Speciale 3-posti (2 built) Pininfarina 1965 Ferrari 365P Berlinetta Speciale 3-posti (2 built) 1965 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1965 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale
1965 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1965 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale 1967 Pininfarina BMC-1800 Berlina-Aerodinamica 1967 BMC 1800 Berlina-Aerodinamica
1967 Pininfarina BMC-1800 Berlina-Aerodinamica 1967 BMC 1800 Berlina-Aerodinamica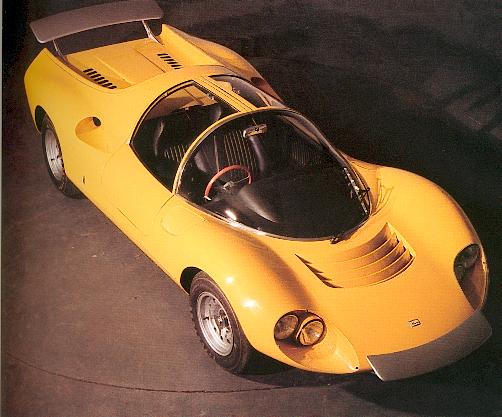 1967 Ferrari Dino 206 Competizione (Pininfarina) 1967 Ferrari Dino 206 Competizione
1967 Ferrari Dino 206 Competizione (Pininfarina) 1967 Ferrari Dino 206 Competizione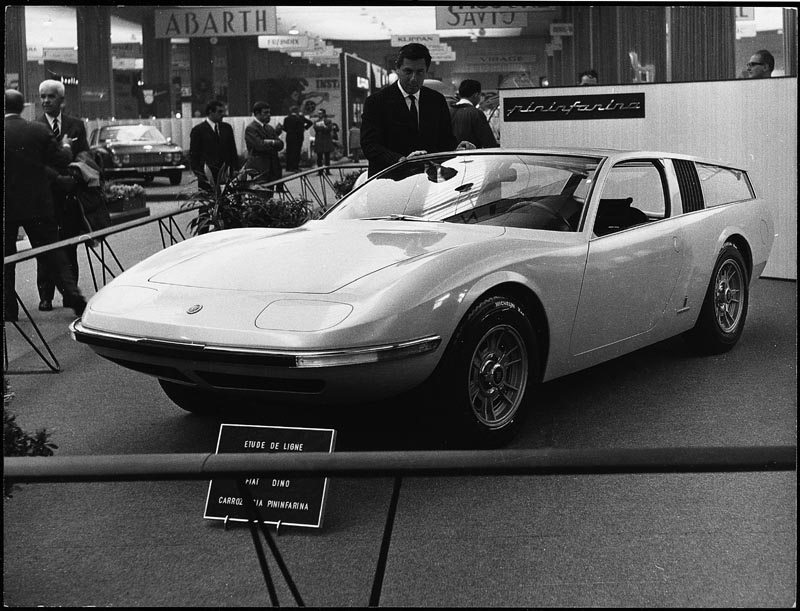 1967 Fiat Dino Parigi (Pininfarina) Paris 1967 Fiat Dino Parigi
1967 Fiat Dino Parigi (Pininfarina) Paris 1967 Fiat Dino Parigi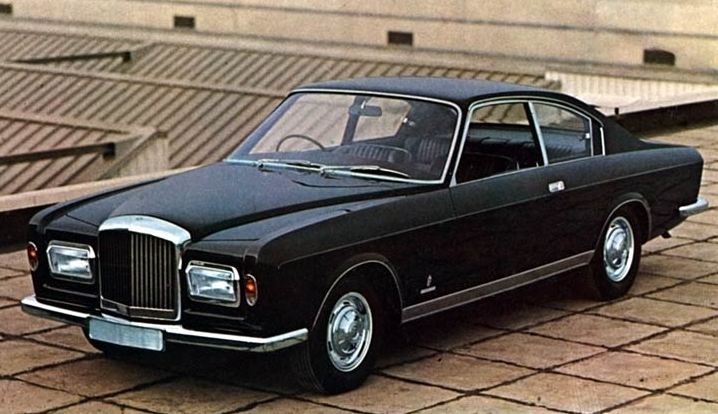 1968 Bentley T1 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1968 Bentley T1 Coupe Speciale
1968 Bentley T1 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina) 1968 Bentley T1 Coupe Speciale 1968 Pininfarina BLMC-1100 Berlina-Aerodinamica 1968 Pininfarina BLMC 1100
1968 Pininfarina BLMC-1100 Berlina-Aerodinamica 1968 Pininfarina BLMC 1100 1968 Alfa Romeo Tipo 33 La Roadster Pininfarina
1968 Alfa Romeo Tipo 33 La Roadster Pininfarina 1968 Ferrari P6 Berlinetta Speciale Pininfarina
1968 Ferrari P6 Berlinetta Speciale Pininfarina 1968 MG EX.234 Roadster Pininfarina 1968 MG EX.234 Roadster
1968 MG EX.234 Roadster Pininfarina 1968 MG EX.234 Roadster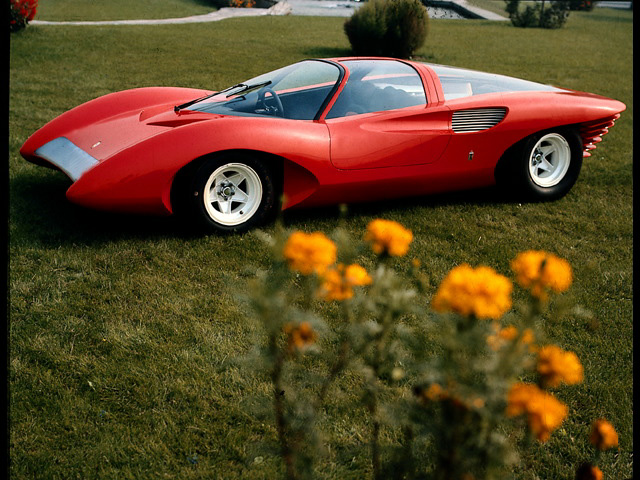 1968 Ferrari 250 P5 (Pininfarina) Speciale 1968 Ferrari 250 P5 Speciale
1968 Ferrari 250 P5 (Pininfarina) Speciale 1968 Ferrari 250 P5 Speciale 1969 Abarth 2000 (Pininfarina) 1969 Abarth 2000
1969 Abarth 2000 (Pininfarina) 1969 Abarth 2000 1969 Alfa Romeo P33 Coupe (Pininfarina) 1969 Alfa Romeo Tipo 33 Coupé 33/2
1969 Alfa Romeo P33 Coupe (Pininfarina) 1969 Alfa Romeo Tipo 33 Coupé 33/2 1969 Pininfarina Sigma Grand Prix monoposto F1 1969 Ferrari Sigma Grand Prix monoposto F1
1969 Pininfarina Sigma Grand Prix monoposto F1 1969 Ferrari Sigma Grand Prix monoposto F1 1969 Ferrari 512S Speciale (Pininfarina) 1969 Ferrari 512S Berlinetta Speciale
1969 Ferrari 512S Speciale (Pininfarina) 1969 Ferrari 512S Berlinetta Speciale 1969 Pininfarina Fiat 128 Teenager Beach Buggy 1969 Fiat 128 Teenager
1969 Pininfarina Fiat 128 Teenager Beach Buggy 1969 Fiat 128 Teenager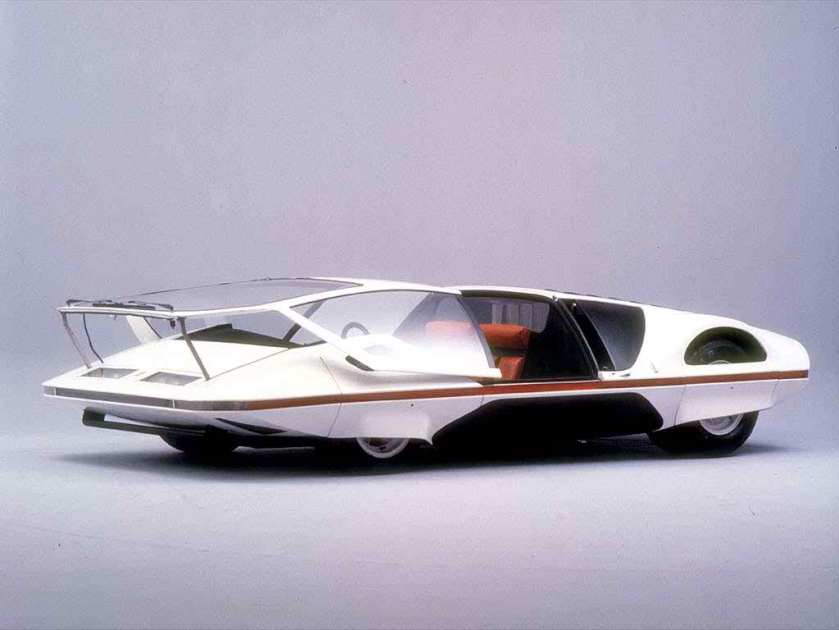 1970 Ferrari 512S Modulo Pininfarina Concept 1 1970 Ferrari 512 S Modulo
1970 Ferrari 512S Modulo Pininfarina Concept 1 1970 Ferrari 512 S Modulo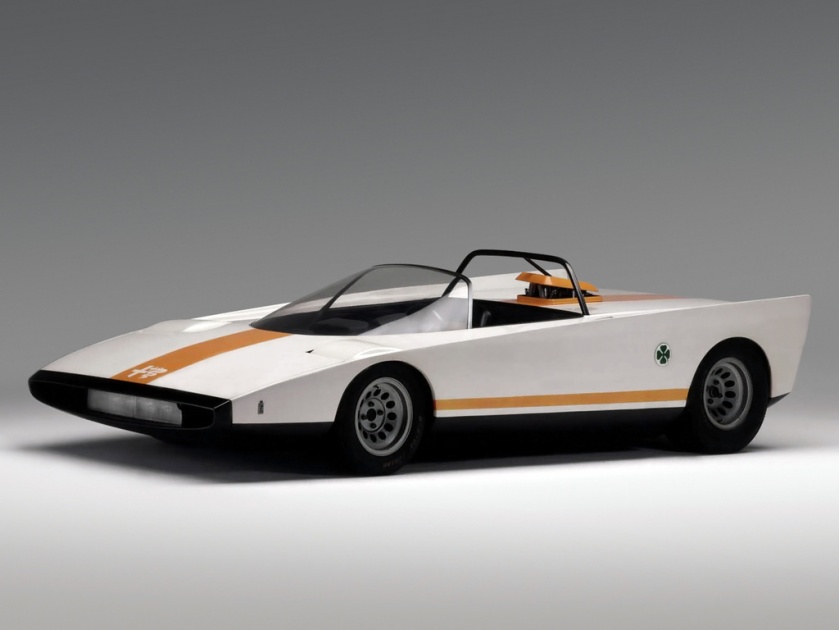 1971 Alfa Romeo P33 Cuneo (Pininfarina) 1971 Alfa Romeo Tipo 33 Cuneo Spider 33/2
1971 Alfa Romeo P33 Cuneo (Pininfarina) 1971 Alfa Romeo Tipo 33 Cuneo Spider 33/2 1971 Peugeot 504 Break Riviera (Pininfarina) 1971 Peugeot Break Riviera
1971 Peugeot 504 Break Riviera (Pininfarina) 1971 Peugeot Break Riviera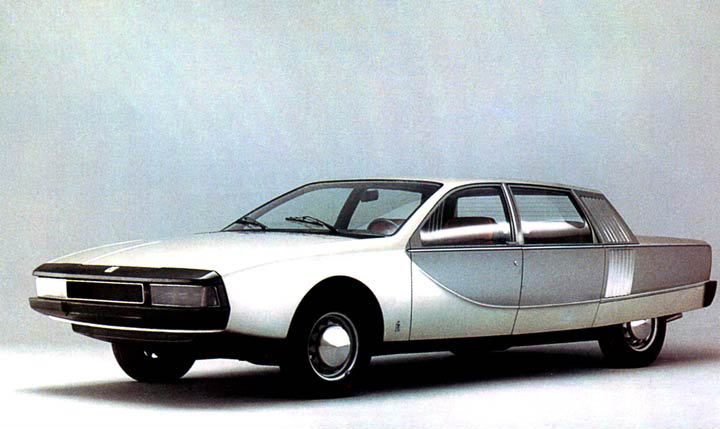 1971 Pininfarina NSU RO-80 01 1971 NSU Ro 80
1971 Pininfarina NSU RO-80 01 1971 NSU Ro 80 1973 Alfa Romeo Alfetta Spider (Pininfarina) 1973 Alfa Romeo Alfetta Spider
1973 Alfa Romeo Alfetta Spider (Pininfarina) 1973 Alfa Romeo Alfetta Spider 1973 Autobianchi A 112 Giovani (Pininfarina) 1973 Autobianchi A 112 Giovani
1973 Autobianchi A 112 Giovani (Pininfarina) 1973 Autobianchi A 112 Giovani 1973 Chevrolet XP-897GT Two-Rotor (Pininfarina) 1973 Chevrolet Corvette XP-897GT – Designed by GM, built by Pininfarina
1973 Chevrolet XP-897GT Two-Rotor (Pininfarina) 1973 Chevrolet Corvette XP-897GT – Designed by GM, built by Pininfarina 1974 Ferrari CR 25 (Pininfarina) 1974 Ferrari CR 25
1974 Ferrari CR 25 (Pininfarina) 1974 Ferrari CR 25 1974 Fiat 130 Maremma (Pininfarina) 1974 Fiat 130 Maremma
1974 Fiat 130 Maremma (Pininfarina) 1974 Fiat 130 Maremma  1975 Alfa Romeo Eagle (Pininfarina) 1975 Alfa Romeo Eagle
1975 Alfa Romeo Eagle (Pininfarina) 1975 Alfa Romeo Eagle 1975 Fiat 130 Opera (Pininfarina) 1975 Fiat 130 Opera sedan
1975 Fiat 130 Opera (Pininfarina) 1975 Fiat 130 Opera sedan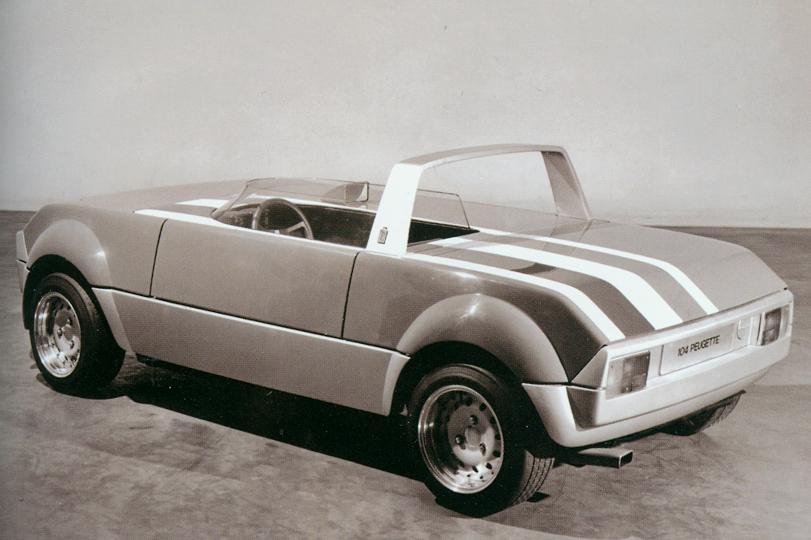 1975 Peugeot Peugette (Pininfarina) b-w 1975 Peugeot Peugette
1975 Peugeot Peugette (Pininfarina) b-w 1975 Peugeot Peugette 1978 Fiat Ecos (Pininfarina) 1978 Fiat Ecos
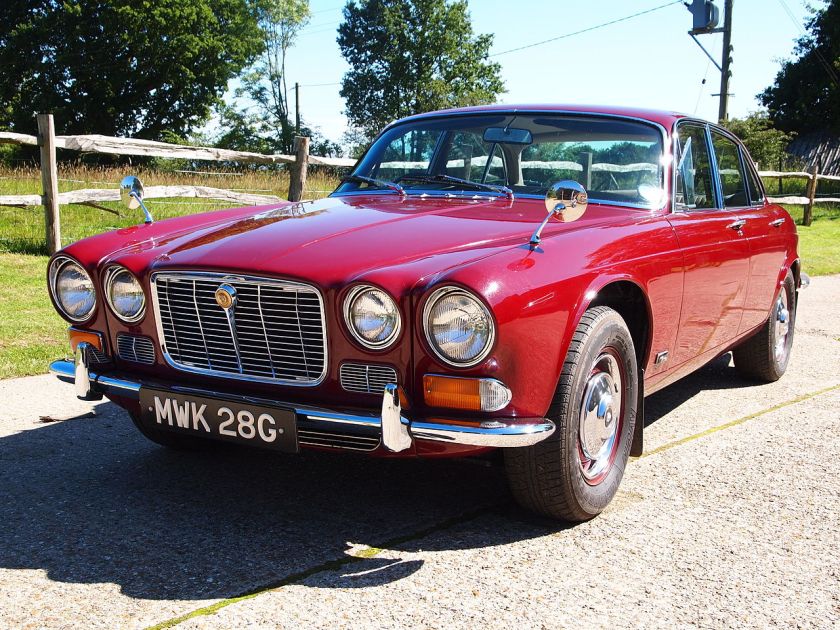
1978 Fiat Ecos (Pininfarina) 1978 Fiat Ecos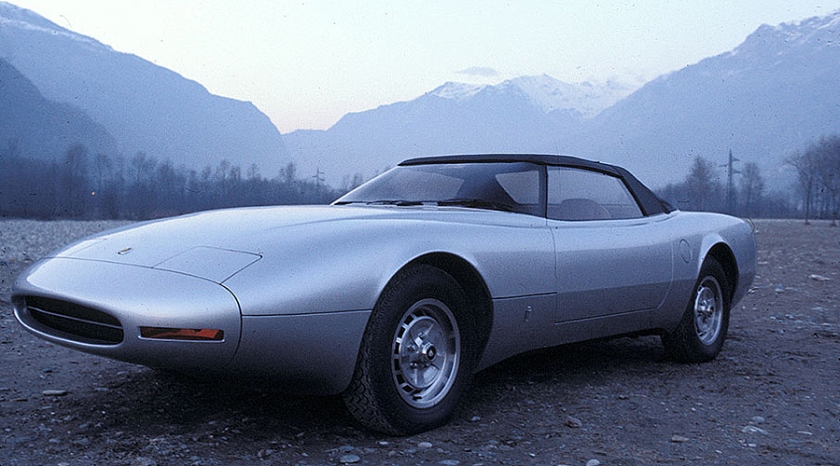 1978 Jaguar XJ Spider (Pininfarina) 1978 Jaguar XJ Spider
1978 Jaguar XJ Spider (Pininfarina) 1978 Jaguar XJ Spider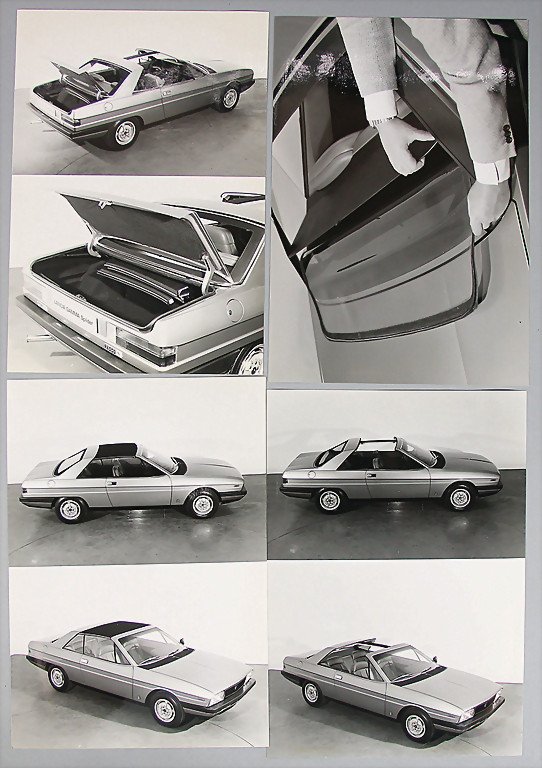 1978 Lancia Gamma Spider (Pininfarina) 1978 Lancia Gamma Spider
1978 Lancia Gamma Spider (Pininfarina) 1978 Lancia Gamma Spider 1978 Pininfarina Studio CNR 1978 Pininfarina CNR-PF
1978 Pininfarina Studio CNR 1978 Pininfarina CNR-PF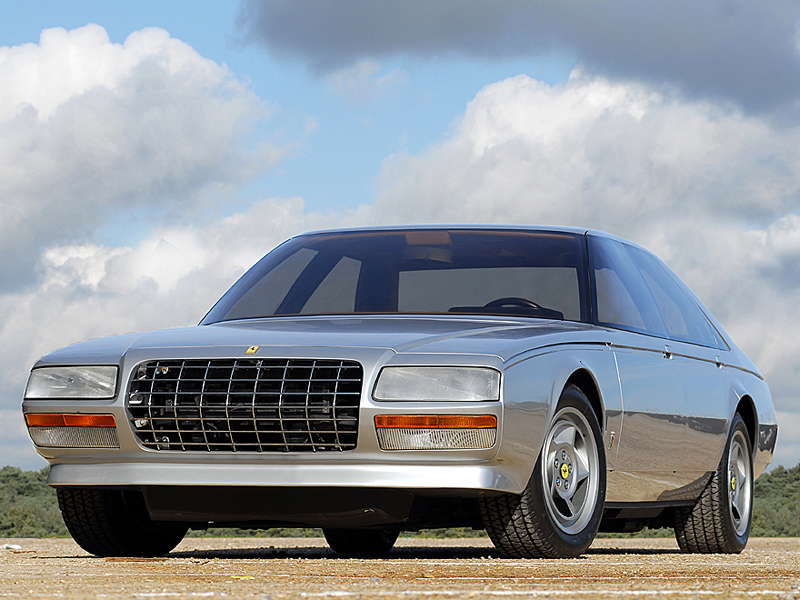 1980 Ferrari Pinin (Pininfarina) 1980 Ferrari Pinin
1980 Ferrari Pinin (Pininfarina) 1980 Ferrari Pinin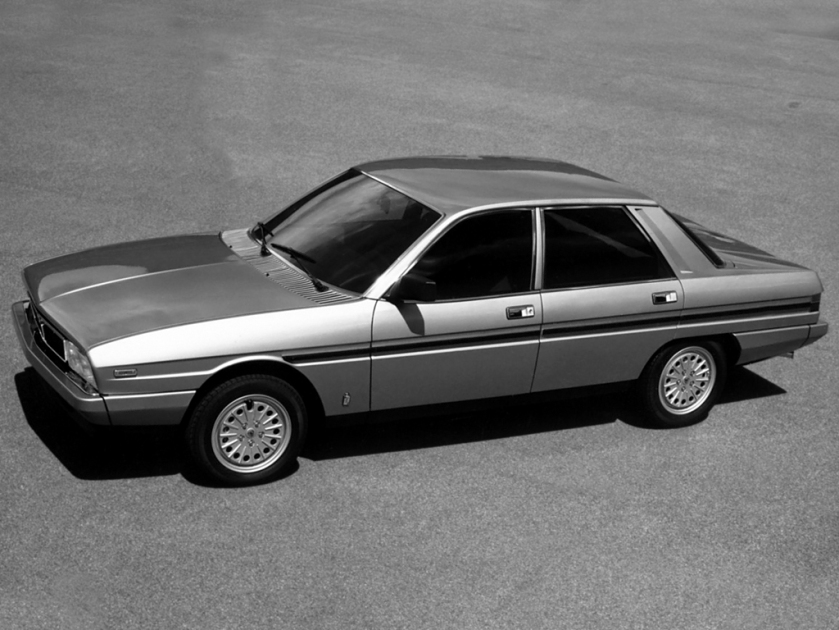 1980 Lancia Gamma Scala (Pininfarina) 1980 Lancia Gamma Scala sedan
1980 Lancia Gamma Scala (Pininfarina) 1980 Lancia Gamma Scala sedan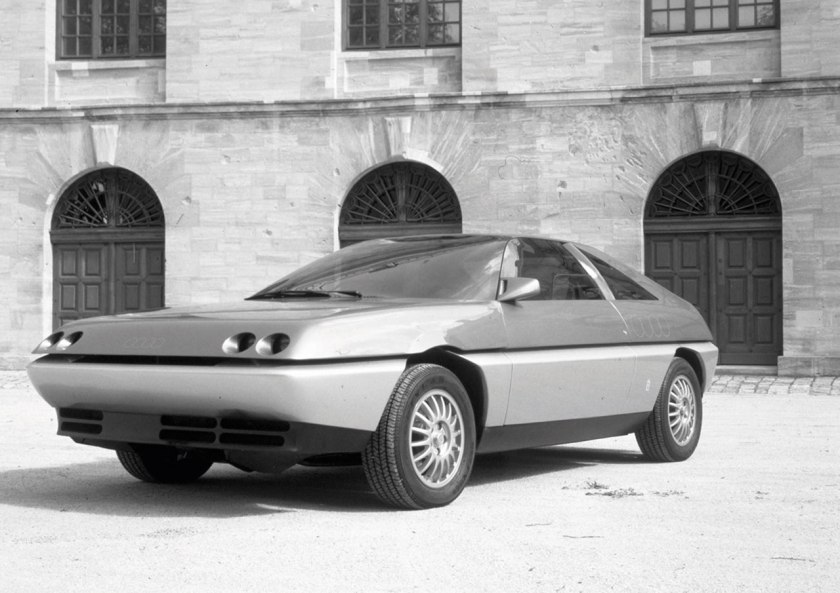 1981 Audi Quartz (Pininfarina) 1981 Audi Quartz
1981 Audi Quartz (Pininfarina) 1981 Audi Quartz 1982 Lancia Gamma Olgiata (Pininfarina) 1982 Lancia Gamma Olgiata
1982 Lancia Gamma Olgiata (Pininfarina) 1982 Lancia Gamma Olgiata 1983 Fiat Ritmo Coupe (Pininfarina) 1983 Pininfarina Brio – based on Fiat Ritmo Abarth 125 TC
1983 Fiat Ritmo Coupe (Pininfarina) 1983 Pininfarina Brio – based on Fiat Ritmo Abarth 125 TC 1984 Honda HP-X (Pininfarina) 1984 Honda HP-X concept car
1984 Honda HP-X (Pininfarina) 1984 Honda HP-X concept car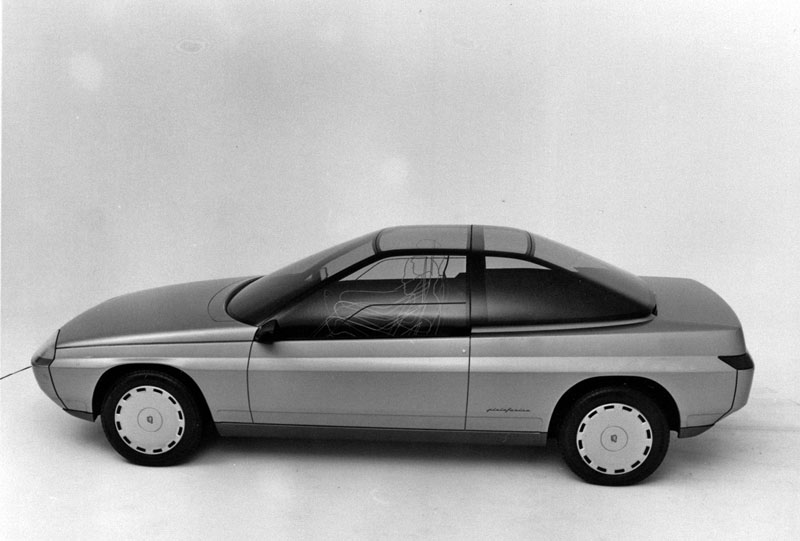 1985 Peugeot Griffe 4 (Pininfarina) 1985 Peugeot Griffe 4
1985 Peugeot Griffe 4 (Pininfarina) 1985 Peugeot Griffe 4 1986 Alfa Romeo Vivace Coupe and Spider (Pininfarina) 1986 Alfa Romeo Vivace Coupe and Spider
1986 Alfa Romeo Vivace Coupe and Spider (Pininfarina) 1986 Alfa Romeo Vivace Coupe and Spider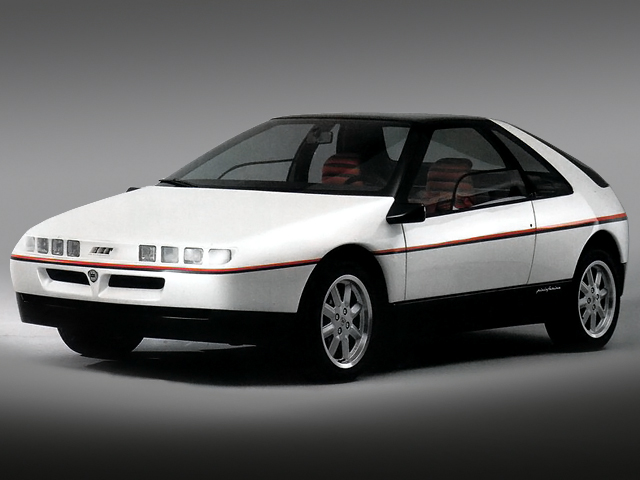
 1988 Lancia HIT (Pininfarina) 1988 Lancia HIT
1988 Lancia HIT (Pininfarina) 1988 Lancia HIT
 1989 pininfarina ferrari mythos 1989 Ferrari Mythos
1989 pininfarina ferrari mythos 1989 Ferrari Mythos 1990 Pininfarina CNR E2
1990 Pininfarina CNR E2 1991 Opel Chronos Pininfarina
1991 Opel Chronos Pininfarina 1992 Fiat Cinquecento 4×4 pick-up
1992 Fiat Cinquecento 4×4 pick-up 1992 Pininfarina Ethos
1992 Pininfarina Ethos 1993 Pininfarina Ethos 2
1993 Pininfarina Ethos 2 1994 Fiat Spunto
1994 Fiat Spunto 1994 Pininfarina Ethos 3
1994 Pininfarina Ethos 3  1995 Honda Argento Vivo (Pininfarina) 1995 Honda Argento Vivo
1995 Honda Argento Vivo (Pininfarina) 1995 Honda Argento Vivo 1995 Honda SSM (Pininfarina) 1995 Honda SSM
1995 Honda SSM (Pininfarina) 1995 Honda SSM 1996 Fiat Sing e Song – a pair of concept cars based on the Fiat Bravo and Brava Pininfarina
1996 Fiat Sing e Song – a pair of concept cars based on the Fiat Bravo and Brava Pininfarina



 1996 Pininfarina etabeta
1996 Pininfarina etabeta



 1997 Peugeot Nautilus concept designed by Pininfarina
1997 Peugeot Nautilus concept designed by Pininfarina




 1998 Alfa Romeo Dardo Spider Pininfarina
1998 Alfa Romeo Dardo Spider Pininfarina

 1999 Fiat Wish Cabriolet / Coupé Pininfarina
1999 Fiat Wish Cabriolet / Coupé Pininfarina



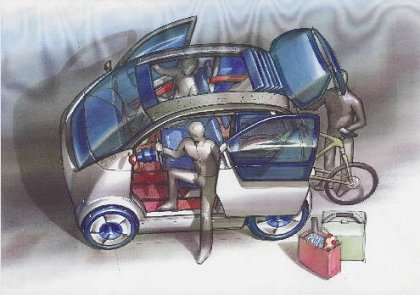

 1999 Pininfarina Metrocubo
1999 Pininfarina Metrocubo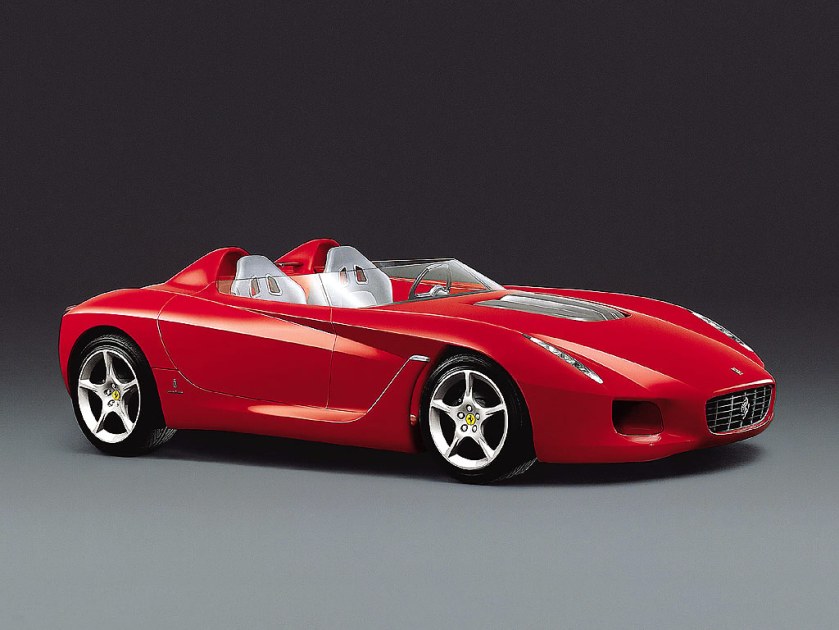 2000 Ferrari Rossa Pininfarina
2000 Ferrari Rossa Pininfarina


 2001 Ford Start (Pininfarina) 2001 Ford Start
2001 Ford Start (Pininfarina) 2001 Ford Start




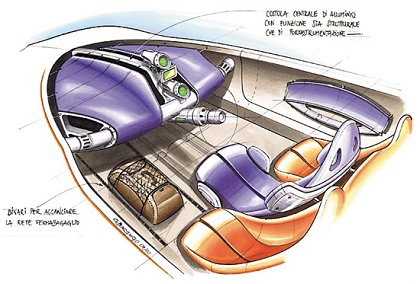 2001 Citroën Osée Pininfarina
2001 Citroën Osée Pininfarina 2002 Hafei HF Fantasy Pininfarina
2002 Hafei HF Fantasy Pininfarina

 2003 Pininfarina Lotus Enjoy
2003 Pininfarina Lotus Enjoy













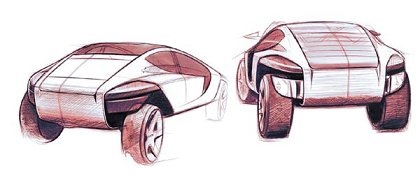
 2004 Pininfarina Double-Face
2004 Pininfarina Double-Face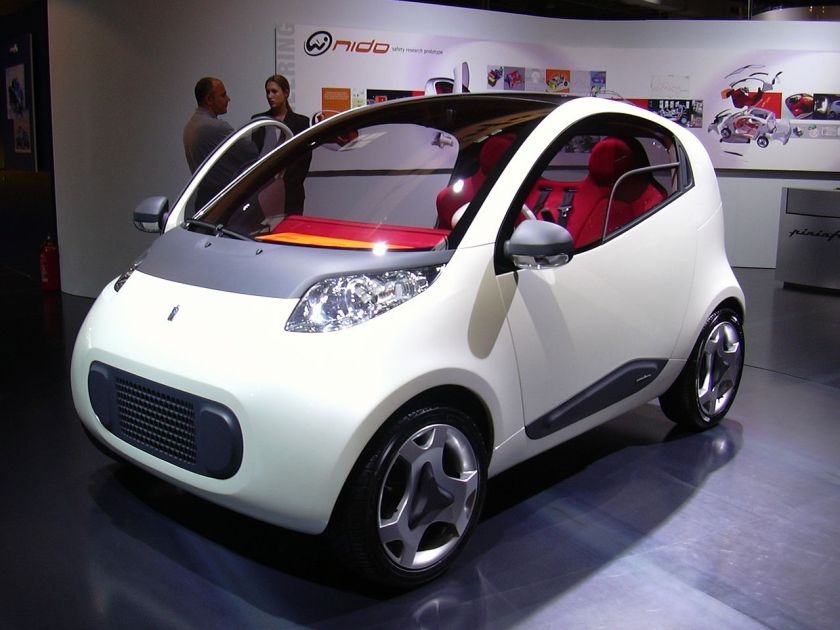
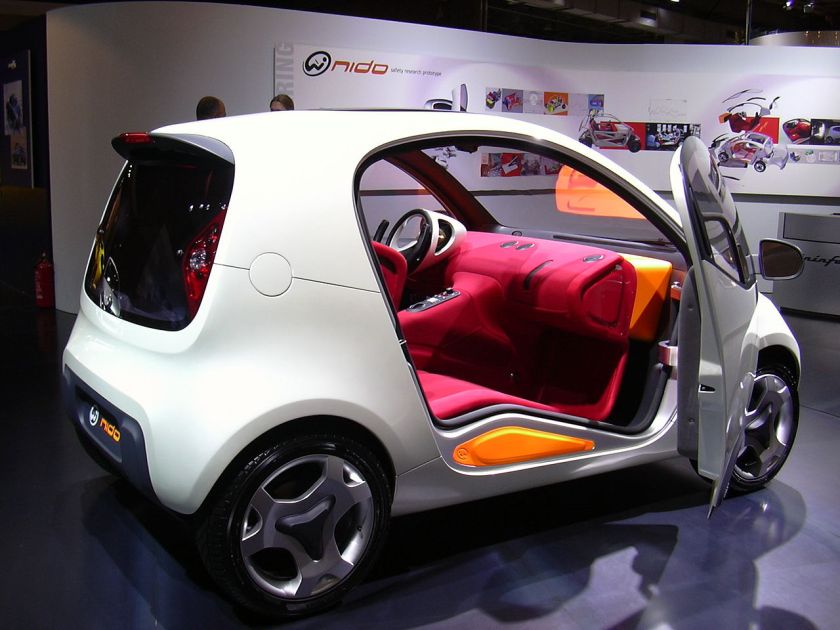 2004 Pininfarina Nido
2004 Pininfarina Nido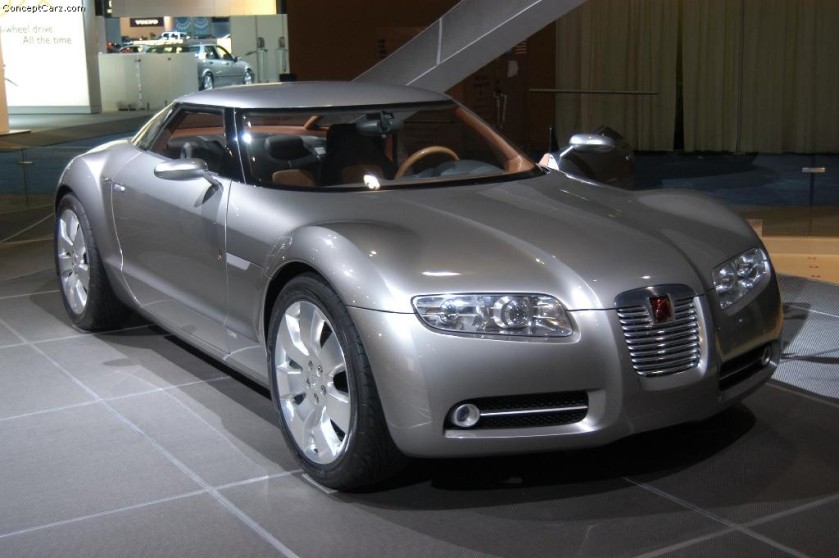 2004 Saturn Curve – Built by Pininfarina, designed by GM in Sweden
2004 Saturn Curve – Built by Pininfarina, designed by GM in Sweden



 2005 Chery M14 (Pininfarina) 2005 Chery M14
2005 Chery M14 (Pininfarina) 2005 Chery M14

 2005 Maserati Birdcage 75th Pininfarina
2005 Maserati Birdcage 75th Pininfarina

 2006 Ferrari 612 Scaglietti “Kappa” one-off for Peter S. Kalikow
2006 Ferrari 612 Scaglietti “Kappa” one-off for Peter S. Kalikow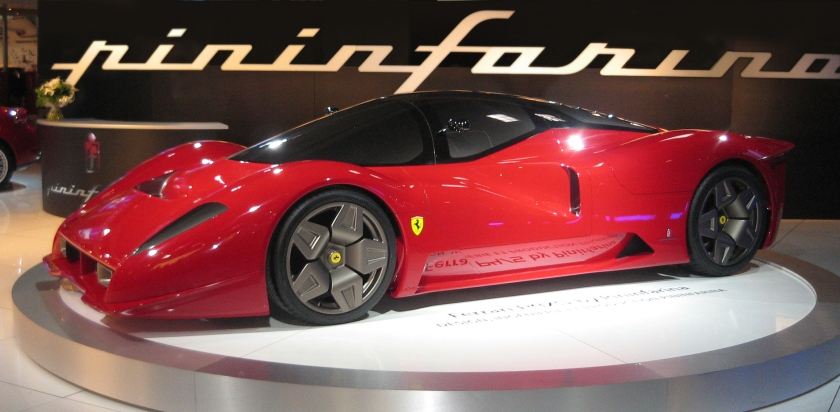 2006 Ferrari P4/5 by Pininfarina
2006 Ferrari P4/5 by Pininfarina 2008 Pininfarina B0 electric car
2008 Pininfarina B0 electric car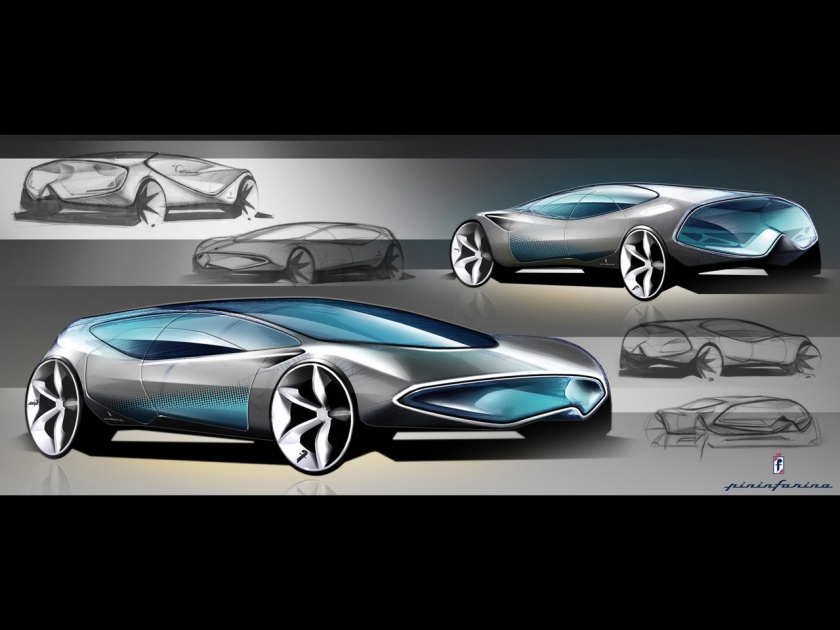 2008 Pininfarina Sintesi
2008 Pininfarina Sintesi 2008 Rolls-Royce Phantom Drophead Coupé Hyperion designed by Pininfarina 2008 Rolls-Royce Phantom Drophead Coupé Hyperion
2008 Rolls-Royce Phantom Drophead Coupé Hyperion designed by Pininfarina 2008 Rolls-Royce Phantom Drophead Coupé Hyperion 2009 Tata Pr1ma concept car designed by Pininfarina 2009 Tata Pr1ma concept car
2009 Tata Pr1ma concept car designed by Pininfarina 2009 Tata Pr1ma concept car 2009 Ferrari P540 Superfast Aperta – one off for Edward Walson, based on the Ferrari 599 Pininfarina2009 Ferrari P540 Superfast Aperta – one off for Edward Walson, based on the Ferrari 599
2009 Ferrari P540 Superfast Aperta – one off for Edward Walson, based on the Ferrari 599 Pininfarina2009 Ferrari P540 Superfast Aperta – one off for Edward Walson, based on the Ferrari 599 2010 Alfa Romeo 2uettottanta concept car Pininfarina 2010 Alfa Romeo 2uettottanta concept car
2010 Alfa Romeo 2uettottanta concept car Pininfarina 2010 Alfa Romeo 2uettottanta concept car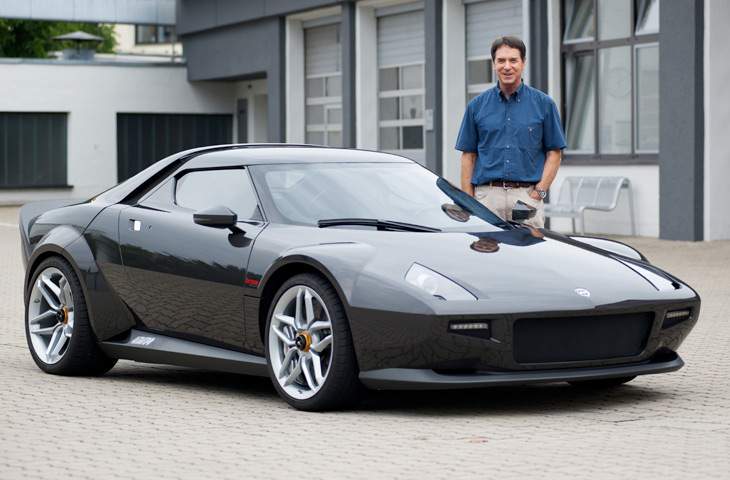 2010 Lancia Stratos for Michael Stoschek pininfarina 2010 Lancia Stratos for Michael Stoschek
2010 Lancia Stratos for Michael Stoschek pininfarina 2010 Lancia Stratos for Michael Stoschek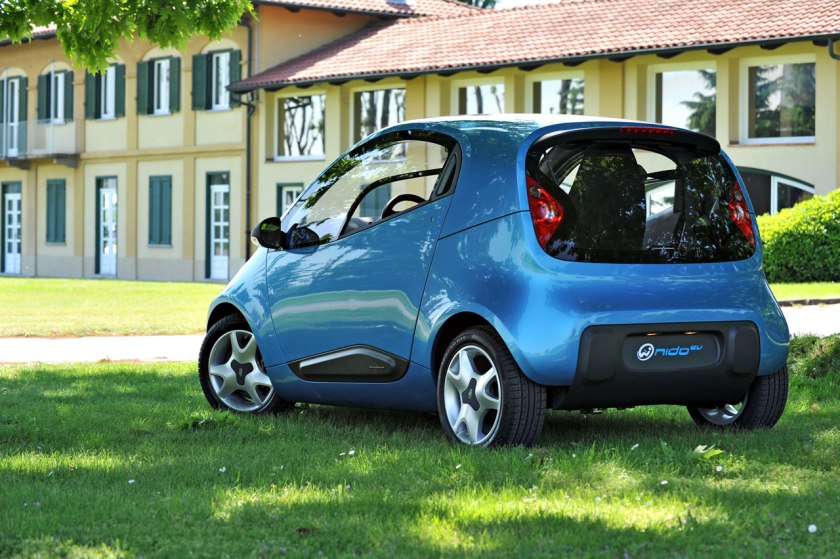
 2010 Pininfarina Nido EV
2010 Pininfarina Nido EV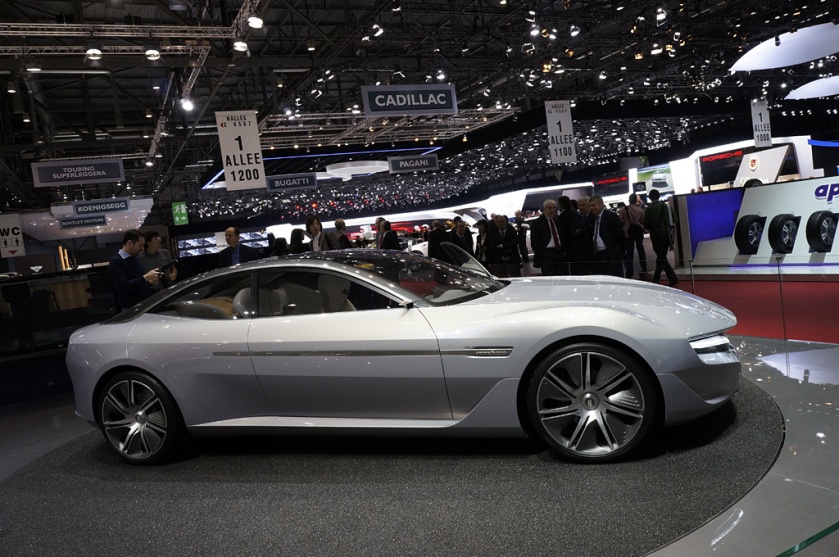 2012 Pininfarina Cambiano concept car
2012 Pininfarina Cambiano concept car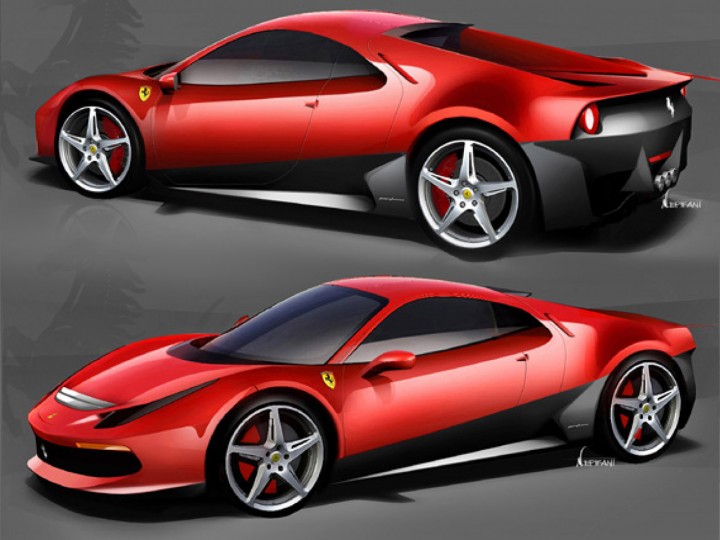 2012 Ferrari SP12 EC one-off for Eric Clapton
2012 Ferrari SP12 EC one-off for Eric Clapton
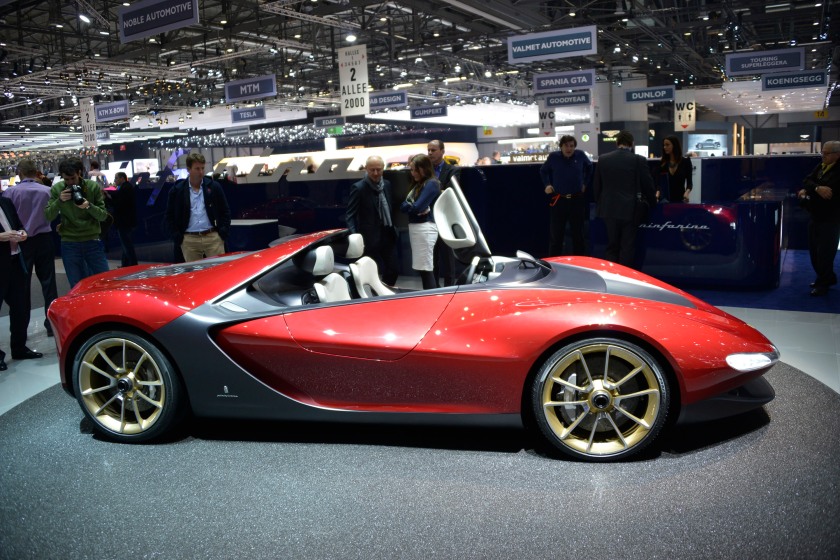
 2013 BMW Pininfarina Gran Lusso Coupe 2013 BMW Gran Lusso Coupé
2013 BMW Pininfarina Gran Lusso Coupe 2013 BMW Gran Lusso Coupé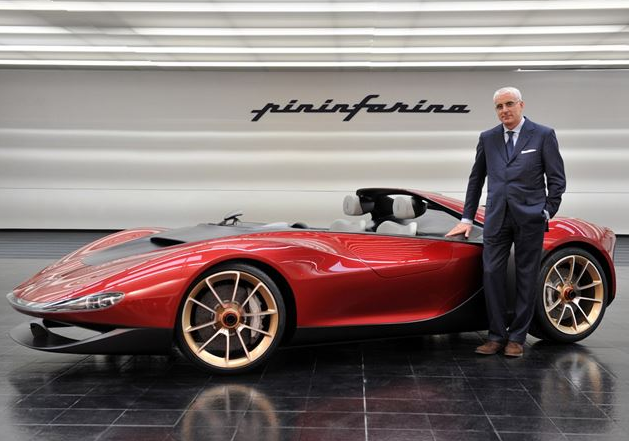 2014 Ferrari Sergio Pininfarina Tribute Car 2014 Ferrari Sergio
2014 Ferrari Sergio Pininfarina Tribute Car 2014 Ferrari Sergio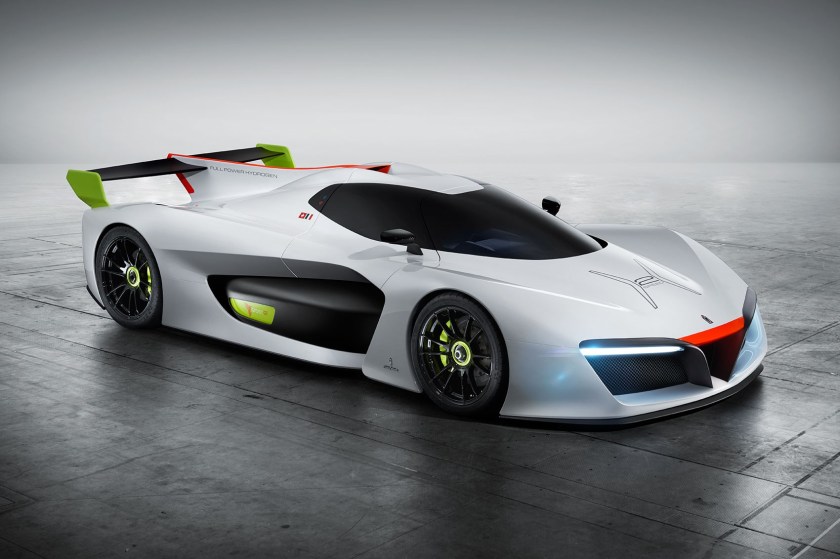 2016 H2 Speed concept car pininfarina 2016 H2 Speed concept car
2016 H2 Speed concept car pininfarina 2016 H2 Speed concept car
Production Cars Designed by Pininfarina
A list of Post WWII cars designed by Pininfarina that went into production.
 1948 Cisitalia 202 SC Coupe by Pininfarina 1948 Cisitalia 202
1948 Cisitalia 202 SC Coupe by Pininfarina 1948 Cisitalia 202
 1949 Simca 8 Sport Pininfarina Coupé
1949 Simca 8 Sport Pininfarina Coupé 1949 Simca 8 Pininfarina Sport Cabriolet 1949 Simca 8 Sport Coupé and Cabriolet
1949 Simca 8 Pininfarina Sport Cabriolet 1949 Simca 8 Sport Coupé and Cabriolet
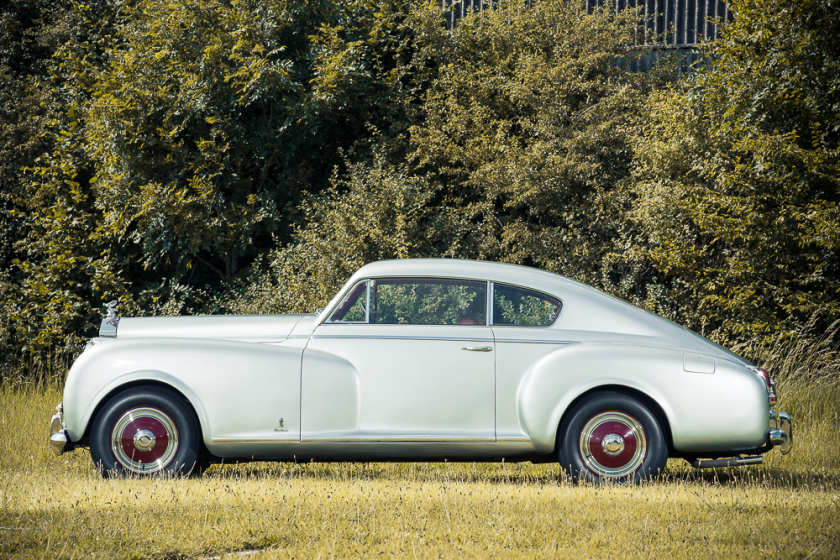
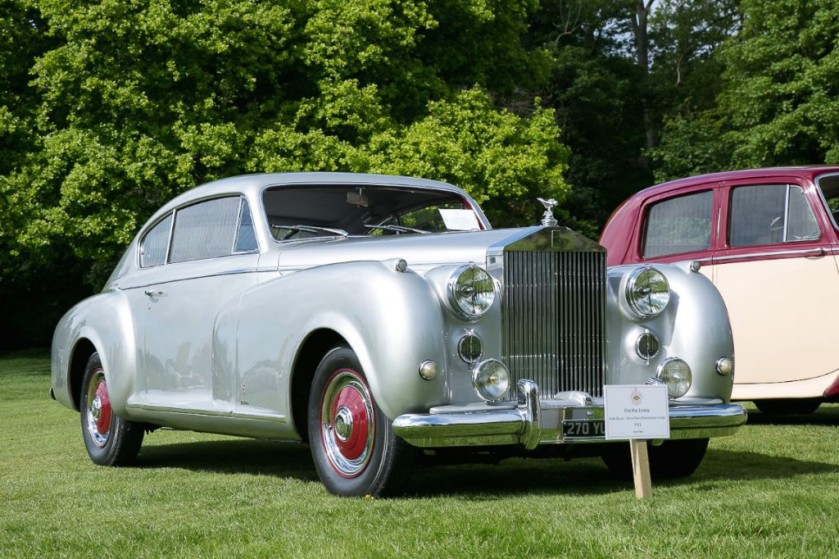

 1951 Rolls-Royce Silver Dawn Pininfarina continental coupe only 1
1951 Rolls-Royce Silver Dawn Pininfarina continental coupe only 1 1952 Ferrari-250-GT-Pininfarina-Coupe-Speciale 1952 Ferrari 250
1952 Ferrari-250-GT-Pininfarina-Coupe-Speciale 1952 Ferrari 250 1952 Nash Ambassador Pininfarina
1952 Nash Ambassador Pininfarina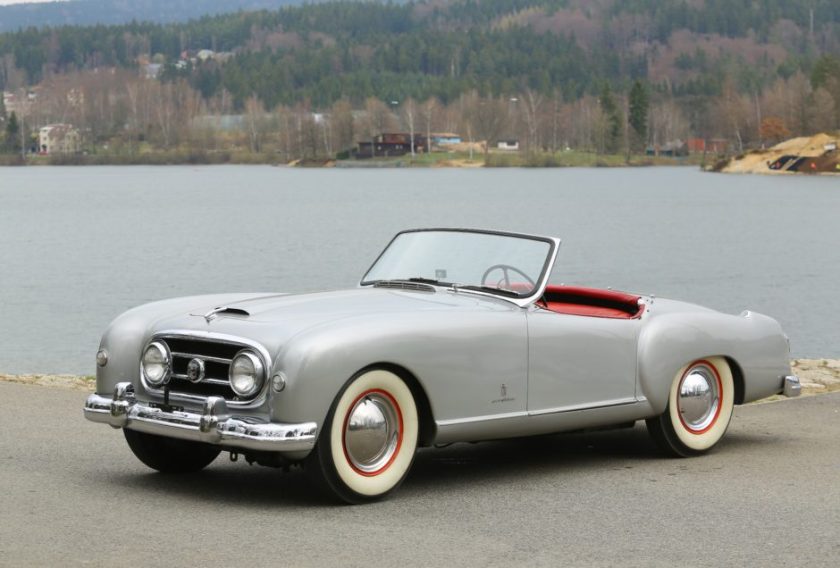 1952 Nash Healey Pininfarina Roadster 1952 Nash-Healey
1952 Nash Healey Pininfarina Roadster 1952 Nash-Healey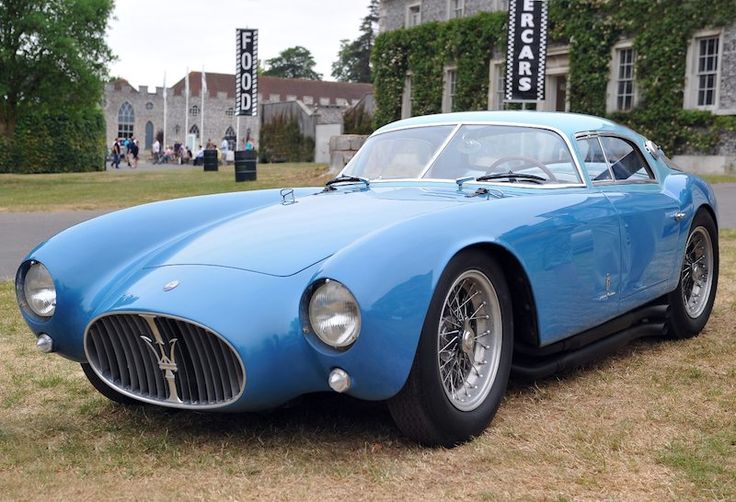 1953 Maserati A6GC53-Berlinetta-PininFarina
1953 Maserati A6GC53-Berlinetta-PininFarina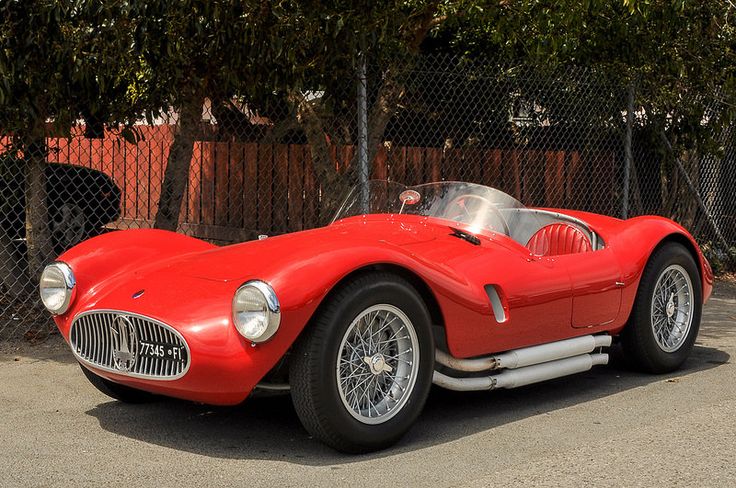 1953 Maserati A6GCS 53 Spyder Pininfarina 1953 Four Berlinetta and one Spyder version of the Maserati A6GCS/53
1953 Maserati A6GCS 53 Spyder Pininfarina 1953 Four Berlinetta and one Spyder version of the Maserati A6GCS/53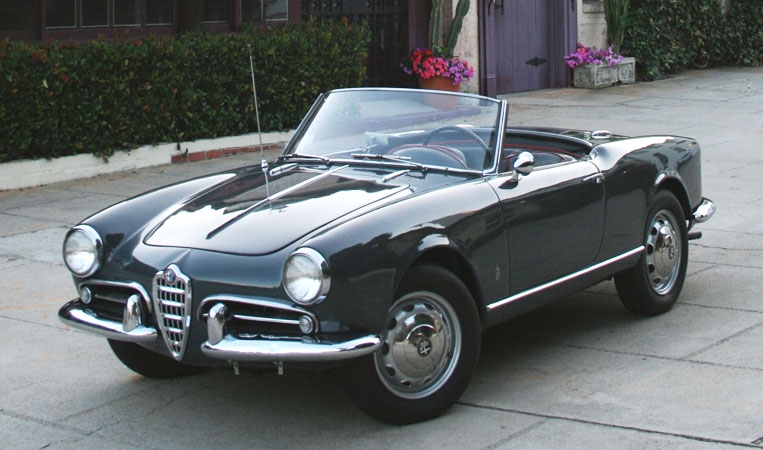 1956 Alfa Romeo Giulietta Pininfarina Spider
1956 Alfa Romeo Giulietta Pininfarina Spider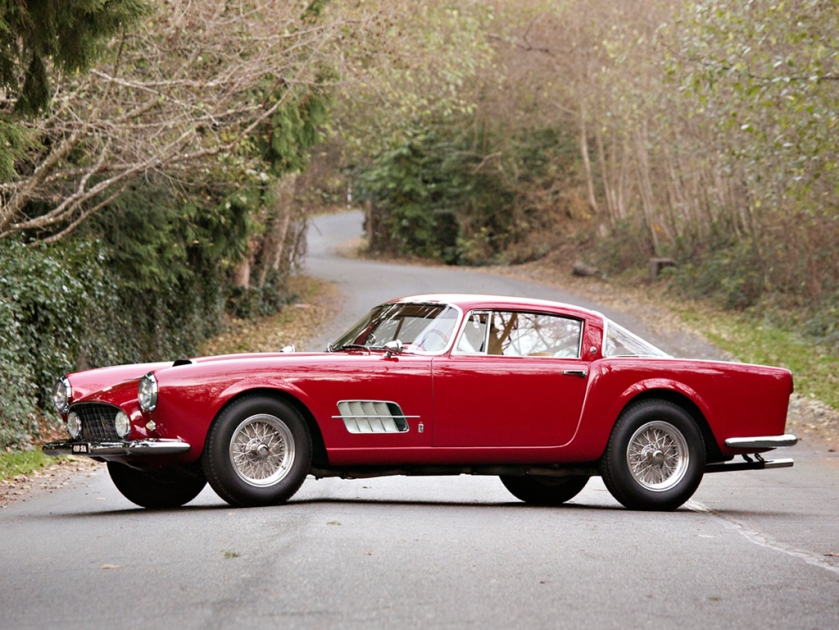 1955 ferrari 410 superamerica pininfarna coupe 1955 Ferrari 410 Superamerica
1955 ferrari 410 superamerica pininfarna coupe 1955 Ferrari 410 Superamerica 1955 Peugeot 403-berline-et-cabriolet pininfarina 1955 Peugeot 403
1955 Peugeot 403-berline-et-cabriolet pininfarina 1955 Peugeot 403 1956 Austin A40 Farina (Mark I) 1956 Austin A40 Farina
1956 Austin A40 Farina (Mark I) 1956 Austin A40 Farina 1957 Lancia-Flaminia-Zagato-Pininfarina Super-Sport-side-view 1957 Lancia Flaminia
1957 Lancia-Flaminia-Zagato-Pininfarina Super-Sport-side-view 1957 Lancia Flaminia
1958 BMC 1800 Landcrab history AROnline Pininfarina 1958 BMC Farina cars

1959 Austin A55 MkII Pininfarina Cambridge rear Austin A55 Cambridge Mk II 1959 mg magnette pininfarina mkIII MG Magnette Mk III
1959 mg magnette pininfarina mkIII MG Magnette Mk III Morris Oxford Farina V
Morris Oxford Farina V Riley 4/68 Pininfarina
Riley 4/68 Pininfarina
 1959-61 Fiat 1800-2100 (112-114) designed by Pininfarina 1959 Fiat 1800/2100
1959-61 Fiat 1800-2100 (112-114) designed by Pininfarina 1959 Fiat 1800/2100 1961 Ferrari 250 GTE Coupe Pininfarina 1960 Ferrari 250 GTE
1961 Ferrari 250 GTE Coupe Pininfarina 1960 Ferrari 250 GTE 1960 peugeot-404 pininfarina 1960 Peugeot 404
1960 peugeot-404 pininfarina 1960 Peugeot 404 1961 Fiat 2300 Pininfarina 1961 Fiat 2300
1961 Fiat 2300 Pininfarina 1961 Fiat 2300 1962 ado16dev pininfarina 10
1962 ado16dev pininfarina 10 1972 BMC ADO16 Austin 1300GT 1380cc Pininfarina 1962 BMC ADO16
1972 BMC ADO16 Austin 1300GT 1380cc Pininfarina 1962 BMC ADO16
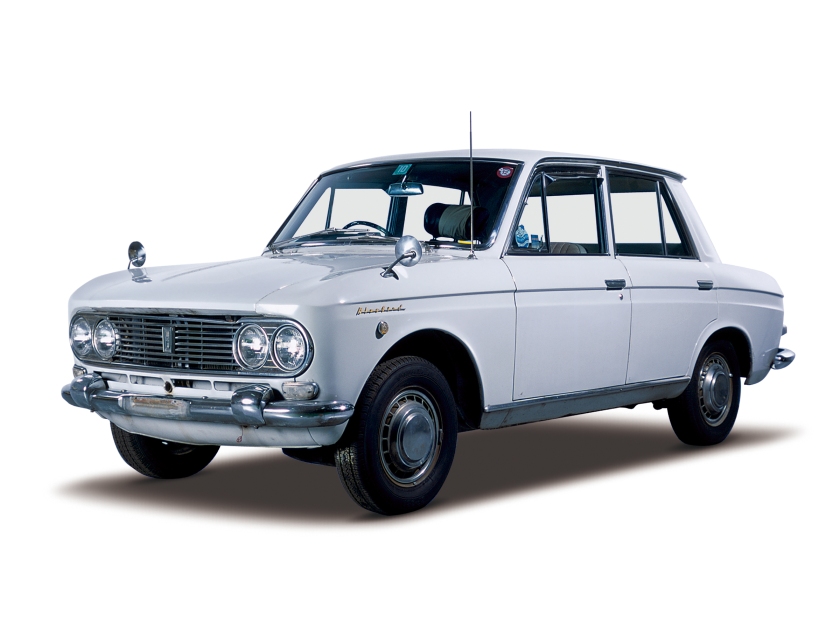
1963 Datsun 1200 Bluebird 410 Pininfarina 1963 Datsun Bluebird 410 1964 BMC ADO17 Pininfarina
1964 BMC ADO17 Pininfarina
 1965 Ferrari-206-P-Dino-Pininfarina-Berlinetta-Speciale 1965 Ferrari Dino 206
1965 Ferrari-206-P-Dino-Pininfarina-Berlinetta-Speciale 1965 Ferrari Dino 206 1965 MGB GT
1965 MGB GT 1965 Nissan Cedric 130
1965 Nissan Cedric 130 1965 Peugeot 204 limo Pininfarina
1965 Peugeot 204 limo Pininfarina 1974 Peugeot 204 Break Pininfarina
1974 Peugeot 204 Break Pininfarina Peugeot 204 Pininfarina Coupé
Peugeot 204 Pininfarina Coupé Peugeot 204 Pininfarina Cabriolet
Peugeot 204 Pininfarina Cabriolet 1966 Alfa Romeo Spider 1600 Duetto Battista Pininfarina
1966 Alfa Romeo Spider 1600 Duetto Battista Pininfarina 1966 Ferrari 275 Pininfarina GTB-4 Steel
1966 Ferrari 275 Pininfarina GTB-4 Steel 1967 Ferrari 275 GTB Pininfarina
1967 Ferrari 275 GTB Pininfarina 1967 Ferrari.275.GTB-4.NART.Spyder Pininfarina 1966 Ferrari 275 GTB/C
1967 Ferrari.275.GTB-4.NART.Spyder Pininfarina 1966 Ferrari 275 GTB/C 1966 Ferrari 330 GT 2 PlNINFARINA 2 DV-07-CC 1966 Ferrari 330 GTC
1966 Ferrari 330 GT 2 PlNINFARINA 2 DV-07-CC 1966 Ferrari 330 GTC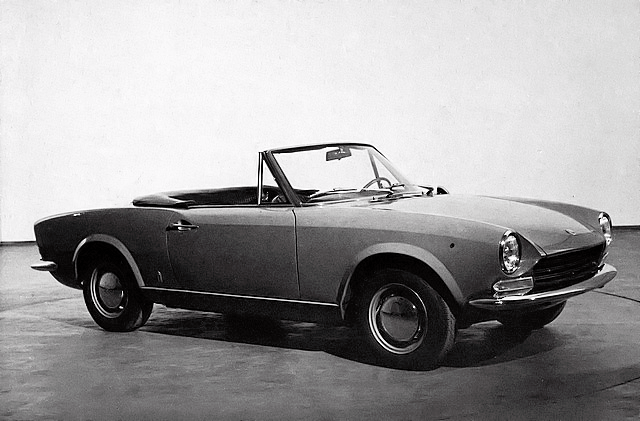 1966 PININFARINA COUPE and the FIAT 124 SPIDER 1966 Fiat 124 Sport Spider
1966 PININFARINA COUPE and the FIAT 124 SPIDER 1966 Fiat 124 Sport Spider 1966-72 fiat-dino-spider-pininfarina 1966 Fiat Dino Spider
1966-72 fiat-dino-spider-pininfarina 1966 Fiat Dino Spider 1966 ika renault torino pininfarina 300 1966 IKA-Renault Torino
1966 ika renault torino pininfarina 300 1966 IKA-Renault Torino 1968 Ferrari Daytona
1968 Ferrari Daytona
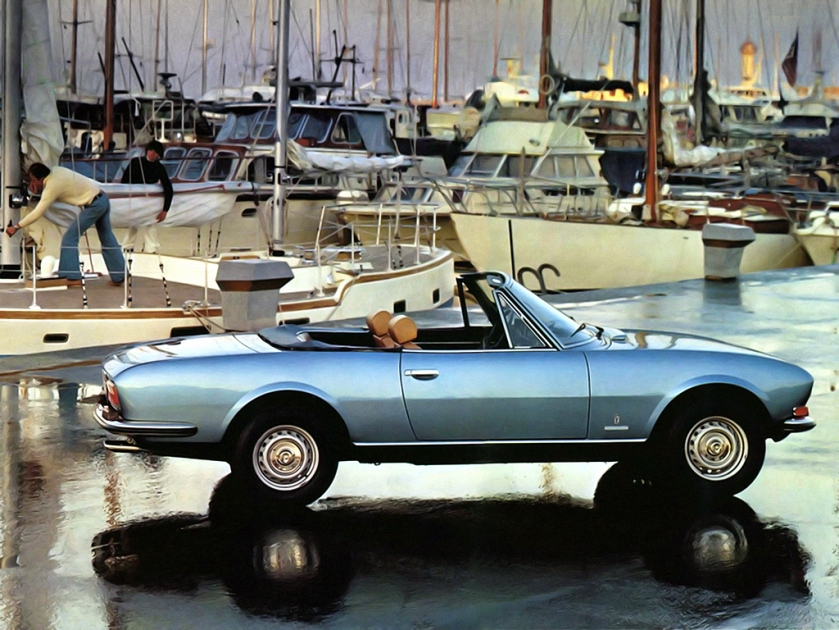 1968 Peugeot 504 Cabriolet and Coupe Pininfarina
1968 Peugeot 504 Cabriolet and Coupe Pininfarina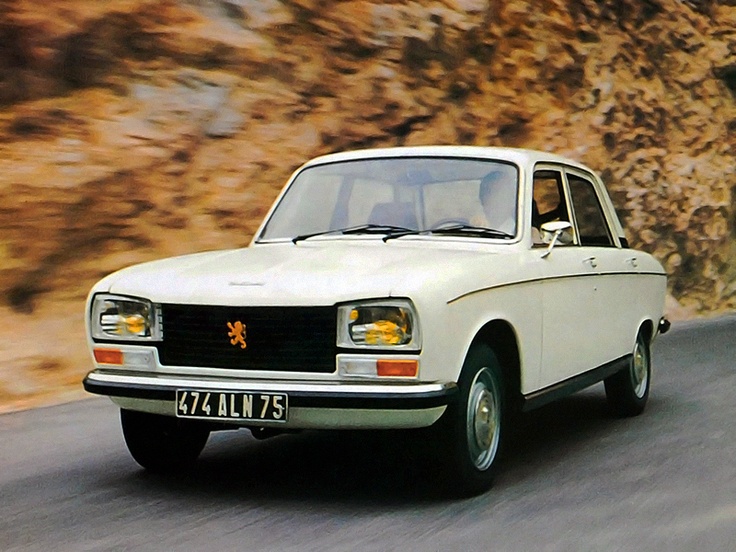
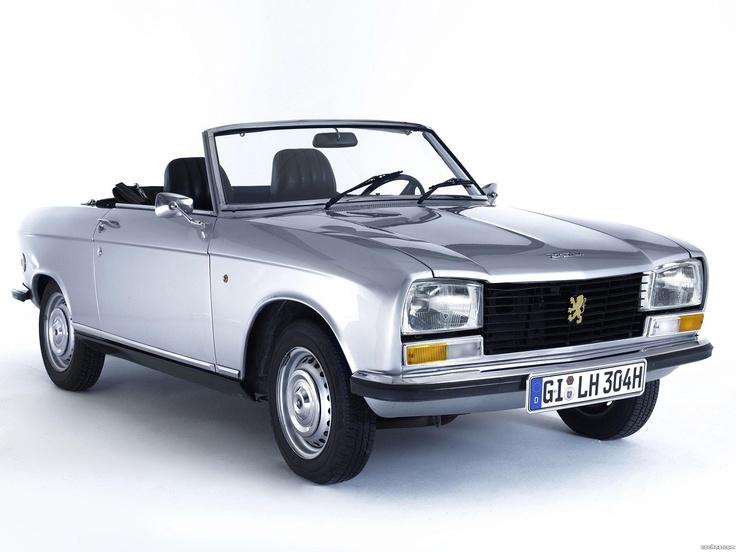
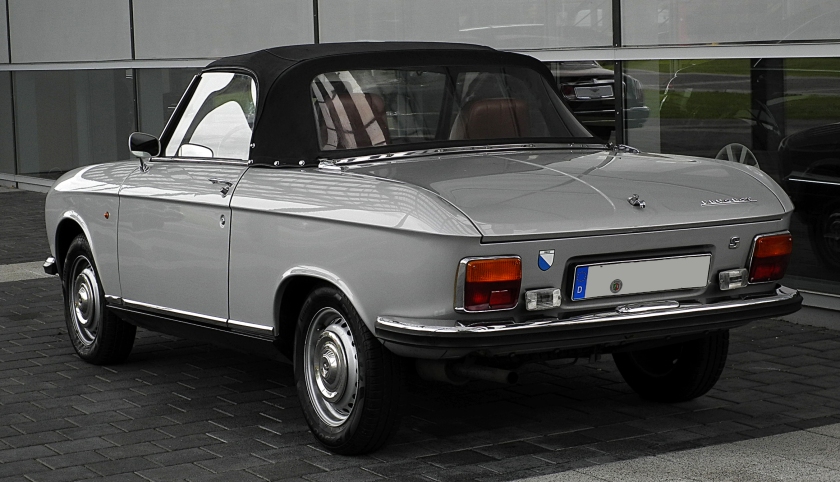

 1969 Peugeot 304 Cabriolet and Coupe Pininfarina
1969 Peugeot 304 Cabriolet and Coupe Pininfarina 1971 Fiat 130 Coupé designed by Pininfarina 1971 Fiat 130 Coupe
1971 Fiat 130 Coupé designed by Pininfarina 1971 Fiat 130 Coupe
 1973 – 1976 Ferrari 365 GT4 BB Pininfarina 1973 Ferrari 365 GT4 BB
1973 – 1976 Ferrari 365 GT4 BB Pininfarina 1973 Ferrari 365 GT4 BB 1977 Ferrari 308 GTS 3 0 Pininfarina 1975 Ferrari 308
1977 Ferrari 308 GTS 3 0 Pininfarina 1975 Ferrari 308 1975-1986 peugeot-604-Pininfarina 1975 Peugeot 604
1975-1986 peugeot-604-Pininfarina 1975 Peugeot 604 1975 Lancia Beta Montecarlo Pininfarina 1975 Lancia Montecarlo
1975 Lancia Beta Montecarlo Pininfarina 1975 Lancia Montecarlo 1975 Rolls-Royce Camargue designed by Pininfarina 1975 Rolls-Royce Camargue
1975 Rolls-Royce Camargue designed by Pininfarina 1975 Rolls-Royce Camargue
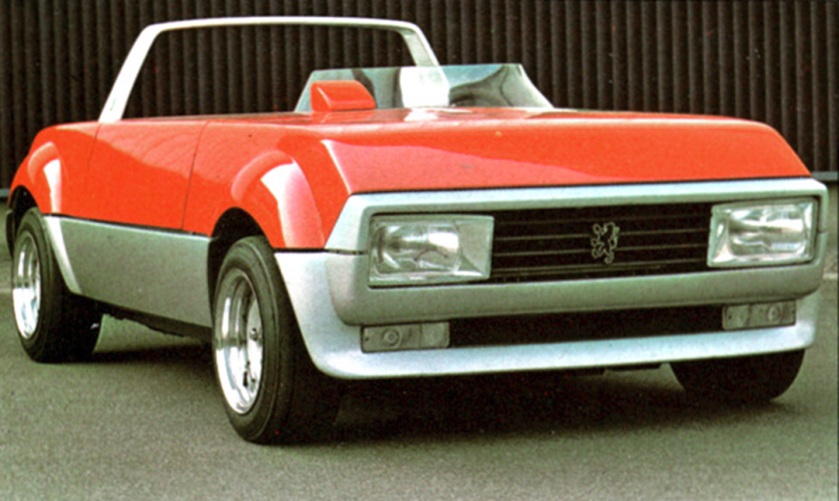
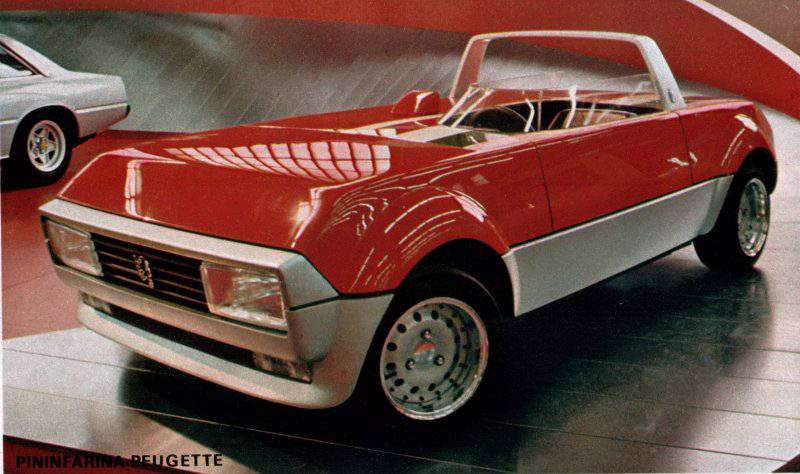
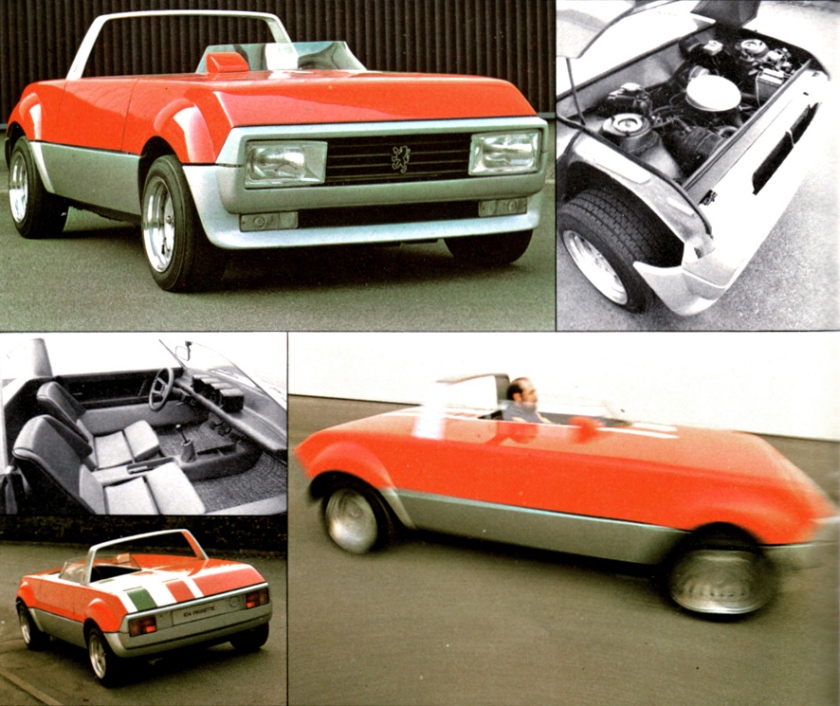


 1976 Peugeot Peugette designed by Pininfarina concept car
1976 Peugeot Peugette designed by Pininfarina concept car 1978 Pininfarina Jaguar XJ VI Spider 1978 Jaguar XJ6
1978 Pininfarina Jaguar XJ VI Spider 1978 Jaguar XJ6 1979 peugeot 505 designed by Pininfarina 1979 Peugeot 505
1979 peugeot 505 designed by Pininfarina 1979 Peugeot 505 1980 Ferrari Mondial Pininfarina 1980 Ferrari Mondial
1980 Ferrari Mondial Pininfarina 1980 Ferrari Mondial 1984 Ferrari Testarossa Pininfarina 1984 Ferrari Testarossa
1984 Ferrari Testarossa Pininfarina 1984 Ferrari Testarossa 1984-87 Ferrari 288 GTO Pininfarina 1984 Ferrari 288 GTO
1984-87 Ferrari 288 GTO Pininfarina 1984 Ferrari 288 GTO 1985-89 Ferrari 328 GTS Pininfarina 1985 Ferrari 328
1985-89 Ferrari 328 GTS Pininfarina 1985 Ferrari 328
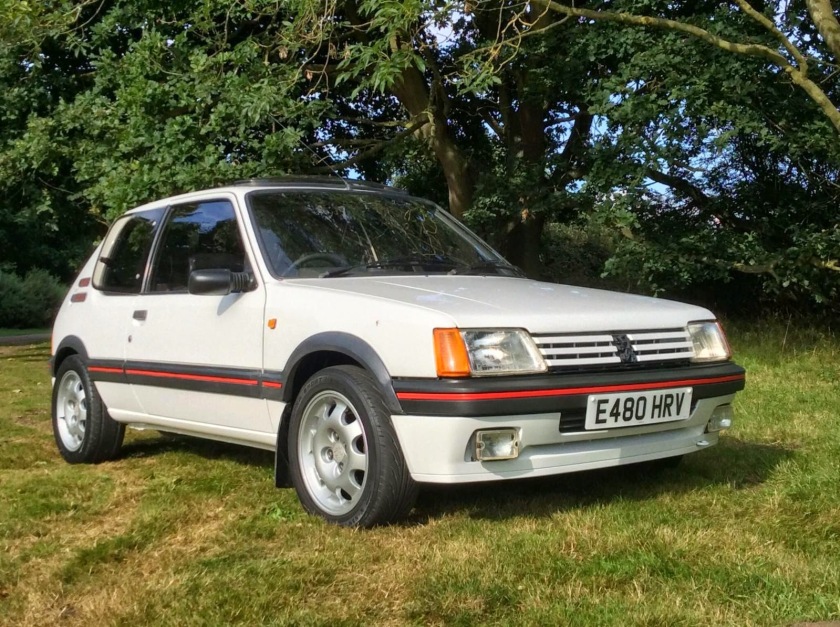
 1985 Peugeot 205 Cabriolet and Saloon (4 doors) based on Peugeot’s Director of Exterior Design, Gerard Welter’s, initial design of the 205 (1983) designed by Pininfarina
1985 Peugeot 205 Cabriolet and Saloon (4 doors) based on Peugeot’s Director of Exterior Design, Gerard Welter’s, initial design of the 205 (1983) designed by Pininfarina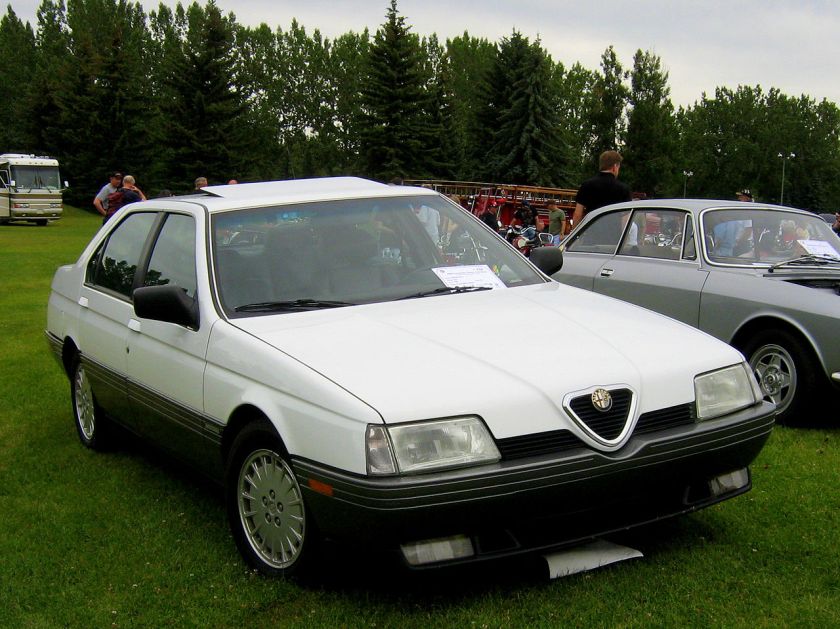 1987-98 Alfa Romeo 164 designed by Pininfarina 1987 Alfa Romeo 164
1987-98 Alfa Romeo 164 designed by Pininfarina 1987 Alfa Romeo 164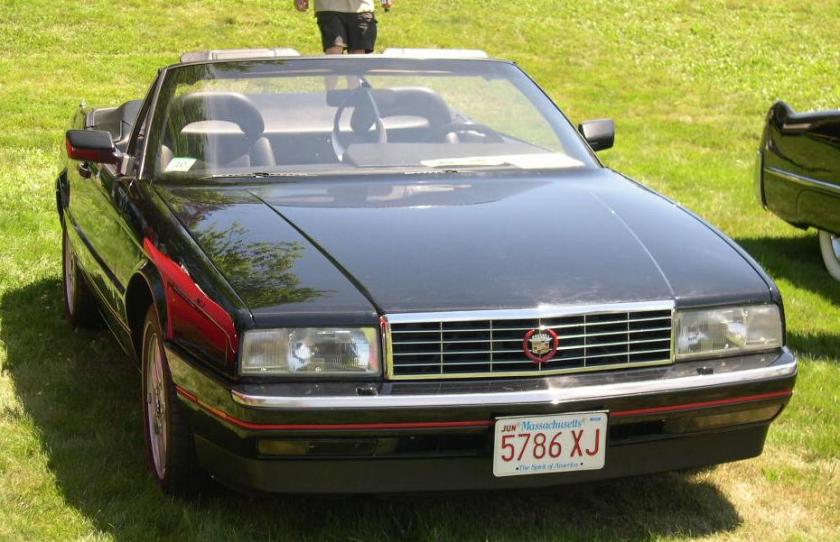 1986-93 Cadillac Allante design by Pininfarina 1987 Cadillac Allanté
1986-93 Cadillac Allante design by Pininfarina 1987 Cadillac Allanté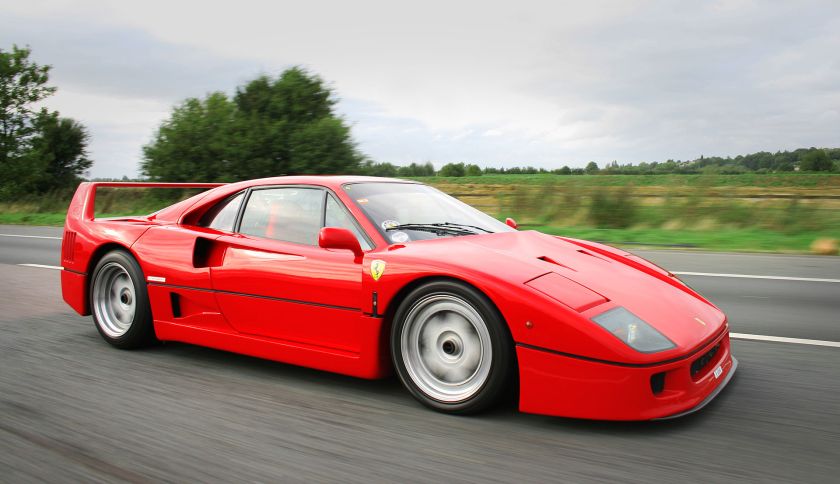 1987-92 Ferrari F40 PininFarina 1987 Ferrari F40
1987-92 Ferrari F40 PininFarina 1987 Ferrari F40 1987 Peugeot 405 Pininfarina
1987 Peugeot 405 Pininfarina 1989-95 Ferrari 348 Pininfarina 1989 Ferrari 348
1989-95 Ferrari 348 Pininfarina 1989 Ferrari 348 1989-99 Peugeot 605 Pininfarina 1989 Peugeot 605
1989-99 Peugeot 605 Pininfarina 1989 Peugeot 605 1991-96 Honda Beat designed by Pininfarina 1991 Honda Beat
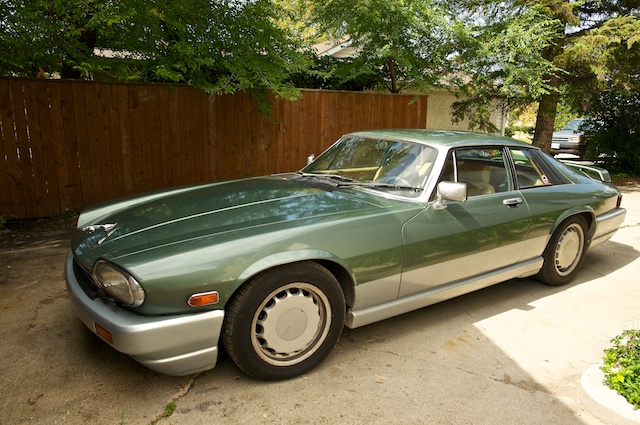
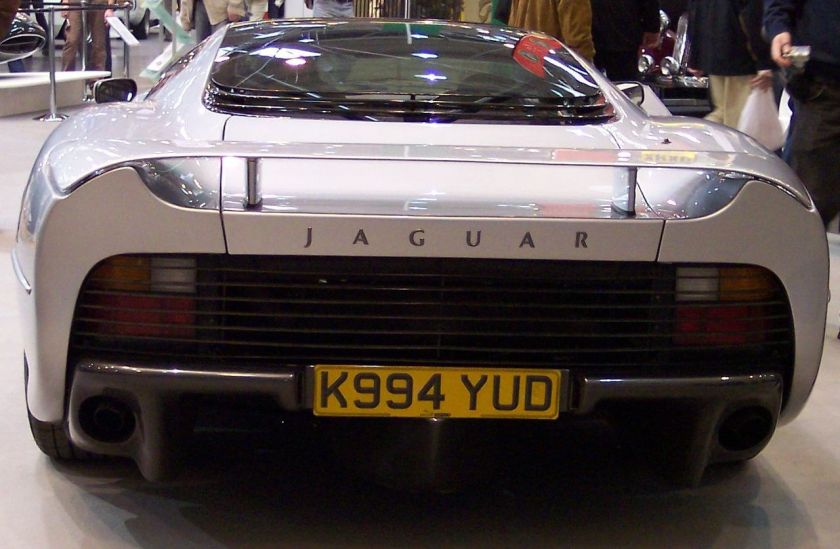
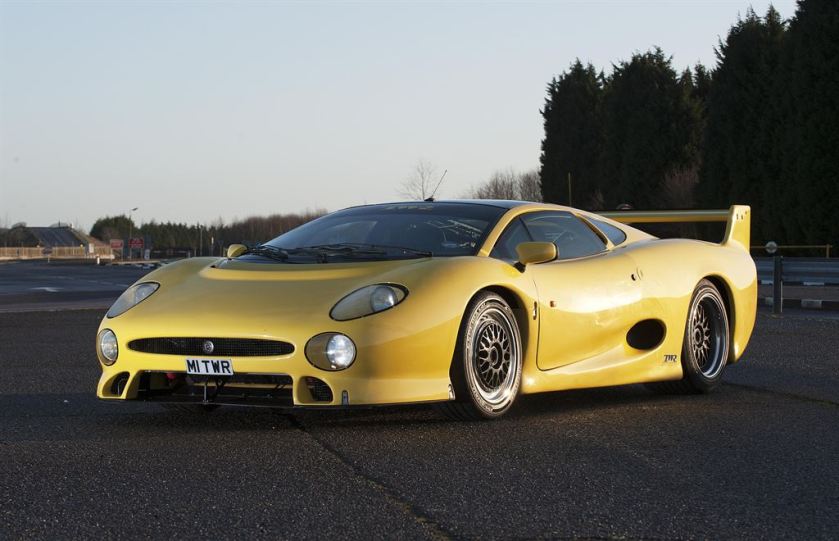
1991-96 Honda Beat designed by Pininfarina 1991 Honda Beat 1992-94 Jaguar XJ220 Pininfarina 1992 Jaguar XJ220—rebodied an unknown number of cars
1992-94 Jaguar XJ220 Pininfarina 1992 Jaguar XJ220—rebodied an unknown number of cars 1992-03 Ferrari 456 GT Pininfarina 1995 1992 Ferrari 456 GT
1992-03 Ferrari 456 GT Pininfarina 1995 1992 Ferrari 456 GT 1993-00 Fiat Coupé Pininfarina
1993-00 Fiat Coupé Pininfarina 1993-00 Fiat Coupè Momo Pininfarina Interiors 1993 Fiat Coupé – Interior only
1993-00 Fiat Coupè Momo Pininfarina Interiors 1993 Fiat Coupé – Interior only 1993-02 Peugeot 306 GTI6 designed by Pininfarina 1993 Peugeot 306
1993-02 Peugeot 306 GTI6 designed by Pininfarina 1993 Peugeot 306 1994-99 Ferrari F355 Berlinetta Pininfarina 1994 Ferrari F355
1994-99 Ferrari F355 Berlinetta Pininfarina 1994 Ferrari F355 1994-03 Opel Omega B Pininfarina 1994 Opel Omega
1994-03 Opel Omega B Pininfarina 1994 Opel Omega 1994–02 Peugeot 306 (N5) cabriolet Pininfarina closed 1994 Peugeot 306 Cabriolet
1994–02 Peugeot 306 (N5) cabriolet Pininfarina closed 1994 Peugeot 306 Cabriolet 1993-06 Alfa Romeo Spider Pininfarina
1993-06 Alfa Romeo Spider Pininfarina Alfa Romeo GTV 3.0 V6 24V rear pininfarina 1995 Alfa Romeo GTV & Spider
Alfa Romeo GTV 3.0 V6 24V rear pininfarina 1995 Alfa Romeo GTV & Spider 1995 Ferrari F355 Spider Pininfarina 1995 Ferrari F355 Spider
1995 Ferrari F355 Spider Pininfarina 1995 Ferrari F355 Spider
? 1995 MG F – Roof Structure only
 1995 Ferrari F50 Pininfarina
1995 Ferrari F50 Pininfarina 1996 Ferrari 550 Maranello Pininfarina
1996 Ferrari 550 Maranello Pininfarina 1996 Lancia Cappa Coupé Pininfarina
1996 Lancia Cappa Coupé Pininfarina 1996 Lancia Kappa SW and coupé pininfarina
1996 Lancia Kappa SW and coupé pininfarina 1996 Lancia Kappa Station Wagon Pininfarina 1996 Lancia Kappa SW
1996 Lancia Kappa Station Wagon Pininfarina 1996 Lancia Kappa SW 1997 Peugeot 406 Coupé rouge lucifer 2.0l 137ch designed by Pininfarina 1997 Peugeot 406 Coupé
1997 Peugeot 406 Coupé rouge lucifer 2.0l 137ch designed by Pininfarina 1997 Peugeot 406 Coupé 1999-05 Ferrari 360 Modena designed by pininfarina 1999 Ferrari 360 Modena
1999-05 Ferrari 360 Modena designed by pininfarina 1999 Ferrari 360 Modena
 1999-present Hafei Zhongyi Pininfarina 1999 Songhuajiang Hafei Zhongyi
1999-present Hafei Zhongyi Pininfarina 1999 Songhuajiang Hafei Zhongyi 2000-present Daewoo Rezzo Pininfarina Front 2000 Daewoo Tacuma
2000-present Daewoo Rezzo Pininfarina Front 2000 Daewoo Tacuma 1999-05 Ferrari 360 Modena Pininfarina
1999-05 Ferrari 360 Modena Pininfarina 2000-2005 Ferrari 360 Spider Pininfarina convertible 2000 Ferrari 360 Spider
2000-2005 Ferrari 360 Spider Pininfarina convertible 2000 Ferrari 360 Spider 2000 Ferrari 550 Barchetta Pininfarina 2000 Ferrari 550 Barchetta
2000 Ferrari 550 Barchetta Pininfarina 2000 Ferrari 550 Barchetta 2001-2004 Hyundai (Matrix)Elantra LaVita (FC) GLS hatchback pininfarina
2001-2004 Hyundai (Matrix)Elantra LaVita (FC) GLS hatchback pininfarina 2011-present Hyundai Matrix 1.6 Comfort Pininfarina 2001 Hyundai Matrix
2011-present Hyundai Matrix 1.6 Comfort Pininfarina 2001 Hyundai Matrix 2002-11 Daewoo Lacetti Pininfarina 2002 Daewoo Nubira/Lacetti saloon and station wagon
2002-11 Daewoo Lacetti Pininfarina 2002 Daewoo Nubira/Lacetti saloon and station wagon 2002-04 Ferrari Enzo Pininfarina Alexandre Prévot (1) 2002 Enzo Ferrari
2002-04 Ferrari Enzo Pininfarina Alexandre Prévot (1) 2002 Enzo Ferrari 2002-06 Ferrari 575M Maranello Pininfarina 2002 Ferrari 575M Maranello
2002-06 Ferrari 575M Maranello Pininfarina 2002 Ferrari 575M Maranello 2002-present Hafei Lobo Pininfarina 2002 Hafei Lobo
2002-present Hafei Lobo Pininfarina 2002 Hafei Lobo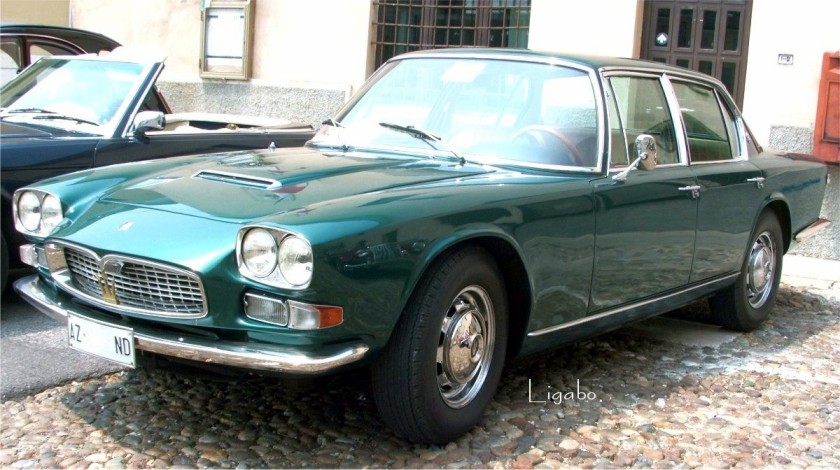 1968 Maserati 4 Porte Pininfarina
1968 Maserati 4 Porte Pininfarina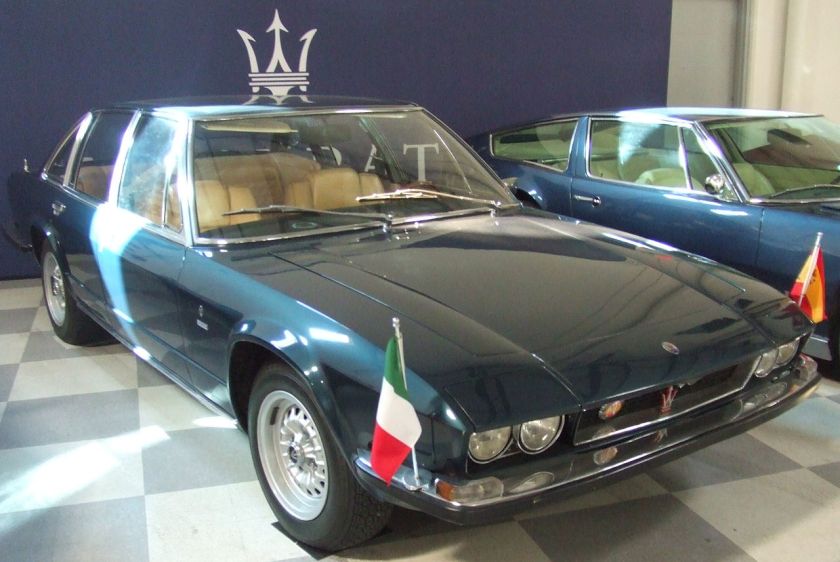 1971 Maserati Quattroporte AM121 Pininfarina
1971 Maserati Quattroporte AM121 Pininfarina 1974 Maserati Medici Pininfarina Show car
1974 Maserati Medici Pininfarina Show car 1986 Maserati Quattroporte III Pininfarina, seen in NY
1986 Maserati Quattroporte III Pininfarina, seen in NY 1987-1990 Maserati Quattroporte III Royale Pininfarina
1987-1990 Maserati Quattroporte III Royale Pininfarina Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina IV 2
Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina IV 2 2003 Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina
2003 Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina 2012 Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina V
2012 Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina V Maserati Quattroporte Sport Pininfarina GT 2003 Maserati Quattroporte
Maserati Quattroporte Sport Pininfarina GT 2003 Maserati Quattroporte Face Lifted Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina
Face Lifted Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina 2015 Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina VI(16810746390)
2015 Maserati Quattroporte Pininfarina VI(16810746390) 2012 Maserati Touring Superleggera Bellagio Pininfarina Fastback at Salon Privé
2012 Maserati Touring Superleggera Bellagio Pininfarina Fastback at Salon Privé 2003 Ford StreetKa Pininfarina
2003 Ford StreetKa Pininfarina 2004-11 Ferrari 612 Scaglietti Pininfarina 2004 Ferrari 612 Scaglietti
2004-11 Ferrari 612 Scaglietti Pininfarina 2004 Ferrari 612 Scaglietti 2004-09 Ferrari F430 Pininfarina 2004 Ferrari F430
2004-09 Ferrari F430 Pininfarina 2004 Ferrari F430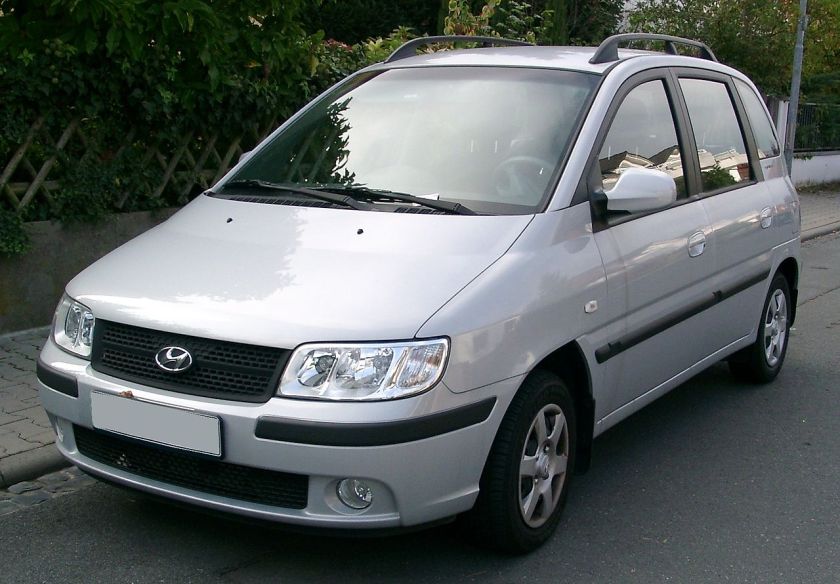 2005-07 Hyundai Matrix Pininfarina front 2005 Hyundai Matrix
2005-07 Hyundai Matrix Pininfarina front 2005 Hyundai Matrix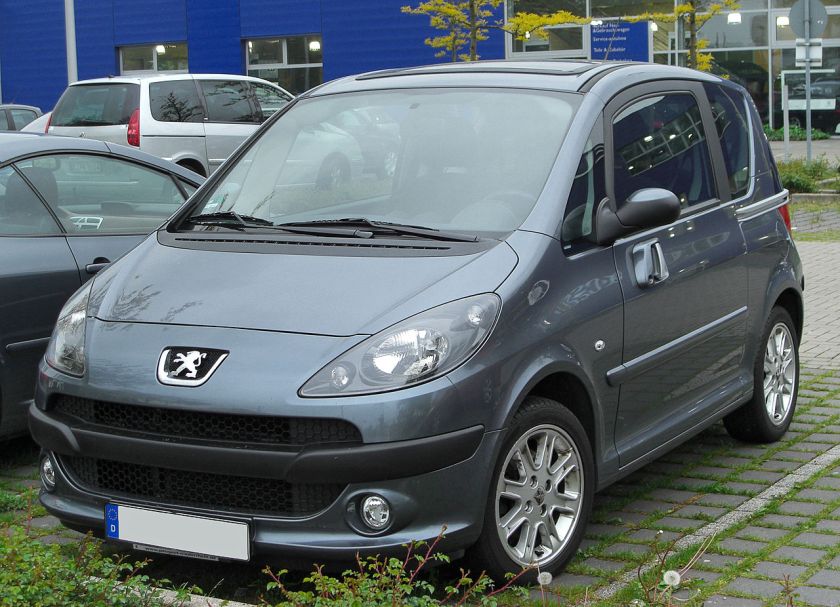 2005-09 Peugeot 1007 Pininfarina 2005 Peugeot 1007
2005-09 Peugeot 1007 Pininfarina 2005 Peugeot 1007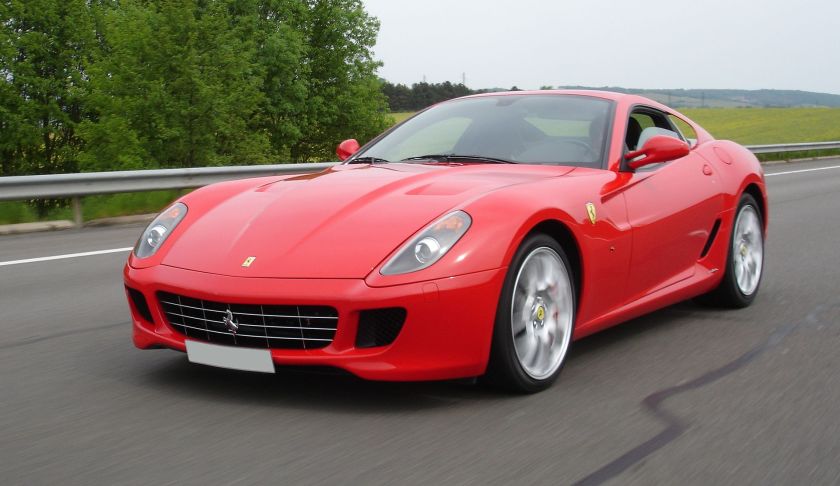 2006-12 Ferrari 599 GTB Fiorano A6 Pininfarina 2006 Ferrari 599 GTB Fiorano
2006-12 Ferrari 599 GTB Fiorano A6 Pininfarina 2006 Ferrari 599 GTB Fiorano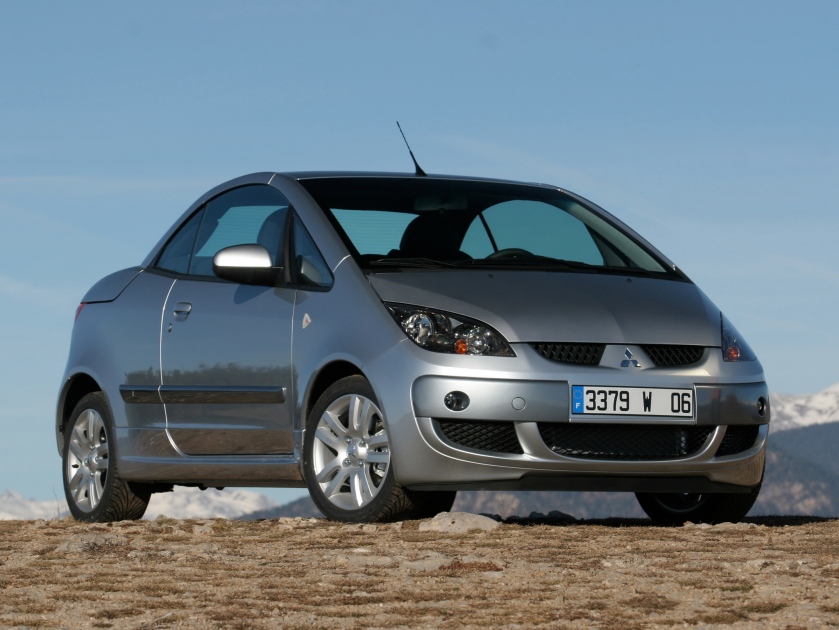 2006 mitsubishi colt czc pininfarina turbo 1
2006 mitsubishi colt czc pininfarina turbo 1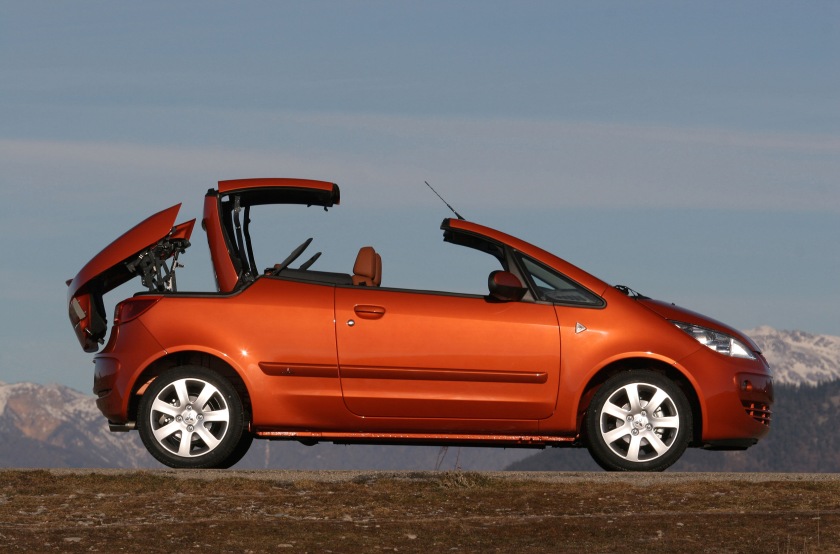 2006-08 Mitsubishi Colt CZC Pininfarina Worldwide
2006-08 Mitsubishi Colt CZC Pininfarina Worldwide 2006-08 Mitsubishi Colt CZC Turbo Pininfarina Worldwide open 2006 Mitsubishi Colt CZC
2006-08 Mitsubishi Colt CZC Turbo Pininfarina Worldwide open 2006 Mitsubishi Colt CZC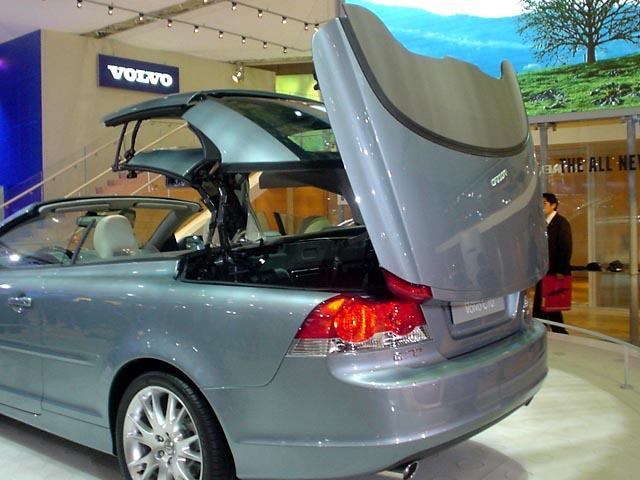 A Volvo C70 with retractable pininfarina hardtop 2006 Volvo C70 – Roof Structure engineering only
A Volvo C70 with retractable pininfarina hardtop 2006 Volvo C70 – Roof Structure engineering only 2007–08 Hyundai Tiburon Pininfarina Coupé 2007 Hyundai Coupe
2007–08 Hyundai Tiburon Pininfarina Coupé 2007 Hyundai Coupe
 2007 Chery A3 designed by Pininfarina 4-door sedan
2007 Chery A3 designed by Pininfarina 4-door sedan 2012 Chery J3 (M1X) hatchback designed by pininfarina 2007 Chery A3 and Chery A3 Sport
2012 Chery J3 (M1X) hatchback designed by pininfarina 2007 Chery A3 and Chery A3 Sport 2007 Ford Focus Coupé-Cabriolet designed by Pininfarina 2007 Ford Focus CC by Pininfarina
2007 Ford Focus Coupé-Cabriolet designed by Pininfarina 2007 Ford Focus CC by Pininfarina 2008-17 Maserati Gran Turismo Pininfarina
2008-17 Maserati Gran Turismo Pininfarina 2013 Maserati GranTurismo Sport Pininfarina 2008 Maserati GranTurismo
2013 Maserati GranTurismo Sport Pininfarina 2008 Maserati GranTurismo 2008-13 Ferrari California designed by Pininfarina 2008 Ferrari California
2008-13 Ferrari California designed by Pininfarina 2008 Ferrari California 2009-15 Ferrari 458 Italia Pininfarina
2009-15 Ferrari 458 Italia Pininfarina 2011-16 Ferrari FF Pininfarina 2011 Ferrari FF
2011-16 Ferrari FF Pininfarina 2011 Ferrari FF 2012-present Ferrari F12 berlinetta Pininfarina 2012 Ferrari F12 Berlinetta
2012-present Ferrari F12 berlinetta Pininfarina 2012 Ferrari F12 Berlinetta 2016 Ferrari F12tdf pininfarina at the 2016 Goodwood Festival of Speed
2016 Ferrari F12tdf pininfarina at the 2016 Goodwood Festival of Speed 2014-present Ferrari California T Pininfarina 2014 Ferrari California T
2014-present Ferrari California T Pininfarina 2014 Ferrari California T
Electric propulsion
Pininfarina has an area dedicated to the new electric car Pininfarina Bolloré. Batteries are produced by the French Bolloré Group.
Pininfarina, has introduced its own electric vehicle concept, the Pininfarina B0 (pronounced “B Zero”). The four-seat hatchback features a solid-state lithium-polymer battery, supercapacitors, and a roof- integrated solar panel to achieve a range of 153 miles (246 km). Developed in partnership with the Bolore Group, the vehicle is slated for limited production in 2009.
Pininfarina will display a turbine-powered plug-in hybrid called the Cambiano at the 2012 Geneva Motor Show.
At the 2016 Geneva Motor Show Pininfarina revealed the H2 Speed, an electric sports car concept. The H2 Speed is a hydrogen vehicle with two race-specification electric motors which are fed by a hydrogen fuel cell. The hydrogen power unit was designed by Swiss company GreenGT.
Other vehicles
Nautical design
- Primatist Aerotop Pininfarina range: G46, G53, B62, G70.
- Magnum Marine 80′ Series
- Pershing 88′ Pininfarina Limited Edition, a one-off body designed by Pininfarina. Yacht was used in a Visa Black Card commercial.
- Fincantieri Ottantacinque by Pininfarina Project.
- Schaefer 620 and 800 by Pininfarina, interiors.
- Persico Marine WallyCento Project.
- Azimut 65 Pininfarina.
Mass transport
- 1999–2007 AnsaldoBredaType 8 Green Line Trolley Car for the MBTA.
- 2000 Hispano CarroceraHabit buses.
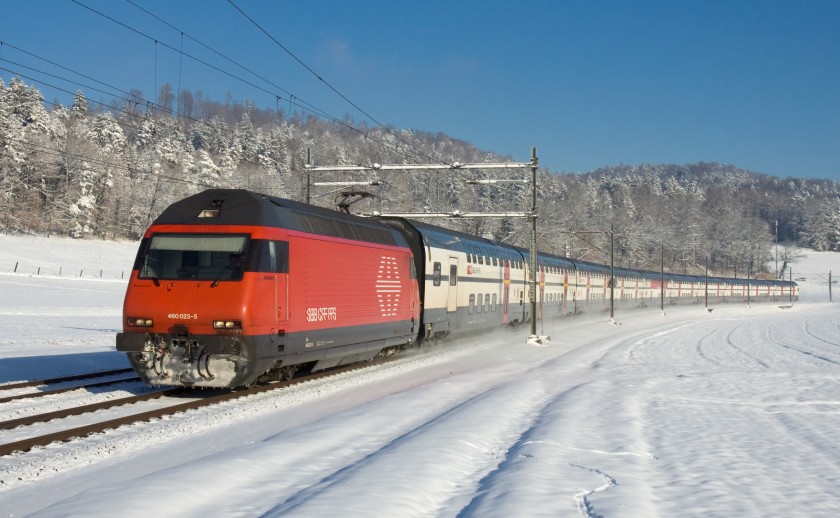
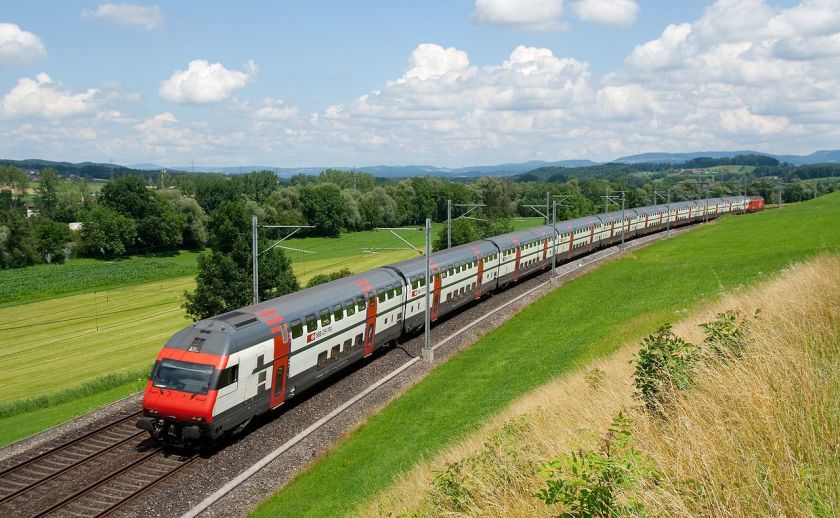
- 2000 SBB-CFF-FFS RABDe 500 (tilting train for the Swiss Federal Railways)
- 2001 AnsaldoBredaBM72electric multiple unit trains for the Norwegian Railways.
- 2001 Cobra tram for Zürich.
- 2004 AnsaldoBredaSirio tram, Athens version
- 2005 AnsaldoBredaIC4 inter-city diesel multiple unit trains for the Danish railways.
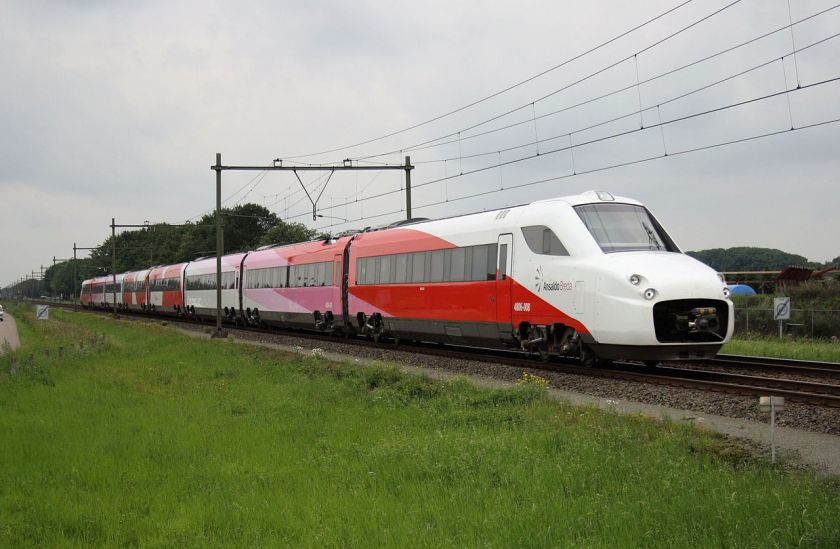 2008 Ansaldo Breda Pininfarina Fyra V250 4806 2008 AnsaldoBredaV250 Albatros high-speed train for NS Hispeed
2008 Ansaldo Breda Pininfarina Fyra V250 4806 2008 AnsaldoBredaV250 Albatros high-speed train for NS Hispeed
- 2009 AnsaldoBreda-Firema Metrostar, suburban train for Circumvesuviana in Naples
- 2009 Eurostar appoints Pininfarina to undertake design work for train refurbishment.
Other works
Pininfarina also works with other companies such as SimpleTech for product design.
Other Pininfarina product designs include the 2006 Winter Olympics torch, cauldron and medals, as well as major appliance collections for Gorenje.
Pininfarina was a design contractor for the development of Coca-Cola Freestyle.
Subsidiaries
Pininfarina Extra, founded in 1986, is the Pininfarina Group design company which does not work in the transport sector. Examples include:
- The Keating Hotel in San Diego, California
- 1100 Millecento Residences interiors in Miami, Florida announced in 2012
- Beachwalk waterfront residences interiors in Hallandale Beach, Florida announced in 2013
- Pininfarina Wine
See also
- Mahindra & Mahindra
- Magna Steyr
- Heuliez
- Valmet Automotive
- Ken Okuyama
- Sergio Pininfarina
- Battista Farina
- Andrea Pininfarina
References
- ^ Nedelea, Andrei (29 March 2013). “Pininfarina Turns a Profit for the First time Since 2004”. carscoops.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ a b “Pininfarina Group: Appointments of New Officers and New Assignments in the Sign of Corporate Continuity” (PDF) (Press release). Pininfarina Group. 12 August 2008. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ a b Philip, Siddharth Vikram; Ebhardt, Tommaso (14 December 2015). “Mahindra Agrees to Purchase of Car-Designer Pininfarina”. Bloomberg. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ a b c d Borgeson, Griff (December 1963). “Pininfarina man, myth, & monopoly”. Road & Track: 37–38.
- ^ “Pininfarina SpA”. Companyspotlight.com. 2013. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “Pininafarina Anniversary”. Concorsodeleganzavilladeste.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “Pinin Farina 1930”. classiccarcatalogue.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ a b c Borgeson, Griff (March 1964). “Pininfarina, The New Generation”. Road & Track: 83.
- ^ Vitello, Paul (3 July 2012). “Sergio Pininfarina, 85, Designer of Sports Cars”. The New York Times.
- ^ “History of the Paris Motor Show - 2006”. Motorshow.cars.uk.msn.com. Archived from the original on 2 June 2013. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Ernesto Caballo, Pininfarina n. 12 1972-73, p.160
- ^ Thompson, Jonathan (March 1976). “The Early Pininfarina Line”. Road & Track: 37.
- ^ Stigh, Daniela (6 April 2012). “Five for Friday (Plus One): MoMA’s Car Collection”. MoMA. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Adolphus, David Traver (1 May 2008). “Days of Ferrari 2008, Day 3: 1952 Ferrari 212 Inter Coupe PF”. Hemmings.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “Divorce, Italian style? No, but a design change at Ferrari”. Automotive News Europe. 28 March 2013. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Thompson, Jonathan (December 1976). “The Early Pininfarina Line”. Road & Track: 54.
- ^ Gino Rancati, Pininfarina n. 12 1972-73, p.162
- ^ Ready, Owen (5 March 2013). “Pininfarina Sergio concept”. Cardesignnews.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Wilson, Wilson. Alfa Romeo Giulietta, p.43
- ^ “Battista Pininfarina Is Dead - Pioneer Automobile Designer”. The New York Times. 3 April 1966. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ “Pininfarina History - The Story of Battista Farina”. Archived from the original on 30 October 2013. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ a b “Pininfarina - Coach Builder Information”. Conceptcarz.com. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ “30 years at the GM wind tunnel”. VideoatGM.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Klassen, Robert; Menor, Larry J. (2006). Cases in Operations Management: Building Customer Value Through World-Class Operations. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE. p. 12. ISBN 978-1-4129-1371-3. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ Klassen, Robert; Menor, Larry J. (2006). Cases in Operations Management: Building Customer Value Through World-Class Operations. Thousand Oaks, California: Sage. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-4129-1371-3. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ Pininfarina Annual Report. Pininfarina. 2004. p. 10.
- ^ Ciferri, Luca (28 August 2008). “Tata wants part of Pininfarina”. Automotive News Europe. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Ireson, Nelson (29 April 2008). “Update: Ferrari, Brembo and Sabelt invest in Pininfarina”. Motorauthority.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Boland, Vincent (1 January 2009). “Pininfarina family to sell stake in car group” (fee required). Financial Times. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Patrascu, Daniel (24 March 2009). “Pininfarina to Get New Owner, Focus on Electric Cars”. Autoevolution.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “BAIC speculation drives up Pininfarina share price”. Just-auto.com. 4 January 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Clark, Jennifer (14 February 2012). “Pininfarina family losing control in debt deal-sources”. Reuters. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Cambieri, Giulia (16 February 2012). “Family business roundup: Pininfarina remains family-controlled while De Tomaso is sold”. Campden FB. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Bowman, Zach (16 May 2012). “Pininfarina turns first net profit since 2004”. Autoblog. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ Ramsey, Jonathon (26 March 2013). “Pininfarina in the black for first time since 2004”. Autoblog. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Pininfarina - Stop alla produzione e mobilità per 127 addetti - Quattroruote” (in Italian). Quattroruote.it. Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ “Pininfarina History”. Retro-speed.co.uk. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Titolo Pagina”. Torino.repubblica.it. Archived from the original on August 19, 2014. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ a b 2010 annual report p13
- ^ Kurt, Ernst. “Lost Cars of the 1980s – Cadillac Allante”. Hemmings. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ a b c 2011 annual report p69
- ^ “Bollore’: intesa con Pininfarina per produzione Bluecar fino a 2016, verso filiale italiana”. http://www.corriere.it. RCS Mediagroup. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ^ Bolduc, Douglas A. “Three bad days for European car plants – and more to come”. Automotive News. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- ^ Lewin, Tony Autor; Borroff, Ryan (2010). How to: Design Cars Like a Pro: AA Comprehensive Guide to Car Design from the Top Professionals. p. 158.
- ^ a b “A Life of Style”. The Auto Channel. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Annual Financial Report. Pininfarina. 2012. p. 12.
- ^ Annual Financial Report. Pininfarina. 2006. p. 11.
- ^ Strohl, Daniel. “Franco Scaglione: Unsung Master of Aerodynamic Design”. Hemmings. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ “Google Translate”. Translate.googleusercontent.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ Nerozzi, Barbara, ed. (January–February 1992). “The Suppliers”. GB Progetti: 48.
- ^ “Ian Cameron”. sparkawards.com. Spark Design Awards. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ^ D’Aprile. “Elvio Elvio D’Aprile”. Linkedin. Retrieved 16 May 2013.
- ^ “Interview met designchef Marco Tencone over de nieuwe Lancia Ypsilon”. EdizioneMedia (in Dutch). 30 June 2011. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ “Maurizio Corbi” (PDF). corbistudios.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “BMW Car Designers throughout history”. BMWism.com. 2013. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ “Jeremy Malick”. Linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “Dimitri Vicedomini”. linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “Luca Borgogno”. linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “Nazzareno Epifani”. Linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “Brano Mauks”. Linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “Carlo Palazzani”. Linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “Felix Kilbertus”. Linkedin. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ Auto Editors of Consumer Guide (20 May 2007). “Maserati Sports Cars”. HowStuffWorks. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Blue survivor: 1949 Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 Cabriolet Pininfarina”. Classic Virus. 29 January 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Alfa Romeo 6C 2500 SS Pinin Farina Cabriolet”. Ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- ^ “1948 Maserati A6 1500 Spider Pininfarina”. automobile-catalog. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- ^ Goldberg, Geoff. “Collectors Corner - Lancia B20 GT - The classic Gran Turismo Coupe”. anamera.com. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- ^ Garcia, Gonzalo Alvarez (1983). Alfa Romeo 1900 Sprint. Milano, Italy: Edizioni della Libreria dell’Automoble. p. 86. ASIN B003B5M3SI. Archived from the original on May 8, 2014. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
- ^ Garcia, Gonzalo Alvarez (1983). Alfa Romeo 1900 Sprint. Milano, Italy: Edizioni della Libreria dell’Automoble. p. 88. ASIN B003B5M3SI. Archived from the original on May 8, 2014. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
- ^ a b “1952 Ferrari 212 Inter Images, Information and History (Road)”. Conceptcarz.com. 1952-10-11. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ a b c d Cezar, Luis. “Lancia D20 & D24”. autoclassic.com. Portal AutoClassic. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ^ McCourt, Mark J. (September 2008). “1952-’53 Nash-Healey: America’s First Post-War Sportster was a Truly International Affair”. Hemmings Motor News. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- ^ Cupler, Justin. “1953 Ferrari 375 MM Spider By Pininfarina”. topspeed.com. Retrieved 5 May 2013.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Lancia D23 Sport Pinin Farina Spyder”. ultimatecarpage. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Lancia D24 Sport Pinin Farina Spyder”. ultimatecarpage. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1957 Fiat 1100 Turismo Veloce Images, Information and History (1100 TV)”. Conceptcarz.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “D25 Sport Pinin Farina Spyder”. ultimatecarpage. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Maserati A6 GCS/53 Pinin Farina Berlinetta”. Ultimatecarpage. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi (1978). Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Milano: emmeti grafica. pp. 857–858.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi (1978). Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Milano, Italy: emmeti grafica. pp. 858–859.
- ^ Ritzinger, Andre. “Lancia Coupes & Convertibles 1950 - 1980”. Ritzsite.nl. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Boe, Alan (April 1982). “The 250 GTE The First Family Ferrari” (PDF). Car Collector and Car Classics: 21. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
- ^ “Lancia Flavia Coupe (1962 - 1970)”. honestjohn.co.uk. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi (1978). Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Milano: emmeti grafica. pp. 862–863.
- ^ Daniel, Vaughan. “1963 Ferrari 330 America”. conceptcarz. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ “1964 330 GT 2+2”. auto.ferrari.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi (1978). Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Milano: emmeti grafica. p. 864.
- ^ Owen, Richard Michael. “1966→1968 Ferrari 330 GTC”. supercars.net. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ “GT 330 2+2: Luxury open sports cars”. FIAT Group. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
- ^ Westen, Anthony. “Fiat 124 Spider Blog”. Fiat 124 Spider Blog. Anthony Westen. Retrieved 17 May 2013.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Ferrari 330 GTC Coupe Speciale”. ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi (1978). Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Milano: emmeti grafica. pp. 864–866.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi (1978). Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Milano: emmeti grafica. pp. 868–870.
- ^ a b Baron, Philippe. “Peugeot 504 Coupé & Cabriolet (1969-1983)”. stubs-auto. Philippe Baron. Retrieved 3 July 2014.
- ^ “Ferrari 365 GTC/4 Detailed Information”. 365gtc4.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ a b c d e f g “PRODUZIONE COMPLESSIVA” (PDF). pininfarina.it. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 2007-08-03.
- ^ “Development of theTalbot Samba cars”. Rootes-chrysler.co.uk. 2007-02-06. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ Nerozzi, Barbara, ed. (January–February 1992). “The Suppliers”. GB Progetti: 104–122.
- ^ “Missing”.
- ^ “Number of Ferrari 456GT’s produced”. 456gt.com. 29 January 2010. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Pininfarina Annual Report 1999–2005
- ^ “Streetka Production figures.”. TalkFord.com. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
- ^ Pininfarina 2006–2010 Annual Reports
- ^ “1969 Fiat Dino - Classic Car Price Guide”. The Hagerty Group. Retrieved 26 December 2013.
- ^ “AUTOMOTIVE HISTORY: Pininfarina”. Automotive-history.blogspot.com. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ “6c 2300 B Lungo #814047 Lukas Hüni AG”. Alfa Bulletin Board. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1936 Lancia Astura Images, Information and History”. Conceptcarz.com. 2012-11-29. Retrieved 2013-05-30.
- ^ Lombard, Stefan (2006-07-28). “Most Expensive Collectible Cars – No. 10: 1937 Alfa Romeo 8C 2900”. Connoisseur’s Guide – Most Expensive Collectible Cars. Forbes.com. Retrieved 2012-02-18
- ^ Thatcher, Sharon. “An Alfa Romeo mystery”. old cars weekly. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ Lienert, Paul. “2008 Paris Auto Show: Pininfarina B0”. Edmunds Inside Line. Archived from the original on 28 July 2008. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “The Pininfarina BO Electric Car”. India. com. 6 October 2008. Archived from the original on 29 January 2009. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Fiordelisi, Francesco. “At Villa d’Este world debut for the BMW Pininfarina Gran Lusso Coupé” (PDF). Pininfarina. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “Postmodernism 1949 -1960: new ideas within the mindset of the past, comfort and beauty”. BMWism.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “Pics & vids: Schloß Dyck Classic Days 2009”. COACHBUILD.com. NAIT Media Ventures. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ a b c d Melissen, Wouter. “Lancia Aurelia B52 PF200 Cabriolet”. http://www.ultimatecarpage.com. ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- ^ a b c d e it:Lancia Aurelia autotelai
- ^ “In deep”. http://www.pininfarina.com. Pininfarina SpA. Retrieved 2 June 2013.
- ^ a b “Aldo Brovarone”. studiotorino.com. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ “1955 Nash Special (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ a b c d “Pininfarina Alfa Romeo 6C 3000 CM Super Flow”. Coachbuild.Com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Foster, Pat (September 2005). “Pinin Farina’s Rambler Palm Beach”. Hemmings Classic Car. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ “The Fiat-Abarth Bertone record car”. Ugofadini.com. 21 December 2007. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ Conceptcarz page on Cadillac ”Jacqueline”, retrieved on 17 December 2010.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Ferrari 250 GT Pininfarina Coupe Speciale”. ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 8 January 2014.
- ^ “1962 Fiat 2300 Coupe Speciale (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1963 Chevrolet Corvair Super Spyder Coupé”. Conceptcarz. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1963 Chevrolet Corvette Rondine Coupé”. Conceptcarz. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Fiat 2300 Cabriolet Speciale (Italy)”. allcarindex.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1964 Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1963 Pininfarina PF Sigma”. allcarindex.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “Ferrari 206 P Dino Pininfarina Berlinetta Speciale”. ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Ferrari 250 LM Pininfarina Stradale Speciale”. Ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- ^ “1965 Ferrari 365P Berlinetta Speciale Luigi ”Coco” Chinetti’s three-seater prototype”. European Car Magazine. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “Fiat 2300 S Coupe Speciale 1965 designed by Pininfarina”. autowp.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Rees, Chris. “Pininfarina’s Greatest Car Designs”. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “Meadow Brook Concours 2009: 1967 Ferrari Dino 206 Competizione by Pininfarina”. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ “Fiat Dino Parigi (Italy)”. allcarindex.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1968 Bentley T1 Coupe Speciale”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1968 Pininfarina BLMC 1100”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi. Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Emmetigrafica, 1978, p. 687.
- ^ “1968 Ferrari P6 (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1968 Pininfarina MG EX.234”. webcarstory.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “1968 Ferrari 250 P5”. ferraridatabase.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1969 Abarth 2000 Pininfarina Coupe Concept specifications”. automobile-catalog.com. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ a b Fusi, Luigi. Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Emmetigrafica, 1978, p. 688.
- ^ “1969 Pininfarina Sigma Grand Prix monoposto F1”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1969 Ferrari 512 S Berlinetta Speciale”. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “1969 Fiat 128 Teenager (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “Concept Cars”. webcarstory.com. Retrieved 29 May 2013.
- ^ “The 504 Model Range”. garage24.net. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ “Pininfarina NSU Ro 80 designed by Paolo Martin”. madle.org. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ Dinarich, Mario. Style Auto Quarterly. Style Auto Editrice s.n.c., April–May–June 1973, p. 26.
- ^ “Missing”. Concept Cars – Passato, Presente e Futuro del Car Design. Archived from the original on December 29, 2010. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ “Chevrolet Corvette XP-897 GT”. lotusespritturbo.com. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ “1974 Ferraris CR 25”. Ferraridatabase.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1974 Fiat 130 Maremma (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “Fiat 130 Opera”. quattro-porte.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1978 Fiat Ecos (Pininfarina)”. ecopolis.org. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Classic Concepts: 1978 Jaguar XJ Spider by Pininfarina”. Archived from the original on January 5, 2013. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “Gamma Spider”. carsfromitaly.net. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ Thompson, Rufus. “Concept Car of the Week: Pininfarina CNR-PF (1978)”. cardesignnews. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “1980 Lancia Gamma Scala”. Christie’s. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1981 Audi Quartz (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “Gamma Olgiata”. carsfromitaly.net. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “Pininfarina Brio (Italy)”. allcarindex.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1984 Honda HP-X concept”. conceptcarz. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1985 Peugeot Griffe 4 (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1986 Alfa Romeo Vivace Coupe and Spider (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1988 Lancia HIT (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “Pininfarina CNR E2 (Italy)”. allcarindex.com. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “1991 Opel Chronos”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1992 Pininfarina Fiat Cinquecento 4×4 pick-up”. webcarstory.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1992 Pininfarina Ethos”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1993 Pininfarina Ethos 2”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1994 Fiat Spunto (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1994 Pininfarina Ethos 3”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Simanaitis, Dennis. “Honda Argento Vito by Pininfarina”. simanaitissays.com. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “1995 Honda SSM (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1996 Fiat Sing e Song (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1996 Pininfarina Eta Beta”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1997 Peugeot Nautilus (Pininfarina)”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Collaborations - Fiat”. Pininfarina. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ Perini, Giancarlo. “Much more than just a cubic metro.”. http://www.cardesign.to. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ Simona. “2000 Ferrari Rossa By Pininfarina”. TopSpeed. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ KIINO, RON. “Pininfarina Start 2001 Frankfurt Auto Show”. Car and Driver. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ Giancarlo, Perini. “Pininfarina develops two new Chinese cars”. Car Design News. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “2003 Lotus Enjoy Concept”. conceptcarz. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ a b Ellison, Edd (12 October 2004). “Over the last fortnight ..”. italiaspeed.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Saturn Curve”. ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Keegan Jr., Walter J. “Chery M14 wins ”Best New Car in Show””. autoblog. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Ferrari 612 Scaglietti ”K” by Pininfarina”. Pininfarina. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ^ “Concept car Sintesi”. Pininfarina. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ McCausland, Evan. “Ferrari Builds One-Off P540 Superfast Aperta”. Automobile Magazine. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ “AUSmotive.com - Pininfarina to woo Alfa Romeo with Spider Concept”, retrieved on February 6, 2010.
- ^ Ramsey, Jonathon (2010-08-25). “Michael Stoschek’s Wild Child: the New Lancia Stratos”. stylelist AOL. Archived from the original on December 30, 2010. Retrieved 2011-09-05.
- ^ “2010 Pininfarina Nido EV”. carstyling.ru. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Deacon, Clinton. “Eric Clapton’s Ferrari SP12 EPC caught on video”. http://www.worldcarfans.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Ciferri, Luca (1 March 2016). “Hydrogen Pininfarina concept wants to make your race track green”. autoweek. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ^ Duffey, Michael. “1951 Simca 8 Super Sport”. Sports Car Market Magazine. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Auto Editors of Consumer Guide (13 September 2007). “1952-1954 Nash Ambassador and Statesman”. auto.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Auto Editors of Consumer Guide (27 October 2007). “1952 Nash-Healey”. auto.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Fusi, Luigi. Alfa Romeo All Cars From 1910. Emmetigrafica, 1978, p. 527.
- ^ Melissen, Wouter. “Ferrari 275 GTB/C”. ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1976 Peugeot Peugette”. Carfolio. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Lamm, John (23 October 2013). “And the Beat Goes On: Honda Bringing S660 Concept to Tokyo [2013 Tokyo Auto Show]”. Car & Driver. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Two car models for China signed by Pininfarina the A3 and the A3 Sport”. Pininfarina. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Weiner, Eric (12 February 2014). “Ferrari California T Set for 2014 Geneva Auto Show Debut”. Automobile Magazine. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Taylor, Edward (6 May 2008). “Start-Ups Race to Produce ’Green’ Cars”. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- ^ “New Electric Minicar from Pinifarina”. Minutia microcars and minicars. 11 October 2008. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Leaked: turbine-powered Pininfarina Cambiano plug-in hybrid”. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Pininfarina returns with hydrogen H2 Speed at Geneva Show”. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- ^ “Pininfarina H2 Speed - hydrogen sports car revealed at Geneva”. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- ^ “Pininfarina showcases silky-smooth, hydrogen-powered H2 Speed concept”. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- ^ “Primatist Aerotop Pininfarina range”. Primatist.
- ^ “Primatist B62”. Pininfarina.
- ^ “Magnum 80’ Series”. Magnum Marine.
- ^ “Pershing 88 Pininfarina”. Acronautic.
- ^ “Ottantacinque by Pininfarina”. Pininfarina.
- ^ “Rio Boat Show presents the Schaefer 800 by Pininfarina”. Schaefer Yachts.
- ^ “Pininfarina joins Persico Marine on fourth WallyCento hull”. Boat International.
- ^ “1980”. Pininfarina. Archived from the original on August 16, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-29.
- ^ IC2000 arrives next year
- ^ “Swiss Tilting Trains Modernisation Programme”. Railway Technology. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Athens Trams Project in Greece”. Railway Technology. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Campione, David (24 November 2008). “Metrostar, i nuovi treni della Circumvesuviana” (in Italian). FOL. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Eurostar refubishment design contract awarded”. Railway Gazette International. 8 April 2009. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “New drives from SimpleTech designed by Pininfarina”. Slashgear. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “Gorenje Pinifarina”. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Collier, Joe Guy (11 May 2010). “Coke targets Freestyle expansion for 2010”. The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ Collier, Joe Guy (16 September 2009). “Coke tests new dispenser in Atlanta”. The Atlanta Journal-Constitution. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ “1100 Millecento Residences Brickell”. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ “Pininfarina SpA : Beachwalk, second Pininfarina project in Florida with The Related Group”. Retrieved 27 September 2013.
External links
- Official website
- Pininfarina Sverige
- Foster, Patrick R. (Winter 2001). “Nashes With an Italian Accent” (PDF). FORWARD: The American Heritage of DaimlerChrysler: 33–37. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 April 2006. Retrieved 19 June 2014.
- BMC 1800 & 1100 – detail on these influential design proposals
- The Cisitalia 2002 at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City.
- Cisitalia Museum
- The Keating Hotel in downtown San Diego.
- Pininfarina Wine
- Pininfarina at coachbuild.com