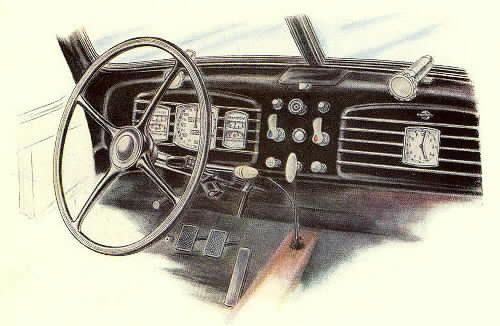
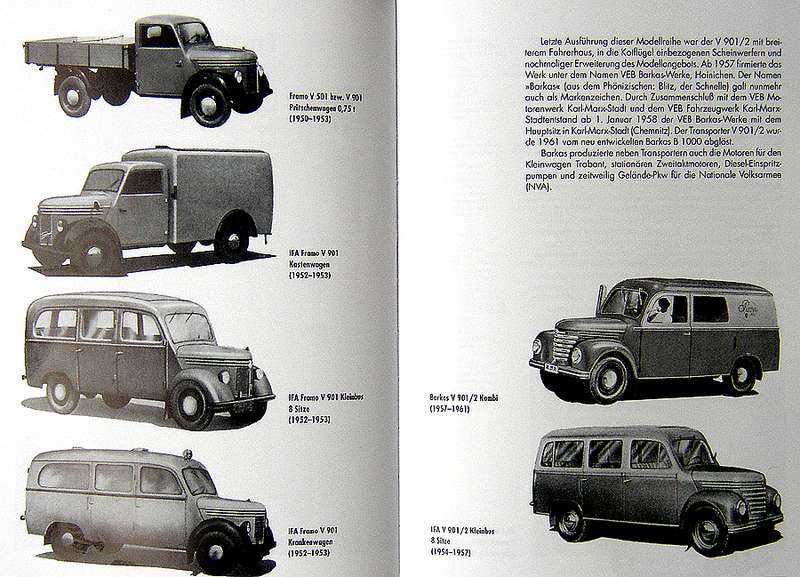
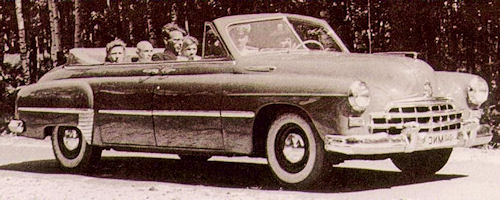
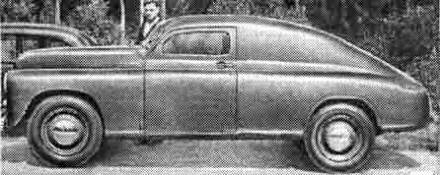
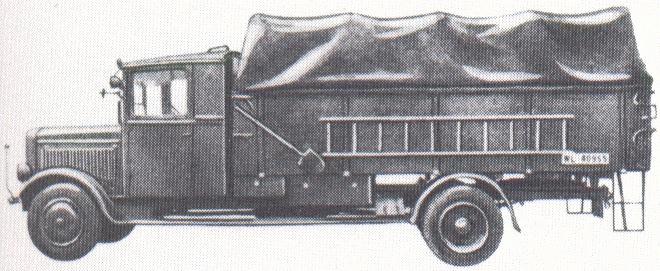
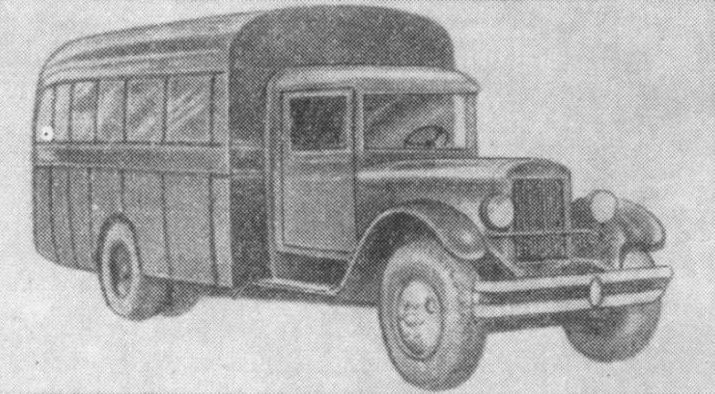
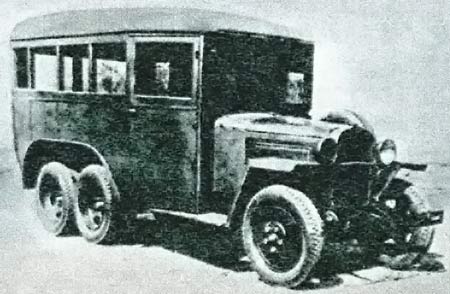
Buses FORD USA & all over the world part I
Ford Motor Company I

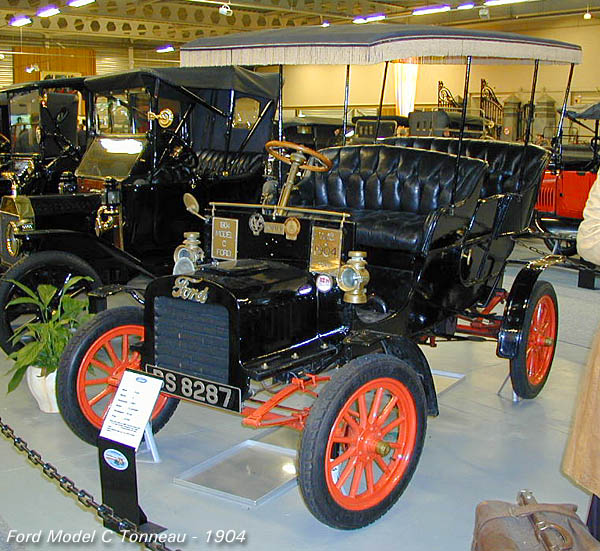
1914 Ford Model T, Four cylinders, 2900cc, 20 Horsepower

“Ford” redirects here. For other uses, see Ford.

1914 Ford T R Spanje ©David Tejedor
Ford Motor Company (also known as simply Ford) is an American multinational automaker headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobiles and commercial vehicles under the Ford brand and luxury cars under the Lincoln brand. In the past it has also produced heavy trucks, tractors and automotive components. Ford owns small stakes in Mazda of Japan and Aston Martin of the United Kingdom. It is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and is controlled by the Ford family, although they have minority ownership.

1916 Ford Model T oldtimer bus L
Ford introduced methods for large-scale manufacturing of cars and large-scale management of an industrial workforce using elaborately engineered manufacturing sequences typified by moving assembly lines; by 1914 these methods were known around the world as Fordism. Ford’s former UK subsidiaries Jaguar and Land Rover, acquired in 1989 and 2000 respectively, were sold to Tata Motors in March 2008. Ford owned the Swedish automaker Volvo from 1999 to 2010. In 2011, Ford discontinued the Mercury brand, under which it had marketed entry-level luxury cars in the United States since 1938.

1916 ford T Depot Hack
Ford is the second-largest U.S.-based automaker and the fifth-largest in the world based on 2010 vehicle sales. At the end of 2010, Ford was the fifth largest automaker in Europe. Ford is the eighth-ranked overall American-based company in the 2010 Fortune 500 list, based on global revenues in 2009 of $118.3 billion. In 2008, Ford produced 5.532 million automobiles and employed about 213,000 employees at around 90 plants and facilities worldwide.

1917 Ford Autobus Model TT

1918 T Ford Bus
History

Henry Ford (ca. 1919)

A 1910 Model T, photographed in Salt Lake City
Main article: History of Ford Motor Company
20th century

1920 Ford bus – DD 475

1921 Harmonicabus op basis van Ford T © Conam
Henry Ford’s first attempt at a car company under his own name was the Henry Ford Company on November 3, 1901, which became the Cadillac Motor Company on August 22, 1902, after Ford left with the rights to his name. The Ford Motor Company was launched in a converted factory in 1903 with $28,000 in cash from twelve investors, most notably John and Horace Dodge (who would later found their own car company). During its early years, the company produced just a few cars a day at its factory on Mack Avenue in Detroit, Michigan. Groups of two or three men worked on each car, assembling it from parts made mostly by supplier companies contracting for Ford. Within a decade the company would lead the world in the expansion and refinement of the assembly line concept; and Ford soon brought much of the part production in-house in a vertical integration that seemed a better path for the era.
1922 Ford
Henry Ford was 39 years old when he founded the Ford Motor Company, which would go on to become one of the world’s largest and most profitable companies, as well as being one to survive the Great Depression. As one of the largest family-controlled companies in the world, the Ford Motor Company has been in continuous family control for over 100 years.

1922 FORD T-OMNIBUS
After the first modern automobile was already created in the year 1886 by German inventor Carl Benz (Benz Patent-Motorwagen), more efficient production methods were needed to make the automobile affordable for the middle-class; which Ford contributed to, for instance by introducing the first moving assembly line in 1913.
In 1908 Ford introduced the first engine with a removable cylinder head, in the Model T. In 1930, Ford introduced the Model A, the first car with safety glass in the windshield. Ford launched the first low priced V8 engine powered car in 1932.

1922 Henry Ford I ©HenryFord.ORG TheOldMotor
Ford offered the Lifeguard safety package from 1956, which included such innovations as a standard deep-dish steering wheel, optional front, and, for the first time in a car, rear seatbelts, and an optional padded dash. Ford introduced child-proof door locks into its products in 1957, and in the same year offered the first retractable hardtop on a mass-produced six-seater car. The Ford Mustang was introduced in 1964. In 1965 Ford introduced the seat belt reminder light.
With the 1980s, Ford introduced several highly successful vehicles around the world. During the 1980s, Ford began using the advertising slogan, “Have you driven a Ford, lately?” to introduce new customers to their brand and make their vehicles appear more modern. In 1990 and 1994 respectively, Ford also acquired Jaguar Cars and Aston Martin. During the mid- to late 1990s, Ford continued to sell large numbers of vehicles, in a booming American economy with a soaring stock market and low fuel prices.

1922 Henry Fordson II ©HenryFord.ORG TheOldMotor
With the dawn of the new century, legacy healthcare costs, higher fuel prices, and a faltering economy led to falling market shares, declining sales, and diminished profit margins. Most of the corporate profits came from financing consumer automobile loans through Ford Motor Credit Company.
21st century

William Clay Ford, Jr., great-grandson of Henry Ford, serves as the executive chairman at the board of Ford Motor Company.
By 2005, both Ford and GM‘s corporate bonds had been downgraded to junk status, as a result of high U.S. health care costs for an aging workforce, soaring gasoline prices, eroding market share, and an over dependence on declining SUV sales. Profit margins decreased on large vehicles due to increased “incentives” (in the form of rebates or low interest financing) to offset declining demand. In the latter half of 2005, Chairman Bill Ford asked newly appointed Ford Americas Division President Mark Fields to develop a plan to return the company to profitability. Fields previewed the Plan, named The Way Forward, at the December 7, 2005 board meeting of the company and it was unveiled to the public on January 23, 2006. “The Way Forward” included resizing the company to match market realities, dropping some unprofitable and inefficient models, consolidating production lines, closing 14 factories and cutting 30,000 jobs.

1923 Ford A R Spanje ©Lluis Cuesta
Ford moved to introduce a range of new vehicles, including “Crossover SUVs” built on unibody car platforms, rather than more body-on-frame chassis. In developing the hybrid electric powertrain technologies for the Ford Escape Hybrid SUV, Ford licensed similar Toyota hybrid technologies to avoid patent infringements. Ford announced that it will team up with electricity supply company Southern California Edison (SCE) to examine the future of plug-in hybrids in terms of how home and vehicle energy systems will work with the electrical grid. Under the multi-million-dollar, multi-year project, Ford will convert a demonstration fleet of Ford Escape Hybrids into plug-in hybrids, and SCE will evaluate how the vehicles might interact with the home and the utility’s electrical grid. Some of the vehicles will be evaluated “in typical customer settings”, according to Ford.

1923 Ford Amaac Uruquay
William Clay Ford Jr., great-grandson of Henry Ford (and better known by his nickname “Bill”), was appointed Executive Chairman in 1998, and also became Chief Executive Officer of the company in 2001, with the departure of Jacques Nasser, becoming the first member of the Ford family to head the company since the retirement of his uncle, Henry Ford II, in 1982. Upon the retirement of President and Chief Operation Officer Jim Padilla in April 2006, Bill Ford assumed his roles as well. Five months later, in September, Ford named Alan Mulally as President and CEO, with Ford continuing as Executive Chairman. In December 2006, the company raised its borrowing capacity to about $25 billion, placing substantially all corporate assets as collateral. Chairman Bill Ford has stated that “bankruptcy is not an option”. Ford and theUnited Auto Workers, representing approximately 46,000 hourly workers in North America, agreed to a historic contract settlement in November 2007 giving the company a substantial break in terms of its ongoing retiree health care costs and other economic issues. The agreement included the establishment of a company-funded, independently run Voluntary Employee Beneficiary Association (VEBA) trust to shift the burden of retiree health care from the company’s books, thereby improving its balance sheet. This arrangement took effect on January 1, 2010. As a sign of its currently strong cash position, Ford contributed its entire current liability (estimated at approximately US$5.5 billion as of December 31, 2009) to the VEBA in cash, and also pre-paid US$500 million of its future liabilities to the fund. The agreement also gives hourly workers the job security they were seeking by having the company commit to substantial investments in most of its factories.

1923 Ford T 12-13 zitpl B-6185 NL
The automaker reported the largest annual loss in company history in 2006 of $12.7 billion, and estimated that it would not return to profitability until 2009. However, Ford surprised Wall Street in the second quarter of 2007 by posting a $750 million profit. Despite the gains, the company finished the year with a $2.7 billion loss, largely attributed to finance restructuring at Volvo.

1923 Ford T B-6185 Ameland NL
On June 2, 2008, Ford sold its Jaguar and Land Rover operations to Tata Motors for $2.3 billion.
During November 2008, Ford, together with Chrysler and General Motors, sought government bridge loans at Congressional hearings in Washington, D.C. in the face of conditions caused by the 2008 financial crisis. The three companies presented action plans for the sustainability of the industry. Ford opted not to seek government loans. GM and Chrysler received government loans and financing through T.A.R.P. legislation funding provisions. On December 19, the cost of credit default swaps to insure the debt of Ford was 68 percent the sum insured for five years in addition to annual payments of 5 percent. That meant $6.8 million paid upfront to insure $10 million in debt, in addition to payments of $500,000 per year. In January 2009, Ford reported a $14.6 billion loss in the preceding year, a record for the company. The company retained sufficient liquidity to fund its operations. Through April 2009, Ford’s strategy of debt for equity exchanges erased $9.9 billion in liabilities (28% of its total) in order to leverage its cash position. These actions yielded Ford a $2.7 billion profit in fiscal year 2009, the company’s first full-year profit in four years.

1923 Ford T Ford 20pk carr Verheul GTM1 NL
In 2012, Ford’s corporate bonds were upgraded from junk to investment grade again, citing sustainable, lasting improvements.
On October 29, 2012, Ford announced the sale of its climate control components business, its last remaining automotive components operation, to Detroit Thermal Systems LLC for an undisclosed price.

1923 Ford T NL
On November 1, 2012, Ford announced that CEO Alan Mulally will stay with the company until 2014. Ford also named Mark Fields, the president of operations in Americas, as its new chief operating officer
Corporate affairs

Ford World Headquarters in Dearborn, Michigan, USA, known as the Glass House.
Executive management
Members of the Ford board as of 2012 are: Richard A. Gephardt, Stephen Butler, Ellen Marram, Kimberly Casiano, Alan Mulally (President and CEO), Edsel Ford II, Homer Neal, William Clay Ford Jr. (Executive Chairman), Jorma Ollila, Irvine Hockaday Jr., John L. Thornton, and William Clay Ford, Sr. (Director Emeritus).

1923 FORDSON BUS
The main corporate officers are: Lewis Booth (Executive Vice President, Chairman (PAG) and Ford of Europe), Mark Fields (Executive Vice President, President of The Americas), Donat Leclair (Executive Vice President and CFO), Mark A. Schulz (Executive Vice President, President of International Operations), and Michael E. Bannister (Group Vice President; Chairman & CEO Ford Motor Credit). Paul Mascarenas (Vice President of Engineering, The Americas Product Development)
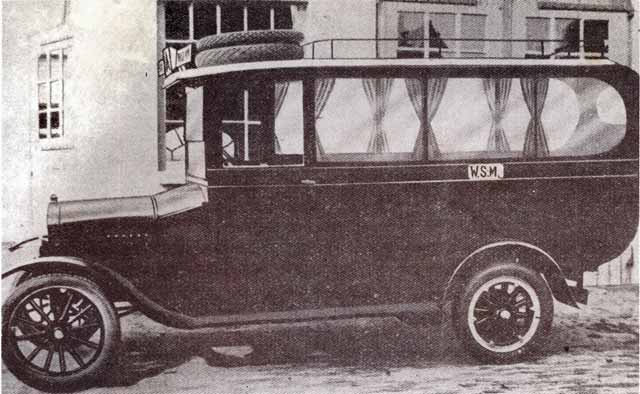
1923 Ford-T WSM
Financial results
In 2010, Ford earned a net profit of $6.6 billion and reduced its debt from $33.6 billion to $14.5 billion lowering interest payments by $1 billion following its 2009 net profit of $2.7 billion. In the U.S., the F-Series was the best-selling vehicle for 2010. Ford sold 528,349 F-Series trucks during the year, a 27.7% increase over 2009, out of a total sales of 1.9 million vehicles, or every one out of four vehicles Ford sold. Trucks sales accounts for a big slice of Ford’s profits, according to USA Today. Ford’s realignment also included the sale of its wholly owned subsidiary, Hertz Rent-a-Car to a private equity group for $15 billion in cash and debt acquisition. The sale was completed on December 22, 2005. A 50–50 joint venture with Mahindra & Mahindra of India, called Mahindra Ford India, Limited (MIFL), ended with Ford buying out Mahindra’s remaining stake in the company in 2005. Ford had previously upped its stake to 72% in 1998.

1924 tet ford-bussen

1925 Ford T Carr. v d Bos & Br NL
Operations
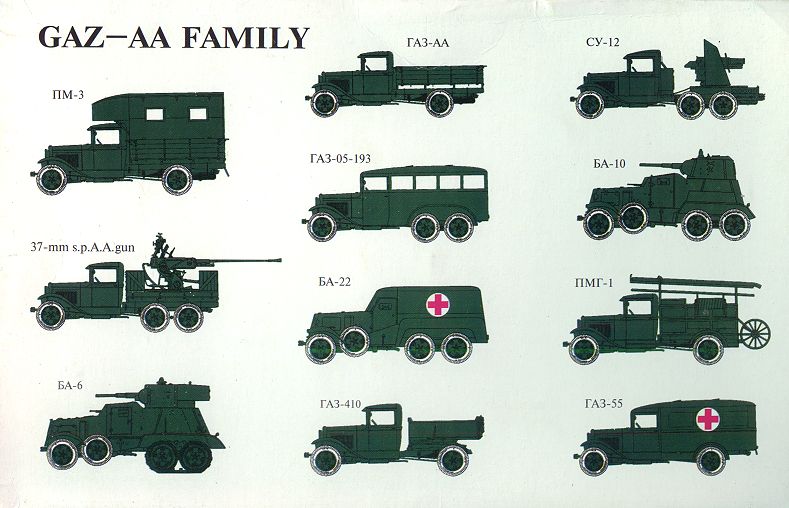
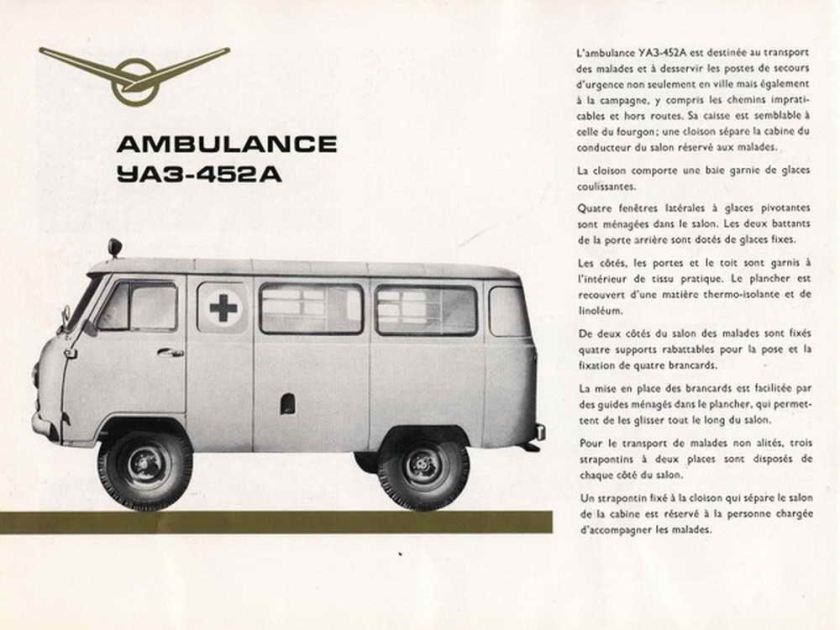
Ford has manufacturing operations worldwide, including in the United States, Canada, Mexico, China, the United Kingdom, Germany, Turkey, Brazil, Argentina, Australia and South Africa. Ford also has a cooperative agreement with Russian automaker GAZ.

1925 Ford T carr. Hainje Heerenveen B-5225 NL
North America
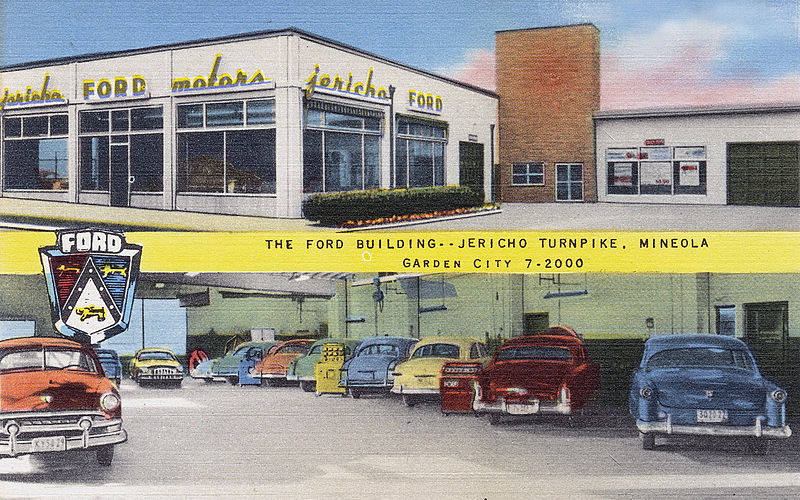
Ford dealer in Garden City, New York, ca. 1930-1945
In the first five months of 2010, auto sales in the U.S. rose to 4.6 million cars and light trucks, an increase of 17% from a year earlier. The rise was mainly caused by the return of commercial customers that had all but stopped buying in 2009 during the recession. Sales to individual customers at dealerships have increased 13%, while fleet sales have jumped 32%. Ford reported that 37% of its sales in May came from fleet sales when it announced its sales for the month increased 23%. In the first seven months of 2010, vehicle sales of Ford increased 24%, including retail and fleet sales. Fleet sales of Ford for the same period rose 35% to 386,000 units while retail sales increase 19%. Fleet sales account for 39 percent of Chrysler’s sales and 31 percent for GM’s.

1927-ford-blue-bird-school-bus
Europe

1927-ford-blue-bird-school-bus
Main article: Ford of Europe

Ford’s Dunton Technical Centre inLaindon, United Kingdom, the largest automotive research and development facility in the country

The Ford Research Center in Aachen, Germany
At first, Ford in Germany and Ford in Britain built different models from one another until the late 1960s, with the Ford Escort and then the Ford Capri being common to both companies. Later on, the Ford Taunus and Ford Cortina became identical, produced in left hand drive and right hand drive respectively. Rationalisation of model ranges meant that production of many models in the UK switched to elsewhere in Europe, including Belgium and Spain as well as Germany. The Ford Sierra replaced the Taunus and Cortina in 1982, drawing criticism for its radical aerodynamic styling, which was soon given nicknames such as “Jellymould” and “The Salesman’s Spaceship.”

1928-Poelgeest-bussen ©Amstelveenweb.com

1928 Ford V8 Hainje Heerenveen B-9274 NL
Increasingly, the Ford Motor Company has looked to Ford of Europe for its “world cars”, such as the Mondeo, Focus, and Fiesta, although sales of European-sourced Fords in the U.S. have been disappointing. The Focus has been one exception to this, which has become America’s best selling compact car since its launch in 2000
In February 2002, Ford ended car production in the UK. It was the first time in 90 years that Ford cars had not been made in Britain, although production of the Transit van continues at the company’s Southampton facility, engines at Bridgend and Dagenham, and transmissions at Halewood. Development of European Ford is broadly split between Dunton in Essex (powertrain, Fiesta/Ka, and commercial vehicles) and Cologne (body, chassis, electrical, Focus, Mondeo) in Germany. Ford also produced the Thames range of commercial vehicles, although the use of this brand name was discontinued circa 1965. Elsewhere in continental Europe, Ford assembles the Mondeo range in Genk (Belgium), Fiesta in Valencia (Spain) and Cologne (Germany), Ka in Valencia, and Focus in Valencia, Saarlouis (Germany) and Vsevolozhsk (Russia). Transit production is in Kocaeli (Turkey), Southampton (UK), and Transit Connect in Kocaeli.

1928 Ford NL
Ford also owns a joint-venture production plant in Turkey. Ford-Otosan, established in the 1970s, manufactures the Transit Connect compact panel van as well as the “Jumbo” and long-wheelbase versions of the full-size Transit. This new production facility was set up near Kocaeli in 2002, and its opening marked the end of Transit assembly in Genk.

1929 Ford
Another joint venture plant near Setúbal in Portugal, set up in collaboration with Volkswagen, formerly assembled the Galaxy people-carrier as well as its sister ships, the VW Sharan and SEAT Alhambra. With the introduction of the third generation of the Galaxy, Ford has moved the production of the people-carrier to the Genk plant, with Volkswagen taking over sole ownership of the Setúbal facility.

1931 Ford V8 Cupido uitvoering 5 B-27189 NL
In 2008, Ford acquired a majority stake in Automobile Craiova, Romania. Starting 2009, the Ford Transit Connect was Ford’s first model produced in Craiova, followed, in 2012, by low-capacity car engines and a new small class car, the B-Max.
Ford Europe has broken new ground with a number of relatively futuristic car launches over the last 50 years.

1931 Ford AA Bus
Its 1959 Anglia two-door saloon was one of the most quirky-looking small family cars in Europe at the time of its launch, but buyers soon became accustomed to its looks and it was hugely popular with British buyers in particular. It was still selling well when replaced by the more practical Escort in 1967.
The third incarnation of the Ford Escort was launched in 1980 and marked the company’s move from rear-wheel drive saloons to front-wheel drive hatchbacks in the small family car sector.

1931 Ford-Hainje Cupido 8 NL
The fourth generation Escort was produced from 1990 until 2000, although its successor – the Focus – had been on sale since 1998. On its launch, the Focus was arguably the most dramatic-looking and fine-handling small family cars on sale, and sold in huge volumes right up to the launch of the next generation Focus at the end of 2004.

1932 Ford – Den Oudsten, Woerden – Domburg A’dam NL
The 1982 Ford Sierra – replacement for the long-running and massively popular Cortina and Taunus models – was a style-setter at the time of its launch. Its ultramodern aerodynamic design was a world away from a boxy, sharp-edged Cortina, and it was massively popular just about everywhere it was sold. A series of updates kept it looking relatively fresh until it was replaced by the front-wheel drive Mondeo at the start of 1993.

1932 Ford A Visser B-13634a NL
The rise in popularity of small cars during the 1970s saw Ford enter the mini-car market in 1976 with its Fiesta hatchback. Most of its production was concentrated at Valencia in Spain, and the Fiesta sold in huge figures from the very start. An update in 1983 and the launch of an all-new model in 1989 strengthened its position in the small car market.
On October 24, 2012, Ford announced that it would be closing its Genk assembly plant in eastern Belgium by the end of 2014.

1932 Ford A Visser B-13634b NL
Asia Pacific

1932 Ford A Visser B-13634 NL
Ford formed its first passenger-vehicle joint venture in China in 2001, six years behind GM and more than a decade after VW. It has spent as of 2013 $4.9 billion to expand its lineup and double production capacity in China to 600,000 vehicles This includes Ford’s largest-ever factory complex in the southwestern city of Chongqing. Ford had 2.5 percent of the Chinese market in 2013, while VW controlled 14.5 percent and GM had 15.6 percent, according to consultant LMC Automotive. GM outsells Ford in China by more than six-to-one.

The Ford stamping plant in Geelong, Australia
The Ford India plant in Chennai, Tamil Nadu
In Australia and New Zealand, the popular Ford Falcon has long been considered the average family car and is considerably larger than the Mondeo, Ford’s largest car sold in Europe. Between 1960 and 1972, the Falcon was based on a U.S. model of the same name, but since then has been entirely designed and manufactured in Australia, occasionlly being manufactured in New Zealand. Like its General Motors rival, the Holden Commodore, the Falcon uses a rear wheel drive layout. High performance variants of the Falcon running locally built engines produce up to 362 hp (270 kW). A ute (short for “utility”, known in the US as pickup truck) version is also available with the same range of drivetrains. In addition, Ford Australia sells highly tuned limited-production Falcon sedans and utes through its performance car division, Ford Performance Vehicles.

1932-35 Ford. Bouwjaren NL
In Australia, the Commodore and Falcon have traditionally outsold all other cars and comprise over 20% of the new car market. In New Zealand, Ford was second in market share in the first eight months of 2006 with 14.4 per cent. More recently Ford has axed its Falcon-based LWB variant of its lineup – the Fairlane and LTD ranges, and announced that their Geelong engine manufacturing plant may be shut down from 2013. They have also announced local manufacturing of the Focus small car starting from 2011.

1932-ford-model-b-school-bus ©Old Bus
However, with the acquisition of a stake in Japanese manufacturer Mazda in 1979, Ford began selling Mazda’s Familia and Capella (also known as the 323 and 626) as the Ford Laser and Telstar, replacing the European-sourced Escort and Cortina.
In Australia, the Laser was one of Ford Australia‘s most successful models, and was manufactured in Ford’s Homebush plant from 1981 until the plant’s closure in September 1994. It outsold the Mazda 323, despite being almost identical to it, due to the fact the Laser was manufactured in Australia and Ford was perceived as a local brand.

1933 Ford carr. Postma Rottevalle
In New Zealand, the Ford Laser and Telstar were assembled alongside the Mazda 323 and 626 until 1997, at the Vehicle Assemblers of New Zealand (VANZ) plant in Wiri, Auckland. The Sierra wagon was also assembled in New Zealand, owing to the popularity of station wagons in that market.
Through its relationship with Mazda, Ford also acquired a stake in South Korean manufacturer Kia, which built the (Mazda-based) Ford Festiva from 1988–1993, and the Ford Aspire from 1994–1997 for export to the United States, but later sold their interest to Hyundai (which also manufactured the Ford Cortina until the 1980s). Kia continued to market the Aspire as the Kia Avella, later replaced by the Rio and once again sold in the US.

1933 Ford V8 Carr. Brouwers Holwerd NL
Ford’s presence in Asia has traditionally been much smaller, confined to Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, the Philippines, and Taiwan, where Ford has had a joint venture with Lio Ho since the 1970s. Ford began assembly of cars in Thailand in 1960, but withdrew from the country in 1976, and did not return until 1995, when it formed a joint venture with Mazda called Auto Alliance. Now in Bo-win Sub District, Sriracha District of the Chonburi it is located The Ford Motor Company (Thailand) Limited, making passenger automobiles.
Ford India began production in 1998 at Chennai, Tamil Nadu, with its Ford Escort model, which was later replaced by locally produced Ford Ikon in 2001. It has since added Fusion, Fiesta, Mondeo and Endeavour to its product line.

1934 Ford Carr. Postma Rottervalle NL
On March 9, 2010, Ford Motor Co. launched its first made-for-India compact car. Starting at 349,900 ($7,690), the Figo is Ford’s first car designed and priced for the mass Indian market. On July 28, 2011, Ford India signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the State of Gujarat for the construction of an assembly and engine plant in Sanand, and planned to invest approximately US$1 billion on a 460-acre site.

1934 Ford Lawrie CL-BB Winnipeg ©Foote
The scheduled closure of Ford’s Australian manufacturing base in 2016 was confirmed in late May 2013. Headquartered in the Victorian suburb of Broadmeadows, the company had registered losses worth AU$600 million over the five years prior to the announcement. It was noted that the corporate fleet and government sales that account for two-thirds of large, local car sales in Australia are insufficient to keep Ford’s products profitable and viable in Australia. The decision will affect 1200 Ford workers—over 600 employees in Geelong and more than 500 in Broadmeadows—who will lose their jobs by October 2016.

1934 Ford V8 – Kusters & Lemmens BBA 63 Autobus SVA 63 erfg NL
Ford of Japan
Ford established a manufacturing facility in the port city of Yokohama in February 1925, where Model T vehicles were assembled using imported knock-down kits. The factory subsequently produced 10,000 Model A’s up to 1936. Production ceased in 1940 as a result of political tensions between Japan and the United States.

1934 Ford V8 Kusters & Lemmens- BBA 63 NL
After World War II, Ford did not have a presence in Japan, as the Ford facility was appropriated by the Japanese Government until 1958, when property was returned as a possession of the Ford Motor Company and became a research and development location for Ford partner Mazda. In 1979, Ford acquired a 24.5% ownership stake in Mazda, and in 1982 Ford and Mazda jointly established a sales channel to sell Ford products in Japan, including vehicles manufactured in North America, at a dealership called Autorama (Japanese). The Autorama sales channel was renamed Ford Sales of Japan in 1997.

1934 Ford, type V8-40 Kusters en lemmens UB-93-63 NL
Vehicles sold at Autorama locations were the North American assembled Ford Explorer, Probe (1989–1998), Mustang, Taurus (1989–1997), Thunderbird (1990–1993), Lincoln Continental, and Lincoln LS. Ford products manufactured in Europe that were sold in Japan were the Ford Mondeo, Ka, Focus, Focus C-MAX, Fiesta, and the Galaxy. Mazda manufactured Ford vehicles in Japan and sold them as Fords at the Autorama locations. They were the Ford Telstar (Mazda Capella), Laser, Festiva, Festiva Mini Wagon, Ixion (Mazda Premacy), Freda (Mazda Bondo Friendee), Spectron (Mazda Bongo), and commercial trucks J80 and the J100 (Mazda Bongo truck).

1934 Ford, type V8-40 Kusters en lemmens NL
Ford increased its shareholding in Mazda to 33.4% in 1996. Ford currently sells a small range of vehicles in Japan; as of October 2010, the Ford Mustang, Escape, Explorer (and Explorer truck), Ford Kuga, Lincoln Navigator and Lincoln MKX were available in Japan. Ford maintains a regional office in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
South America

1934 Ford © Hank Suderman
During much of the 20th century, Ford faced protectionist government measures in South America, with the result that it built different models in different countries, without particular regard to rationalization or economy of scale inherent to producing and sharing similar vehicles between the nations. In many cases, new vehicles in a country were based on those of the other manufacturers it had entered into production agreements with, or whose factories it had acquired. For example, the Corcel and Del Rey in Brazil were originally based on Renault vehicles.

1935 Ford B-38868 NL
In 1987, Ford of Brasil and Ford of Argentina merged their operations with the Brazilian and Argentinan operations of Volkswagen Group, forming a new joint-venture company called Autolatina with a shared model range. Sales figures and profitability were disappointing, and Autolatina was dissolved in 1995. With the advent of Mercosur, the regional common market, Ford was finally able to rationalize its product line-ups in those countries. Consequently, the Ford Fiesta and Ford EcoSport are only built in Brazil, and the Ford Focus only built in Argentina, with each plant exporting in large volumes to the neighboring countries. Models like the Ford Mondeo from Europe could now be imported completely built up. Ford of Brazil produces a pick-up truck version of the Fiesta, the Courier, which is also produced in South Africa as the Ford Bantam in right hand drive versions.

1935 Ford V8 Den Oudsten en Domburg B-21037 NL
Africa and Middle East
In Africa, Ford’s market presence has traditionally been strongest in South Africa and neighbouring countries, with only trucks being sold elsewhere on the continent. Ford in South Africa began by importing kits from Canada to be assembled at its Port Elizabeth facility. Later Ford sourced its models from the UK and Australia, with local versions of the Ford Cortina including the XR6, with a 3.0 V6 engine, and aCortina-based ‘bakkie’ or pick-up, which was exported to the UK. In the mid-1980s Ford merged with a rival company, owned by Anglo American, to form the South African Motor Corporation (Samcor).

1935 Ford V8 Hainje B-20623 Rally Monte Carlo NL
Following international condemnation of apartheid, Ford divested from South Africa in 1988, and sold its stake in Samcor, although it licensed the use of its brand name to the company. Samcor began to assemble Mazdas as well, which affected its product line-up, and saw the European Fords like the Escort and Sierra replaced by the Mazda-based Laser and Telstar. Ford bought a 45 per cent stake in Samcor following the demise of apartheid in 1994, and this later became, once again, a wholly owned subsidiary, the Ford Motor Company of Southern Africa. Ford now sells a local sedan version of the Fiesta (also built in India and Mexico), and the Focus. The Falcon model from Australia was also sold in South Africa, but was dropped in 2003, while the Mondeo, after briefly being assembled locally, was dropped in 2005.

1935 Ford V-8 Intercity Bus
Ford’s market presence in the Middle East has traditionally been even smaller, partly due to previous Arab boycotts of companies dealing with Israel. Ford and Lincoln vehicles are currently marketed in ten countries in the region. Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the UAE are the biggest markets. Ford also established itself in Egypt in 1926, but faced an uphill battle during the 1950s due to the hostile nationalist business environment. Ford’s distributor in Saudi Arabia announced in February 2003 that it had sold 100,000 Ford and Lincoln vehicles since commencing sales in November 1986. Half of the Ford/Lincoln vehicles sold in that country were Ford Crown Victorias. In 2004, Ford sold 30,000 units in the region, falling far short of General Motors‘ 88,852 units and Nissan Motors‘ 75,000 units.
Products and services
Automobiles
See also: List of Ford vehicles and List of Mercury vehicles

The 2013 model year Lincoln MKS
As of 2012 Ford Motor Company sells a broad range of automobiles under the Ford marque worldwide, and an additional range of luxury automobiles under theLincoln marque in the United States. The company has sold vehicles under a number of other marques during its history. The Mercury brand was introduced by Ford in 1939, continuing in production until 2011 when poor sales led to its discontinuation. In 1958, Ford introduced the Edsel brand, but poor sales led to its discontinuation in 1960. In 1985, the Merkur brand was introduced in the United States to market products produced by Ford of Europe; it was discontinued in 1989.

1935 ford-busse-oldtimer
Ford acquired the British sports car maker Aston Martin in 1989, later selling it on March 12, 2007, although retaining a 15% stake, and bought Volvo Cars of Sweden in 1999, selling it to Zhejiang Geely Holding Group in 2010. In November 2008, it reduced its 33.4% controlling interest in Mazda of Japan to a 13.4% non-controlling interest. On November 18, 2010, Ford reduced their stake further to just 3%, citing the reduction of ownership would allow greater flexibility to pursue growth in emerging markets. Ford and Mazda remain strategic partners through exchanges of technological information and joint ventures, including an American joint venture plant in Flat Rock, Michigan called Auto Alliance. Ford sold the United Kingdom-based Jaguar and Land Rover companies and brands to Tata Motors of India in March 2008.

1935 LINDBERGH op Ford R-Series NL ^ Fotograaf
In 2011, J.D. Power ranked Ford 23rd in initial quality, a drop from fifth in 2010. Consumer Reports magazine likewise decided not to recommend several new Ford SUVs, blaming the Sync entertainment and phone system used.
|
Marque
|
Country of origin
|
Years used/owned
|
Markets
|
| Ford |
United States |
1903 to present |
Global |
| Lincoln |
United States |
1922 to present |
North America, Middle East |
| Mercury |
United States |
1939 to 2011 |
North America |
| Edsel |
United States |
1958 to 1960 |
North America |
| Merkur |
United States |
1985 to 1989 |
North America |
| Jaguar |
United Kingdom |
1989 to 2008 |
Global |
| Aston Martin |
United Kingdom |
1989 to 2007 |
Global |
| Volvo |
Sweden |
1999 to 2010 |
Global |
|
Land Rover
|
United Kingdom
|
2000 to 2008
|
Global
|
Trucks

An advert for the 1939 Ford V-8 pick-up truck

An advert for the 1961 Ford H-Series truck
Ford has produced trucks since 1908. Countries where Ford commercial vehicles are or were made include Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada (badged Mercury too), France, Germany, India, Netherlands, Philippines, Spain (badged Ebro too), Turkey, UK (badged also Fordson and Thames) and USA.

1936 Ford V8 Hainje NL
From the 1940s to late 1970s Ford’s Ford F-Series were used as the base for light trucks for the North American market.
Most of these ventures are now extinct. The European one that lasted longest was the lorries arm of Ford of Britain, which was eventually sold to Iveco group in 1986, and whose last significant models were the Transcontinental and the Cargo.
In the United States, Ford’s heavy trucks division (Classes 7 and 8) was sold in 1997 to Freightliner Trucks, which rebranded the lineup as Sterling. Freightliner is in the process of discontinuing this line.

1936 Ford V8 New Zealand
Line of heavy trucks made by Ford for the North American market:

1936 Ford V-8 Transit Bus
Ford continues to manufacture medium duty trucks under the F-650 and F-750 badges. In 2001, the company entered into a joint venture with Navistar International to produce medium duty commercial trucks. The first new model from the new corporation, known as Blue Diamond Truck Company LLC, was the 2006 model year LCF, the first Ford branded cab-over-engine design in the United States since Freightliner’s acquisition of the Cargo in the mid-1990s. The LCF was discontinued in 2009 and Ford’s 2011 medium-duty commercial offerings are limited to the two F-Series.
In 1999 the end of the F800 meant Ford was not producing in any F-series heavy truck chassis.
In Europe, Ford manufactures the Ford Transit jumbo van which is classed as a Large Goods Vehicle and has a payload of up to 2,265 kg, there are options of a panel van, pickup or chassis cab. The Ford Transit is also available as a light van called the Ford Transit Connect and the Ford Ranger pickup is available.
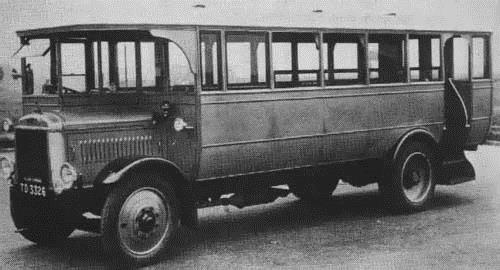
Buses

A Ford B700 bus chassis, with a body byThomas Built
Ford manufactured complete buses in the company’s early history, but today the role of the company has changed to that of a second stage manufacturer. In North America, the E-Series is still used as a chassis for small school buses and the F-650 is used in commercial bus markets. In the 1980s and 1990s, the medium-duty B700 was a popular chassis used by school bus body manufacturers including Thomas Built, Ward and Blue Bird, but Ford lost its market share due to industry contraction and agreements between body manufacturers. Older bus models included:
Prior to 1939, Ford buses were based on truck bodies:
- Model B – 1930s
- Model T – 1920s
- F-105 school bus

1936 Ford V8T carr. Hainje Heerenveen B-7387 NL
During World War II Ford manufactured Ford Transit bus, a series of small transit buses with bodies built by second party:
- 09-B/19-B City transit bus – 1939–1941
- 19-B/29-B City transit bus – 1941–1942
- 49-B/79-B City transit bus – 1944–1947
- 69-B City transit bus – 1946–1947
- 29-B City transit bus – 1946–1947
- 72-T transit bus – 1944–1945
After 1946 the Transit City bus was sold as Universal Bus with the roof changed from fabric/wood to all metal:
- 79-B Universal transit bus – 1946–1947
Succeeding the Ford Transit bus was the Ford 8M buses:
- 8MB transit bus – with Wayne Works 1948–?
Following World War II and from 1950s onwards Ford lost out to General Motors. This led to the end of transit buses for Ford in North America.
- B500 or B-series – 1950-1990s based on Ford F-series truck chassis used by school bus body manufacturers
In Europe, Ford manufactures the Ford Transit Minibus which is classed in Europe as a Passenger Carrying Vehicle and there are options of 12, 15 or 17 seaters. In the past European models included:
- EM
- N-138
- D series buses (Australia)

1936 Ford Verheul NL
Tractors

A Ford N series tractor
The “Henry Ford and Son Company” began making Fordson tractors in Henry’s hometown of Springwells (later part of Dearborn), Michigan from 1907 to 1928, from 1919 to 1932, at Cork, Ireland, and 1933–1964 at Dagenham, England, later transferred to Basildon. They were also produced in Leningrad beginning in 1924.
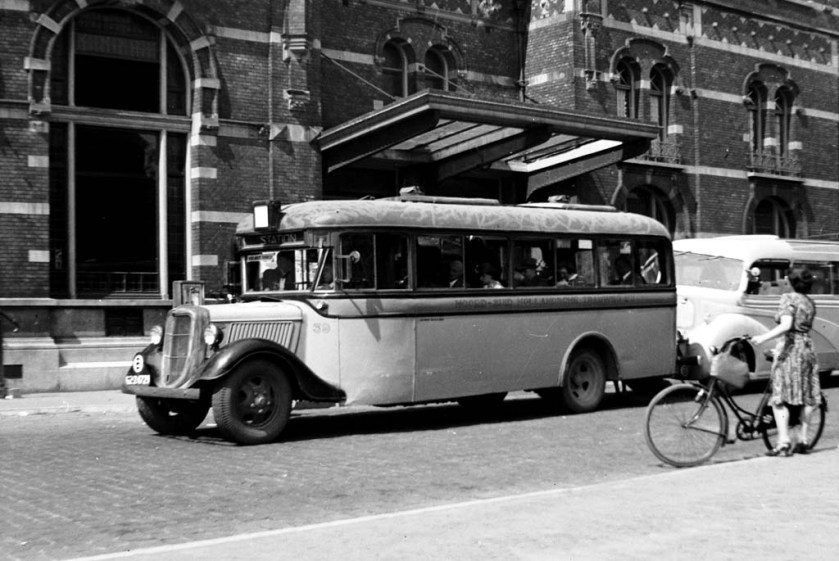
1936 Ford-Hainje, gefotografeerd door ©Jan Voerman op 4-8-1940 in Den Bosch NL
In 1986, Ford expanded its tractor business when it purchased the Sperry-New Holland skid-steer loader and hay baler, hay tools and implement company fromSperry Corporation and formed Ford-New Holland which bought out Versatile tractors in 1988. This company was bought by Fiat in 1993 and the name changed from Ford New Holland to New Holland. New Holland is now part of CNH Global.

1937 Ford carr. Veth ZEGO194 NL
Financial services

1937 Ford Greyhound Bus

1937 Ford Greyhound Bus

1937 Ford Super Coaches Australia
Ford offers automotive finance through Ford Motor Credit Company.
Automotive components

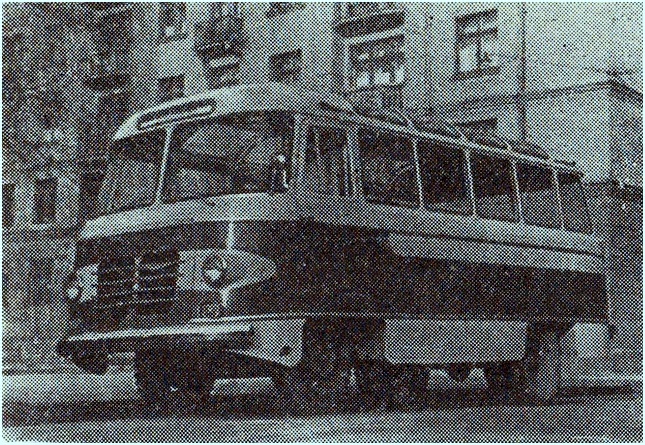
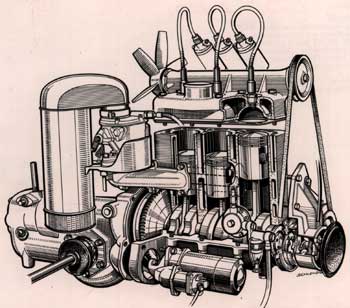
1937 Ford Isobloc met V8 motor F
Ford’s FoMoCo parts division sells aftermarket parts under the Motorcraft brand name. It has spun off its parts division under the name Visteon.
Motorsport

1937 Ford van Koopmans Jubbega met carroserie van Hainje NL
Main article: Ford Racing

1938 Ford A Hainje Heerenveen NL
Along with Shelby and Chevrolet, Ford is one of only three American constructors to win titles on the international scene at the FIA World Championships. As a constructor, Ford won the World Sportscar Championship three times in 1966, 1967 and 1968, and the World Rally Championship three times in 1979, 2006 and 2007.

1938 Ford Hainje B-21375 NL
Stock car racing

NASCAR Ford Fusion race car
Ford is one of four manufacturers in NASCAR‘s three major series: Sprint Cup Series, Nationwide Series, and Camping World Truck Series. Major teams includeRoush Fenway Racing and Yates Racing and Richard Petty Motorsports. Ford is represented by the mid-size Fusion in the Sprint Cup, the Mustang in the Nationwide Series, and by the F-150 in the Camping World Truck Series. Some of the most successful NASCAR Fords were the aerodynamic fastback Ford Torino,Ford Torino Talladega, Mercury Cyclone Spoiler II, and Mercury Montegos, and the aero-era Ford Thunderbirds. The Ford nameplate has won eight manufacturer’s championships in Sprint Cup, while Mercury has won one. In the Sprint Cup Series, Ford earned its 1,000th victory in the 2013 Quicken Loans 400. The Ford Fusion is also used in the ARCA Remax Series.

1938 Ford Kusters & Lemmens VADAH-bus 8 lijn Sittard- Echt-Roermond NL
Formula One
Ford was heavily involved in Formula One for many years, and supplied engines to a large number of teams from 1967 until 2004. These engines were designed and manufactured by Cosworth, the racing division that was owned by Ford from 1998 to 2004. Ford-badged engines won 176 Grands Prix between 1967 and 2003 for teams such as Team Lotus and McLaren. Ford entered Formula One as a constructor in 2000 under the Jaguar Racing name, after buying the Stewart Grand Prixteam which had been its primary ‘works’ team in the series since 1997. Jaguar achieved little success in Formula One, and after a turbulent five seasons, Ford withdrew from the category after the 2004 season, selling both Jaguar Racing (which became Red Bull Racing) and Cosworth (to Gerald Forsythe and Kevin Kalkhoven).

1938 Ford V8 COE B-15822 Hainje NL
Rally

Jari-Matti Latvala driving the Ford Focus RS WRC 09 in 2010.
Main article: Ford World Rally Team

1938 Ford V8, 798W, Hainje NL
Ford has a long history in rallying and has been active in the World Rally Championship since the beginning of the world championship, the 1973 season. Ford took the 1979 manufacturers’ title with Hannu Mikkola, Björn Waldegård and Ari Vatanen driving the Ford Escort RS1800. In the Group B era, Ford achieved success withFord RS200. Since the 1999 season, Ford has used various versions of the Ford Focus WRC to much success. In the 2006 season, BP-Ford World Rally Teamsecured Ford its second manufacturers’ title, with the Focus RS WRC 06 built by M-Sport and driven by “Flying Finns“ Marcus Grönholm and Mikko Hirvonen.Continuing with Grönholm and Hirvonen, Ford successfully defended the manufacturers’ world championship in the 2007 season. Ford is the only manufacturer to score in the points for 92 consecutive races; since the 2002 season opener Monte Carlo Rally.

1938 FordBus
Sports cars
Main article: Ford GT#Racing

1939 Ford AA NL
Ford sports cars have been visible in the world of sports car racing since 1964. Most notably the GT40 won the 24 Hours of Le Mans four times in the 1960s and is the only American car to ever win overall at this prestigious event. Ford also won the 1968 International Championship for Makes with the GT40, which still stands today as one of the all-time greatest racing cars. Swiss team Matech GT Racing, in collaboration with Ford Racing, opened a new chapter with the Ford GT, winning the Teams title in the 2008 FIA GT3 European Championship.

Ford Mustang GT (racing GT car)
Main article: Ford Mustang#Racing

1939 Ford op afsluitdijk B-21037a NL
The Ford Mustang has arguably been Ford’s most successful sports car. Jerry Titus won the 1965 SCCA Pro B National Championship with a Mustang and the model went on to earn Ford the SCCA Trans-Am Championship title in both 1966 and 1967. Ford won the Trans-Am Championship again in 1970 with Parnelli Jonesand George Folmer driving Boss 302 Mustangs for Bud Moore Engineering. Ford took the 1985 and 1986 IMSA GTO Championship with Mustangs driven by John Jones and Scott Pruett before returning to Trans-Am glory with a championship in 1989 with Dorsey Schroeder. Ford dominated Trans-Am in the 1990s with Tommy Kendal winning championships in 1993, 1995, 1996, and 1997 with Paul Gentilozi adding yet another title in 1999. In 2005 the Ford Mustang FR500C took the championship in the Rolex Koni Challenge Series in its first year on the circuit. In 2007 Ford added a victory in the GT4 European Championship. 2008 was the first year of the Mustang Challenge for the Miller Cup, a series which pits a full field of identical factory built Ford Mustang race cars against each other. Also in 2008, Ford won the manufacturers championship in the Koni Challenge Series and HyperSport drivers Joe Foster and Steve Maxwell won the drivers title in a Mustang GT.

1939 Ford-Verheul 2 foto via Frank vd Boogert KLM NL
Touring cars

Ford Performance Racing Ford Falcon V8 Supercar at Eastern Creek in Australia in 2008.
Ford has campaigned touring cars such as the Focus, Falcon, and Contour/Mondeo and the Sierra Cosworth in many different series throughout the years. Notably, Mondeo drivers finished 1,2,3 in the 2000 British Touring Car Championship and Falcon drivers placed 1,2,3 in the 2005 V8 Supercar Championship Series.

1940 Ford met carrosserie van Hainje NL
Other
In the Indianapolis 500, Ford powered IndyCars won 17 times between 1965 and 1996[citation needed]. Ford has also branched out into drifting with the introduction of the new model Mustang. Most noticeable is the Turquoise and Blue Falken Tires Mustang driven by Vaughn Gittin Jr, A.K.A. “JR”. with 750 RWHP (Rear Wheel Horsepower). In drag racing, John Force Racing drivers John Force, Tony Pedregon, and Robert Hight have piloted Ford Mustang Funny Cars to several NHRA titles in recent seasons. Teammates Tim Wilkerson and Bob Tasca III also drive Mustangs in Funny Car. Formula Ford, a formula for single-seater cars without wings and originally on road tires were conceived in 1966 in the UK as an entry-level formula for racing drivers. Many of today’s racing drivers started their car racing careers in this category.

1940 Ford O98W158 carr v Eerten GTW197 M-15291 NL
Environmental initiatives

All Ford’s alternative fuel and hybridmodels are identified by Ford’s leaf road logo badge.

1940 Ford O98W158 carr v Eerten GTW198 M-15292 M-15068 NL
Compressed natural gas
The alternative fossil fuel vehicles, such as some versions of the Crown Victoria especially in fleet and taxi service, operate on compressed natural gas—or CNG. Some CNG vehicles have dual fuel tanks – one for gasoline, the other for CNG – the same engine can operate on either fuel via a selector switch.

1940 Ford V8 Werkspoor met verduisterde koplampen. ATO-13 NL
Flexible fuel vehicles

The Ford Focus Flexifuel was the first E85 flexible fuel vehicle commercially available in the European market.
Flexible fuel vehicles are designed to operate smoothly using a wide range of available ethanol fuel mixtures—from pure gasoline, to bioethanol-gasoline blends such as E85 (85% ethanol and 15% gasoline) or E100 (neat hydrous ethanol) in Brazil. Part of the challenge of successful marketing alternative and flexible fuel vehicles in the U.S., is the general lack of establishment of sufficient fueling stations, which would be essential for these vehicles to be attractive to a wide range of consumers. Significant efforts to ramp up production and distribution of E85 fuels are underway and expanding. Current Ford E100 Flex sold in the Brazilian market are the Courier, Ford EcoSport, Ford Fiesta, Ford Focus and Ford Ka.

1940 Frederiks Ford bus de TET 28 NL
Electric vehicles
Ford expects electric vehicles will represent a “major portion” of its lineup a decade from now as the automaker breaks away from a recent reliance on pickup trucks and SUVs. The stakes are high because Ford’s stepped-up investment is coming at a time when the U.S. government is demanding steep increases in fuel economy and has put money forward to help automakers adopt new fuel-saving technologies.

1942 Ford Q163 UK
Ford will partner with Coulomb Technologies to provide nearly 5,000 free in-home charging stations for some of the automaker’s first electric vehicle customers, under the Ford Blue Oval ChargePoint Program.
Hybrid electric vehicles

Ford Escape plug-in hybrid test vehicle.

Mulally (second from left) with then-President George W. Bush at the Kansas City Assembly plant in Claycomo, Missouri on March 20, 2007, touting Ford’s new hybrid cars.
Main article: Hybrid electric vehicle

1942 Ford Transit model 29-B FORD GRAY COACH LINES © William A Luke
In 2004 Ford and Toyota agreed a patent sharing accord which granted Ford access to certain hybrid technology patented by Toyota; in exchange Ford licensed Toyota some of its own patents. In 2005 Ford introduced the Hybrid-Electric Escape. With this vehicle, Ford was third to the automotive market with ahybrid electric vehicle and the first hybrid electric SUV to market. This was also the first hybrid electric vehicle with a flexible fuel capability to run on E85. The Escape’s platform mate Mercury Mariner was also available with the hybrid-electric system in the 2006 model year—a full year ahead of schedule. The similarMazda Tribute will also receive a hybrid-electric powertrain option, along with many other vehicles in the Ford vehicle line.

1943 Ford abc tour Auckland Au
In 2005 Ford announced a goal to make 250,000 hybrids a year by 2010, but by mid-2006 announced that it would not meet that goal, due to excessively high costs and the lack of sufficient supplies of the hybrid-electric batteries and drivetrain system components. Instead, Ford has committed to accelerating development of next-generation hybrid-electric power plants in Britain, in collaboration with Volvo. This engineering study is expected to yield more than 100 new hybrid-electric vehicle models and derivatives.

1943 Ford F60 eigen opbouw B-33023 NL During the 2nd WW
In September 2007 Ford announced a partnership with Southern California Edison (SCE) to examine how plug-in hybrids will work with the electrical grid. Under the multi-million-dollar, multi-year project, Ford will convert a demonstration fleet of Ford Escape Hybrids into plug-in hybrids, and SCE will evaluate how the vehicles might interact with the home and the utility’s electrical grid. Some of the vehicles will be evaluated “in typical customer settings”, according to Ford.
On June 12, 2008 USDOE expanded its own fleet of alternative fuel and advanced technology vehicles with the addition of a Ford Escape Plug-In Hybrid Flex-Fuel Vehicle. The vehicle is equipped with a 10-kilowatt (13 hp) lithium-ion battery supplied by Johnson Controls-Saft that stores enough electric energy to drive up to 30 miles (48 km) at speeds of up to 40 mph (64 km/h)

1943 FORD Transit Model 29-B PS194329-B NL
In March 2009 Ford launched hybrid versions of the Ford Fusion Hybrid and the Mercury Milan Hybrid in the United States, both as 2010 models.
Current and planned Ford hybrid electric vehicles include the Ford Escape Hybrid (2004–present), Mercury Mariner (2006–present), Ford Fusion Hybrid/Mercury Milan (2009–present) and Ford Edge/Lincoln MKX (2009/10–present).

1944 Ford 342 NL
All-electric vehicles
Ford ended the Think City experiment and ordered all the cars repossessed and destroyed, even as many of the people leasing them begged to be able to buy the cars from Ford. After outcry from the lessees and activists in the US and Norway, Ford returned the cars to Norway for sale.

1944 Ford Bus
Bill Ford was one of the first top industry executives to make regular use of an battery electric vehicle, a Ford Ranger EV, while the company contracted with the United States Postal Service to deliver electric postal vans based on the Ranger EV platform..Ford discontinued a line of electric Ranger pickup trucks and ordered them destroyed, though it reversed in January 2005, after environmentalist protest.
The North American Focus EV is based on next generation Focus fuel vehicle, converted to an electric propulsion system as a Production EV by Magna International, and is planned to be launched in late 2011. Ford plans to have 10,000 Focus EVs on the road beginning in late 2011 in partnership with Magna International and it will be a global vehicle that will be sold in the three key markets of North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Focus EV has a maximum range of about 160 kilometers or 100 miles, and a top speed of about 120+ kilometers or 75+ miles per hour.

1944 Ford Transit
Current and planned Ford electric vehicles include the all-electric Transit Connect (2010–present), the Ford Focus EV (2011–present), the C-MAX Energi (on sale from third quarter 2012) and the Ford Fusion EV (on sale from third quarter 2012).

1944 Ford Transit
Ford battery electric vehicle (BEV) demonstrators are included in a British project that is part of the UK government’s zero carbon vehicle fleet of Focus BEVs. The BEV demonstrator fleet is being developed partly with public funding from the government’s Technology Strategy Board (TSB), which promotes innovative industry-led projects that reduce CO2 while benefiting the UK’s transport system.

1944 V-03-Hercules Ford bus C49133
Hydrogen
Ford also continues to study Fuel Cell-powered electric powertrains, and has demonstrated hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engine technologies, as well as developing the next-generation hybrid-electric systems. Compared with conventional vehicles, hybrid vehicles and/or fuel cell vehicles decrease air pollution emissions as well as sound levels, with favorable impacts upon respiratory health and decrease of noise health effects.

1945 Ford NL
Ford has launched the production of hydrogen-powered shuttle buses, using hydrogen instead of gasoline in a standard internal combustion engine, for use at airports and convention centers. At the 2006Greater Los Angeles Auto Show, Ford showcased a hydrogen fuel cell version of its Explorer SUV. The Fuel cell Explorer has a combined output of 174 hp (130 kW). It has a large hydrogen storage tank which is situated in the center of the car taking the original place of the conventional model’s automatic transmission. The centered position of the tank assists the vehicle reach a notable range of 350 miles (563 km), the farthest for a fuel cell vehicle so far. The fuel cell Explorer the first in a series of prototypes partly funded by the United States Department of Energy to expand efforts to determine the feasibility of hydrogen- powered vehicles. The fuel cell Explorer is one of several vehicles with green technology being featured at the L.A. show, including the 2008 Ford Escape Hybrid, PZEV emissions compliant Fusion and Focus models and a 2008 Ford F-Series Super Duty outfitted with Ford’s clean diesel technology.

1946 ABC Ford V8 number 82 as a Movan

1946 Hist Bus FordThames
Increased fuel efficiency

All Ford’s models with EcoBoost engines are identified by Ford’s leaf road logo badge.
Ford Motor Company announced it will accelerate its plans to produce more fuel-efficient cars, changing both its North American manufacturing plans and its lineup of vehicles available in the United States. In terms of North American manufacturing, the company will convert three existing truck and sport utility vehicle (SUV) plants for small car production, with the first conversion at its Michigan Truck Plant. In addition, Ford’s assembly plants near Mexico City, Mexico, and in Louisville, Kentucky, will convert from pickups and SUVs to small cars, including the Ford Fiesta, by 2011. Ford will also introduce to North America six of its European small vehicles, including two versions of the Ford Fiesta, by the end of 2012. And last but not least, Ford is stepping up its production of fuel-efficient “EcoBoost” V-6 and four-cylinder engines, while increasing its production of hybrid vehicles.

1946 Ford 69-B
Ford of Europe developed the ECOnetic programme to address the market and legislative need for higher fuel efficiency and lower CO2 emissions. As opposed to the hybrid engine technology used in competitor products such as the Toyota Prius, ECOnetic improves existing technology. Using lower consuming Duratorq TDCi diesel engines, and based on a combination of improved aerodynamics, lower resistance and improved efficiency, the Ford Fiesta is currently the lowest emitting mass-produced car in Europe, while the 2012 Ford Focus ECOnetic will have better fuel consumption that the Prius or the Volkswagen Golf BlueMotion.ECOnetic is not presently planned to be sold in North American due to current perceived lower consumer demand.

1946 Ford CAP carr. De Haas 18 NL
Ford has challenged University teams to create a vehicle that is simple, durable, lightweight and come equipped with a base target price of only $7,000 The students from Aachen University created the “2015 Ford Model T“.
In 2000, under the leadership of the current Ford chairman, William Clay Ford, the Company announced a planned 25 percent improvement in the average mileage of its light truck fleet – including its popular SUVs – to be completed by the 2005 calendar year. In 2003, Ford announced that competitive market conditions and technological and cost challenges would prevent the company from achieving this goal.

1946 Ford F5 V8 carr.Heida Wolvega B-33225 NL
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have, however, listed Ford as the seventh-worst corporate producer of air pollution, primarily because of the manganese compounds, 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene, and glycol ethers released from its casting, truck, and assembly plants. The United States Environmental Protection Agency has linked Ford to 54 Superfund toxic waste sites, twelve of which have been cleaned up and deleted from the list.
For the 2007 model year, Ford had thirteen U.S. models that achieve 30 miles per gallon or better (based on the highway fuel economy estimates of the EPA) and several of Ford’s vehicles were recognized in the EPA and Department of Energy Fuel Economy Guide for best-in-class fuel economy. Ford claimed to have eliminated nearly three million pounds of smog-forming emissions from their U.S. cars and light trucks over the 2004 to 2006 model years.

1946 Ford nr 40 Hengelo Tet 004 NL
PC power management

1946 Ford Tour Buses at The River Rouge ©THEOldMotor.COM
On March 2010, Ford announced its PC power management system which it developed with NightWatchman software from 1E. The company is expected to save $1.2m on power cost and reduce carbon footprint by an estimated 16,000 to 25,000 metric tons annually when the system is fully implemented.
PC power management is being rolled out to all Ford computer users in US this month and it will be used in Ford operations around the world later in the year. Computers with this power profile enabled will monitor its usage patterns and decides when it can be turned off. PC user will be alerted of the approaching power down time and given the opportunity to delay it.

1946 Ford V8 Cupido B-27189 NL
According to company reduction in carbon footprint and power cost will be achieved by developing ‘Power Profiles’ for every PC in the company.

1946 Ford v8 carr.Jonckheere B ©Groep Waaslandia

1946 Ford V8 carr.Postma Rottevalle

1946 Ford carr.Verheul

1946 Ford 59b Bus

1946 Ford-Thames noodautobussen voor 31 personen, carr.Verheul mei 1946 NL

1946-1952 Ford carr. De Groot door © Bramani NB-21-81

1947 Ford 15 Rotterdam carr. Allan NL

1947 Ford 59B Bus BBA (SVA) carr. Jongerius NL

1947 Ford B59 Transit Ford 100pk carr Jongerius GTW 998 NL

1947 Ford B59 Transit Ford 100pk carr Jongerius GTW 998 NL

1945 Ford B-21037b carr. Den Oudsten-Domburg NL

1947 Ford carr. onb

1947 Ford carr Jongerius Huisstijl BBA Stadsbus 353 NB-33-79 NL

1947 Ford F5 C 694 B carr. Wayne GTW 25 NL

1947 Ford carr.Jongerius NL

1947 Ford Trambus B-31898 NL

1947 Ford V8 carr. Brouwers NL

1947 Ford, 59 B carr.Verheul NL

1947 Ford, 59B carr.Jongerius NL

1947 Ford, 59B carr.Jongerius NL

1947 Ford-carr.Hoogeveen (trambus) 046 NL

1947 Ford-carr.Verheul (trambus) 056 NL

1947-1952 Ford 6G-C694B carr. Roset NB-36-90 NL

1948 Ford 6 600 Perkins 6cyl motor Carr. Agosti Hecha de Madera por artesanos ¡Un espectaculo el interior!

1948 Ford Bus School Old

1948 Ford carr.Hoogeveen (trambus) 042a NL

1948 Ford Schoolbus carr.Jongerius bus-7 NL

1948 Ford Schoolbussen

1948 Ford Schoolbussen

1948 Ford Wayne schoolbus Cupido B-27186 NB-50-80 NL

1949 Ford-Highlander

1949 Ford-Wayne-Hercules-Cambell

This is the end of part I
Filed Under: ALLAN, Aston Martin, Brouwers, Cambell, Craiova, de Groot, DEN OUDSTEN,DOMBURG, EBRO, Edsel, FOKKER, Ford, Fordson, GAZ, GREYHOUND, Hainje, HEIDA,Hercules, Hoogeveen, ISOBLOC, IVECO, Jaguar, Jonckheere, Jongerius, KIA, Kusters & Lemmens, Land-Rover, Lincoln, LIO HO, Mahindra, Mazda, Mercury, Merkur, Motorcraft,Postma, Roset, SAMCOR, SEAT, TATA Motors, Thames, v d Bos & Br, van Eerten,VERHEUL, Veth, Visser, VOLVO, VW, Wayne, WERKSPOOR, Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, ZIS
0.000000
0.000000



 KIM-10-52 (1945) 4-door compact car
KIM-10-52 (1945) 4-door compact car Moskvitch 400-420 Flathead engine 23 hp (1946-1954), copy of 1939 Opel Kadett K38
Moskvitch 400-420 Flathead engine 23 hp (1946-1954), copy of 1939 Opel Kadett K38 Moskvitch 400-420A (4-door convertible, was priced below closed models, but anyway was not popular) (1949–52)
Moskvitch 400-420A (4-door convertible, was priced below closed models, but anyway was not popular) (1949–52) Moskvitch-402, probably a Moskvitch-402B (with hand controls for disabled drivers) Moskvitch 400-420B (version of 400 for disabled persons)
Moskvitch-402, probably a Moskvitch-402B (with hand controls for disabled drivers) Moskvitch 400-420B (version of 400 for disabled persons) 1953 Москвич 401 – cab Moskvitch 400-420K (cab-chassis version of 400)
1953 Москвич 401 – cab Moskvitch 400-420K (cab-chassis version of 400) moskvich 400-3 ambulance car Moskvitch 400-420M (medical sedan version of 400)
moskvich 400-3 ambulance car Moskvitch 400-420M (medical sedan version of 400)
 Moskvitch 400-422 (three-door “woodie” station wagon version of 400) (1949)
Moskvitch 400-422 (three-door “woodie” station wagon version of 400) (1949) Moskvitch 400-424 (prototype for 401)
Moskvitch 400-424 (prototype for 401) Moskvitch 400P-431-441 (prototype truck based on 400) (1951)
Moskvitch 400P-431-441 (prototype truck based on 400) (1951) Moskvitch 401-420 Flathead engine 26 hp (1954-1956)
Moskvitch 401-420 Flathead engine 26 hp (1954-1956) Moskvitch 401-420B (invalid car version of 401)
Moskvitch 401-420B (invalid car version of 401)  Moskvitch 401-420K (cab-chassis version of 401)
Moskvitch 401-420K (cab-chassis version of 401)
 Moskvitch 401-422 (“woodie” station wagon version of 401) (1954)
Moskvitch 401-422 (“woodie” station wagon version of 401) (1954) Moskvitch 401-423 (prototype redesigned version of 401) (1949-1951)
Moskvitch 401-423 (prototype redesigned version of 401) (1949-1951)
 Moskvitch 412 (1967-1975) (latterly known as a Moskvitch 1500 for the Western export market)
Moskvitch 412 (1967-1975) (latterly known as a Moskvitch 1500 for the Western export market) Moskvitch 426 (station wagon version of 408) (1967-1975)
Moskvitch 426 (station wagon version of 408) (1967-1975) Moskvitch 427 (station wagon version of 412) (1967-1975)
Moskvitch 427 (station wagon version of 412) (1967-1975) Moskvitch-2140 (1976-1988) (carried on the scheme of using the Moskvitch 1500 name for Western exports)
Moskvitch-2140 (1976-1988) (carried on the scheme of using the Moskvitch 1500 name for Western exports) Moskvitch 2136 (similar to 2137, but with 408 engine) (1976)
Moskvitch 2136 (similar to 2137, but with 408 engine) (1976) Moskvitch 2137 (station wagon version of 2140) (1976-1988)
Moskvitch 2137 (station wagon version of 2140) (1976-1988) Moskvitch 2734 (panel van version of 2140) (1976-1981)
Moskvitch 2734 (panel van version of 2140) (1976-1981) Moskvitch 2138 (similar to 2140, but with 408 engine) (1976-1982)
Moskvitch 2138 (similar to 2140, but with 408 engine) (1976-1982)
 Moskvitch 2142 (1997)
Moskvitch 2142 (1997)
 Moskvitch 2336 (cab-chassis truck based on 2141)
Moskvitch 2336 (cab-chassis truck based on 2141)

 Moskvitch 2141 Moskvitch Sviatogor (1997) (a name taken from the Russian mythology)
Moskvitch 2141 Moskvitch Sviatogor (1997) (a name taken from the Russian mythology) Moskvitch 2142 Dolgorukiy (1997) (named after Yuri Dolgorukiy, founder of Moscow)
Moskvitch 2142 Dolgorukiy (1997) (named after Yuri Dolgorukiy, founder of Moscow) Moskvitch 2142 Kalita (1998) (named after Ivan Kalita, a 14th-century Russian prince)
Moskvitch 2142 Kalita (1998) (named after Ivan Kalita, a 14th-century Russian prince) Moskvitch 412R (1972)
Moskvitch 412R (1972) Moskvitch G1 (1955)
Moskvitch G1 (1955)




 Moskvitch 415 (1959)
Moskvitch 415 (1959) Moskvitch 415S (1966, improved 415)
Moskvitch 415S (1966, improved 415) Moskvitch 3-5-2 (1970, based on the M-408)
Moskvitch 3-5-2 (1970, based on the M-408) Moskvitch 3-5-3 (station wagon version of 3-5-2)
Moskvitch 3-5-3 (station wagon version of 3-5-2) Moskvitch 3-5-4 (modernized 3-5-2)
Moskvitch 3-5-4 (modernized 3-5-2) Moskvitch 3-5-5 (1972, based on the 3-5-2)
Moskvitch 3-5-5 (1972, based on the 3-5-2)
 Moskvitch S1 (1975)
Moskvitch S1 (1975) Moskvitch S2 (developed from the S1)
Moskvitch S2 (developed from the S1)
 Moskvitch X1
Moskvitch X1






























































































![Resize of moskvitch-431-19[1] Resize of moskvitch-431-19[1]](https://i0.wp.com/myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/resize-of-moskvitch-431-191.jpg?w=413&h=275&ssl=1)











































































































































![Moskvitch 416 Tuning [RUSSIAN CARS] Moskvitch 416 Tuning [RUSSIAN CARS]](https://i0.wp.com/myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/moskvitch-416-tuning-russian-cars.jpg?w=295&h=166&ssl=1)















































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































![Moskvitch 416 Tuning [RUSSIAN CARS] Moskvitch 416 Tuning [RUSSIAN CARS]](https://i0.wp.com/myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/moskvitch-416-tuning-russian-cars1.jpg?w=424&h=239&ssl=1)























![Moskvitch 2142 Knyaz Vladimir [RUSSIAN AUTO TUNING] 1 Moskvitch 2142 Knyaz Vladimir [RUSSIAN AUTO TUNING] 1](https://i0.wp.com/myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/moskvitch-2142-knyaz-vladimir-russian-auto-tuning-1.jpg?w=501&h=376&ssl=1)
![Moskvitch 2142 Knyaz Vladimir [RUSSIAN AUTO TUNING] Moskvitch 2142 Knyaz Vladimir [RUSSIAN AUTO TUNING]](https://i0.wp.com/myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/moskvitch-2142-knyaz-vladimir-russian-auto-tuning.jpg?w=331&h=186&ssl=1)















































































![Resize of moskvitch-431-19[1] Resize of moskvitch-431-19[1]](https://i0.wp.com/myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/resize-of-moskvitch-431-191.jpg?w=312&h=208&ssl=1)





















































































































































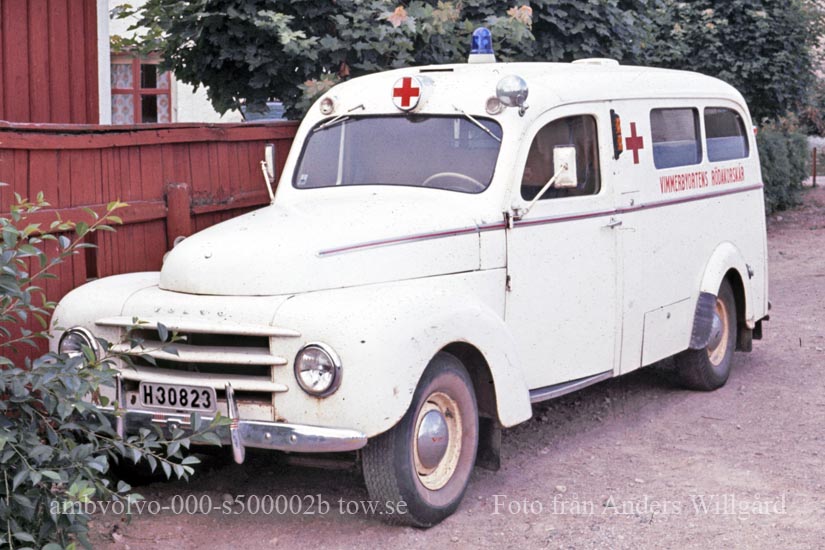





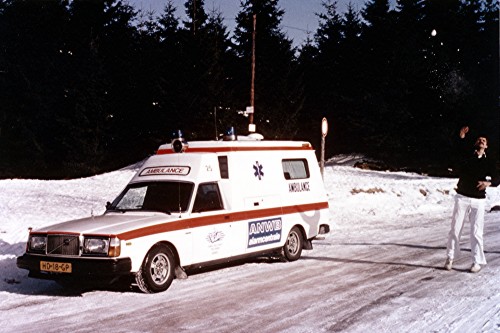





















































































 Volvo Ambulances Hearses and ex-Hearses
Volvo Ambulances Hearses and ex-Hearses











































































































































 All Volkswagen (ex) Ambulances and Hearses
All Volkswagen (ex) Ambulances and Hearses











 Wartburg Ambulance (and models)
Wartburg Ambulance (and models)






















































 Kaiser WILLYS Overland Siebert Ambulances and Hearses
Kaiser WILLYS Overland Siebert Ambulances and Hearses




















































 ZIS Ambulances and Hearses
ZIS Ambulances and Hearses






















































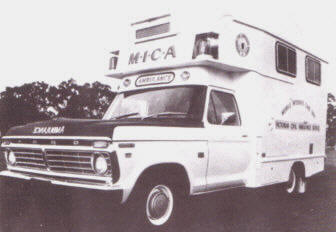











































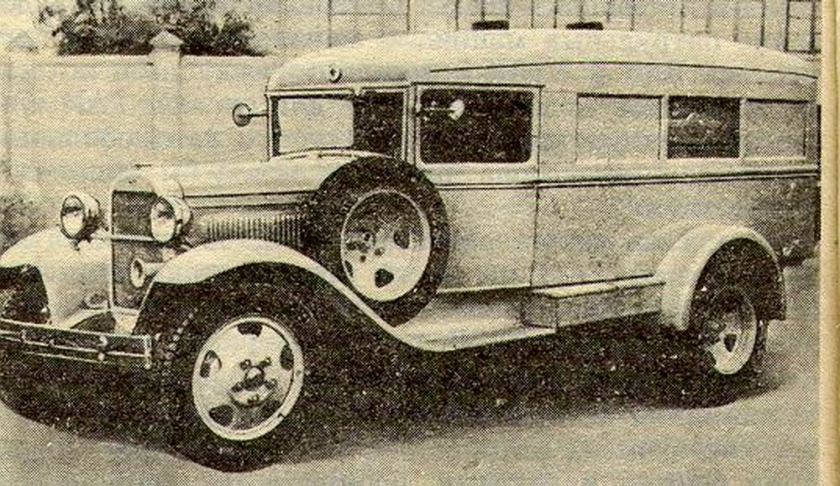
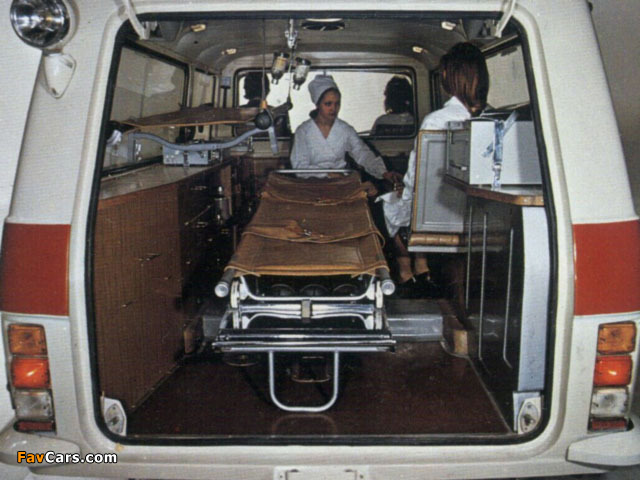
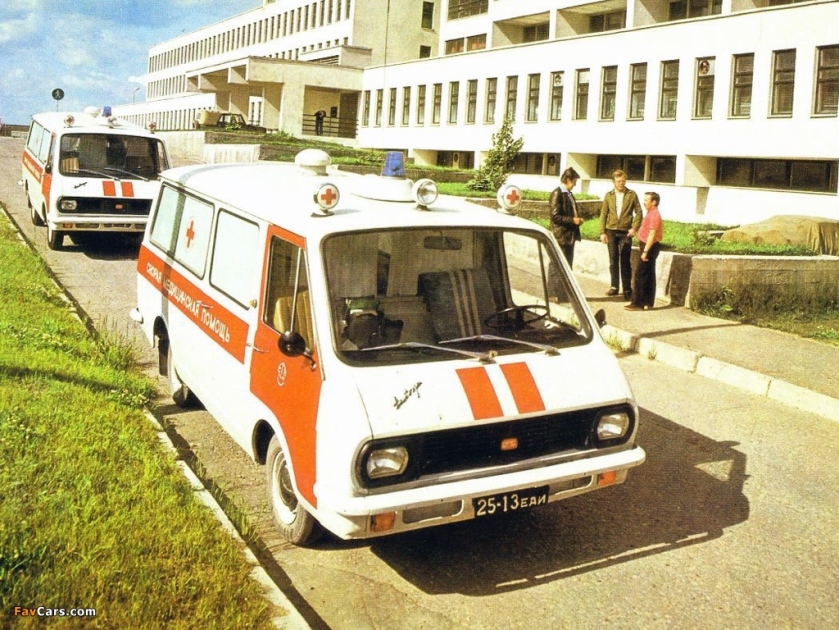
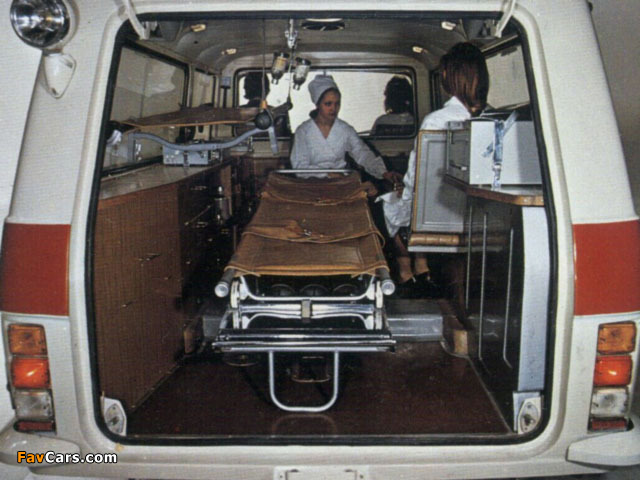
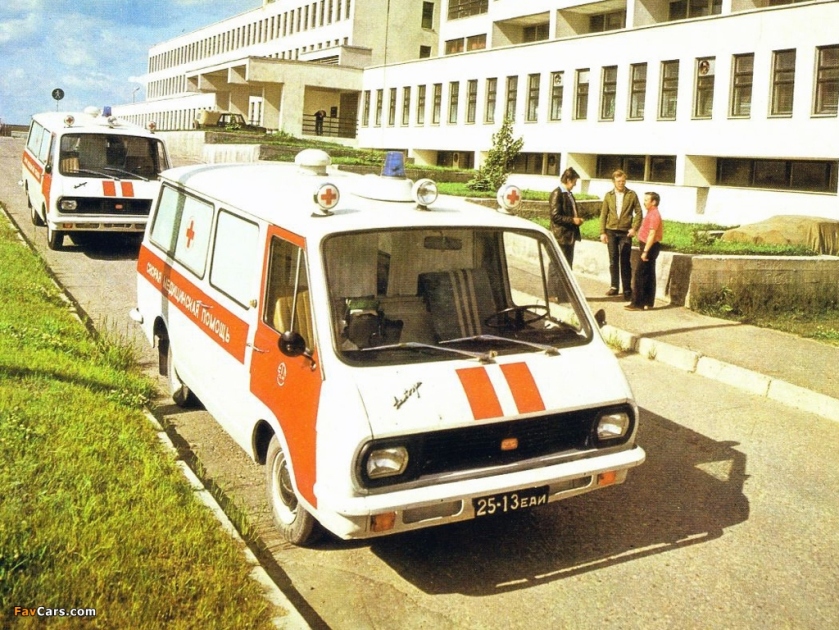
 Ford Ambulances 1909 till recent
Ford Ambulances 1909 till recent


















 Freightliner (Mercedes-Benz Sprinter) Ambulances
Freightliner (Mercedes-Benz Sprinter) Ambulances


















 Fuso-Mitsubishi Ambulance-Hospital Buses – Trucks
Fuso-Mitsubishi Ambulance-Hospital Buses – Trucks










 Garant 27 -Garant 30 – Garant Granit – Garant Sankra
Garant 27 -Garant 30 – Garant Granit – Garant Sankra




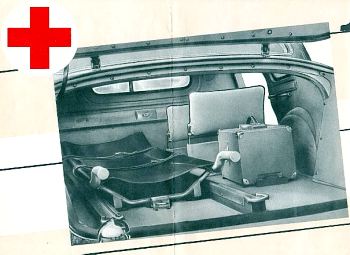



















 GAZ Ambulance from 1938 – recent
GAZ Ambulance from 1938 – recent





























 GMC Ambulances and Hearses from 1914 – recent
GMC Ambulances and Hearses from 1914 – recent





























 Pyeonghwa Paso 990.
Pyeonghwa Paso 990.










































































































































































































































































































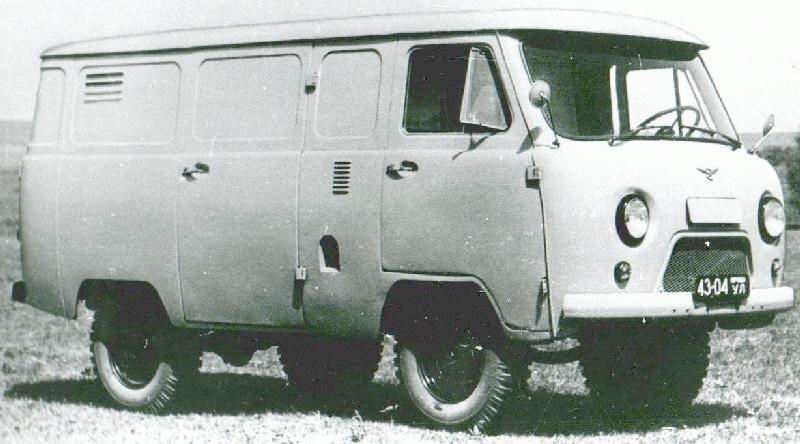































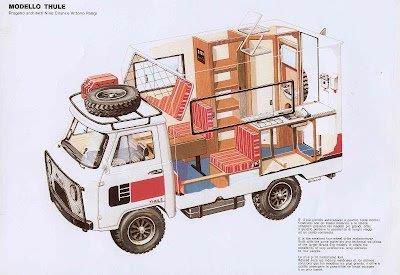






























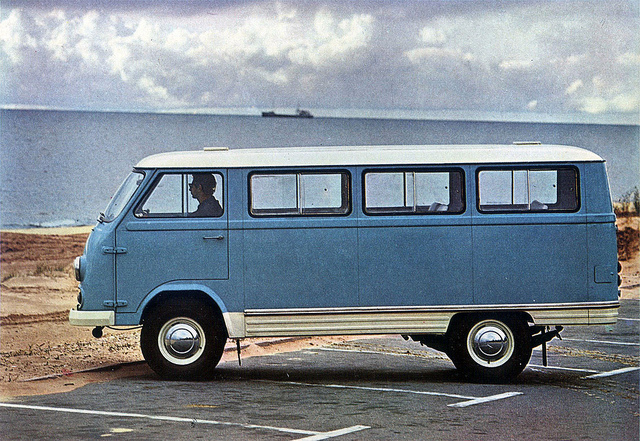



























































































































































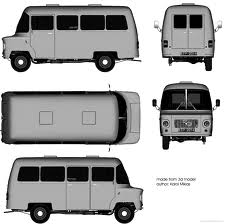






























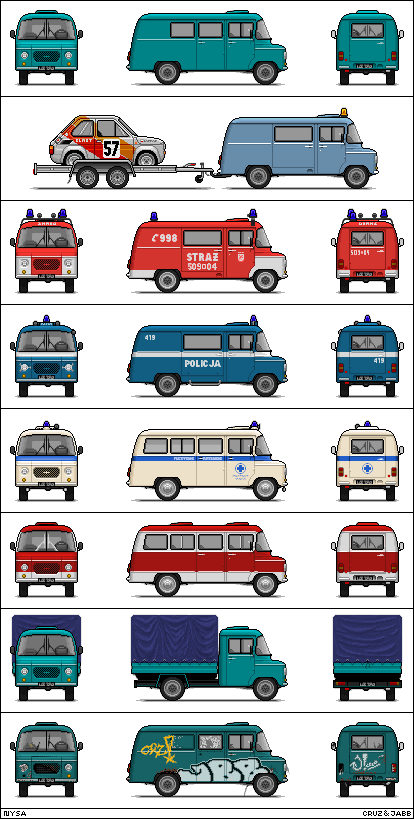























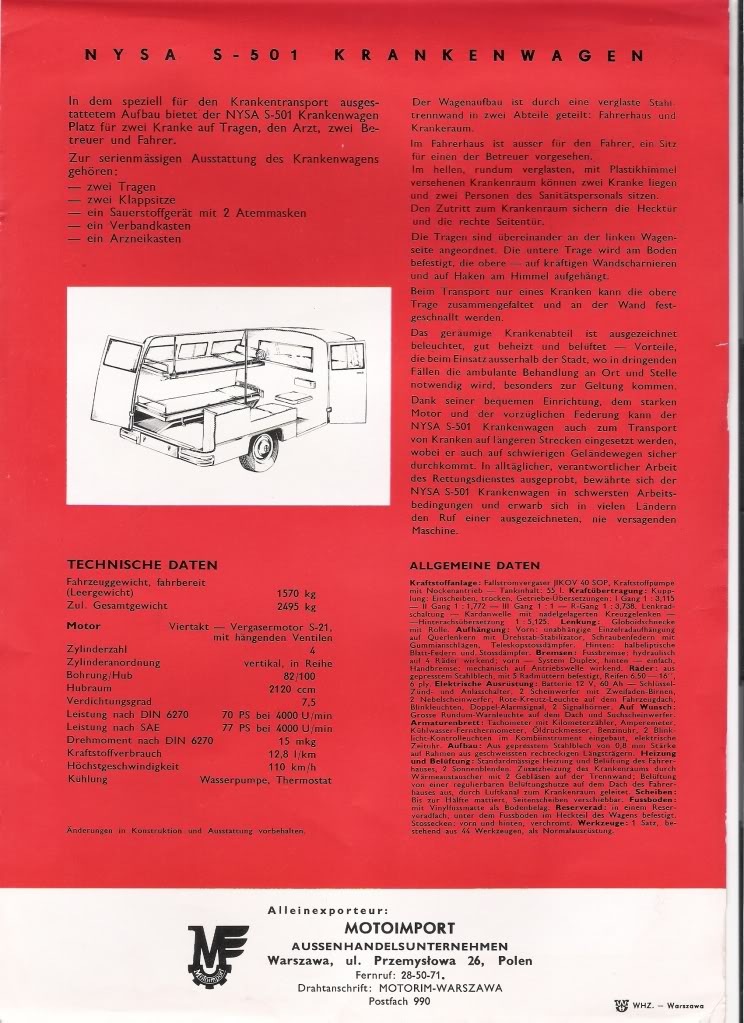















![1991 Leyland DAF 400 [V400]](https://myntransportblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/1991-leyland-daf-400-v400.jpg?w=840)